Understanding Soil Formation and Importance
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Mollisol
Soil formed in sandstone - SE Minnesota
Soil
The "living" skin of the Earth, a natural body consisting of solids, liquids, gases, distinguishable from parent material due to pedogenesis.
Parent material
The original material from which soil is formed.
Pedogenic
Processes involved in soil formation.
Importance of Soils
Soils hold more carbon than the atmosphere and organisms combined.
Reservoir Gigatons C
Soils: 1,500-2,400; Oceans: 38,000; Atmosphere: 730; Land Organisms: 500-700; Marine organisms: 3; Rocks: 60,000,000; Permafrost Soils: ~1,700.
Soil Morphology
The physical properties of soil, described by texture, structure, color, and others.
Soil texture
The percentage of sand, silt, and clay in the soil.
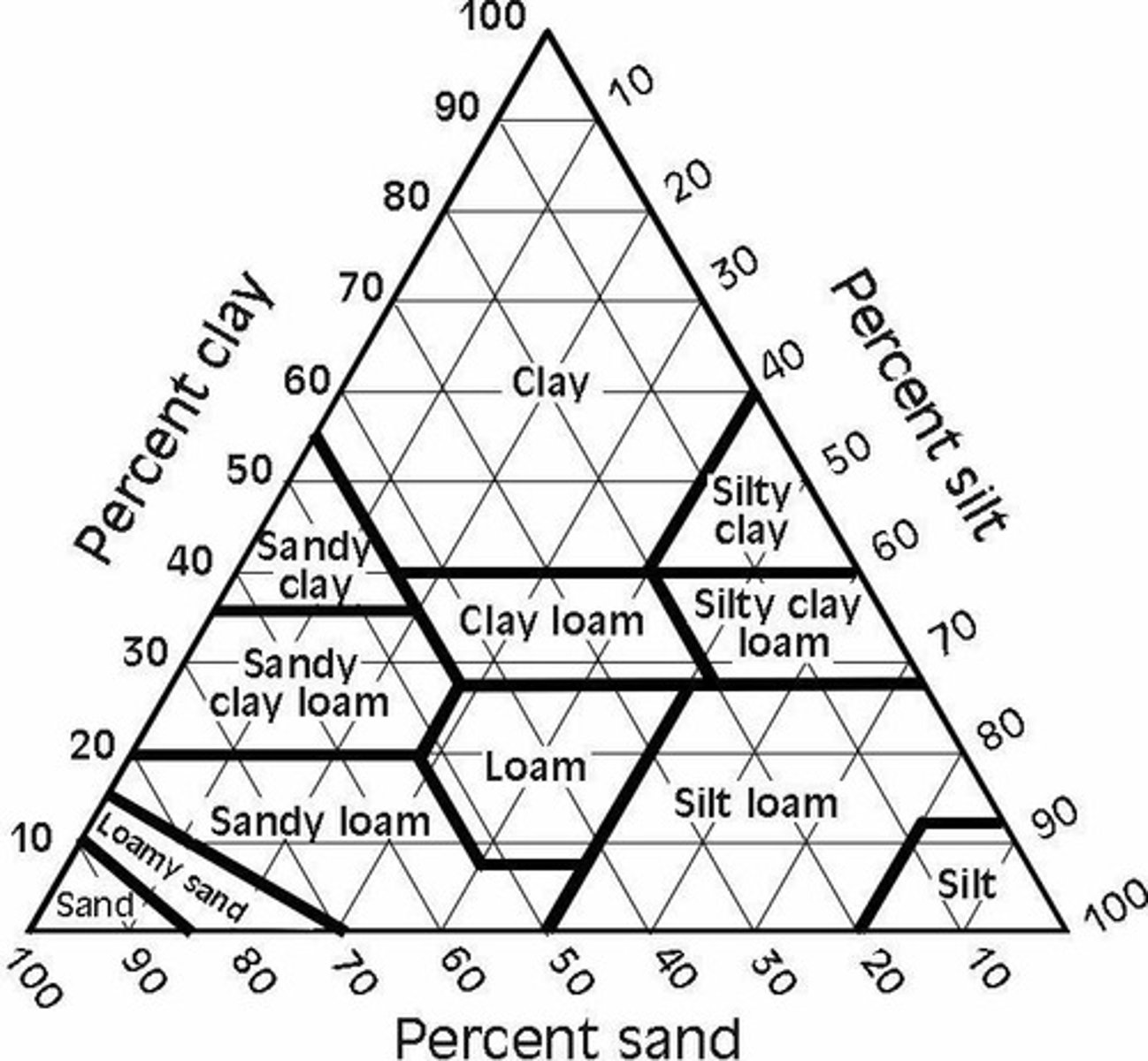
Sand
Soil texture with grain size of 2-0.050 mm (2000-50 μm), described as gritty.
Silt
Soil texture with grain size of 0.050-0.002 mm (50-2 μm), described as slippery.
Clay
Soil texture with grain size of <0.002 mm (<2 μm), described as sticky.
Soil structure
Aggregates of individual soil particles formed by clumping from electrostatic attraction and binding by organic materials.
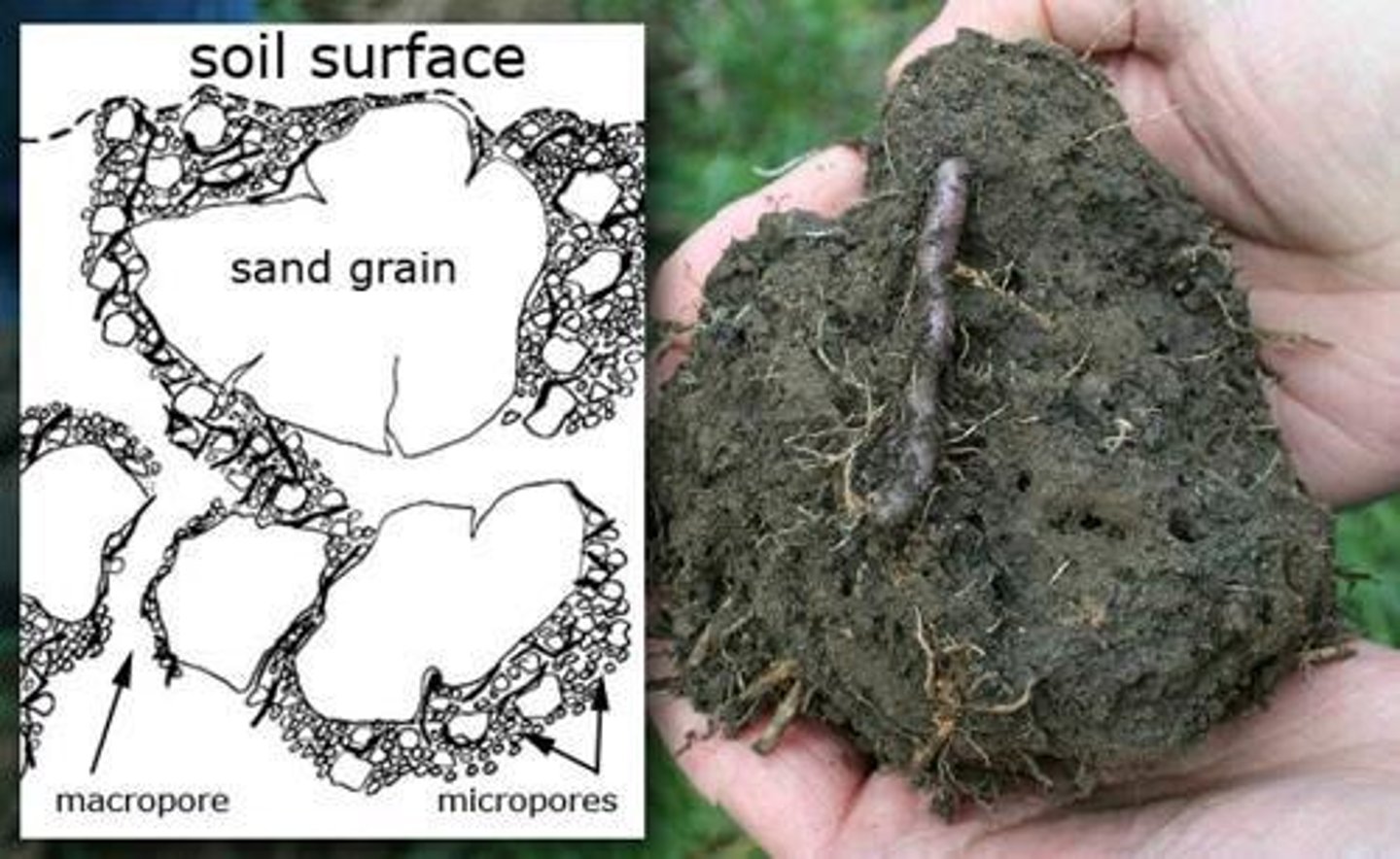

Granular structure
Soil structure formed from burrowing animals and organic matter.
Blocky structure
Soil structure resulting from clay particle buildup.
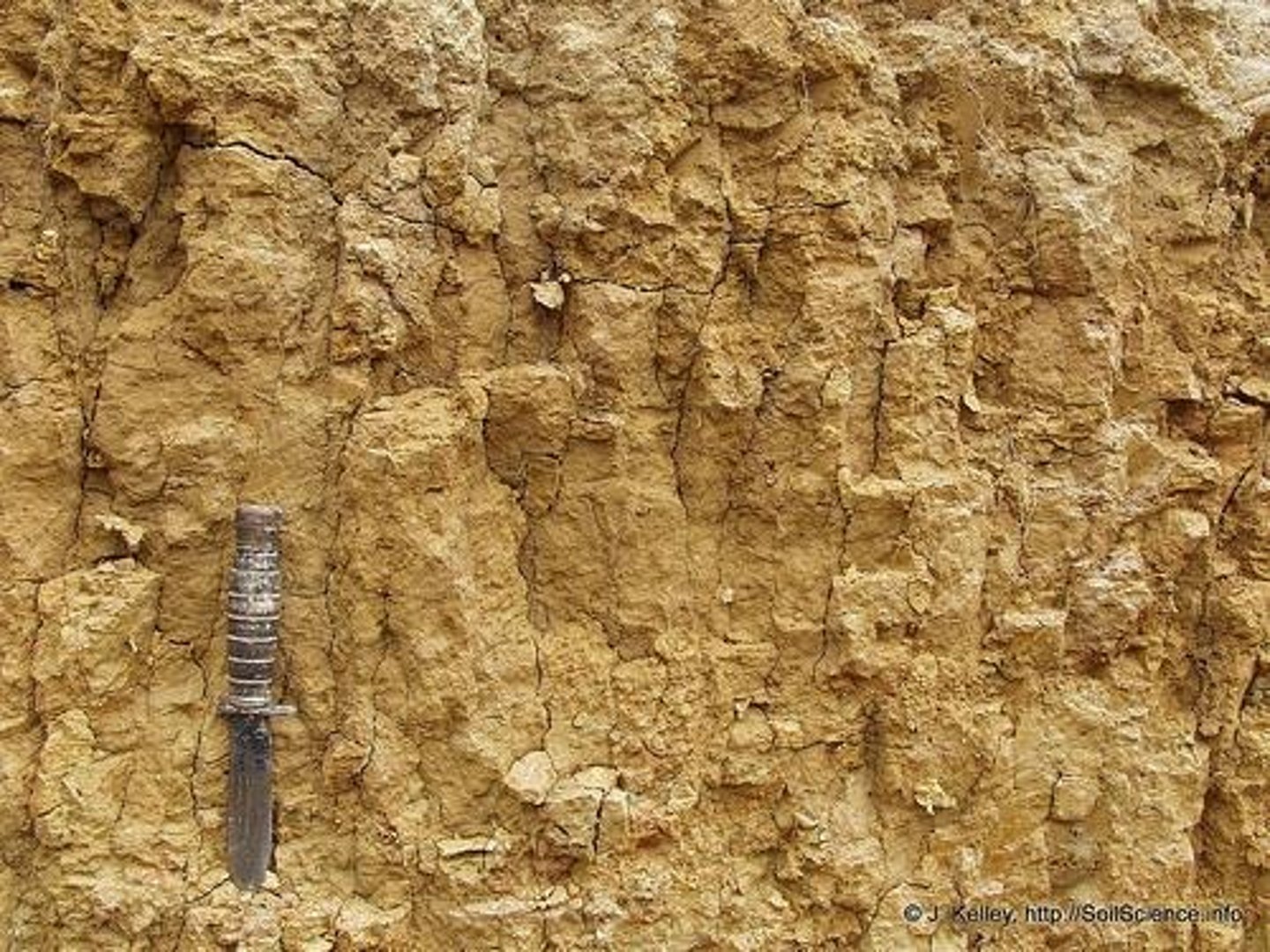

Prismatic structure
Soil structure formed from repeated wetting and drying.
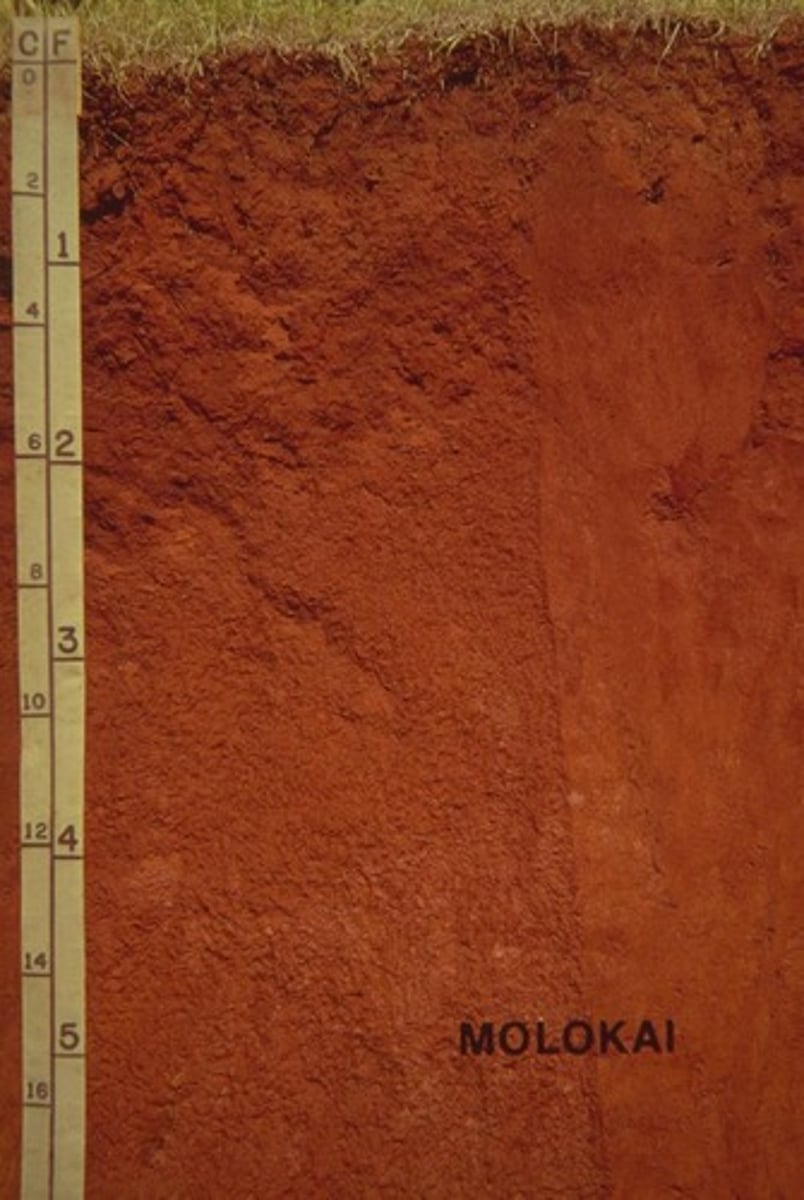

Soil color
Varies considerably within the same soil, influenced by organic matter, types of minerals, and moisture content.
Soil horizons
Roughly horizontal layers formed as a result of pedogenesis, characterized by uniform texture, structure, and color.
Master horizons
Layers in soil: O (organic layer), A (organic matter + mineral grains), E (eluviated horizon), B (illuvial horizon), C (parent material).
O Horizon
Organic layer consisting of plant litter.
A Horizon
Layer rich in organic matter mixed with mineral grains.
E Horizon
Eluviated horizon characterized by losses of iron and aluminum.
B Horizon
Illuvial horizon where iron and aluminum are added back into the soil.
A soil layer where materials like clay, iron, and aluminum from upper layers are deposited, making it denser and often red or brown in color.
C Horizon
Parent material layer in soil.
Translocation
Physical movement of clay and other materials by water in soil.
Soil Formation Factors
Soils are the result of five factors: Climate, Organisms, Relief (Topography), Parent material, Time.
Residual Soil
Parent material is the bedrock.
Transported Soil
Parent material has been carried from elsewhere and deposited.
Climate
The most influential control of soil formation, affecting temperature and precipitation.
Weathering
Influences the rate and depth of soil weathering.
Leaching
Amount of precipitation influences the rate materials are leached from the soil.
Tropical vs. Temperate Soils
Different climates lead to different soil types.
Organisms
Plants and animals, including microorganisms, influence the soil's physical and chemical properties.
Humus
Decaying plant and animal debris that forms organic acids and furnishes organic matter to soil.
Soil Moisture Retention
Organisms help retain soil moisture.
Soil Temperature
Orientation of the slope influences soil temperature.
Soil Degradation
Activities which lower the capacity of the soil to support life.
Causes of Soil Degradation
Includes agriculture, overgrazing, industrialization, and deforestation.
Vegetation's Role
Vegetation reduces degradation by protecting soil from raindrop impacts.
Soil Erosion
Occurs following logging and fire.
Soil Taxonomy
Grouping soils based on their properties in a hierarchical system.
Alfisol
Characterized by a thin A horizon, light colored E horizon, clay accumulation in B horizon, found in deciduous forest soils.
Mollisols
Thick, dark A horizons found in grasslands, the most naturally fertile soils in the world.
Mollisol Formation
Dry climate favors grasses
(fire helps)
• Roots add OM belowground
• Abundant burrowing animals
also mix OM down
• Dry, cool climate leads to slow
OM decay
Results in Thick, dark, Om-rich, a horizon.
Thin and Rocky Soil
Most likely found on a steep slope with a high erosion rate, indicating dominance of relief.
Thick, Dark A Horizon
Indicates a soil formed under grassland, characteristic of Mollisol.