Thermal Energy, Temperature and Heat
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
temperature
average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
heat
The flow of thermal energy from an area of higher temperature to an area of lower temperature
thermal energy
total kinetic and potential energy of particles that make up a material
radiation
transfer of thermal energy as electromagnetic waves

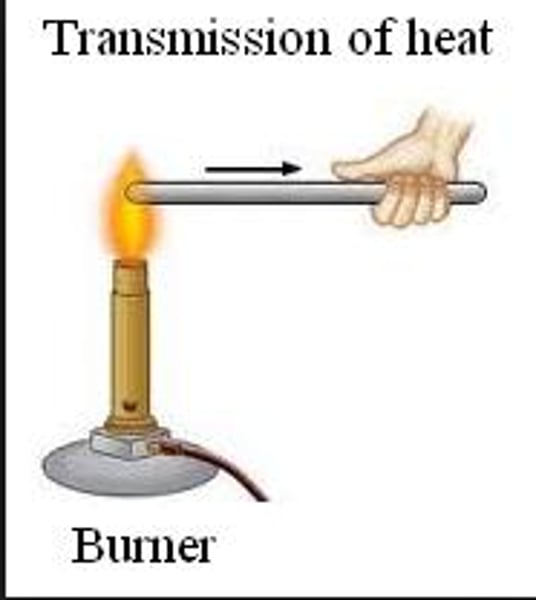
conduction
transfer of thermal energy through direct contact
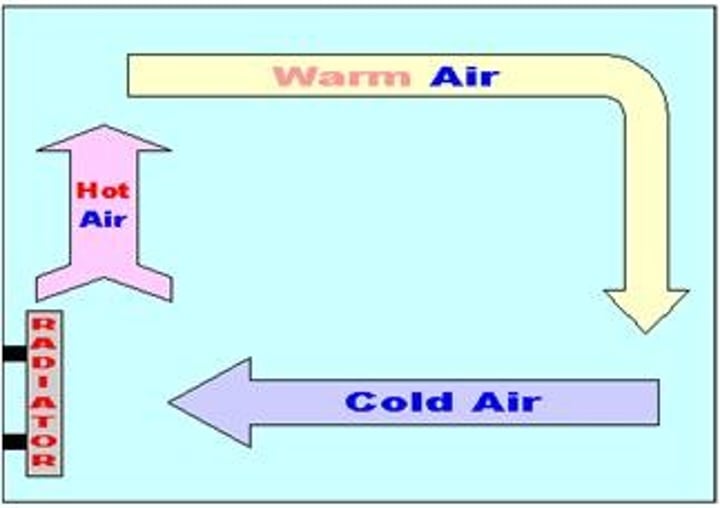
convection
transfer of thermal energy due to movement particles within a fluid
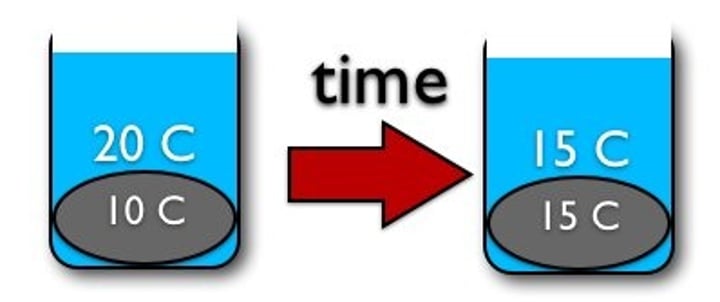
thermal equilibrium
When substances of different temperatures finally come to the same temperature
thermometer
measures temperature
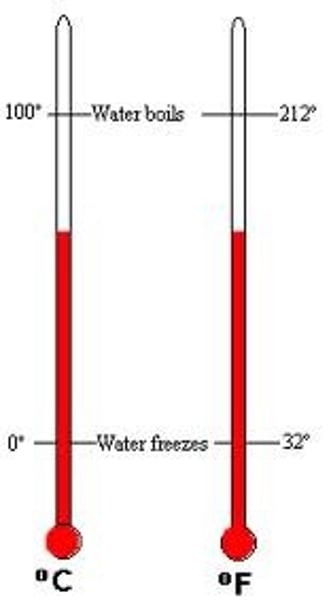
Celsius
a temperature scale used by scientists (and most of the world!)
Kelvin
water freezes at 273 and boils at 373 on this scale
conductor
material that allows thermal energy to flow easily
insulator
material that doesn't allow thermal energy to flow easily
thermal expansion
increase in volume due to an increase in total energy of the particles
examples of good conductors
silver, gold, copper
examples of good insulators
air, paper, wood
0 degrees
SI temperature at which water freezes
37 degrees
equivalent to average human body temperature
212 degrees
F scale temperature of boiling water
absolute zero
0 Kelvin
joule
SI unit for thermal energy measurement
vaporization
all changes from liquid to gas
boiling
vaporization throughout the entire liquid
evaporation
vaporization from the surface only
condensation
change from gas to liquid
melting
change from solid to liquid
freezing
change from liquid to solid
sublimation
change from solid to gas
deposition
change from gas to solid
direction of heat
always from warmer to colder
heat engine
any device that transforms thermal energy to mechanical energy
Celsius
SI unit for temperature
Kelvin
temperature scale used by physicists
Fahrenheit
temperature scale used by US