10: Leaf
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
store water
succulent modified stem function
for climbing
tendrils
to deter herbivores + reduce water loss
function of thorns/spikes
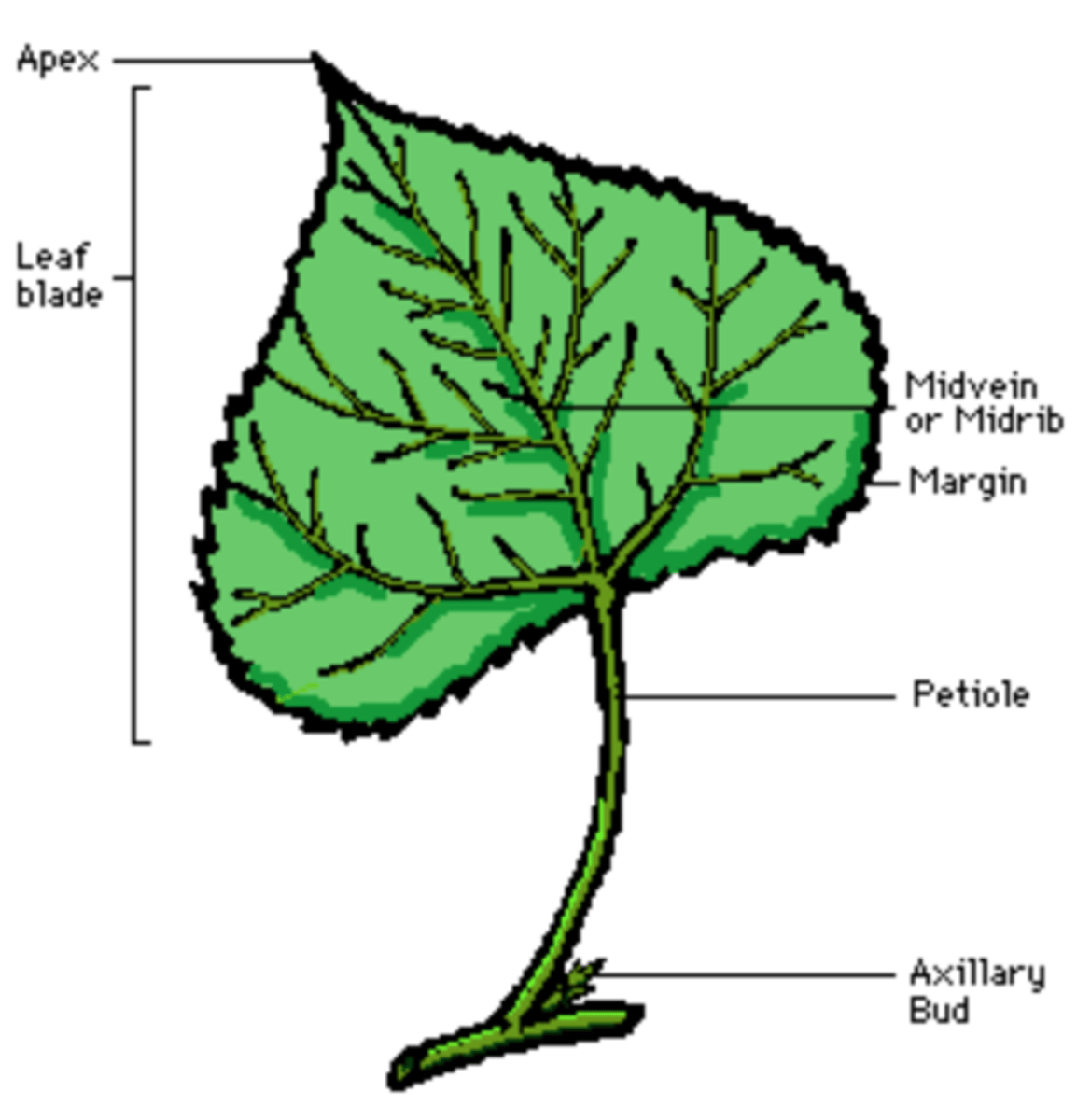
- Blade or lamina
- Apex, Base, Margin
- Veins (vascular bundles)
- Petiole (Stalk)
- Stipules
leaves external anatomy
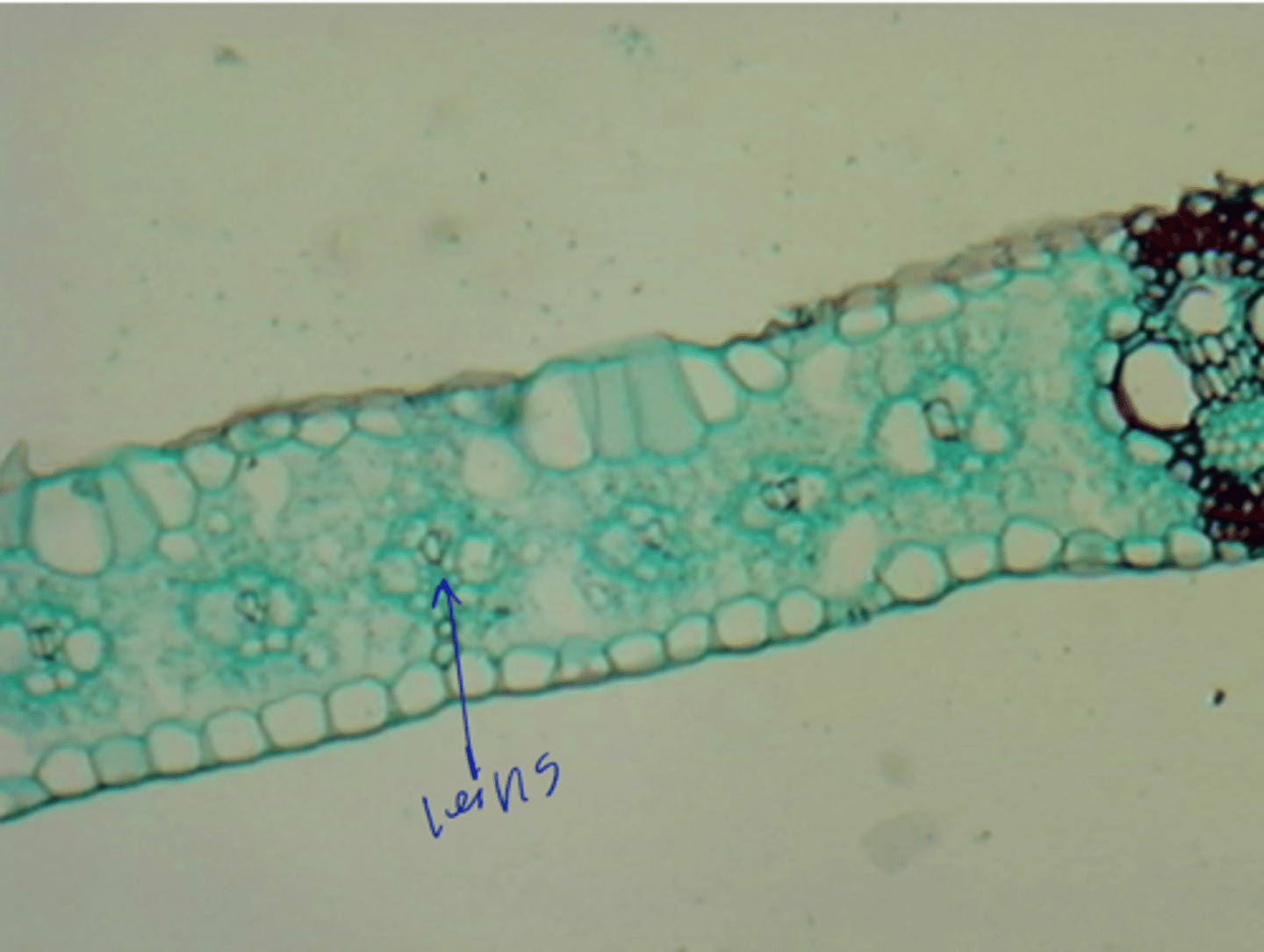
expanded petiole in monocots bc they have no stalk
leaf sheath definition
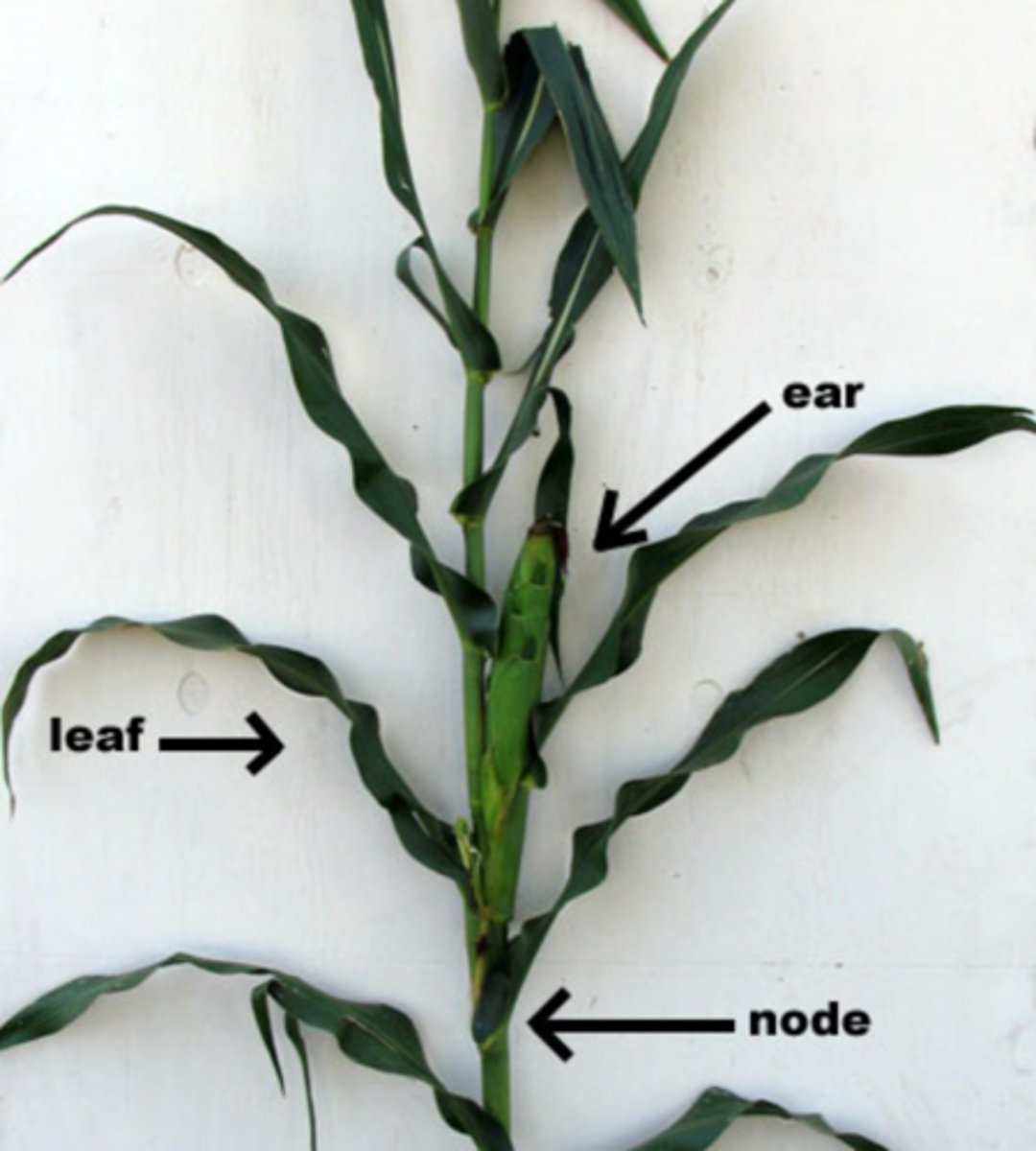
phyllotaxy
arrangement of leaves on a stem
opposite
phyllotaxy if 2 leaves on a node
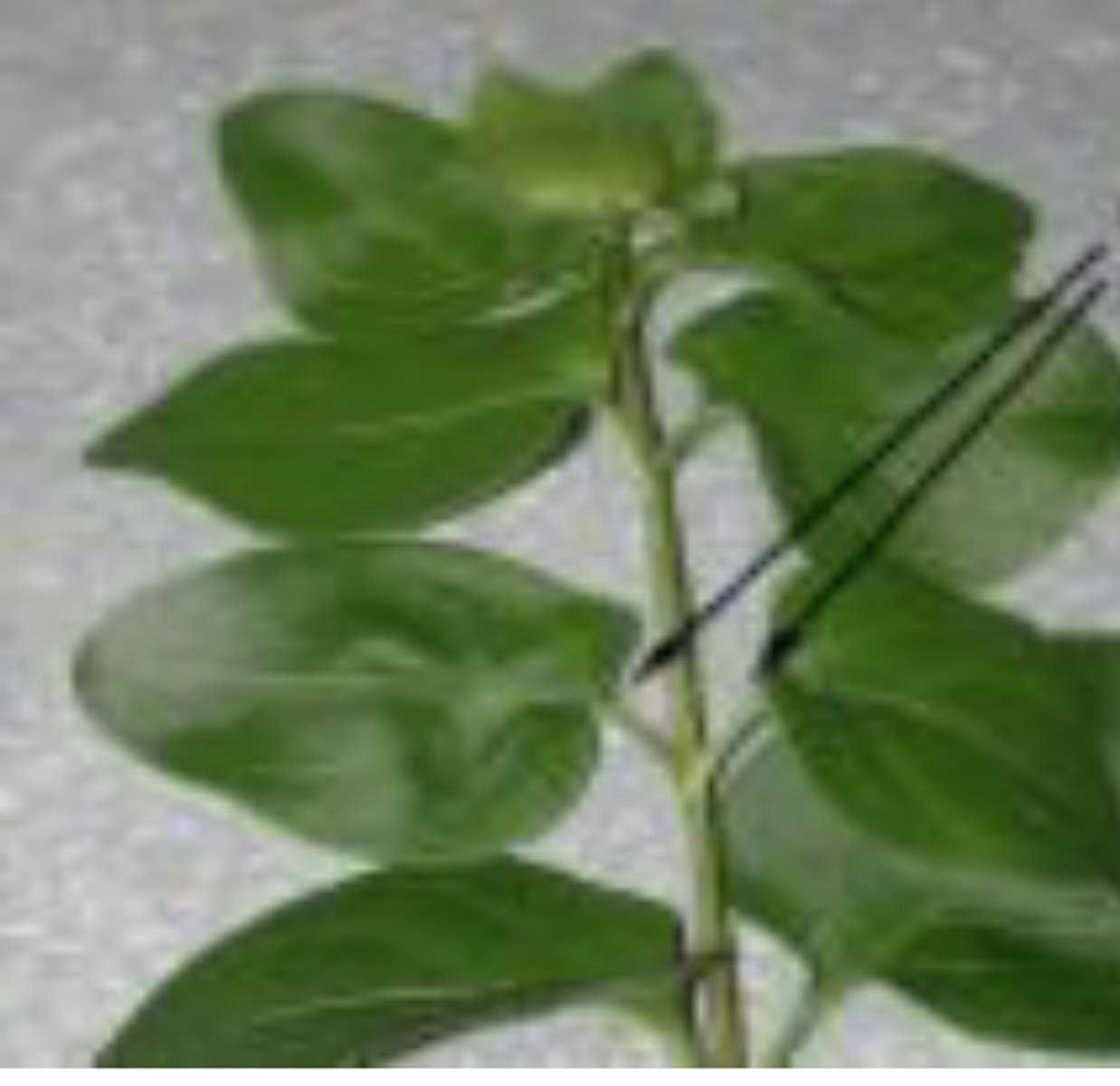

alternate
phyllotaxy if 1 leaf on a node
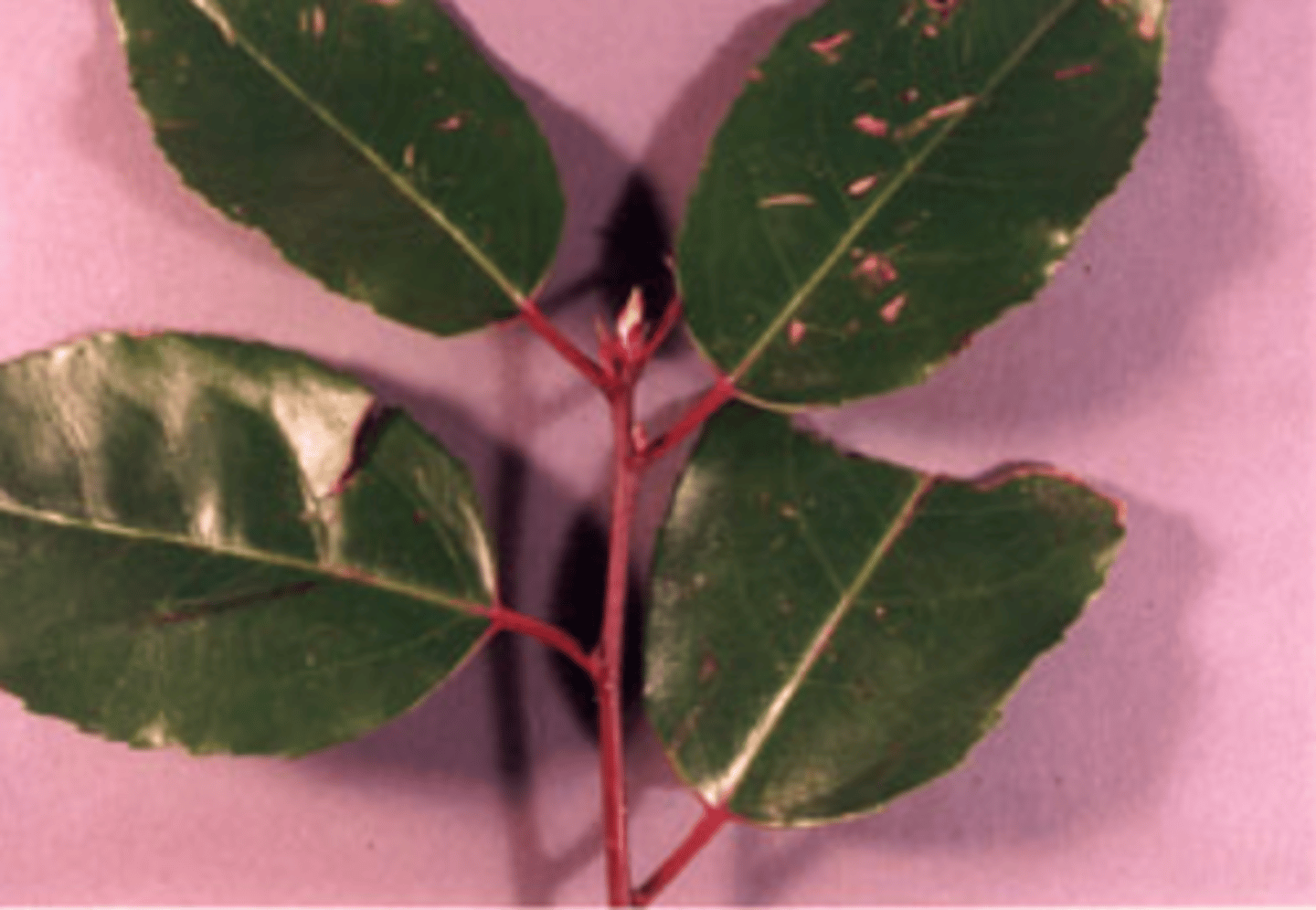

whorled
phyllotaxy if multiple leaves on a node
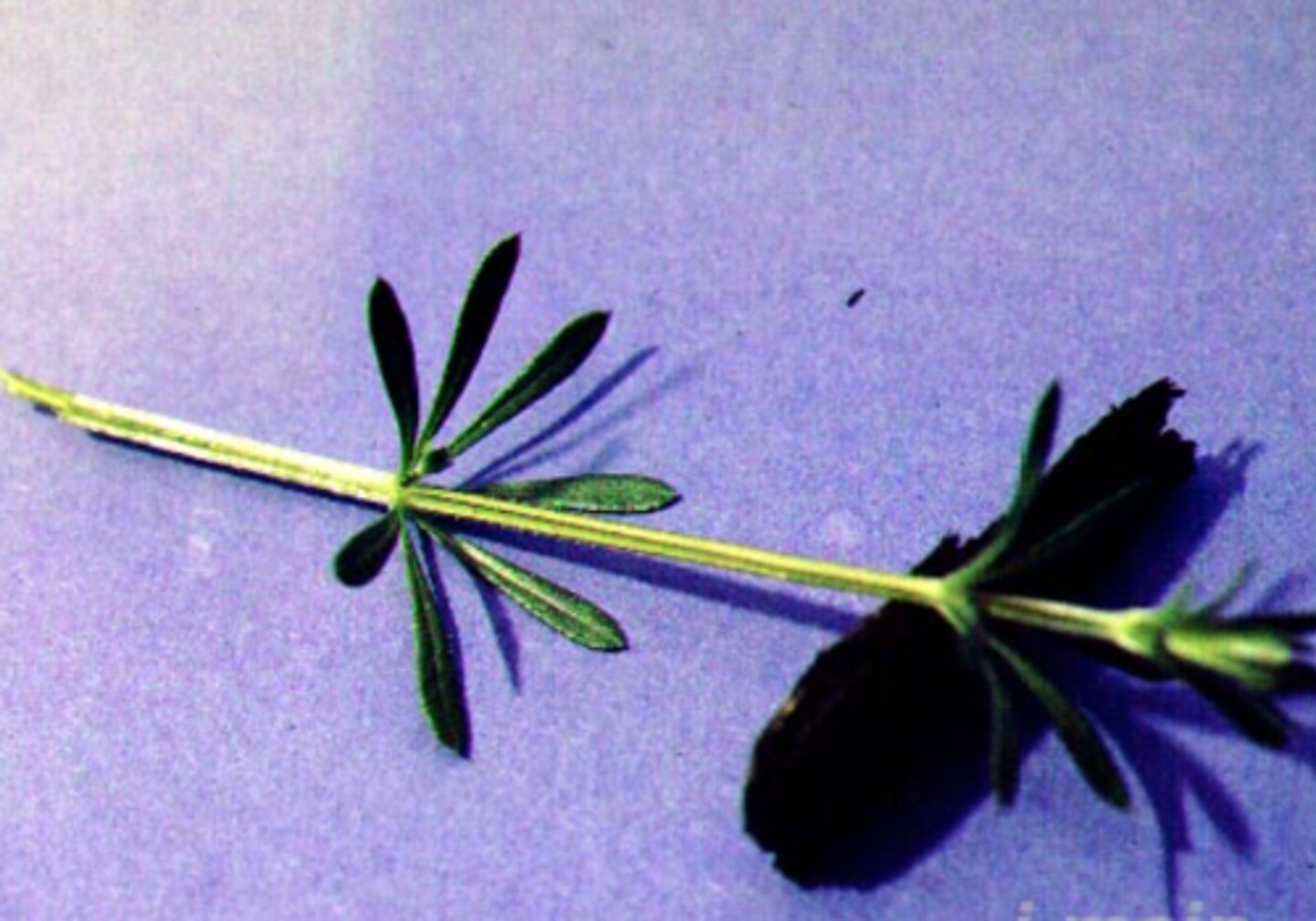

basal
phyllotaxy if leaves are nasa baba

Decussate
special type of opposite phyllotaxy; 2 pairs of leaves 90 degrees to each other

undivided blade with a single axillary bud at the base of its petiole
simple leaf definition
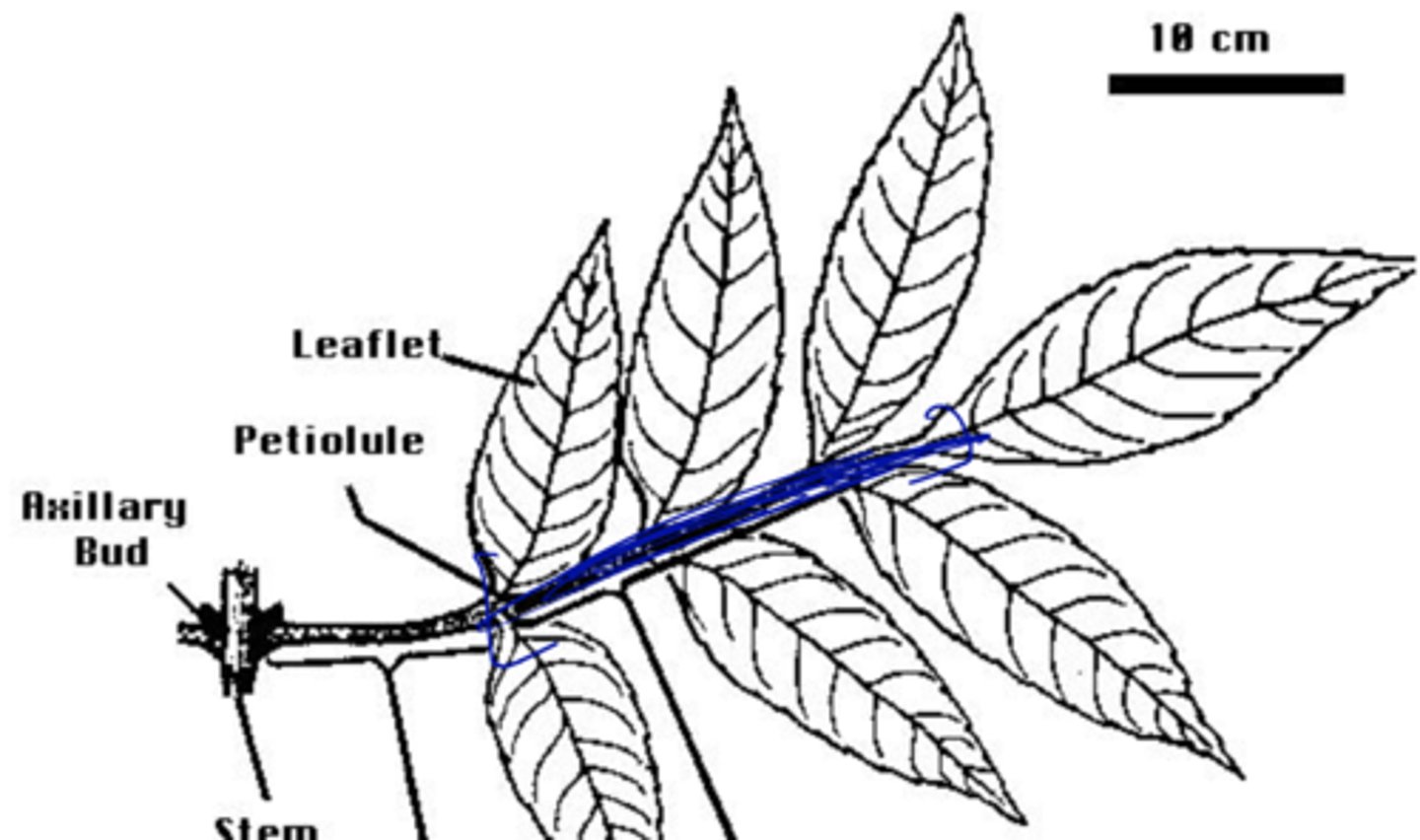
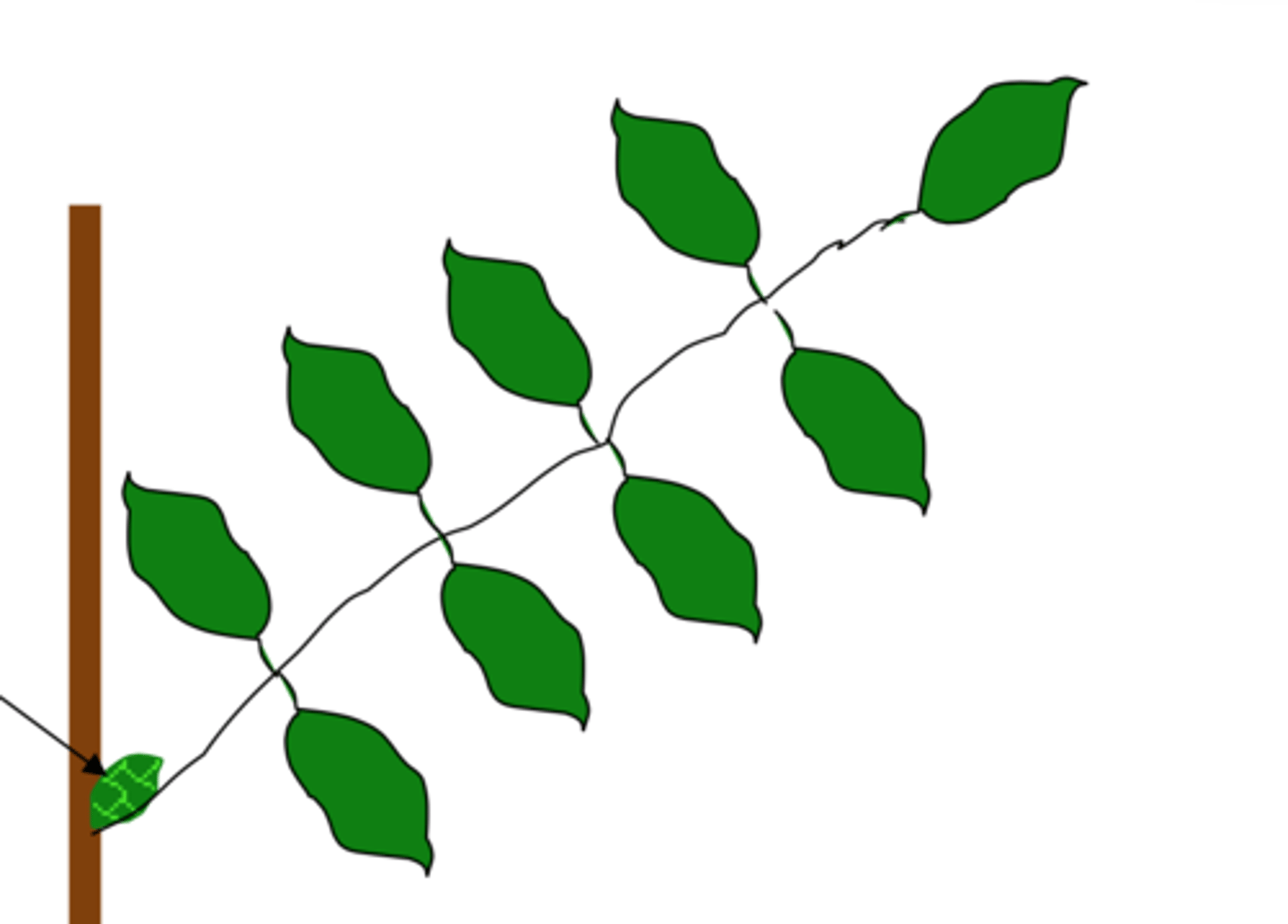
pinnately-compound leaves
- leaflets in pairs
- rachis
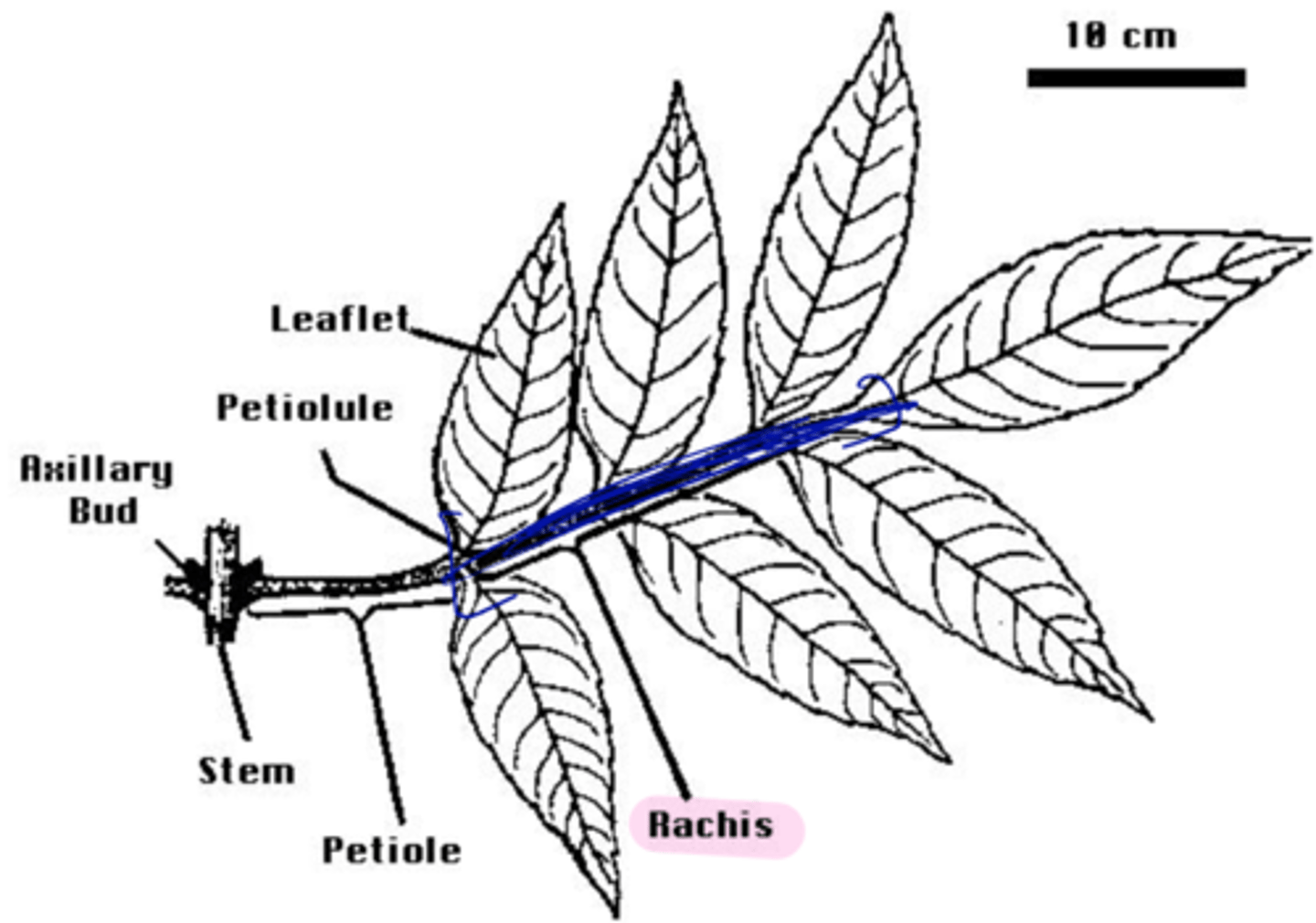
extension of the petiole in pinnately-compound leaves
rachis definition
palmately-compound leaves
no rachis, leaflets attached at the same point at the end of the petiole
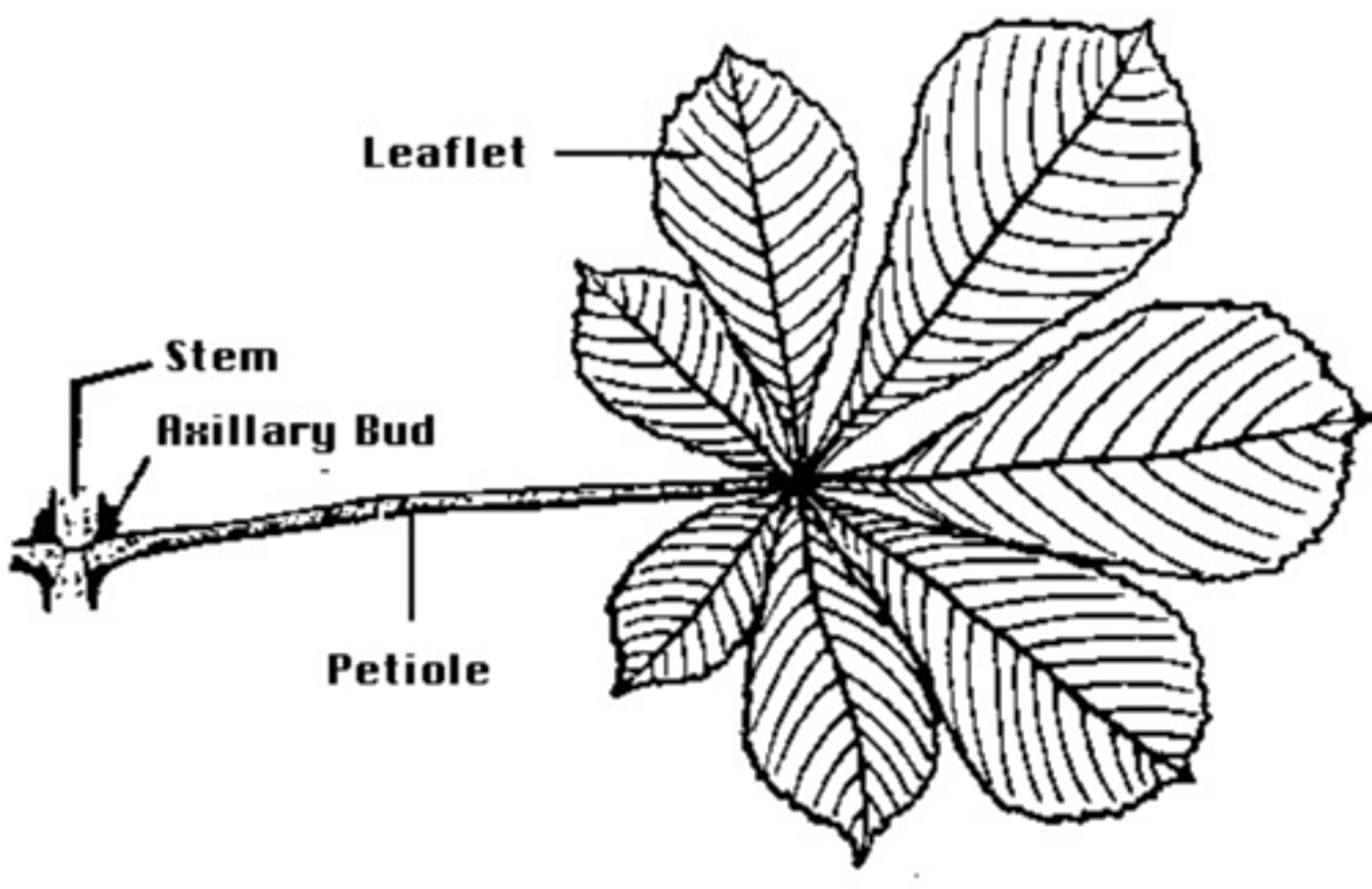
always at base of leaf (above the petiole)
location of axillary bud
only primary growth
type of growth of leaves
arrangement of tissues dictated by the physical environment (e.g. water availability, light intensity, ecological niche and herbivores)
how are leaves the most plastic/variable organs
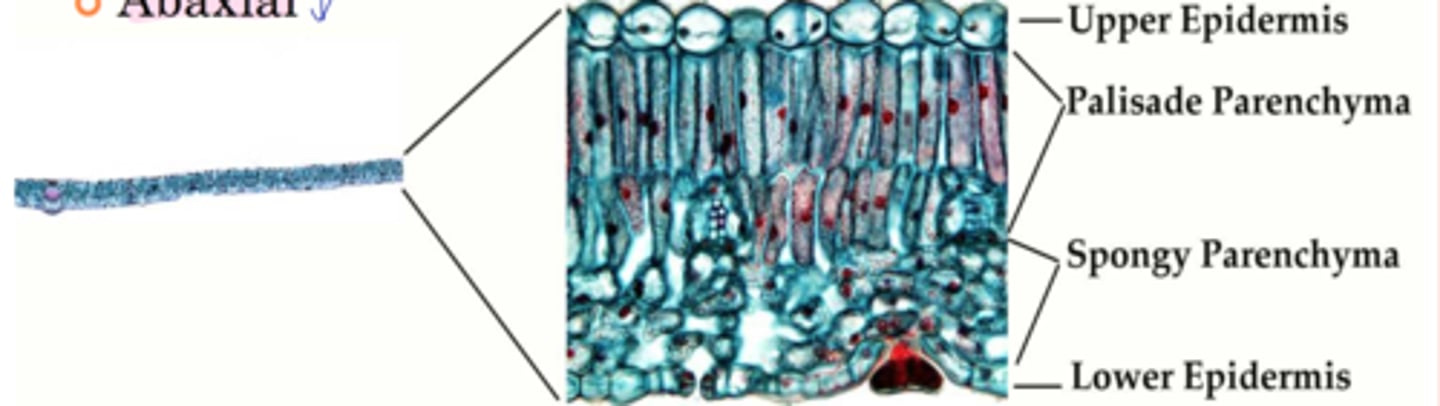
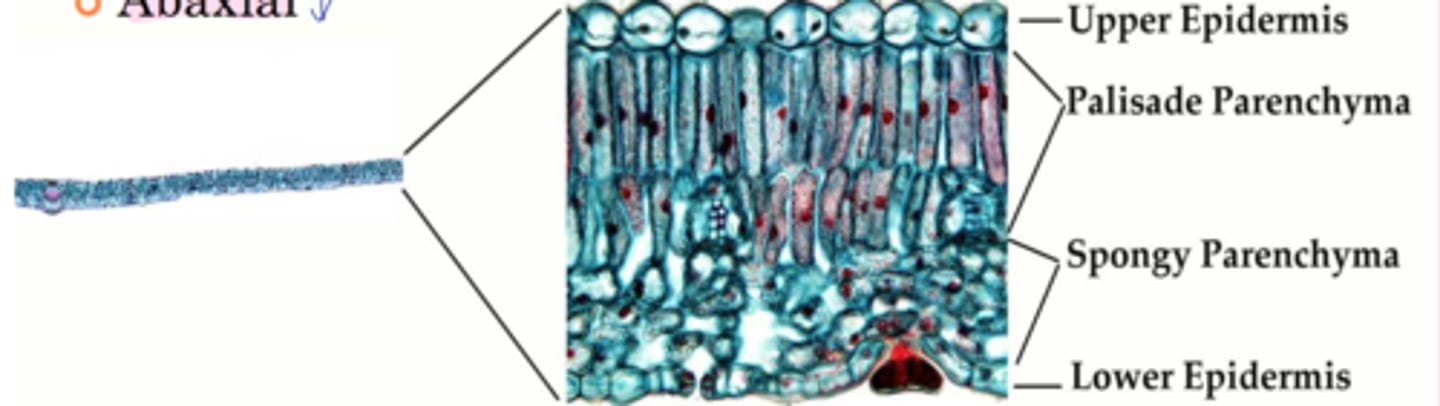
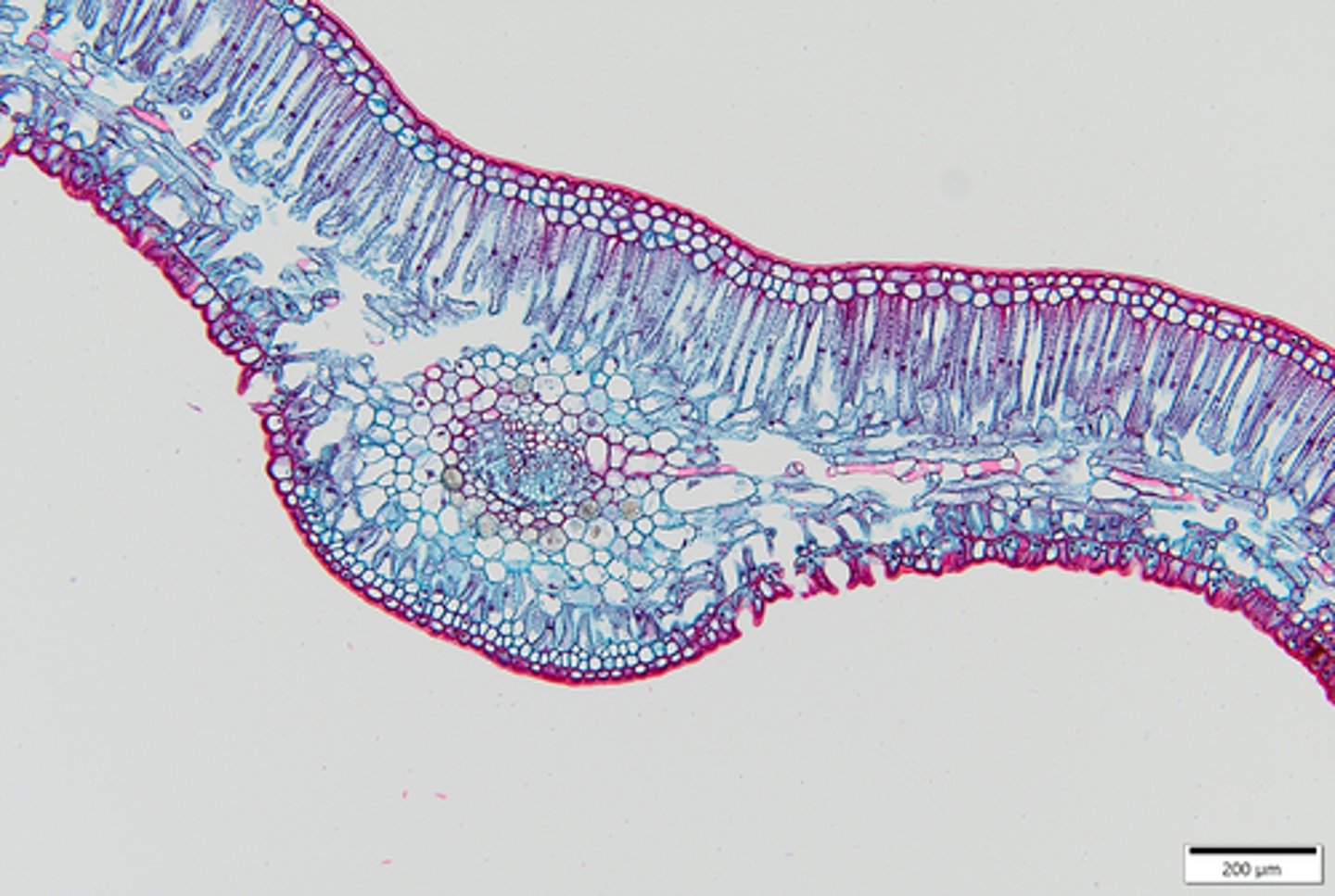
1. Epidermis
2. Mesophyll
3. Vascular tissues
internal parts of leaf lamina
adaxial
closer to the internode above it; faces upward
Abaxial
faces downward
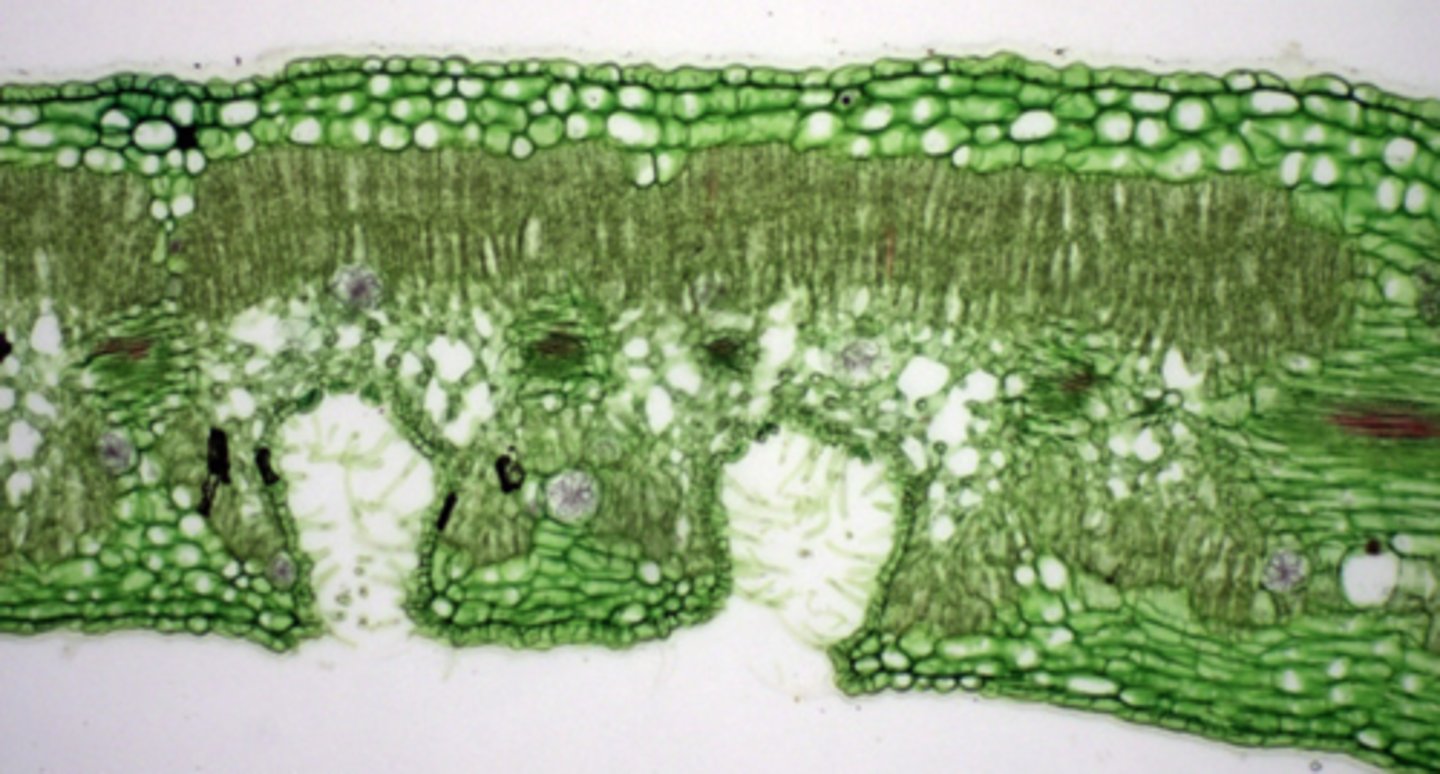
xeromorphic plants; modified structure when water is limited
saan common ang multiple epidermis
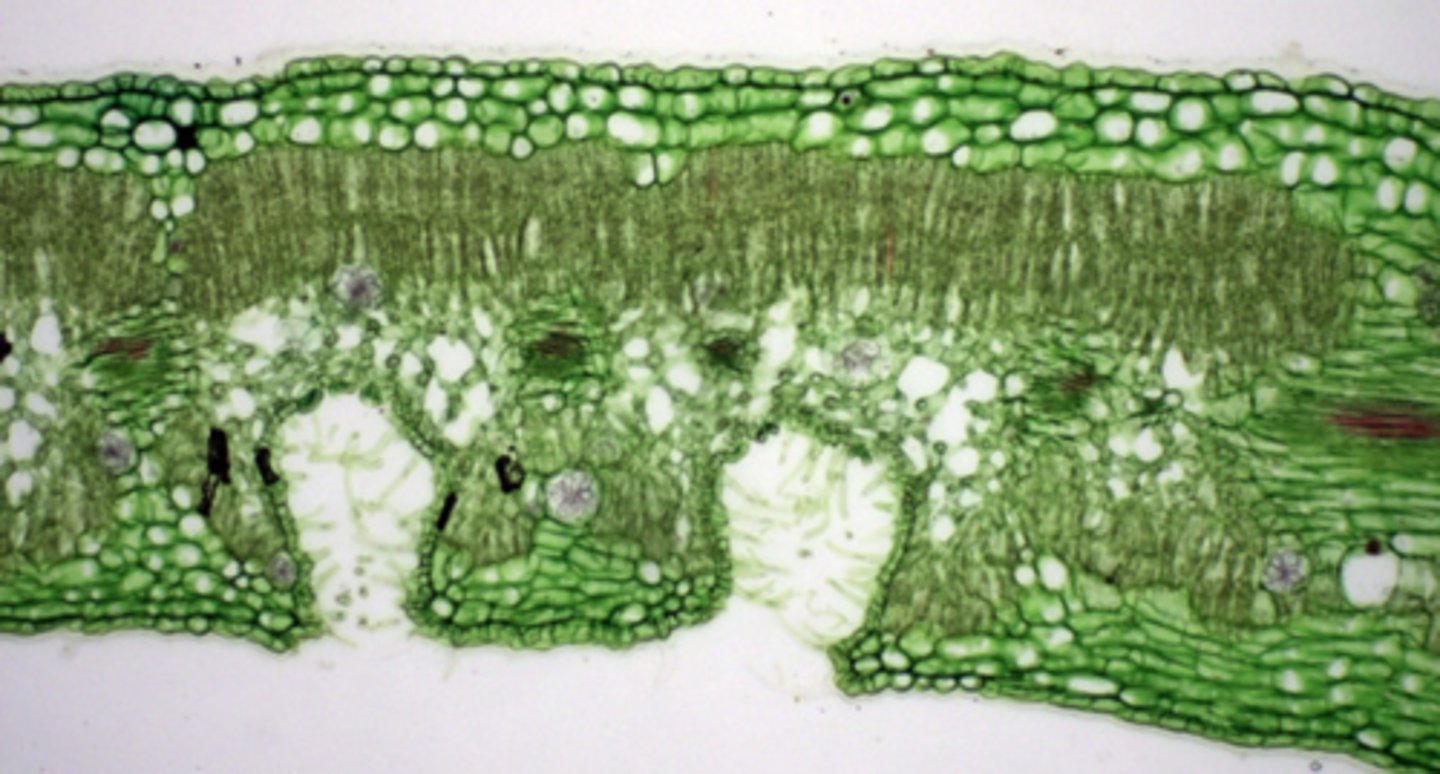
if all true epi, origin is protoderm
if may part of hypodermis (part of mesophyll) galing ground meristem
origins of multiple epidermis
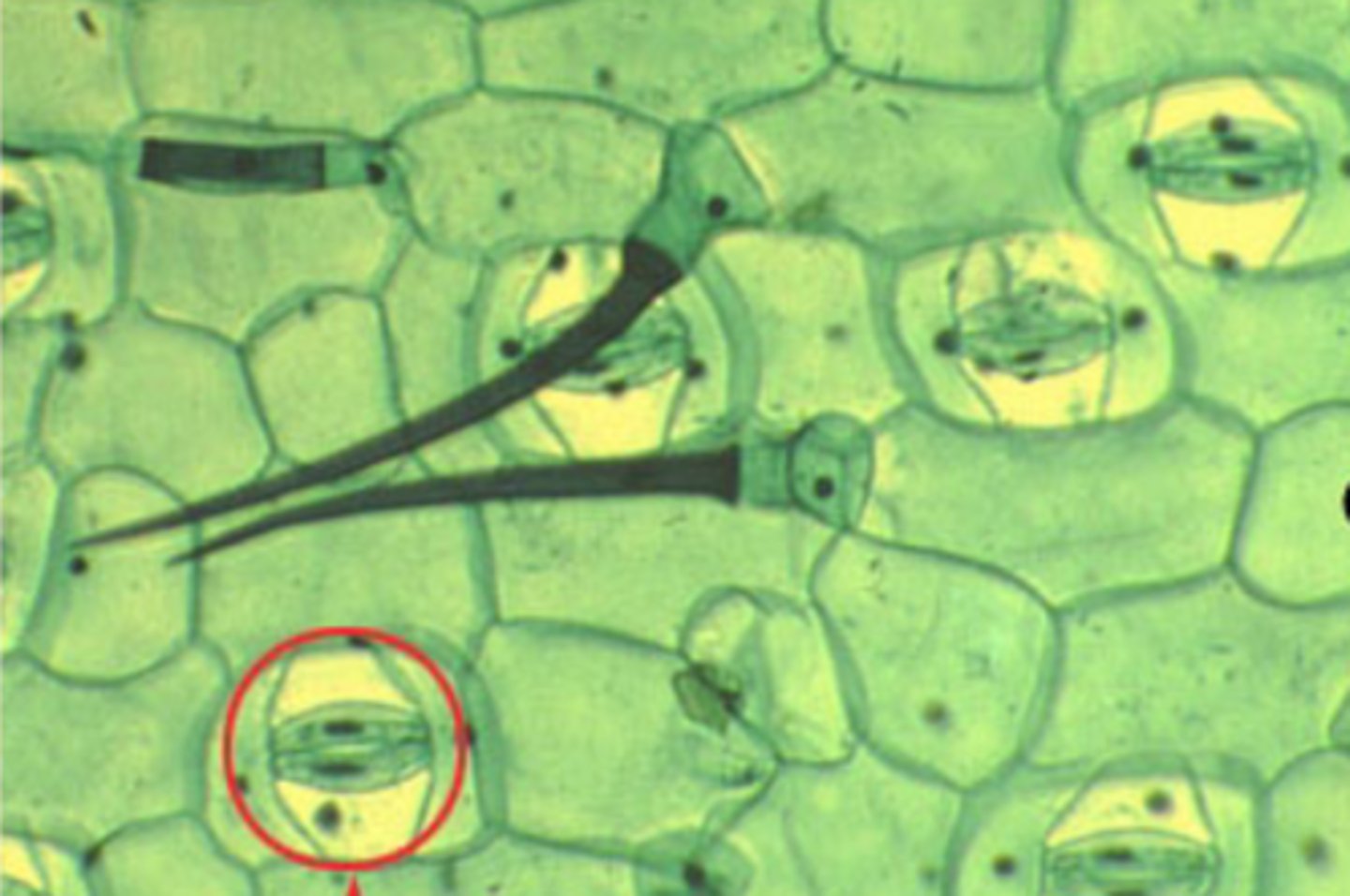
- cuticle (hydrophobic)
- stomata (bc no intercellular spaces)
- trichomes (deters herbivory + reduces water loss)
features/parts of epidermis
parenchymatous ground tissues specialized for photosynthesis
mesophyll definition
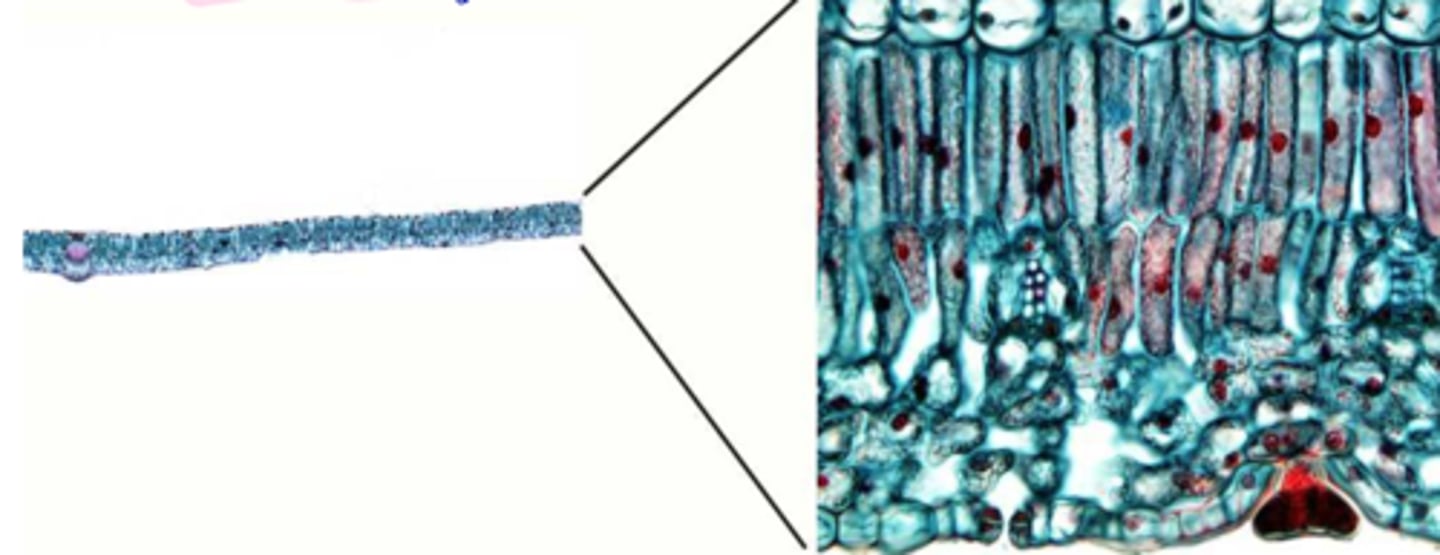
Chlorenchyma
Parenchyma cells containing chloroplasts
Elongated; rod shaped in xs
Arranged in rows
Immediately below the epidermis (uni- or multi-seriate)
On adaxial surface
palisade mesophyll definition
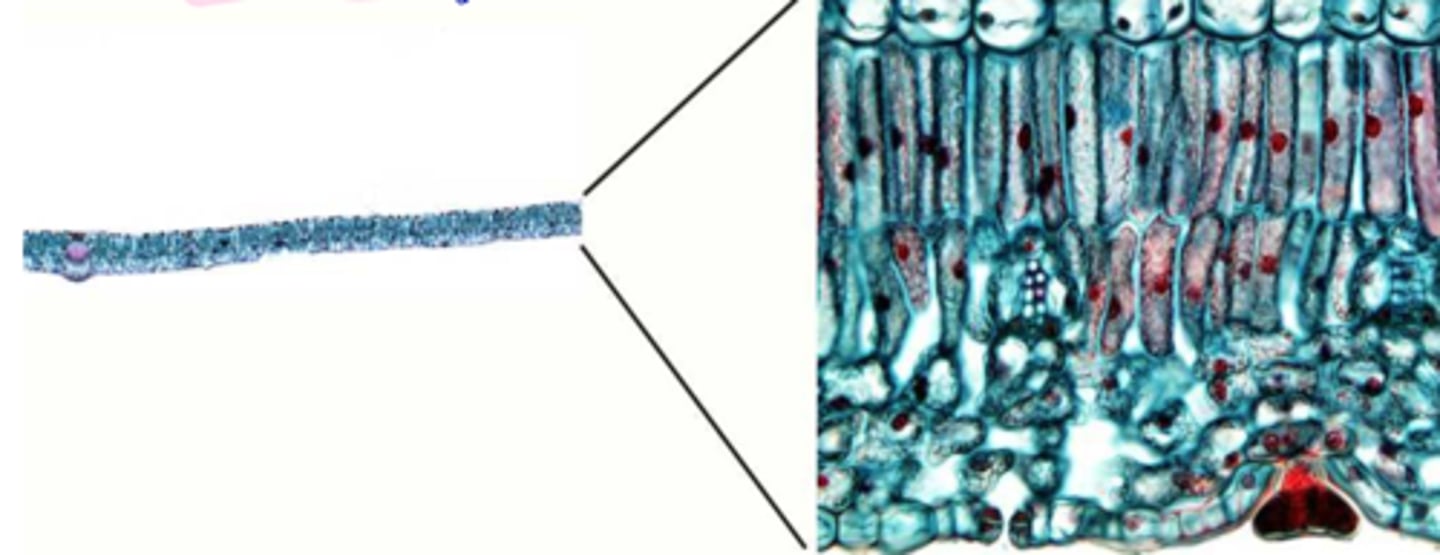
Presence of lobes
Larger volume of intercellular spaces
spongy mesophyll definition
- Majority of the chloroplasts are found in palisade
- intercellular spaces for rapid gas exchange
- external (epidermal) and internal (mesophyll) surface area
reasons for photosynthetic efficiency
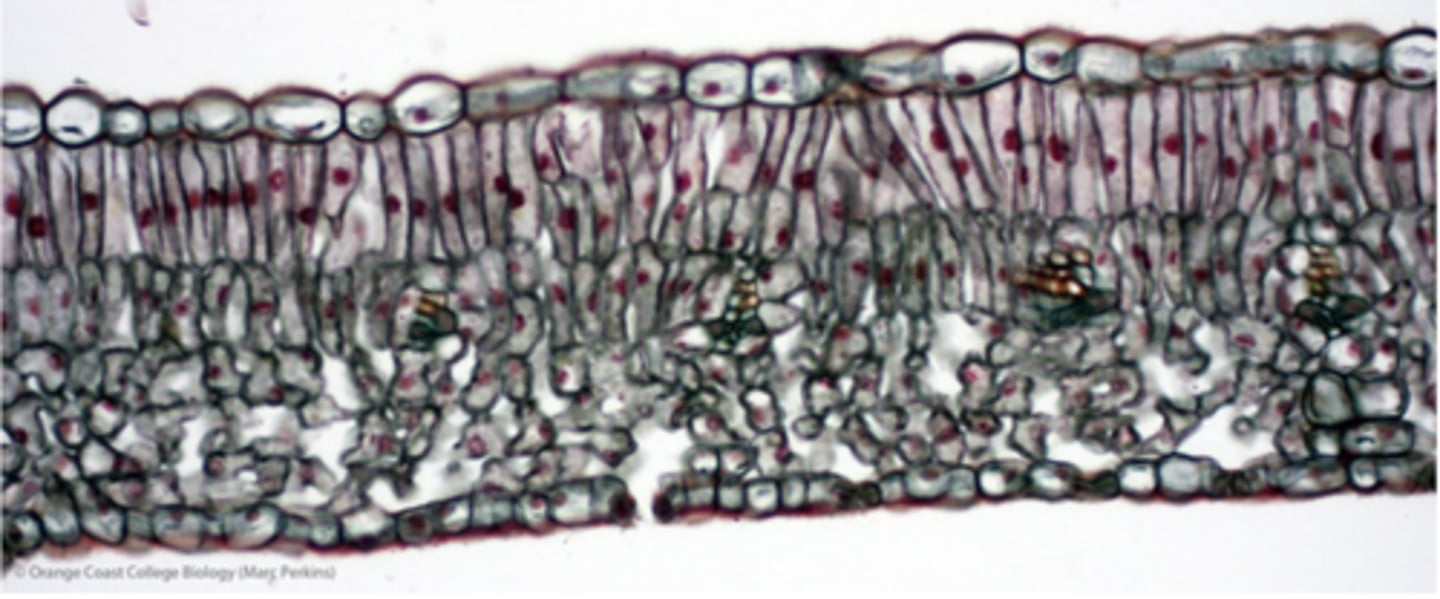
Dorsiventral or bifacial
Type of mesophyll in which the palisade is on one side and spongy mesophyll is on the other side
Isobilateral or isolateral or unifacial
Palisade present on both sides (Ficus)
Eudicot leaf - palisade developed
Monocot leaf - uniform
monocot vs eudicot mesophyll
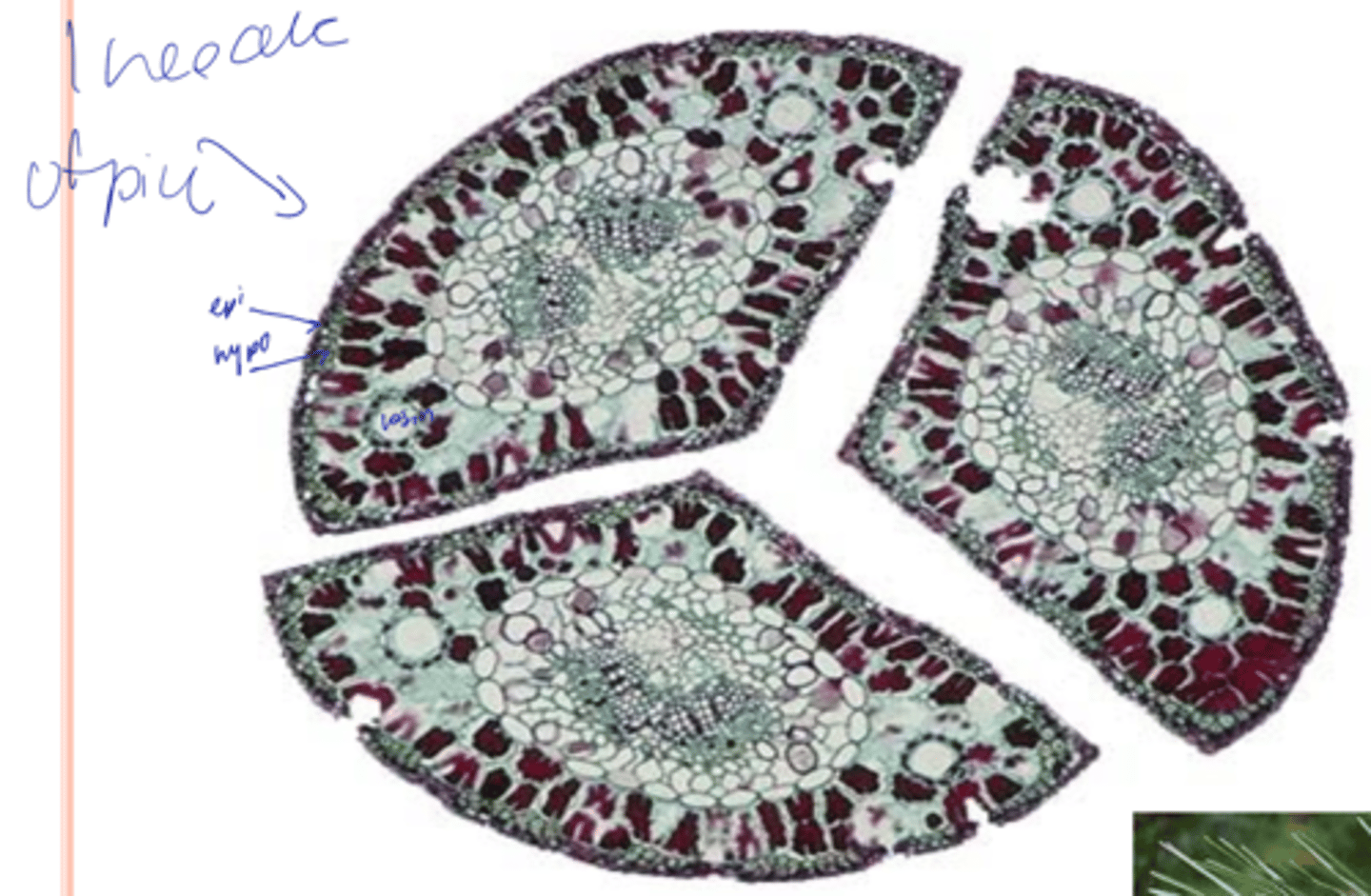
Convergent or uniform
Mesophyll cells look the same; no distinct palisade and spongy parenchyma (Pinus)
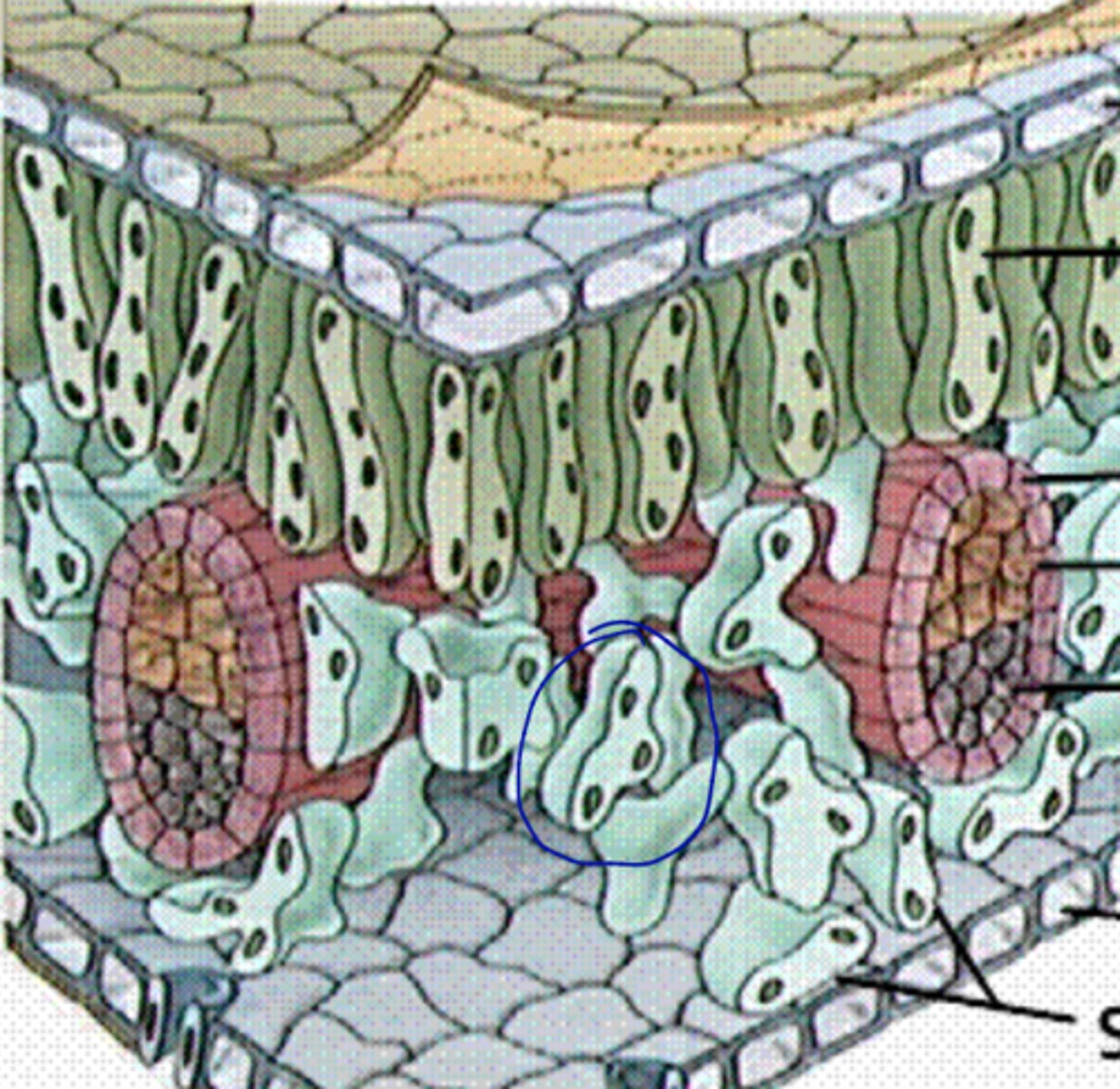
- Vascular bundles or + assoc. non vascular tissues that surround it
- Usually have bundle sheath (parenchymatous)
veins definition
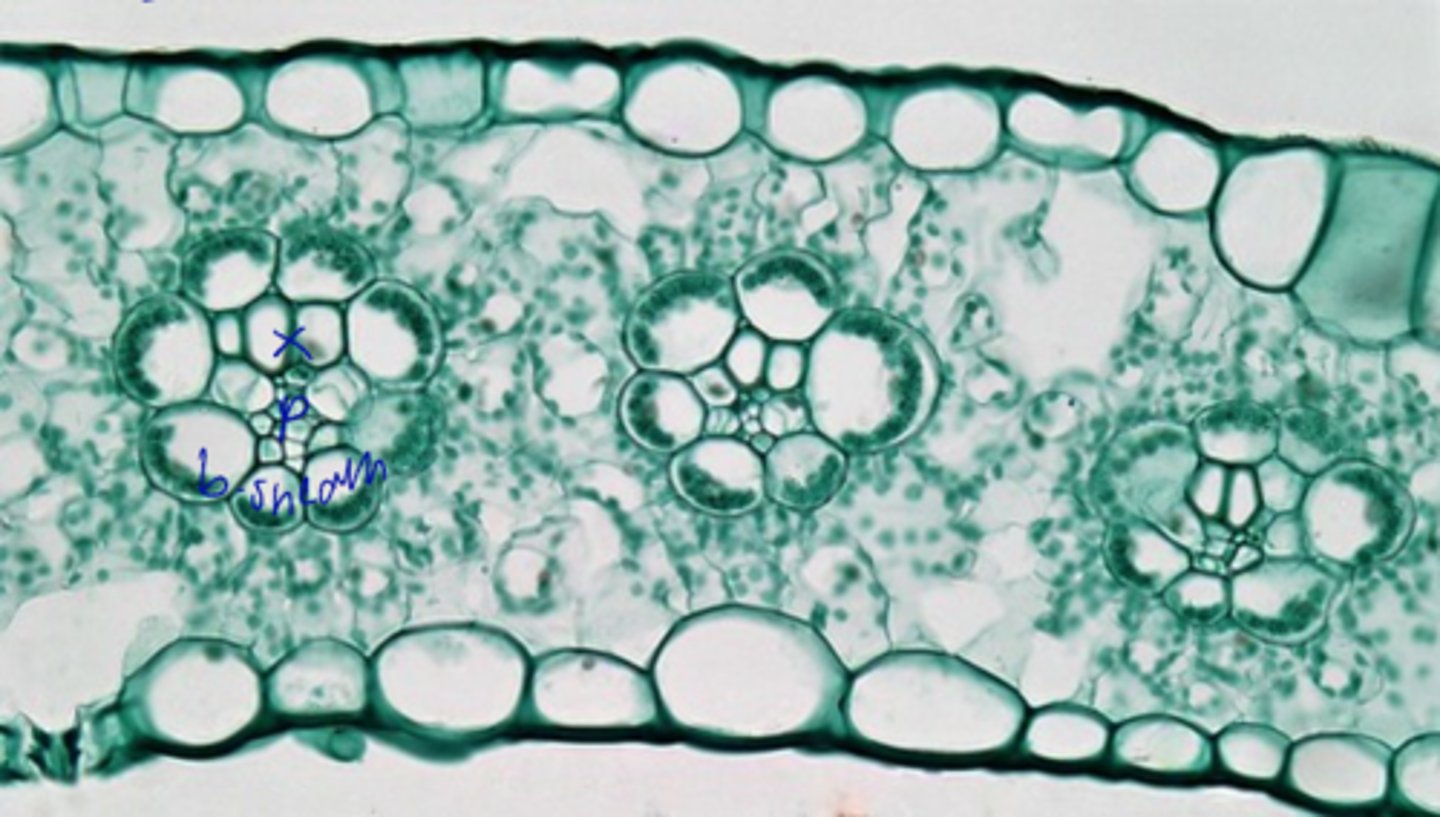
monocot
Vascular Bundles of similar dimensions
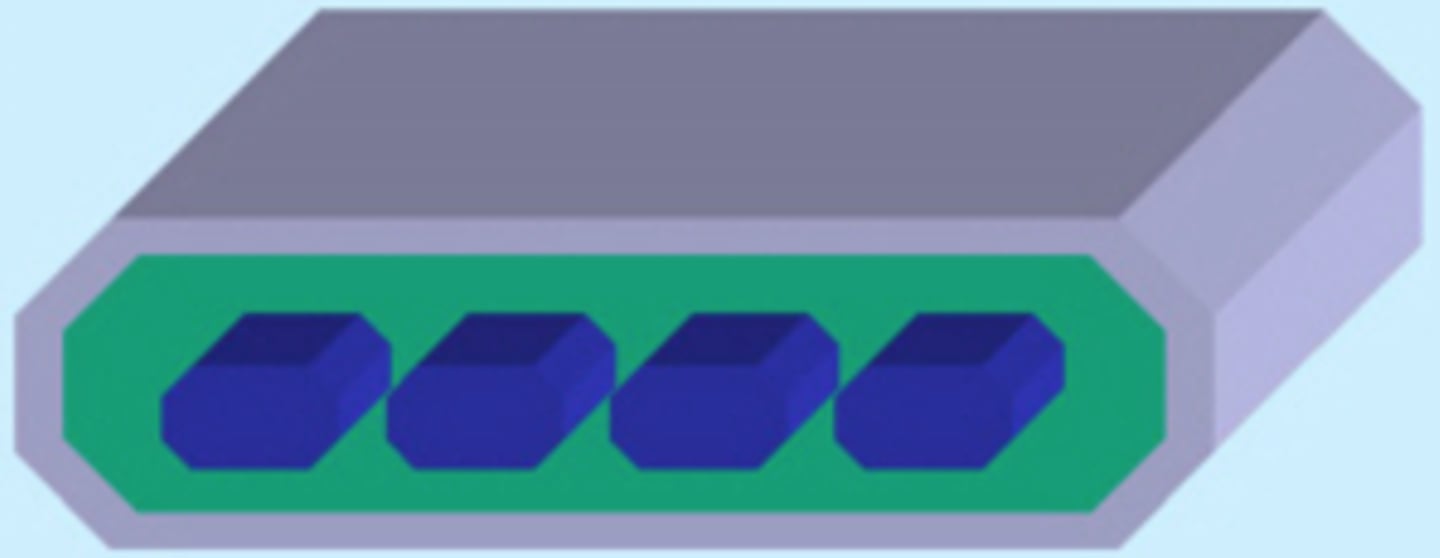

dicot
have a large central Vascular Bundle called a Midrib

C3 plants (normal photosynthesis)
where are bundle sheaths inconspicuous
C4 plants bc they store CO2 in bundle sheaths where calvin cycle happens
where are bundle sheaths enlarged
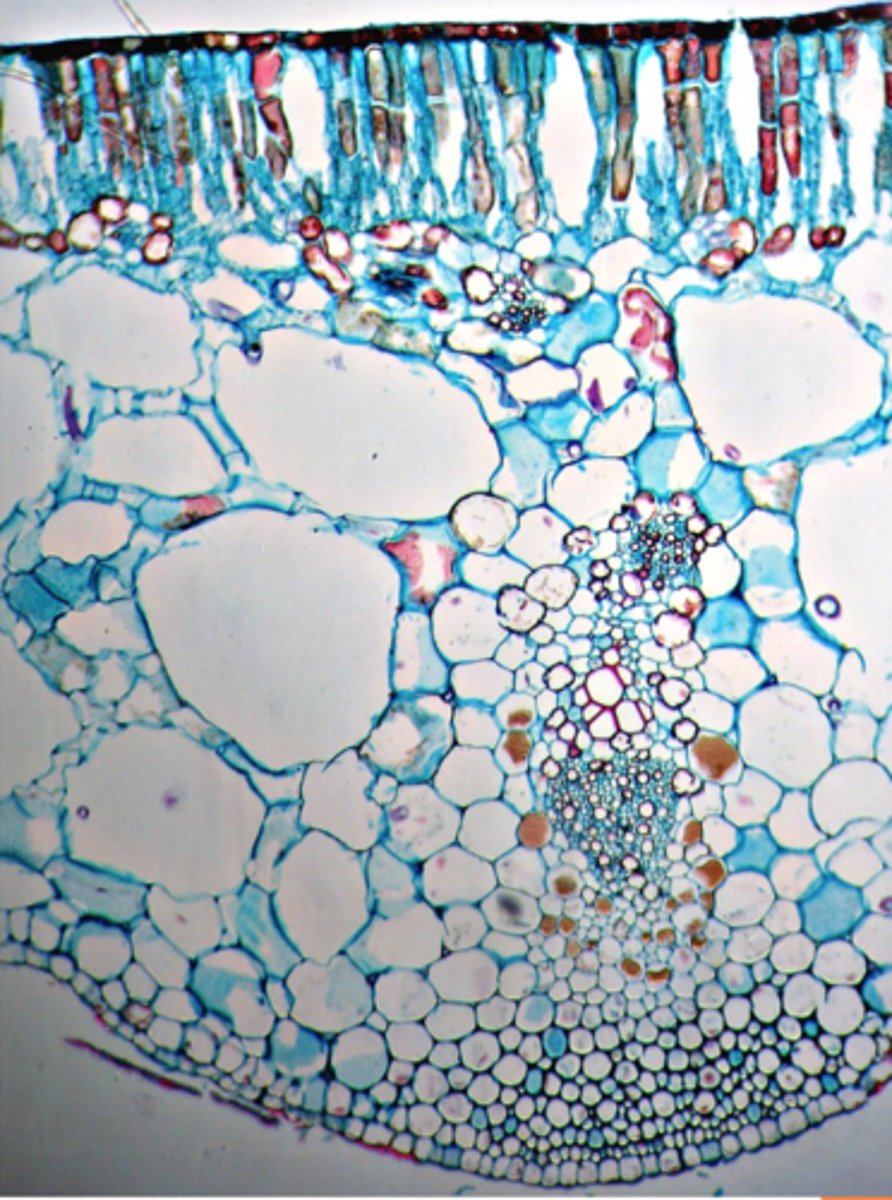
leaf - x outer, p inner
stem - x inner, p outer
leaf vs stem xy and phlo
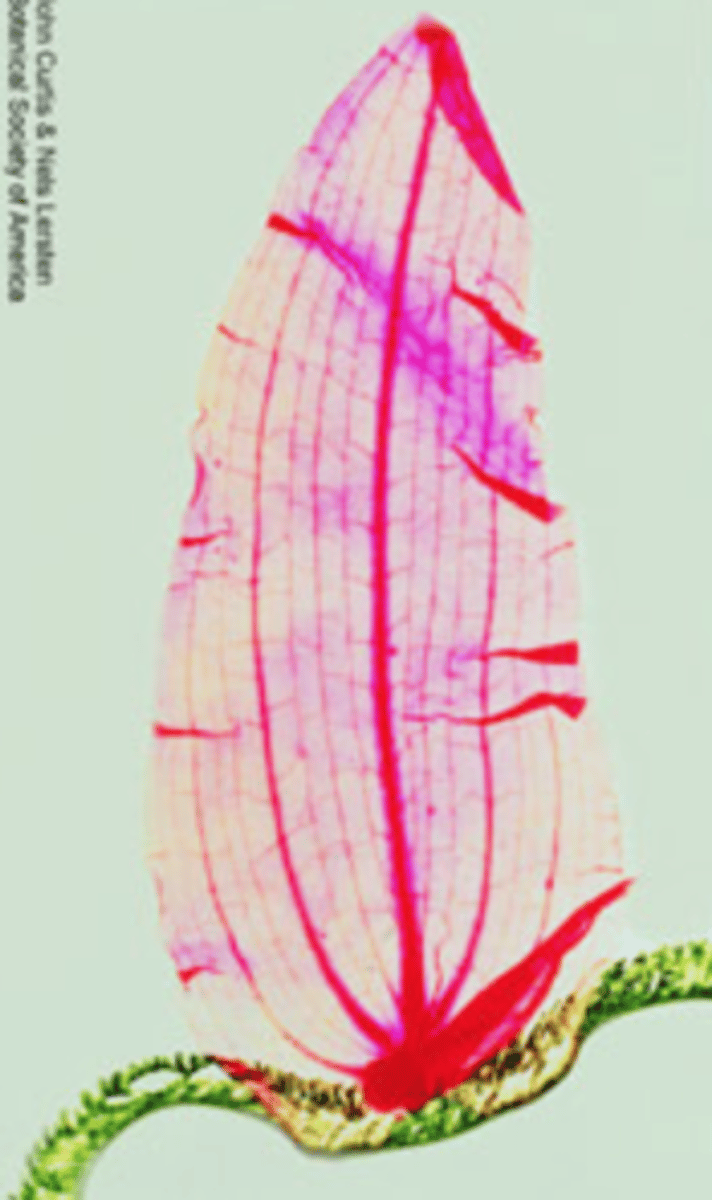
venation
arrangement of veins in a leaf
common to eudicots and some nonflowering plants
where can u find netted venation (pinnately and palmately)
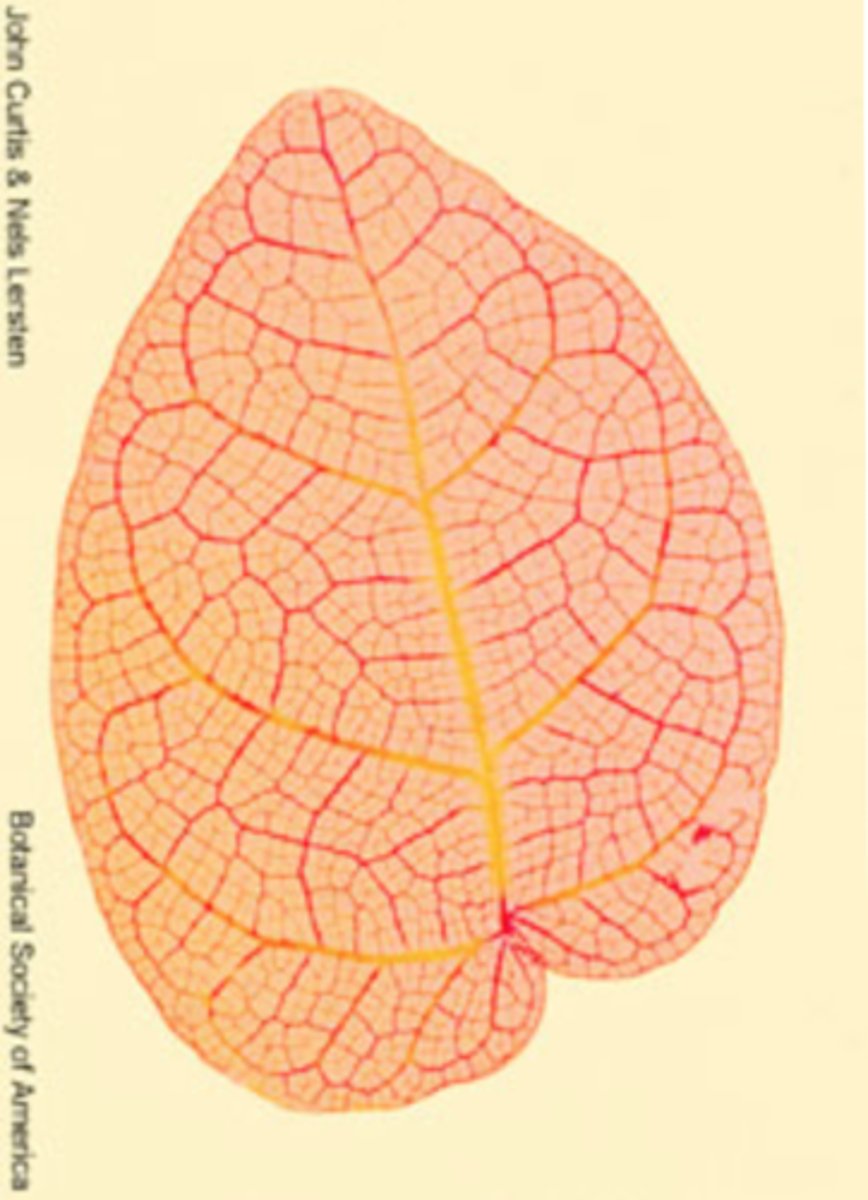
monocots
where can u find parallel venation
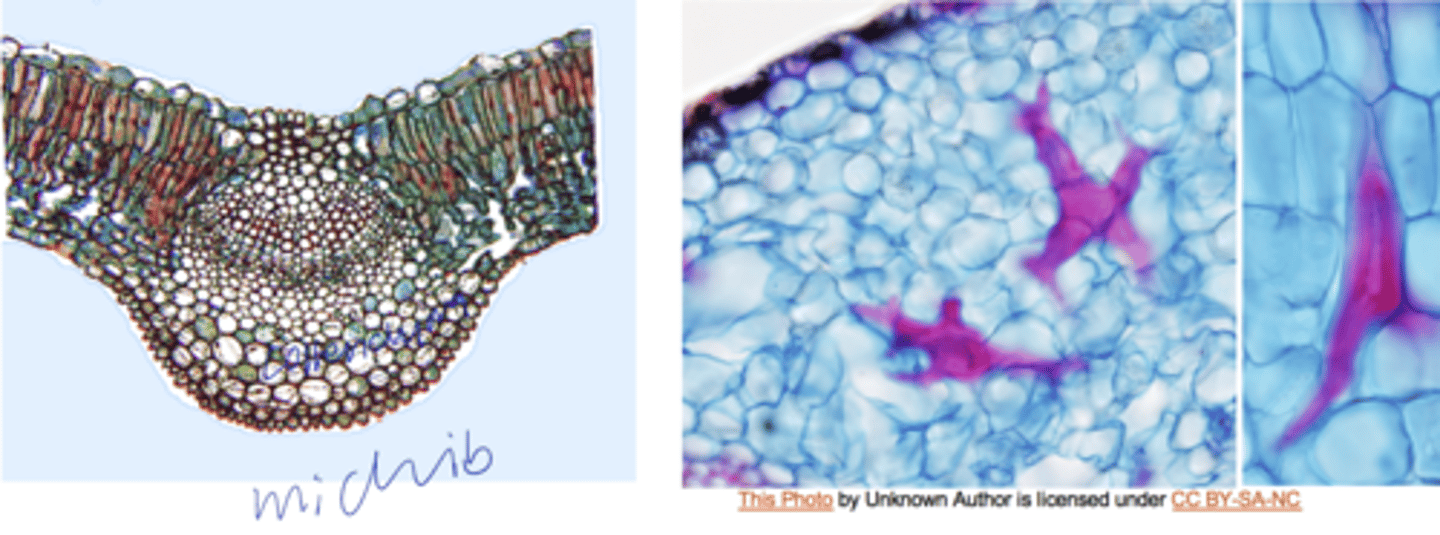
- epidermis
- Collenchyma close to the larger veins
- vascular bundles with fibers in monocots
- Sclereids in aqua plants
4 supporting tissues of the leaf
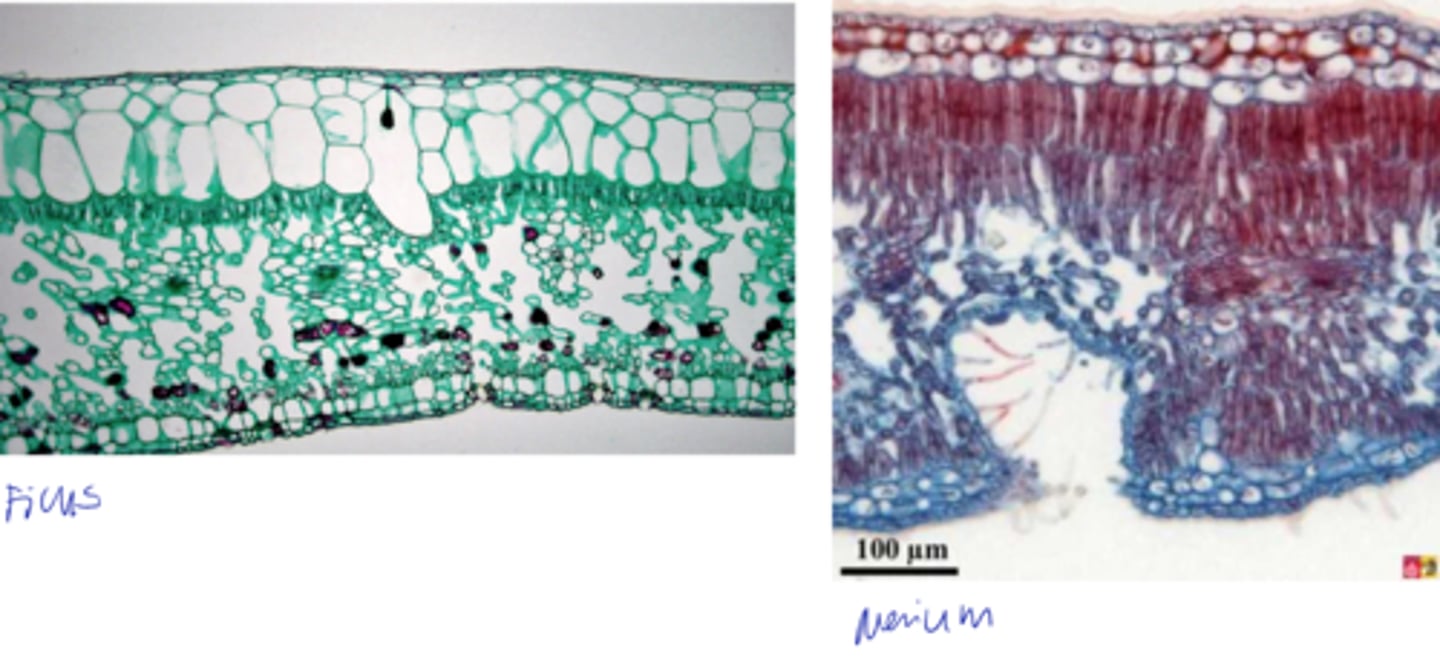
- Epidermis continuous with stem
- Parenchyma contains a few chloroplasts
- collenchyma and sclerenchyma
- Collateral vascular bundle
petiole description: type of ground tissue present? vascular bundle type?
v large vacuole to fold up + reduce water loss
bulliform/motor cells function

- Grow in arid habitats
- Decreased transpiration under conditions of water deficiency
xerophytes definition

- small + narrow leaves to lessen water loss
- Thick walls w cuticle and sclerenchyma
external specializations of xeromorphic plants

- multiseriate epidermis
- stomatal crypts
- abundant trichomes
- tendency to be isobilateral
- Involution of leaves through bulliform cells
5 internal specializations of xeromorphic plants
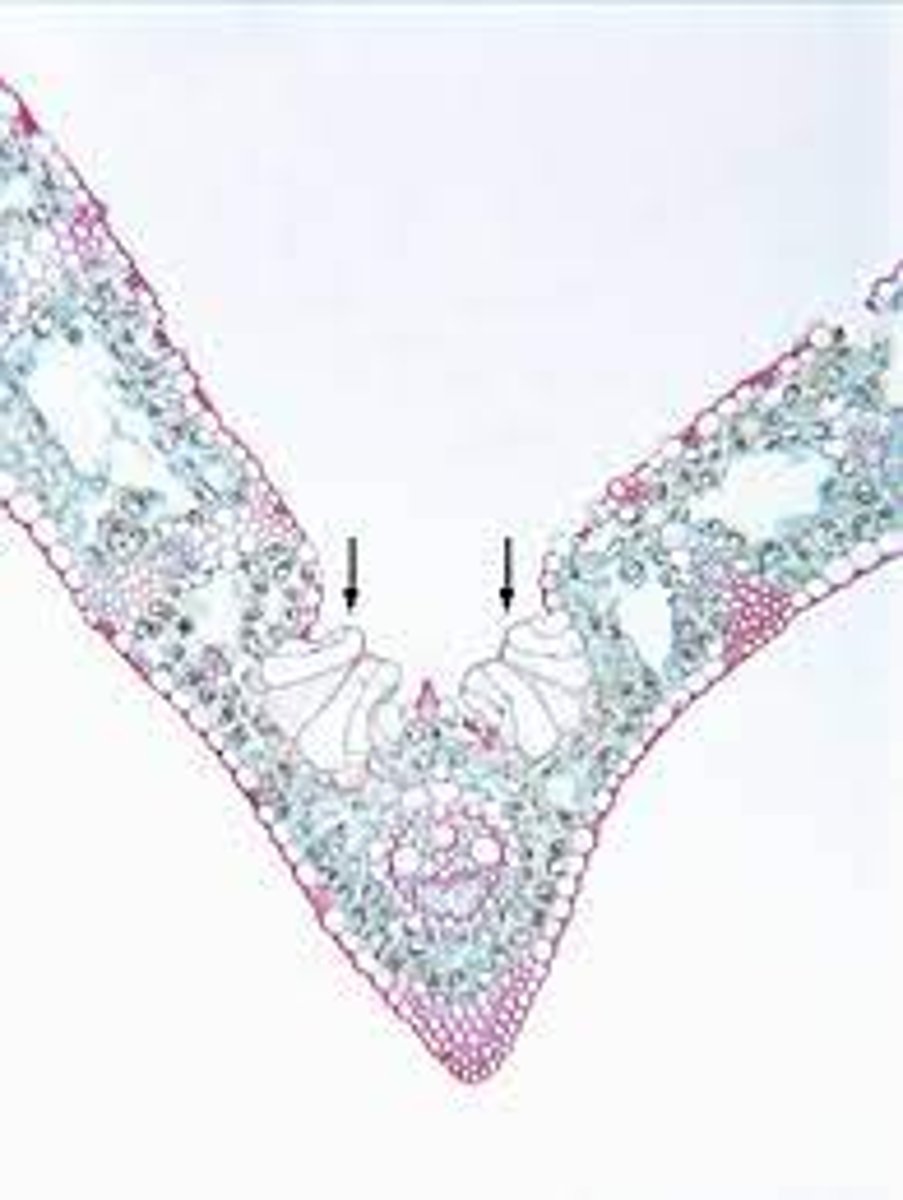
hide the stomata, invaginations in lower epi + maraming 3chomes
stomatal crypts definition
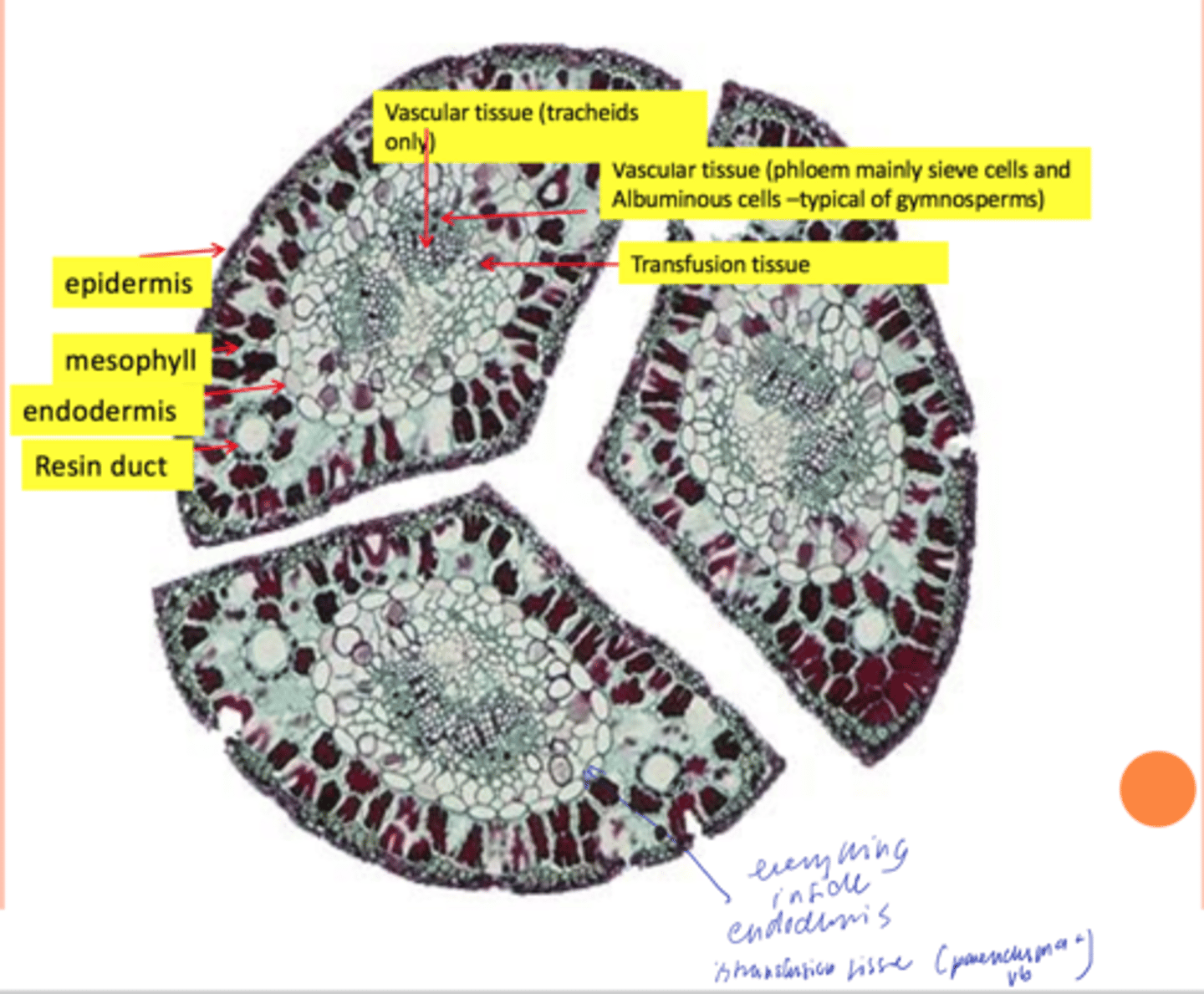
gymnosperms
examples ng xeromorphic
- consists of tracheids and elongated parenchyma cells
- characteristic of gymnosperms
- passage of water and nutrient substances between the bundle and the mesophyll
Transfusion tissue consists of what and its function
- Thick wall and thick cuticle
- Stomata are sunken and overarched by subsidiary cells
- Hypodermis
- Mesophyll walls have ridge-like invaginations into the cells; contain chloroplasts
- Transfusion tissue
- Endodermis
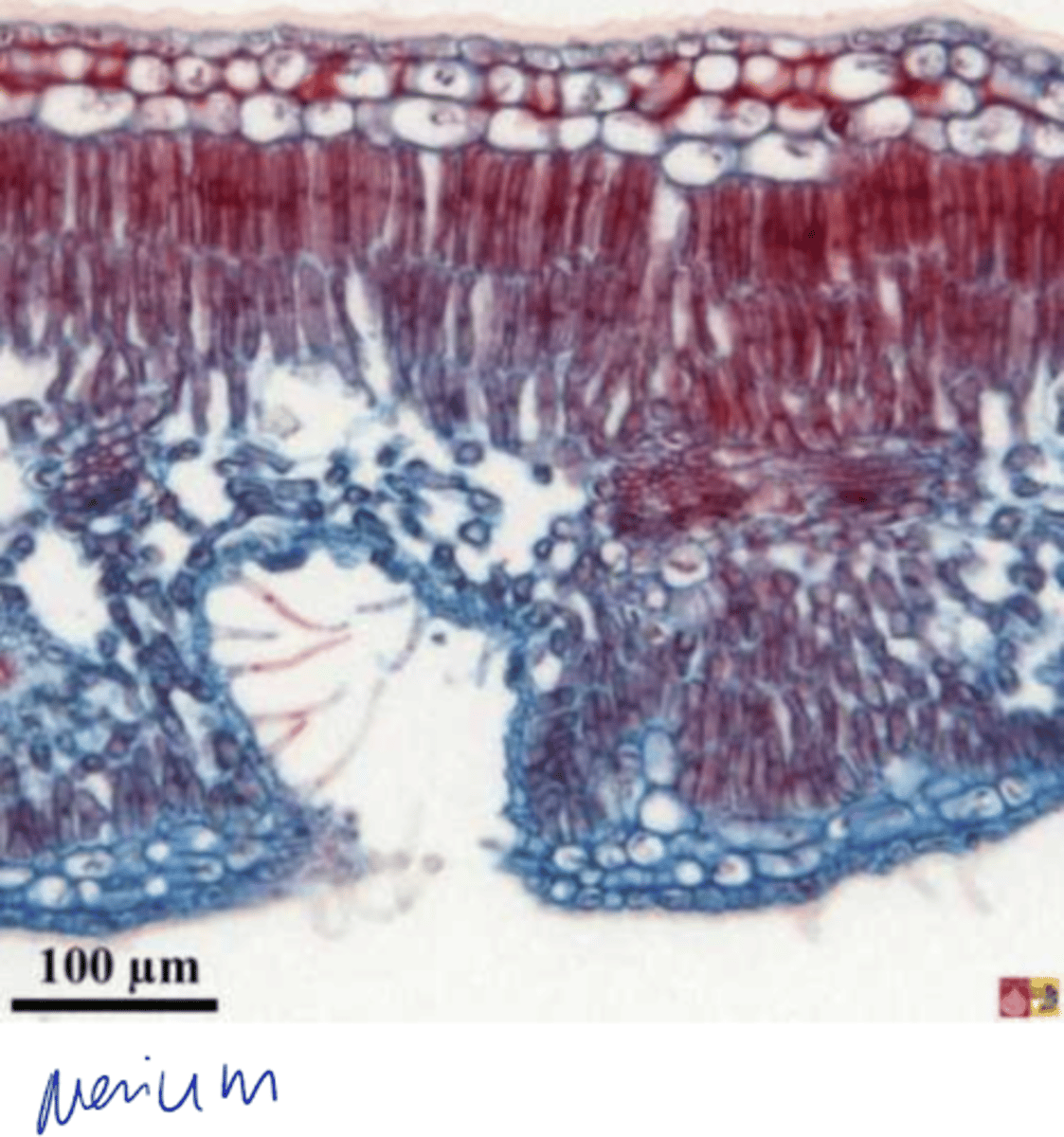
features of pinus leaves
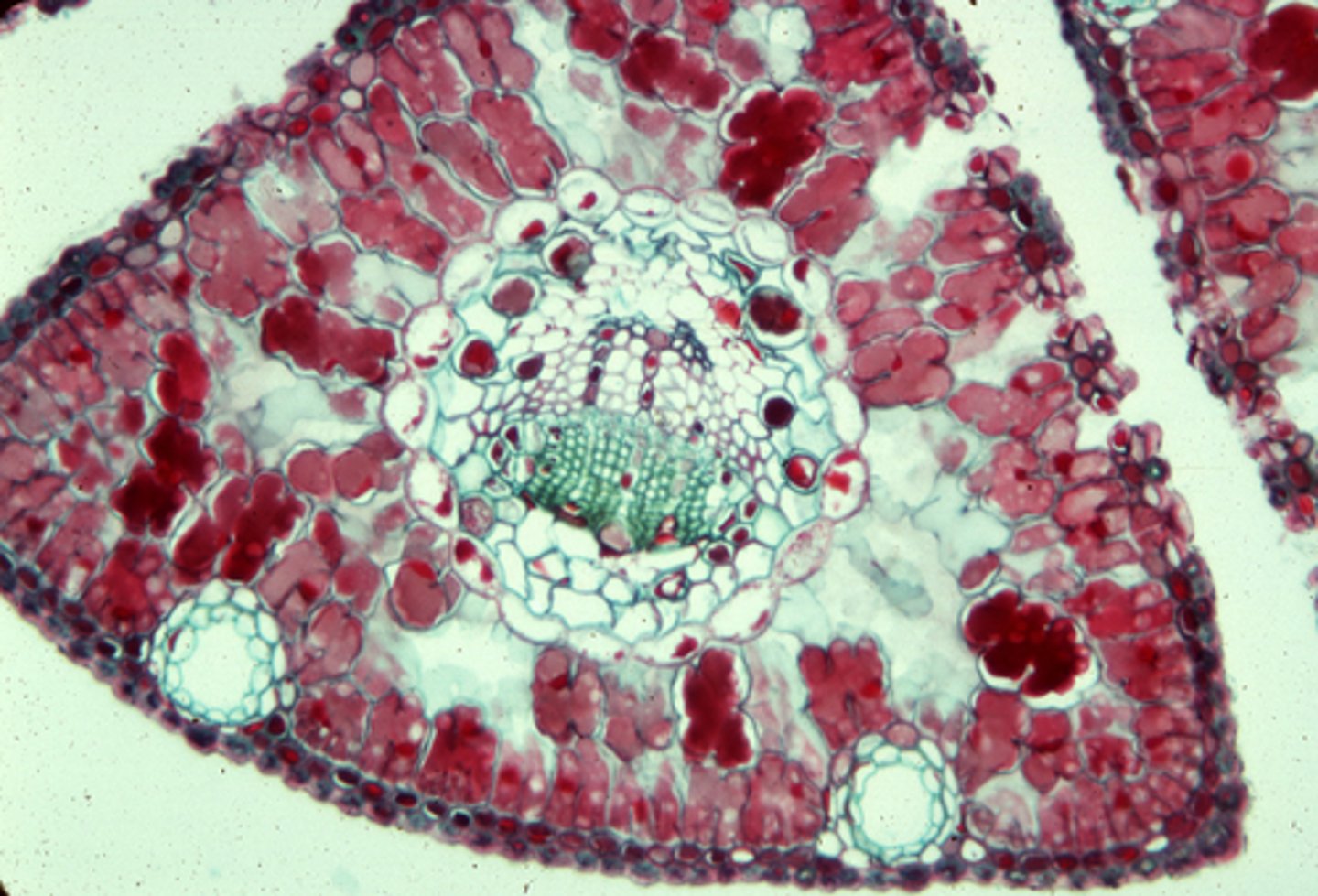
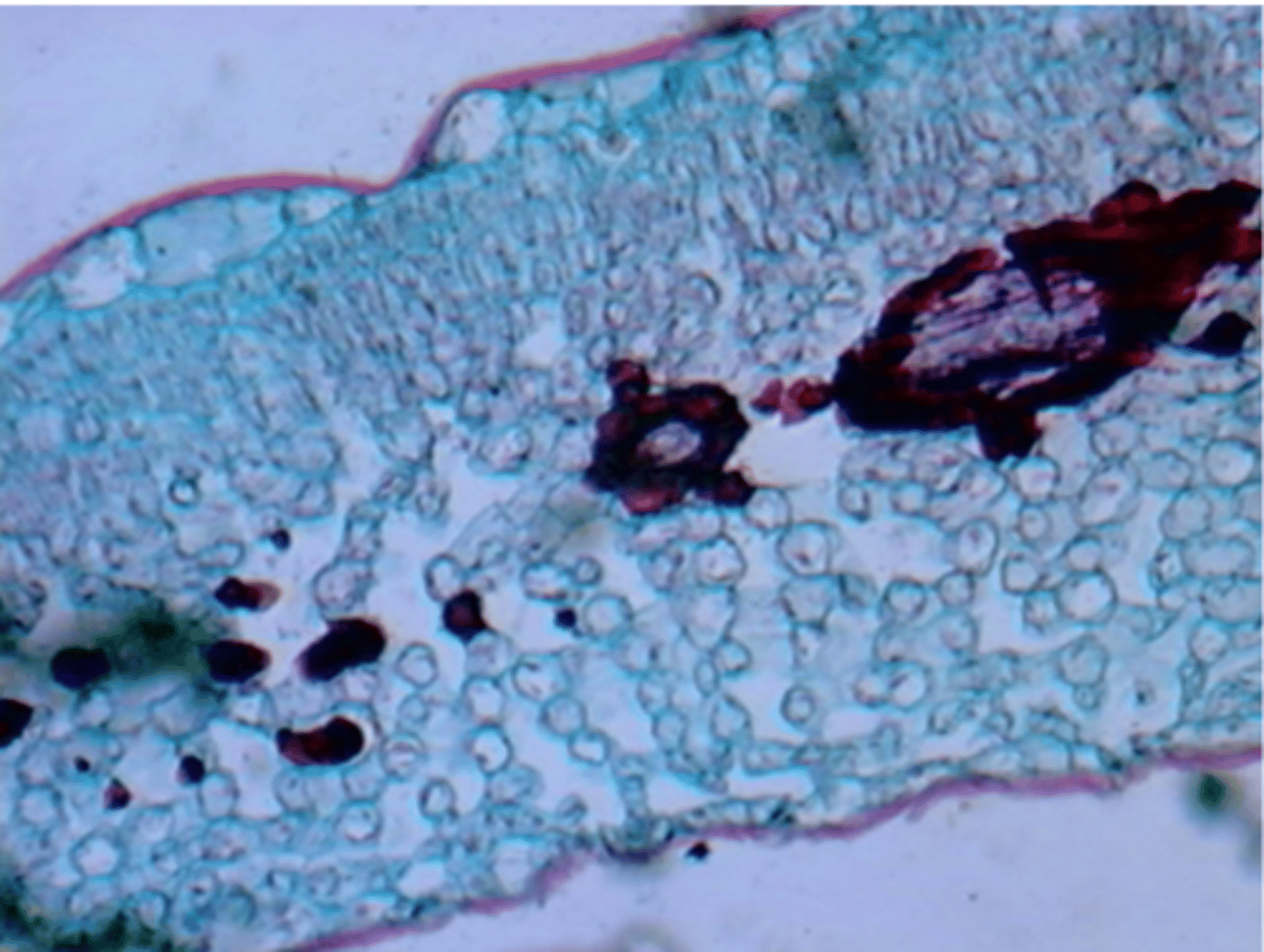
- Epidermal cell thick walled and thick cuticle
- Stomata are sunken and abaxial surface
- Hypodermis
- Vein surrounded by endodermis
features of cycas leaves
- Reduction of supporting (water supports) and protective tissues
- Decrease vascular tissue esp xylem
- Presence of air chambers for filtration
- very thin cuticle
- Aerenchyma
5 features of hydrophytes
Epistomatic (floating)
hydrophytes stomata
very reduced
hydrophytes root system
- periclinal
- sides of the apex/peripheral zone
- come from apical meristem
leaf initiation
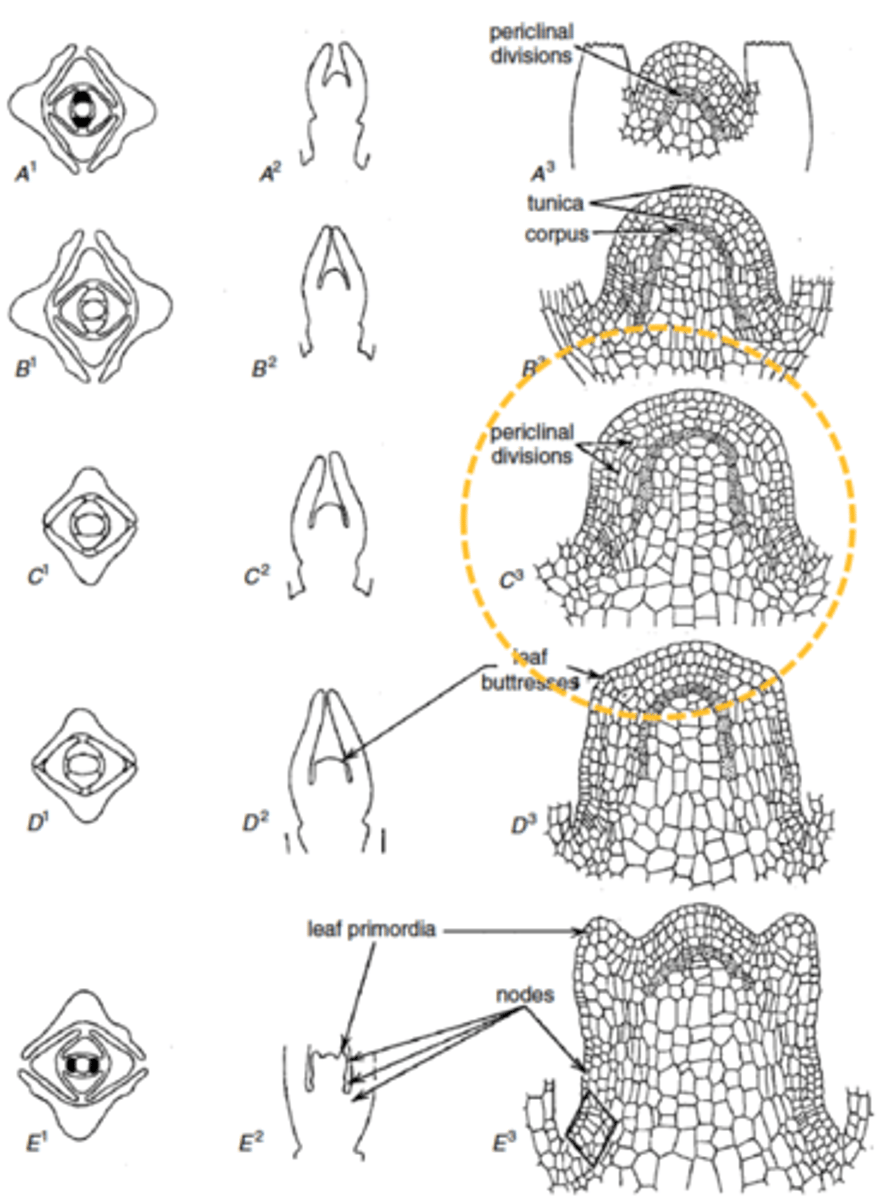
Protrusion in the peripheral zone that will turn into leaf primordia
leaf buttress definition
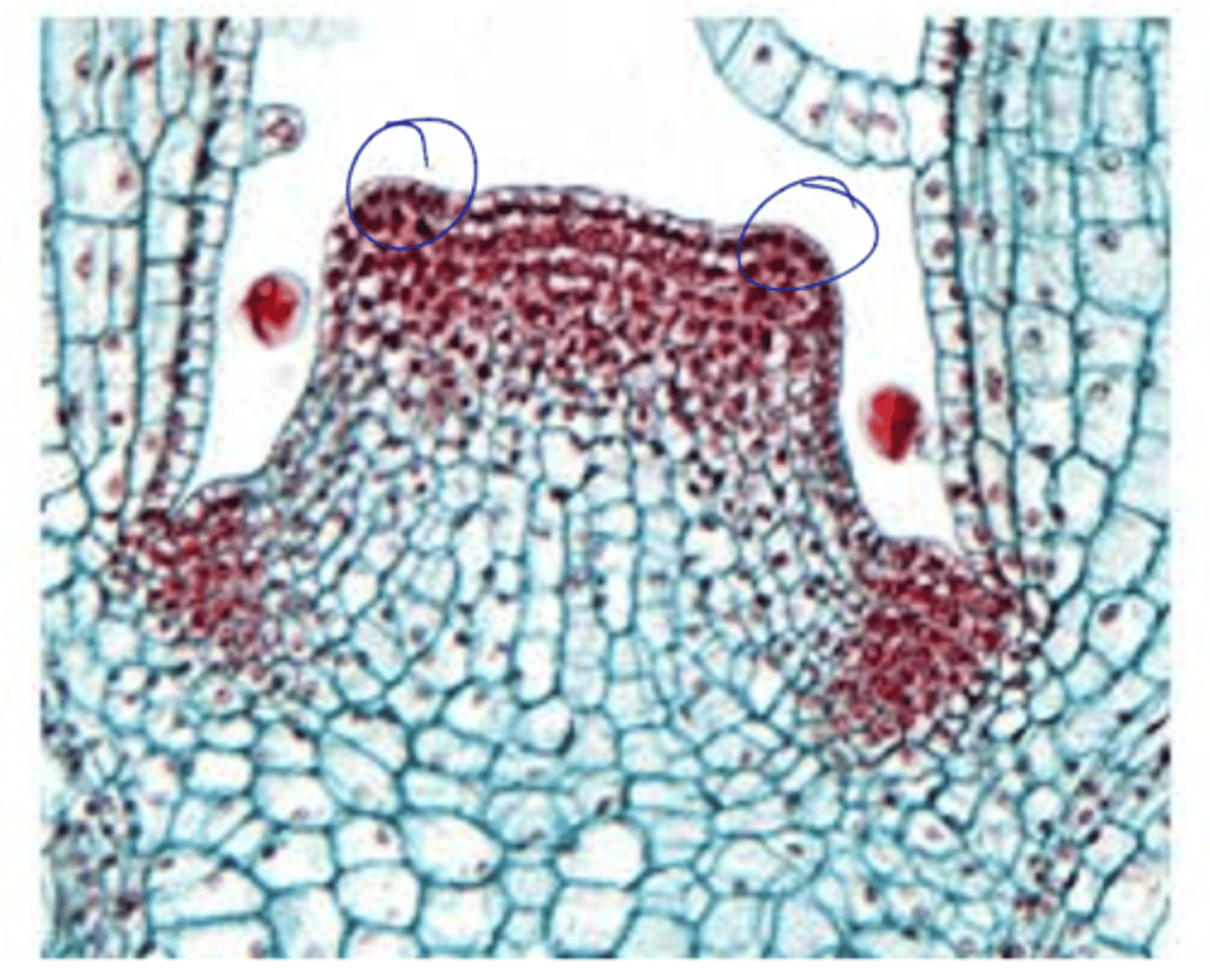
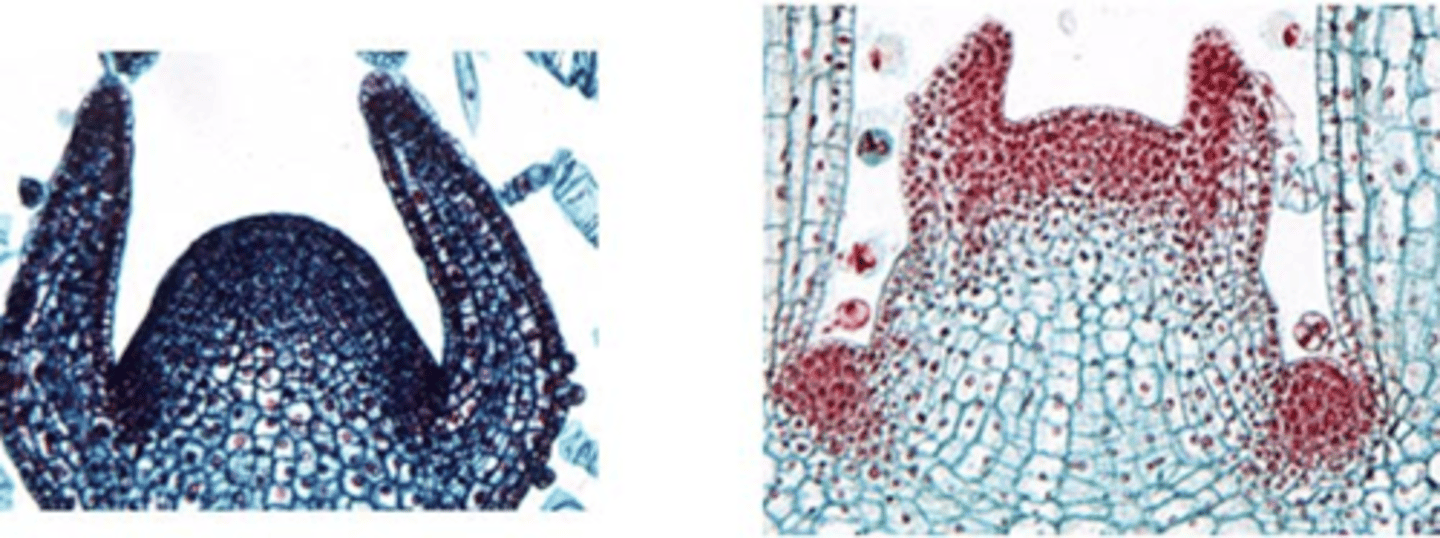
at sites that are correlated with the phyllotaxis of the shoot
where do leaf primordia arise
2. Transport
3. Transpiration
4. Modified Functions
blade divided into leaflets
compound leaf defimition
False, above petiole
Axillary bud is always at base of leaf below the petiole (True or False)
True
Mesophyll is parenchymatous !!!! (True or False)
2. Palisade mesophyll are located at the adaxial portion
3. Well-developed intercellular spaces for rapid gas exchange
perform calvin cycle in their bundle sheath
C4 plants differ from C3 and CAM plants in that C4 plants _____.
True, photorespiration
In C4 plants like corn, they have specialized structure called bundle sheath where they store carbon dioxide in which it happens to combat what?