sex differences lecture 1
structure of a neuron - draw and describe
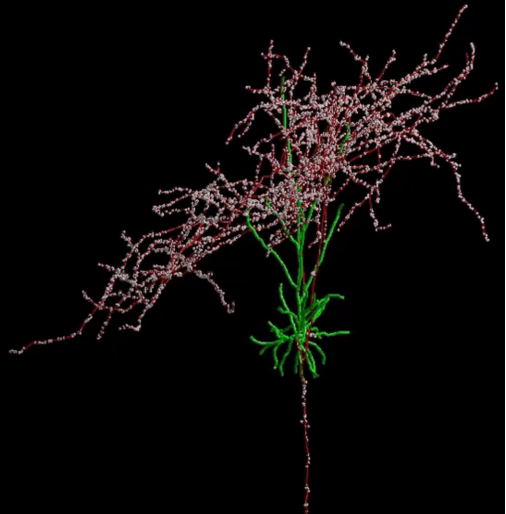
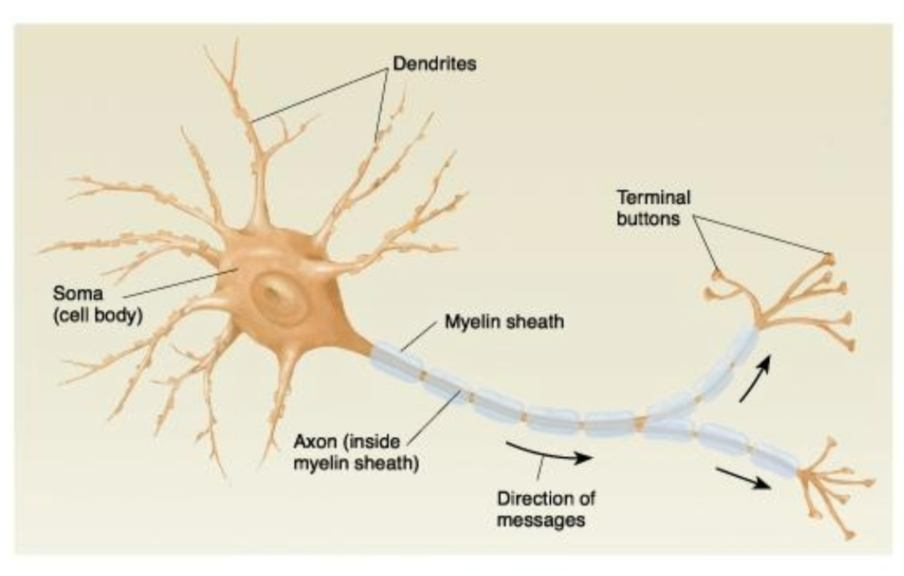

what is this an image of, list different structural components
Structure of a real neuron (3d reconstruction of neuron in a cats visual cortex - don’t need to remember this but
Green = dendrites
Red = axon and soma
White = synapses made with other neuons
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
structure of a neuron - draw and describe


what is this an image of, list different structural components
Structure of a real neuron (3d reconstruction of neuron in a cats visual cortex - don’t need to remember this but
Green = dendrites
Red = axon and soma
White = synapses made with other neuons
How are neurons connected?
Neurons form circuits
If 2 inhibitory and one excitatory action potential generated (assuming all synapses are as powerful will it fire?
In this case it ownt because theres more inhibition than excitation due to all or nothing law (but in real life depends on locations , action potential threshold and strength of other neurons detrimins if input is strong enough to produce an action potential)
how does neurotransmission occur
via synapses
is it inevitable synapse per neuon?
Each neuron can have 100s of synapses – if action potential arrives and is generates – AP does choose which direction just pslots and electrical current transported dwon various neurons – synapes can be located at ddendrites/ somas/ axons fo other neurons/ other synpases
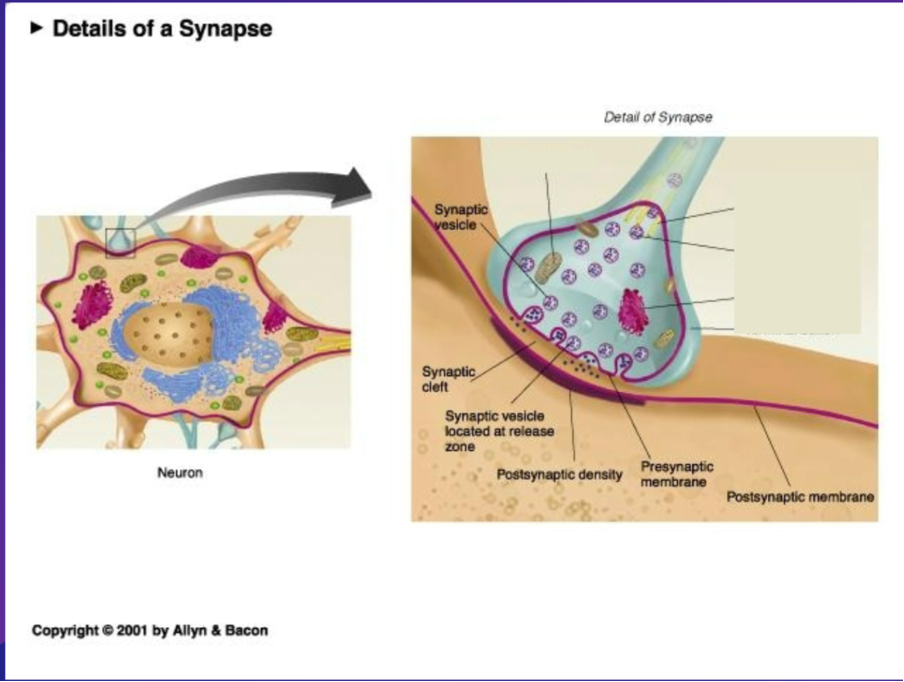
draw and list each element present in a synapse
Post-Synaptic Membrane – end of a neurons axon
Post synaptic density – a membrane region in the target cell full of receptors/ receptor molecules
Receptor molecules – proteins located in the post synaptic density
Pre synaptic cleft – space between pre synaptic and psot synaptic terminal
Neurochemical Messengers
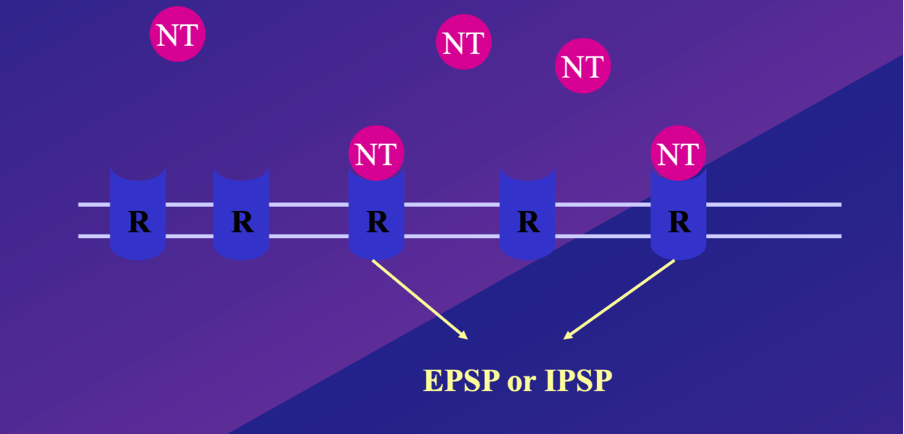
what does each element symbolise in this image/ what does this diagram show
^ post synaptic density
R = receptor molecules
NT= neurotransmitter, which diffuse through synaptic cleft, where they then bind to receptors on post synaptic terminal where N binds to specific Receptor sites, this binding results in either an IPSP or EPSP
EPSP – excitatory post synaptic potential
IPSP – inhibitory post synaptic potential
Does the splitting of the action potential laong acxons reduce the strength of the action potential?
No because of the all or nothing principle
define Neurotransmitter
A molecule is a neurotransmitter when it
– Transfer signals From one neuron to the next
– conducts Local action (just at a synapse)
– Effects can be activation or inhibition (neurotransmitter can do both), depending on the transmitter/receptor combination
– moelcules can have multiple functions – being a neurotransmitter is not a physiological property but a functional propert
can a molecule only be a neurotransmitter if it is a neurotransmitter ?
moelcules can have multiple functions – being a neurotransmitter is not a physiological property but a functional propert, cn also be n e.g. hormone in certain contexts and a neurotransmitter in another brain region
list molecules which can be neurotransmitters:
only need to remember those that are mentioned again in other lectures – just highlights moelcules can be different things and NTs
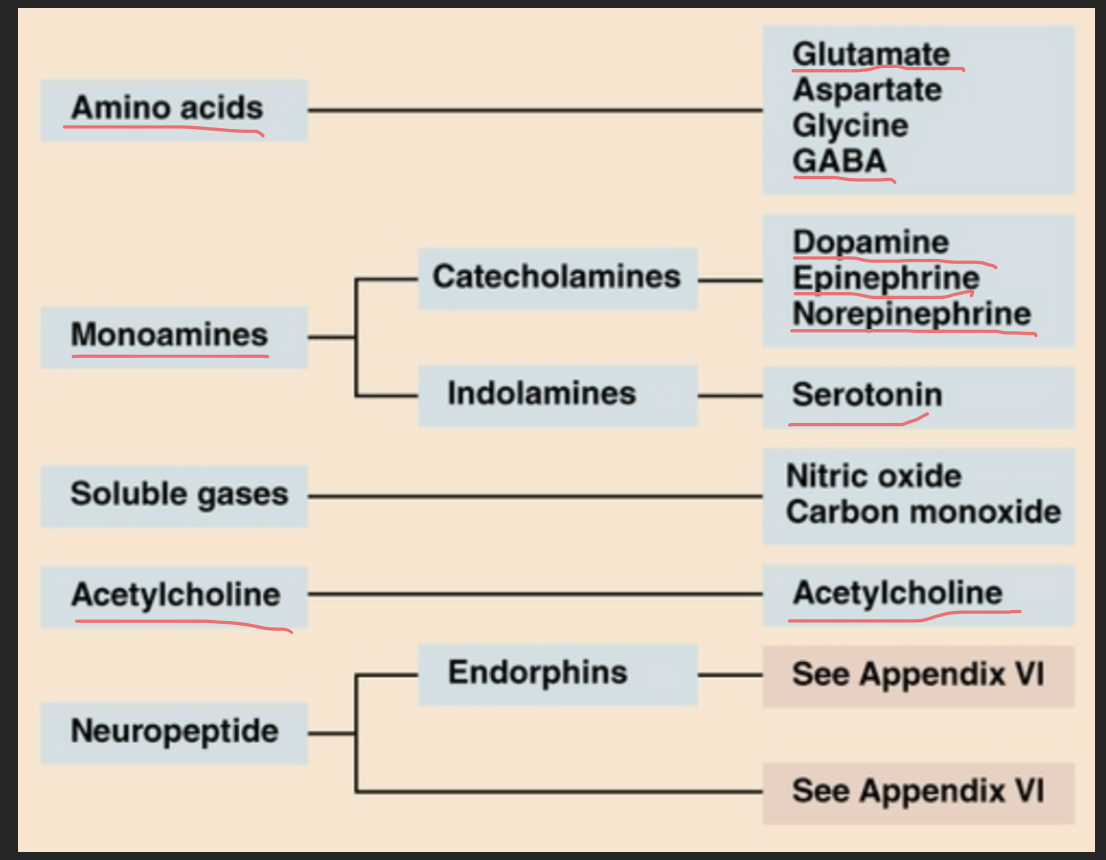
Which can be neurotransmitters?
A) Adrenaline
B) Noradrenaline
C) Dopamine
D) Serotonin
E) Acetylcholine
F) Testoerone
G) Cortisol
Answer – a, B, C, D, E
Adrenaline – never a neurotransmitter, only a hormone in our body
F, G only ever used as a hormone in our bodies
Which can be hormones?
A) Adrenaline
B) Noradrenaline
C) Dopamine
D) Serotonin
E) Acetylcholine
F) Testoerone
G) Cortisol
Answer –
A, B, F, G
hormone definition
⁃ a chemical messenger molecule that is released into and travels Through the bloodstream to bind to its target receptor
⁃ conducts Global action (affect multiple organs or tissues throughout the body, not just the nearby cells / tissue where they were released.
Effects can be varied, depending on the hormone/receptor combination
neurotransmitter definition
-chemical messengers used in the communication from one neurone to the next across a synaptic cleft.
⁃ From one neuron to the next
⁃ Local action
⁃ Effects can be activation or inhibition, depending on the transmitter/receptor combination
is only released into a synapse, never intentionally into the bloodstream