acing anatomy skeletal test
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Hyoid
The only bone that does not articulate with another
hemopoiesis
epiphysis site of
nutrients
arteries supply bones with
outside
periosteum is ____ covering of diaphysis
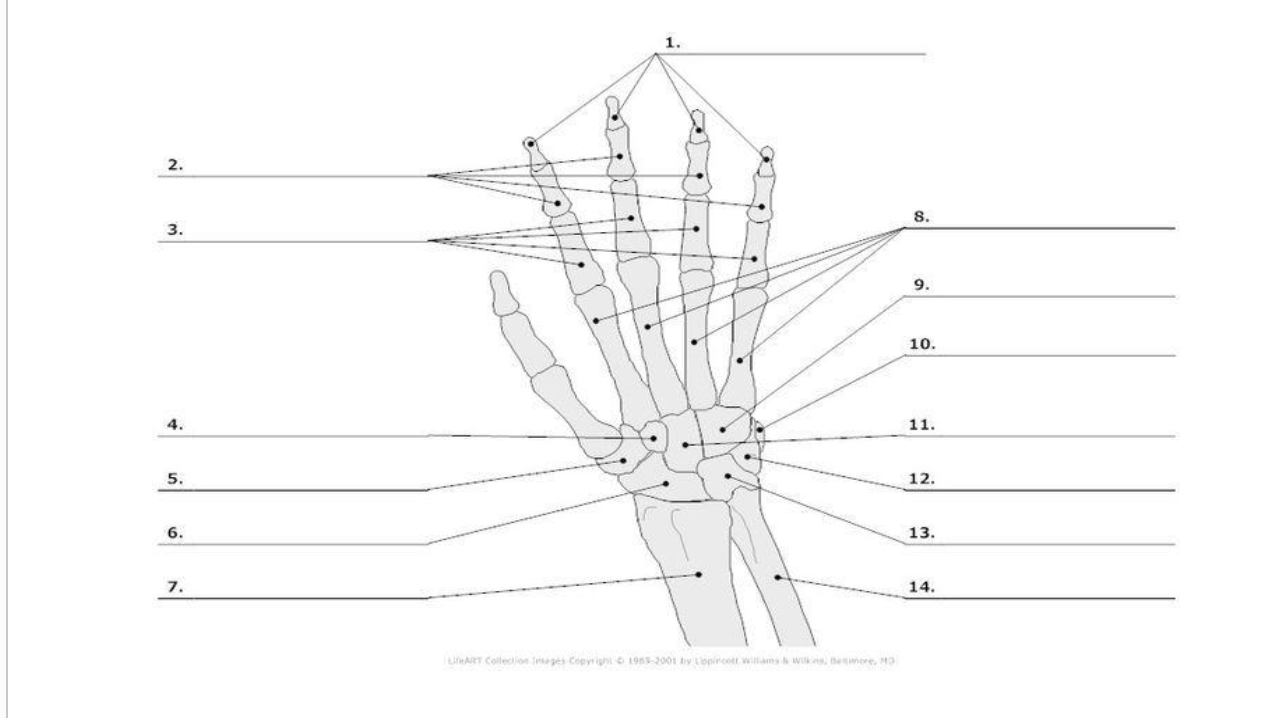
Distal Phalange
1.)
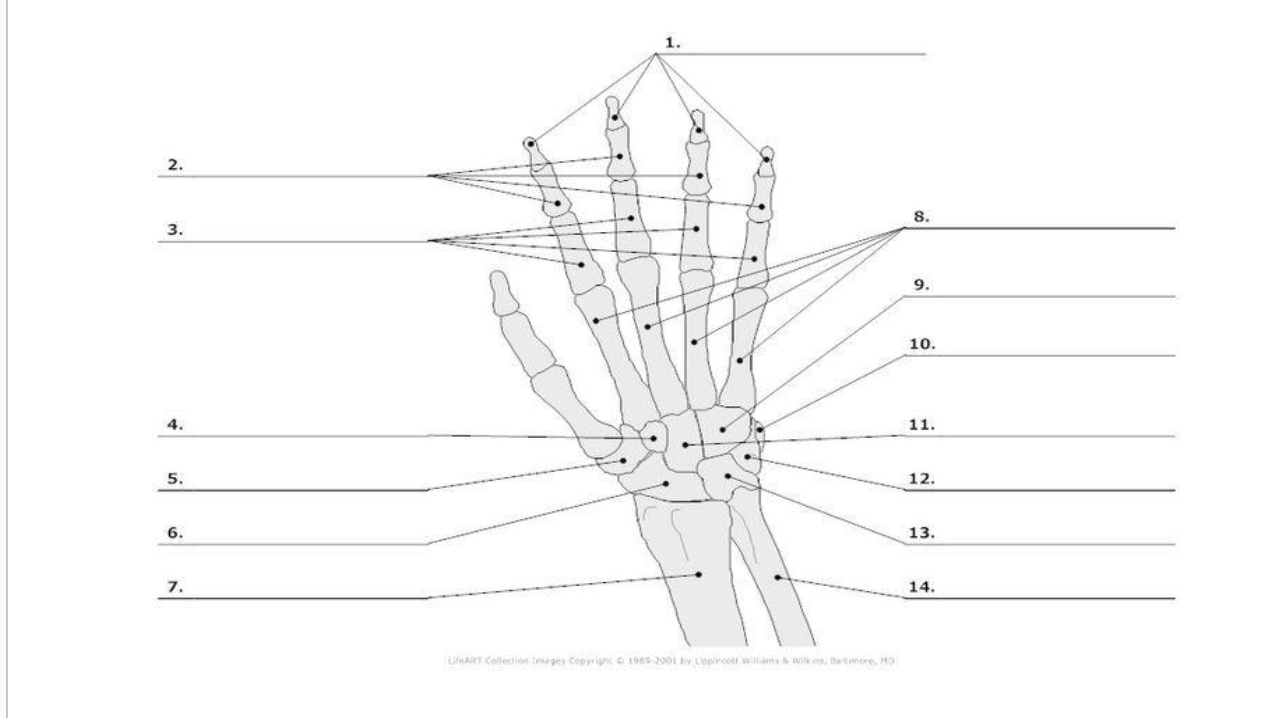
Middle Phalange
2.)
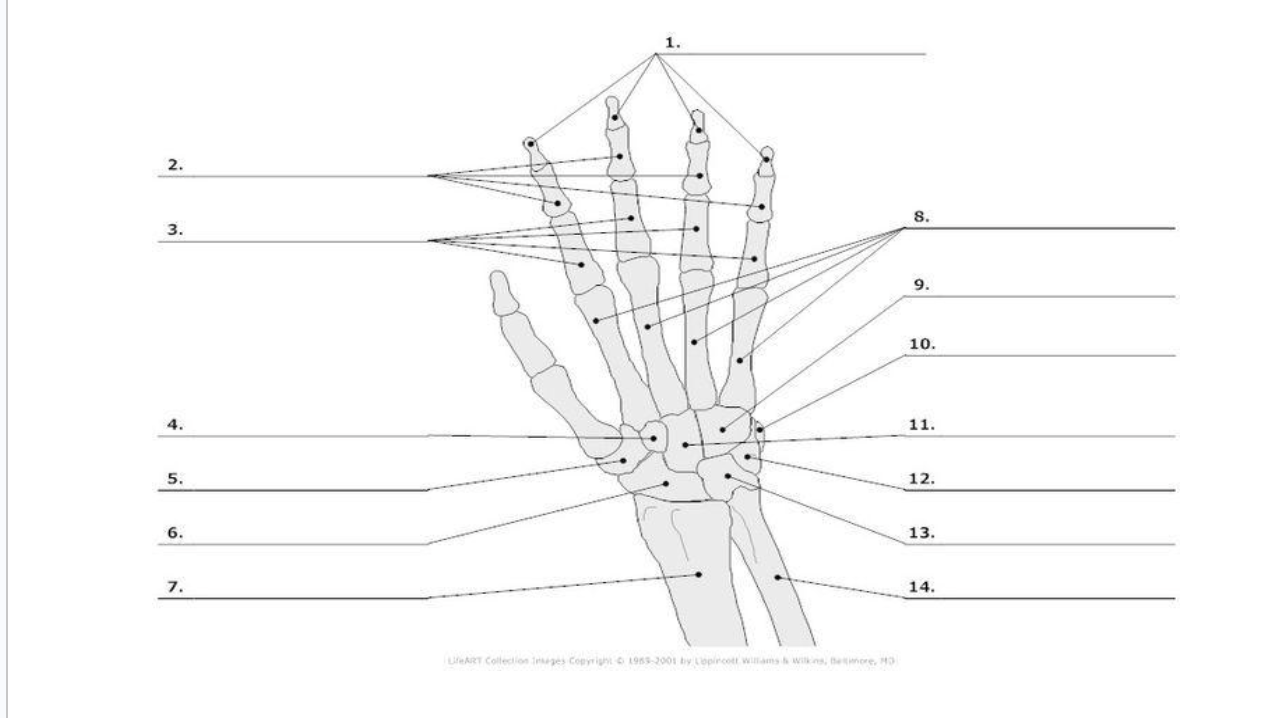
Proximal Phalange
3.)
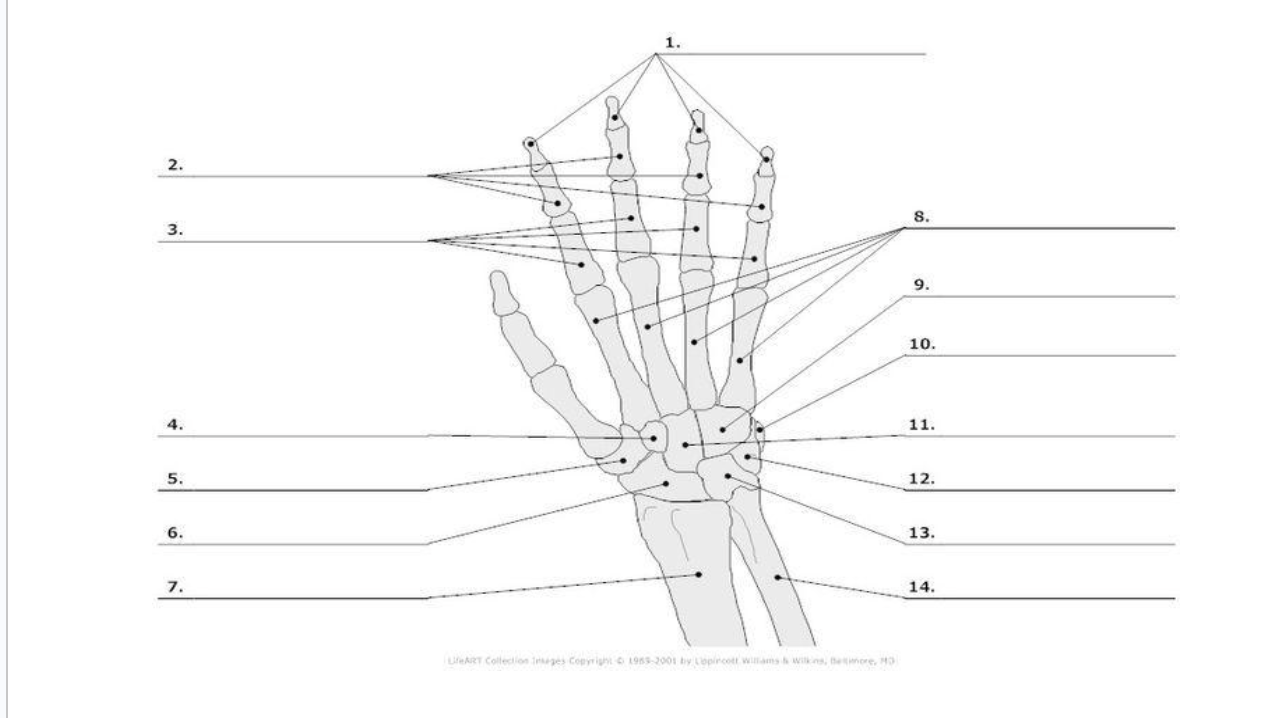
Trapezoid
4.)
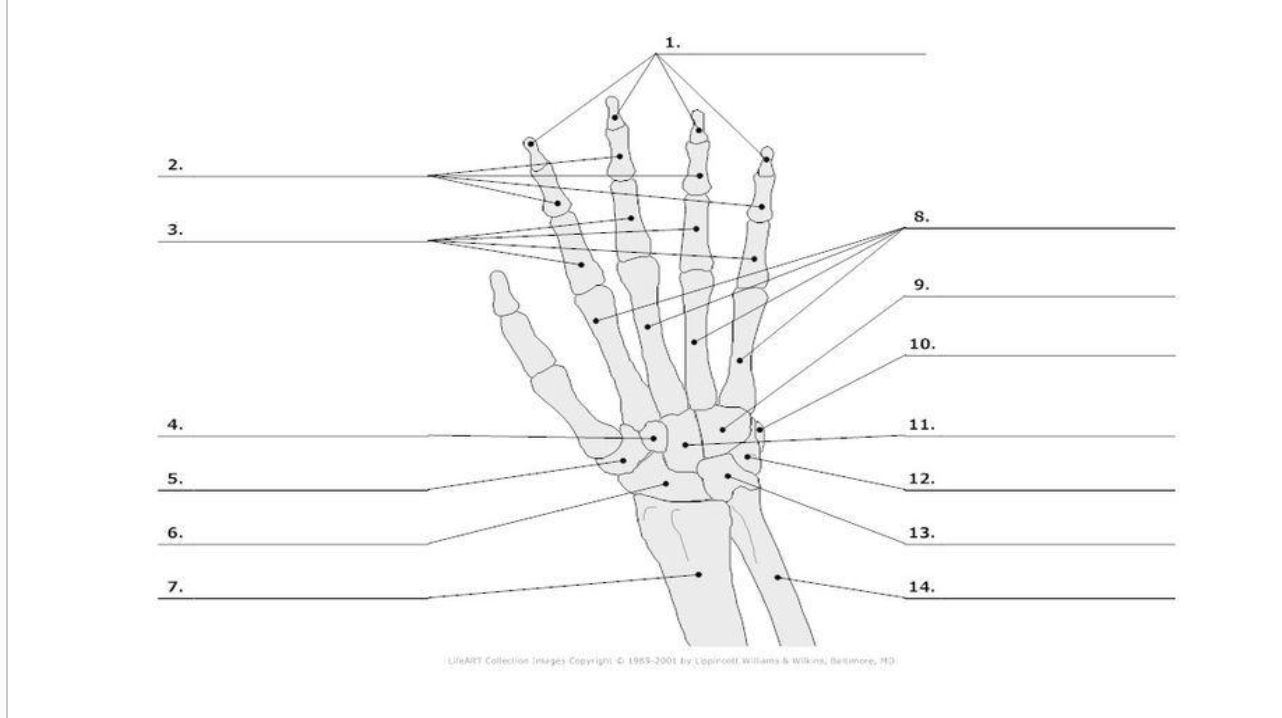
Trapezium
5.)
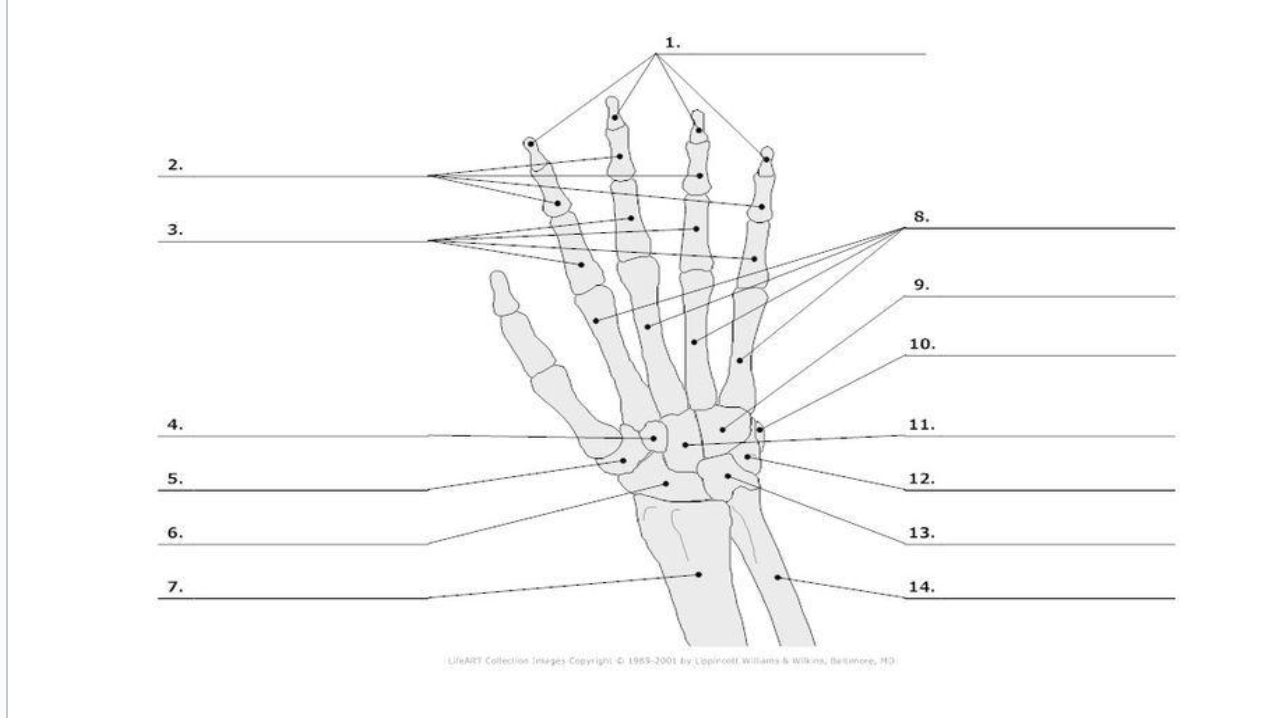
Scaphoid
6.)
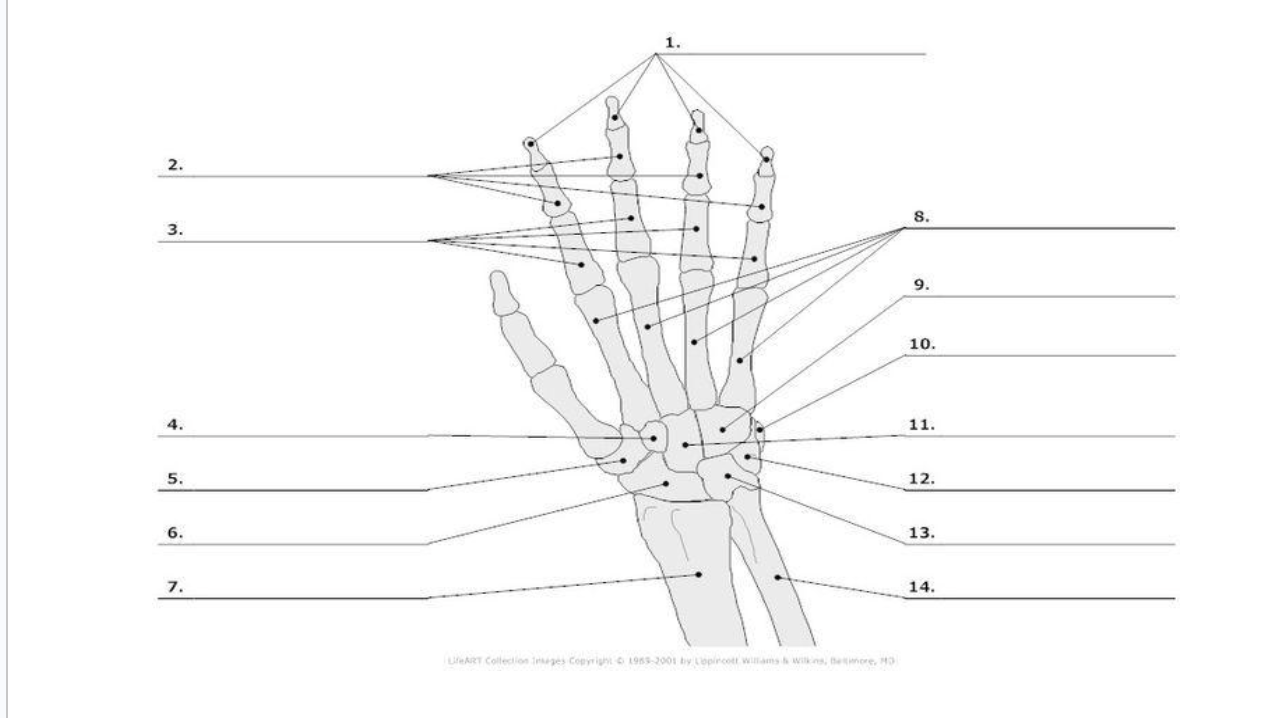
metacarpals
8.)
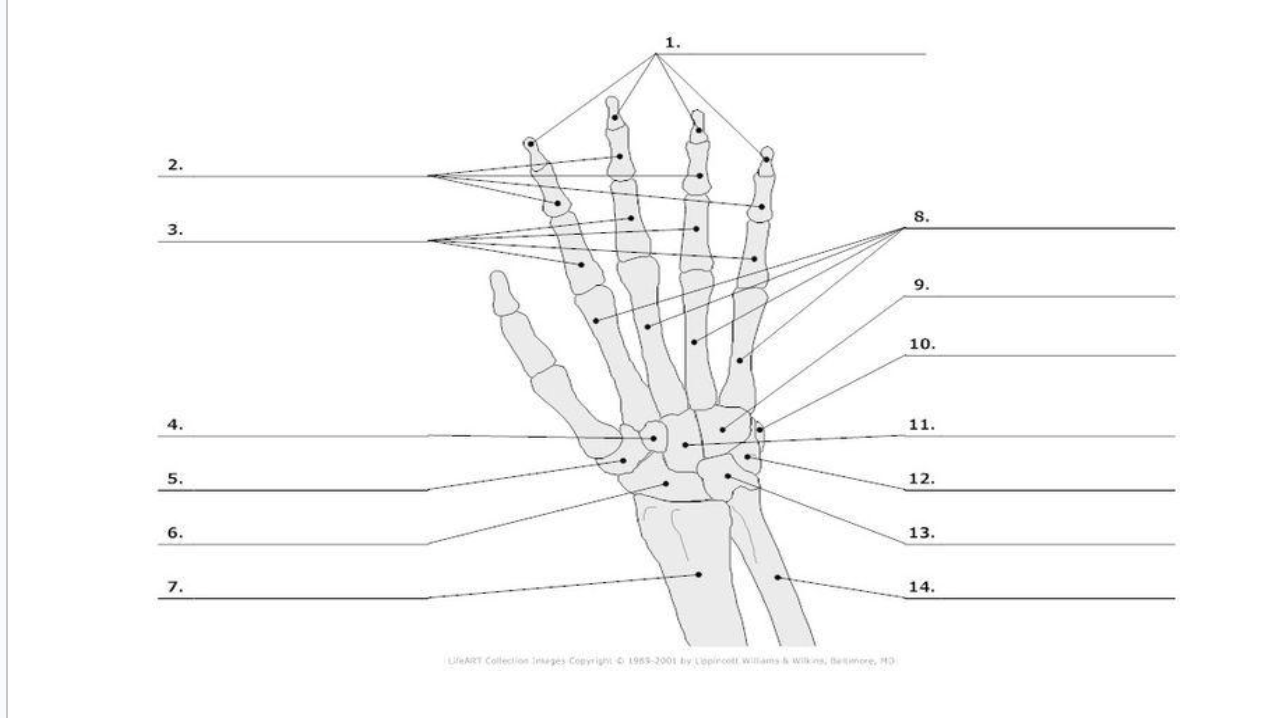
hamate
9.)
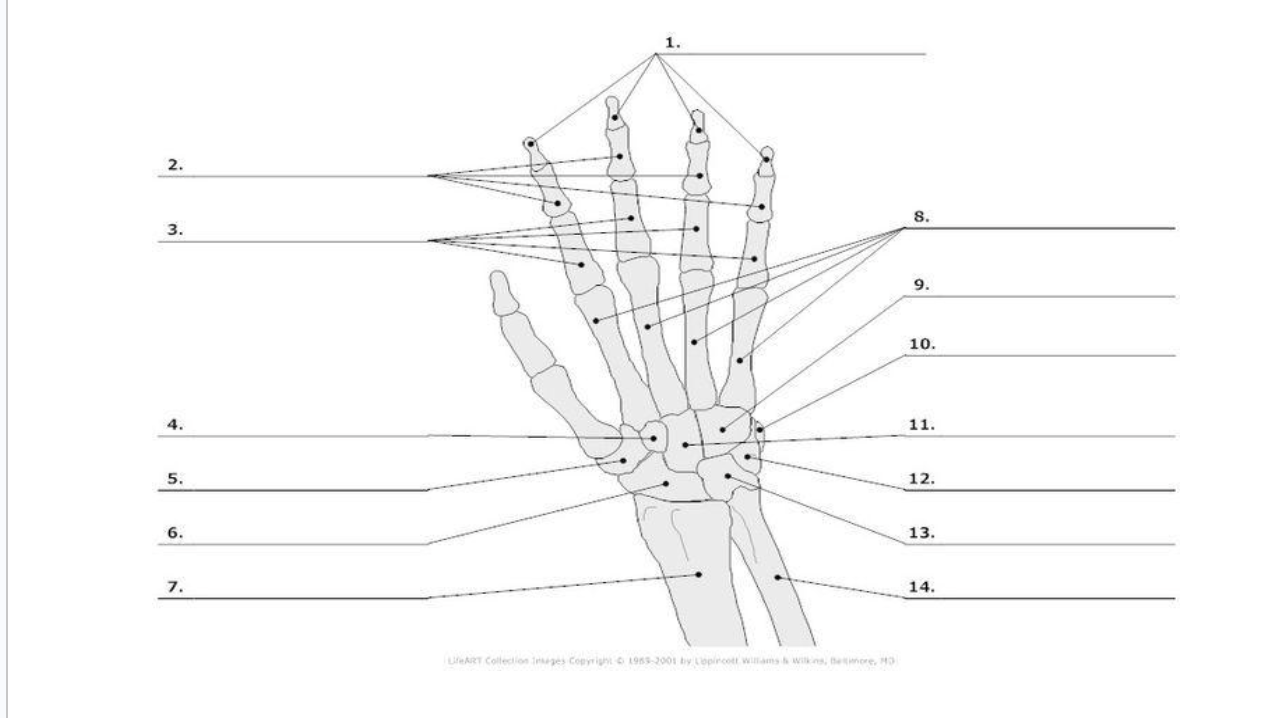
pisoform
10.)
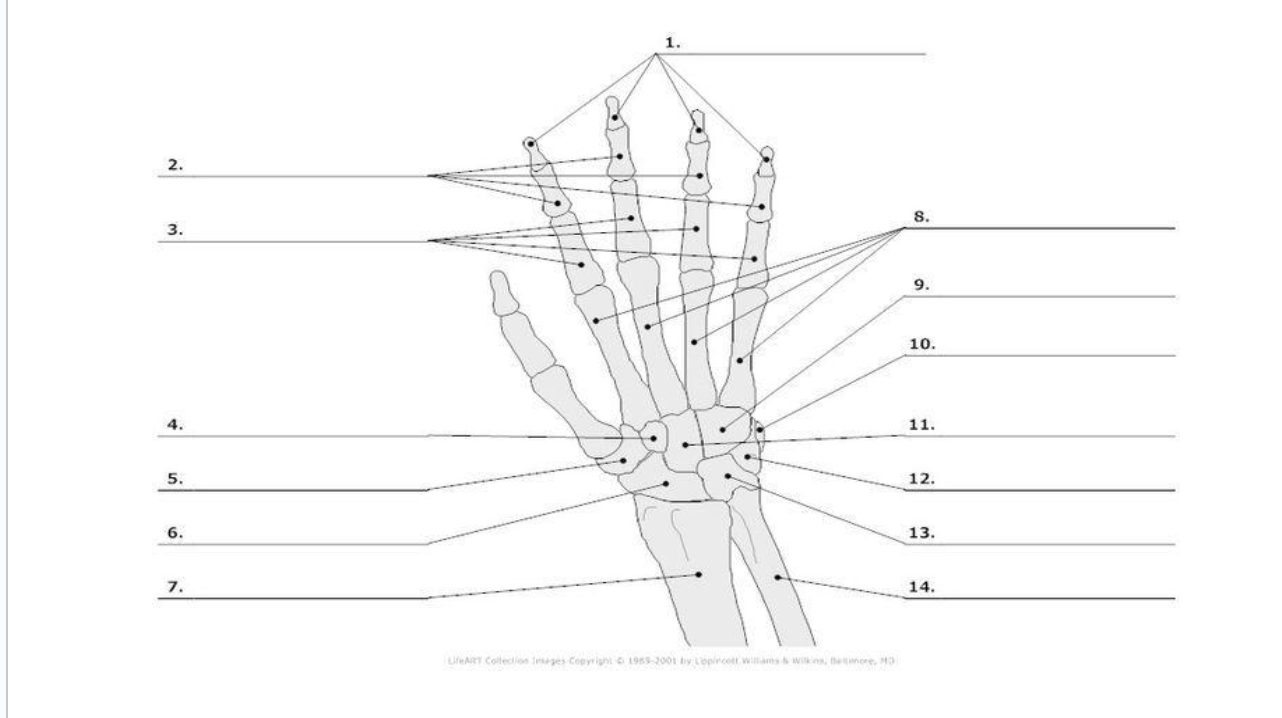
11.) capitate
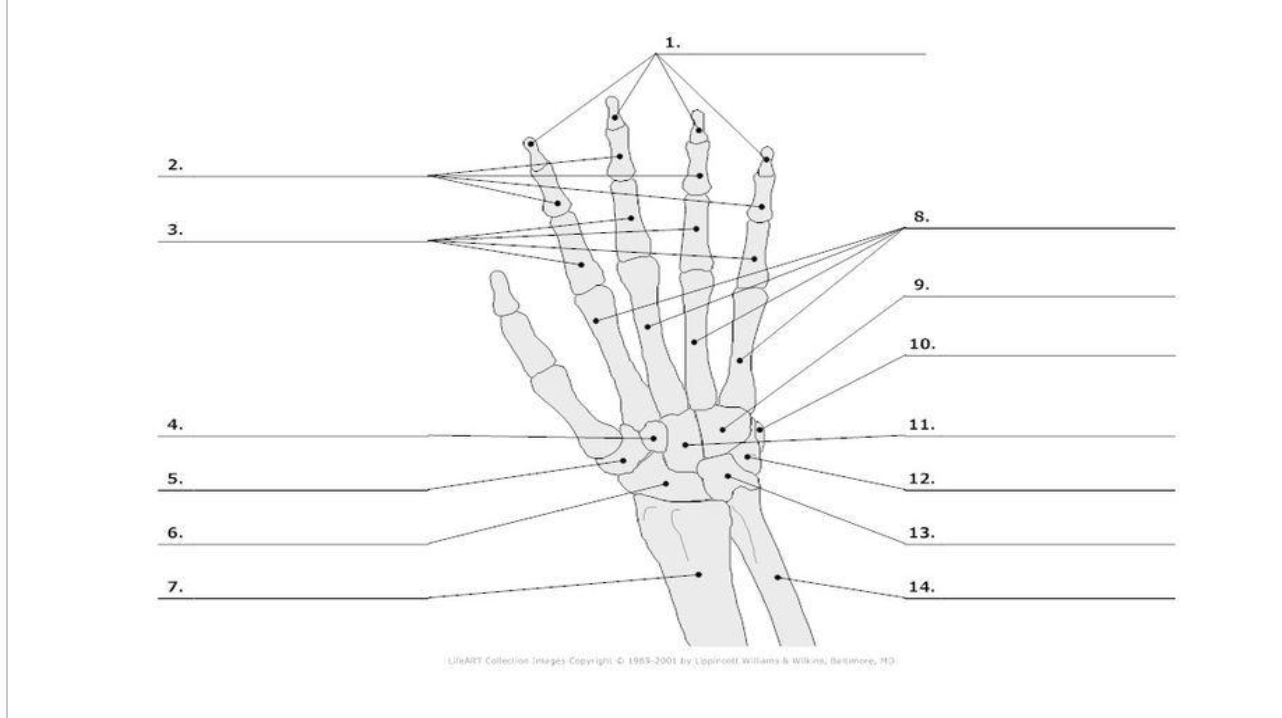
Triquerium
12.)
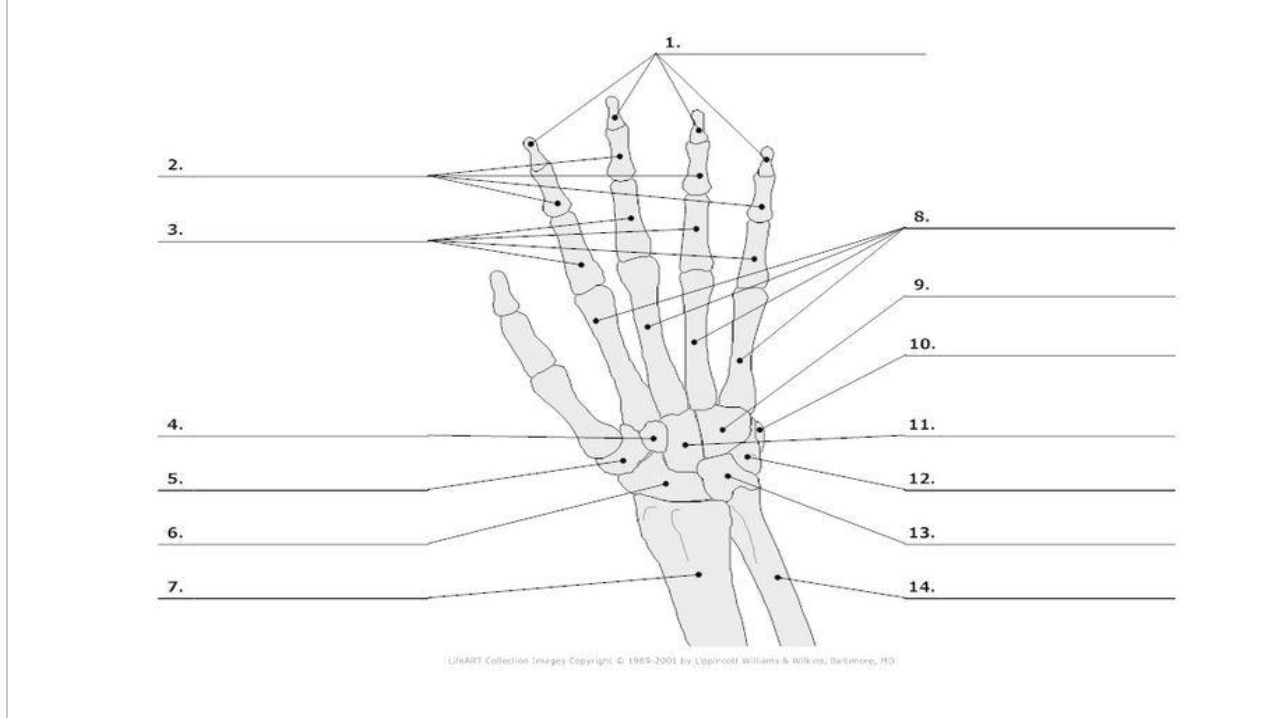
Lunate
13.)
hyaline cartilage
at fetus long bones are formed of
fiborous membranes
as fetus flat bones begin as
2
at birth fontanels remain until around
osteoarthritus
most common chronic arthrits
rheumatoid arthritis
auttomine disease immune system attacks joints often leads to deformaties
gouty arthritus
inflamattion of joints / depostion of uric acid cyrstals from the blood
bursae
flattened fiborous sacs
burase
lined wuth synovial membranes filled with synvoial fluid not part of joint
tendon sheath
elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon
synovial
____fluid is found in the joint cavity
fibrous articular
capsule encloses joint surfaces
cartilagenious joints
slightly movable immoavke connected by cartilage
fibrous joints
immoavble united by fibrous tissue
joints
articulation of bones
fibrous
synarthroses
cartilagenous
amphiarthroses
synovial
diathroses
arches
bones of fooot are arranged to form
2 longtitudal 1 transverse
arches of foot
7
total tarsals in foot
5
total metatarsals in foot
calcaneus
heel bone
metatarsals
sole
phalanges
toes
larger and circular
female inlet is
shallower
female pelvis is
laterally
female illia flare more
shorter less curved
female sacrum is
ilium ischium pubis
3 parts of pelvic girdle
8
carpals total in hand
5
metacarpals total in hand
14
phalanges total
medial
ulna is ___ bone
lateral
radius is ___ bone
free movement
clavice and scapula allow upper limb to have
pectioral girdle limbs pelvic girdle
appendicular skelton composed of
bony throax
forms a cage to protect major organs
sternum ribs, throacic vetebrae
three parts of bony throax
manubirum body xiphoid process
3 parts of sternum
true ribs, false ribs, floating ribs
parts of ribs
sacrum
formed by fusion of five vetebrae
coccyx
formed by fusion of three to five vetebrae
secondary
spinal curvatures ofthe cervical and lumbar regions develop after birth
primary
present from birth spinal curatures of throacic and sacral regions
5
number of lumbar vetebrae in column
12
number of thoracic vetbrae in column
7
number of cervical vetebrae
paranasal
hollow portions of bones surronding nasal cavity lighten the skull give resonance and amplifcation to voice
275 bones
at 12 weeks the fetus has
closed reduction
manual manipulation (skin intact)
open reduction
requires surgey (plates, screws)
tarnsverse
right angke to bone axis
oblique
break slopes
spiral
bone is twisted
pitutary gland
human growth hormone is produced by
appostional growth
bones grow in width
epiphesal plate
allow for lengthwise groth of long bones during childhood
osteoblasts
what is the action that helps bones replace catilage on the diaphyseal plate
chondrocytes
as child groes what are produced on the epipheysal side of plate
viatmen c
vitamin for collagen formation
vitamin k and b
vitamen for protein synthesis