НУ ПІПЕЦ БЛІН
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Morphology
The study of the internal structure of words.
Different Types of Words
1. SIMPLE WORDS
2. COMPLEX WORDS
3. MULTI-WORD WORDS
4. CLITICS
5. UNITS SMALLER THAN WORDS
Simple Words (Simplex/Simplicia)
Words with a root/base and no additional elements.
e.g. car (n.) – drive (v.) – fast (adj.) – always (adv.) – across (prep.) …
Complex Words
Words with a root/base plus additional modifying elements.
e.g self-driving (adj.) – technologically (adv.) – outsmart (v.) – upgrade (n./v.)
Multi-Word Words
Contain more than one word to express one single meaning.
e.g. to be in the driver's seat (= to lead) – off the cuff (unprepared)
Clitics
Fuse two words (one of them functional) into a single word unit.
e.g. mustn't – won't – wouldn't – she's – he'd
Units smaller than words
elements with a residue meaning that attach to roots/bases
e.g. un (harmed) – (magn) ify – (bibl) ic/al – (king) dom – (govern) ance – (waste)ful
Morpheme Independence
Free vs. Bound.
Morpheme Function
Lexical vs. Grammatical
Free Morpheme
Can stand alone as a word (e.g., car, drive).
Bound Morpheme
Cannot stand alone and must be attached to a root (e.g., -ing, un-).
Lexical Morpheme
Has a dictionary meaning (e.g., car, happy).
Grammatical Morpheme
Expresses grammatical relations (e.g., -ed, -s).
Inflection
Forms grammatical words to fit into sentence contexts. (gramatical)
Word-Formation
The process of creating new words.
Morphemes
Minimal building blocks of words.
smallest meaning - caring the elements/units in language
Derivation
The process of adding affixes to a root to create a new word. (lexical)
Word Formation 4
1.Compounding
2.Conversion
3.Clippings & Shortenings
4.Blending/Blends
Compounding
Combining at least two free lexical morphemes to form a compound.
e.g. air + port = airport
Conversion
Changing the word class of a word without adding any affixes.
e.g. to jump(v) - jump(n)
Clipping
Shortening polysyllabic words by removing some syllables.
e.g. advertisement = ad
Acronymization
Shortening compounds by using the initials to create a new (phonetic) word.
e.g. NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
Abbreviation
Shortening compounds by using the initials and pronouncing them separately.
e.g. United Kingdom - UK
Blending
Shortening two existing words and combining the remainders.
e.g. brunch (breakfast + lunch)
Phonetics
looks at the physical properties of different sounds and their ways of articulation.
e.g. cup /kʌp/ – car /kɑː/ (vowel length)
PHONETICS
①ACOUSTIC
②AUDITORY
③ARTICULATORY
Phonology
looks at the function of speech sounds in larger units of language (e.g. words)
Investigates possible combinations of speech sounds (phonotactics)
e.g. hat /hæt/ – bæt / / (minimal pairs)
squid (n.) /skwɪd / – *psquid /pskwɪd/ (actual – impossible words)
Speech Sounds
The sounds produced by the human vocal tract used in language.
Acoustic Phonetics
measuring audible sound properties.
Auditory Phonetics
researching how we hear speech sounds
Articulatory Phonetics
investigating how speech sounds are formed
Vowel Length
The duration of a vowel sound (e.g., /kʌp/ vs /kɑː/).
Phonotactics
The study of possible combinations of speech sounds in a language.
e.g. "str" is okay at the beginning (like in "street").
But "ng" can't start a word — "ngap" is not an English word.
Minimal Pairs
Pairs of words that differ in only one phoneme.
e.g. goat - coat ; chip - cheap
Vocal Tract
The anatomical structure involved in speech production.
Organs of Speech production
4 NASAL CAVITY
3 TONGUE + ROOF OF MOUTH
2 LIPS + TEETH
1 VOCAL FOLDS
Nasal Cavity
sounds are produced by lettng air pass through the nose
e.g. ring /ŋ/
Tongue + Roof of Mouth
sound use the tongue and the palate/velum;
e.g. all vowels, kick /k/
Lips and Teeth
sound use upper & lower lips and teeth;
e.g. bip /b, p/, thorn /θ/
Voiced sounds
use the vibration of the vocal folds;
e.g. buzz /z/
Voiced Sounds
Sounds produced with vibration of the vocal folds.
Phases of Speech Production
1 INITIATION
2 PHONATION
3 ARTICULATION
Mechanism of Speech Production
The processes and topography involved in producing speech.
Initiation
The lungs produce an air pressure by inhaling, which is then expelled through throat and mouth or nose. (egressive air stream)
Egressive Air Stream
Airflow produced by exhaling, used in speech production.
Phonation
The air stream passes through the larynx and sets the vocal folds/cords in motion. This vibration produces the actual voice. (voiced vs. voiceless sounds)
Articulation
The oscillating air stream passes through pharynx, the mouth or nose and is then modified by articulating speech organs (articulators: e.g. tongue, palate, teeth, lips)
Vowels
little obstruction of the air stream;
more sonorous;
form nuclear of syllable
Consonants
Narrow/complete closure of vocal tract;
less sonorous;
form boundary of syllable
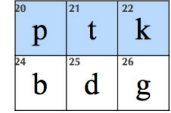
Stops/Plosives
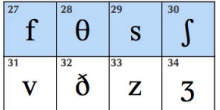
Fricatives
Affricates
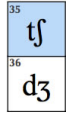
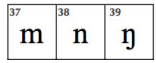
Nasals
Approximants(Laterals/ Semi-vowels)

Glottals
Phonemes
The smallest units of sound that distinguish meaning in a language.
smallest meaning - distinguishing element/unit in language
Phonemes can change a word's meaning, such as "bat" and "pat."
Phoneme Inventory
The set of phonemes in a language.
Phoneme Distribution
The frequency with which phonemes occur in a language.
Syllable Structure
The organization of sounds within a syllable.
CVC Syllable
A basic syllable structure consisting of a consonant-vowel-consonant.
Onset
The beginning consonant(s) of a syllable. e.g. Cat, Sing
Nucleus
The vowel sound within a syllable, often considered its core. e.g cAt, sIng
Coda
The ending consonant(s) of a syllable. e.g. caT , siNG
Suprasegmentals/Prosody
Speech features that extend over syllables, words, or phrases, like stress, tone, or word juncture.
Prosodic Feature
A speech feature such as stress, tone, or word juncture.
Intonation
The rise and fall of pitch in speech.