Medical Imaging Modalities: X-Ray, CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine (addie)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Who produced the first x-ray image and when?
Wilhelm Conrad Röentgen produced the first x-ray image on November 8, 1895.
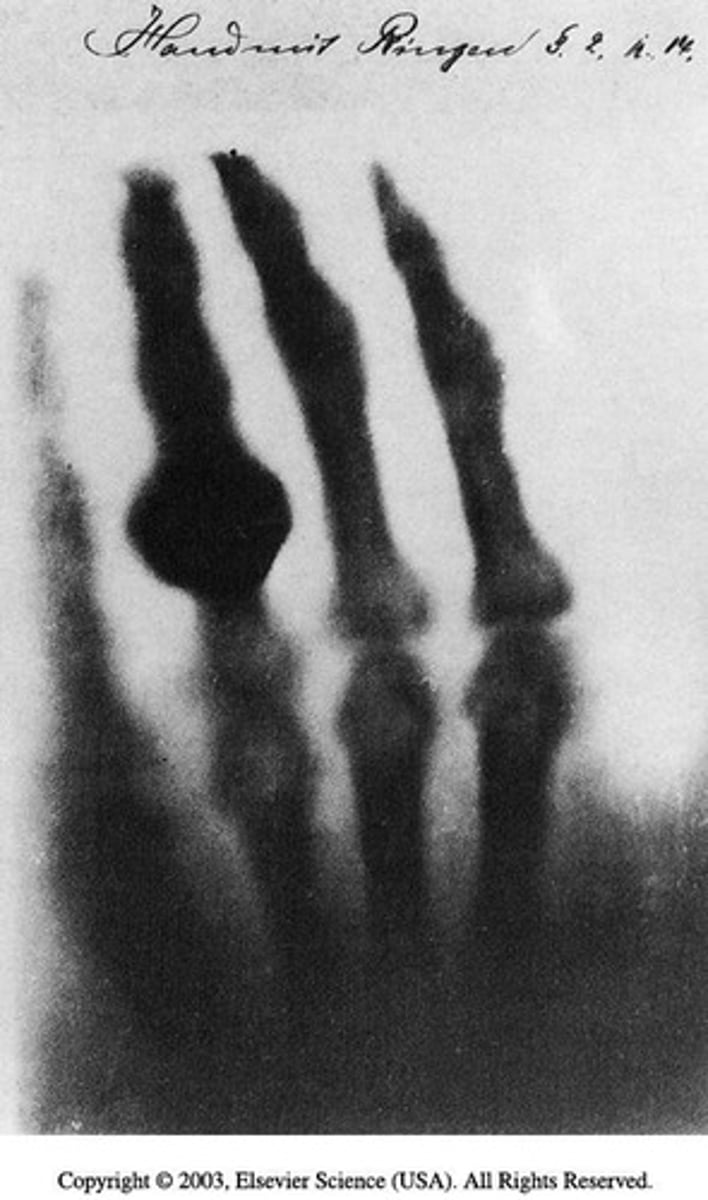
What were x-rays originally called?
They were initially referred to as 'invisible rays' before being named 'x-rays' because 'x' represents an unknown variable.
What is Medical Imaging?
A suite of modalities used to look inside the body for clues or evidence of medical conditions.
Which imaging modalities do not involve radiation?
MRI and Ultrasound.
What is the role of a Radiographer?
A radiologic technologist specializing in the use of x-rays to create images of the body.
What does RT (R) stand for?
Registered Technologist in Radiography.
What is the ARRT?
American Registry of Radiologic Technologists.
What is the primary function of a Radiologist?
A physician who interprets radiographic images and performs specialized diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
What is Radiography?
An imaging modality that uses radiation to look at the inside of the body.
What is Computed Tomography (CT)?
An imaging modality that utilizes cross-sectional images for detailed analysis, using radiation.
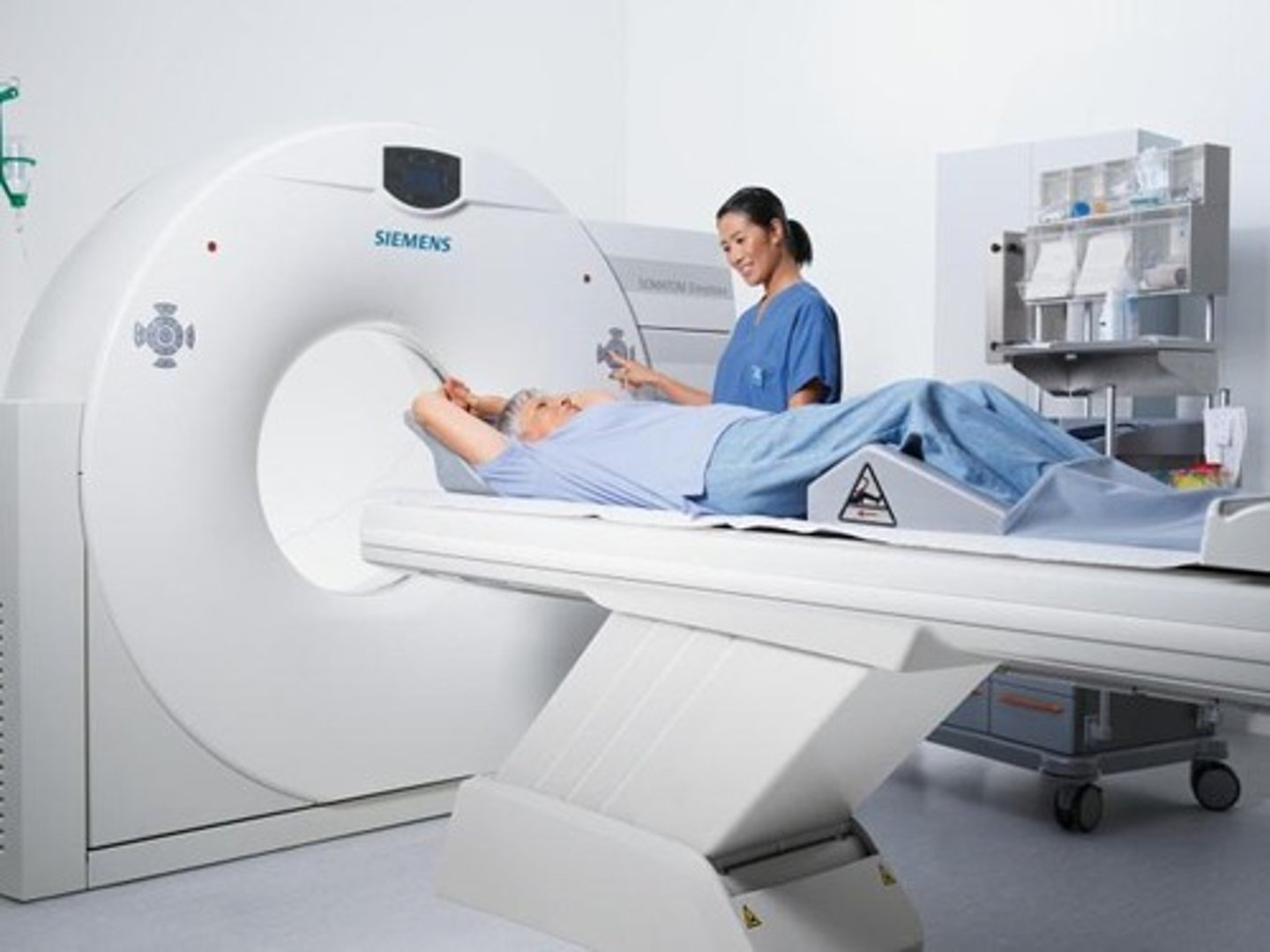
What is the purpose of Nuclear Medicine?
It uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and treat diseases.
What does a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan measure?
It measures body functions such as blood flow, oxygen use, and glucose metabolism.
What is Radiation Therapy?
A type of therapy that uses radiation to control or kill malignant cells in cancer treatment.
What is Dosimetry?
The measurement of the absorbed dose delivered by radiation, often characterized by percentage depth dose curves.
What is Interventional Radiography?
A modality that uses minimally invasive image-guided procedures to diagnose and treat diseases.
What is the goal of Mammography?
The early detection of breast cancer using low energy radiation.
How does Ultrasound work?
It uses high-frequency sound waves transmitted through a gel into the body.
What is the focus of St. Mary's School of Medical Imaging?
Offers a Bachelor of Science in Medical Imaging with various emphases including CT, MRI, and Ultrasound.
What are the pre-requisite courses for the Medical Imaging curriculum at St. Mary's?
Courses include College Algebra, Introductory Physics, Human Anatomy, Human Physiology, Medical Terminology, and Communications.
What is the significance of the 'virtual autopsy' image mentioned in the notes?
It demonstrates the use of CT imaging for forensic analysis, showing detailed images of injuries.
What type of imaging modality is used for Cardiac Catheterization?
Interventional Radiography.
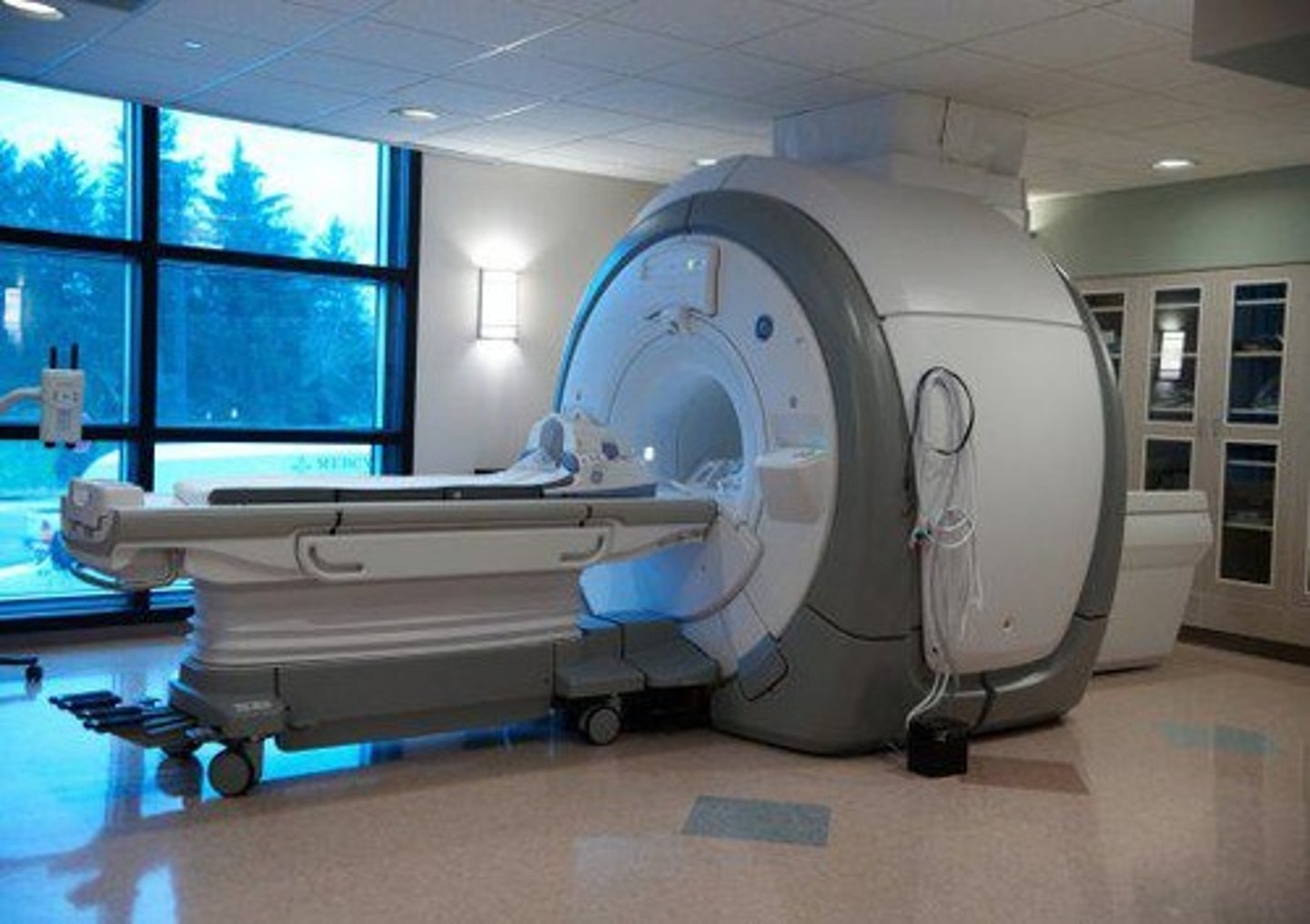
What is the primary imaging technique used in MRI?
MRI uses a magnetic field to generate images instead of radiation.
What is the difference between CT and traditional x-ray?
CT provides cross-sectional images for more detailed analysis compared to traditional x-ray.
What is a common application of Dosimetry in Radiation Therapy?
Planning the delivery of radiation therapy based on measured radiation doses.