17 - oscillations
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
define simple harmonic motion
An oscillation in which the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position, and is directed towards the equilibrium
what is the formula for accleration for an object in simple harmonic motion
a = -ω²𝑥
ω = angular frequency
𝑥 = displacement
formula for angular velocity
ω = 2πf
what conclusions can we draw from an object in SHM about its acceleration and displacement?
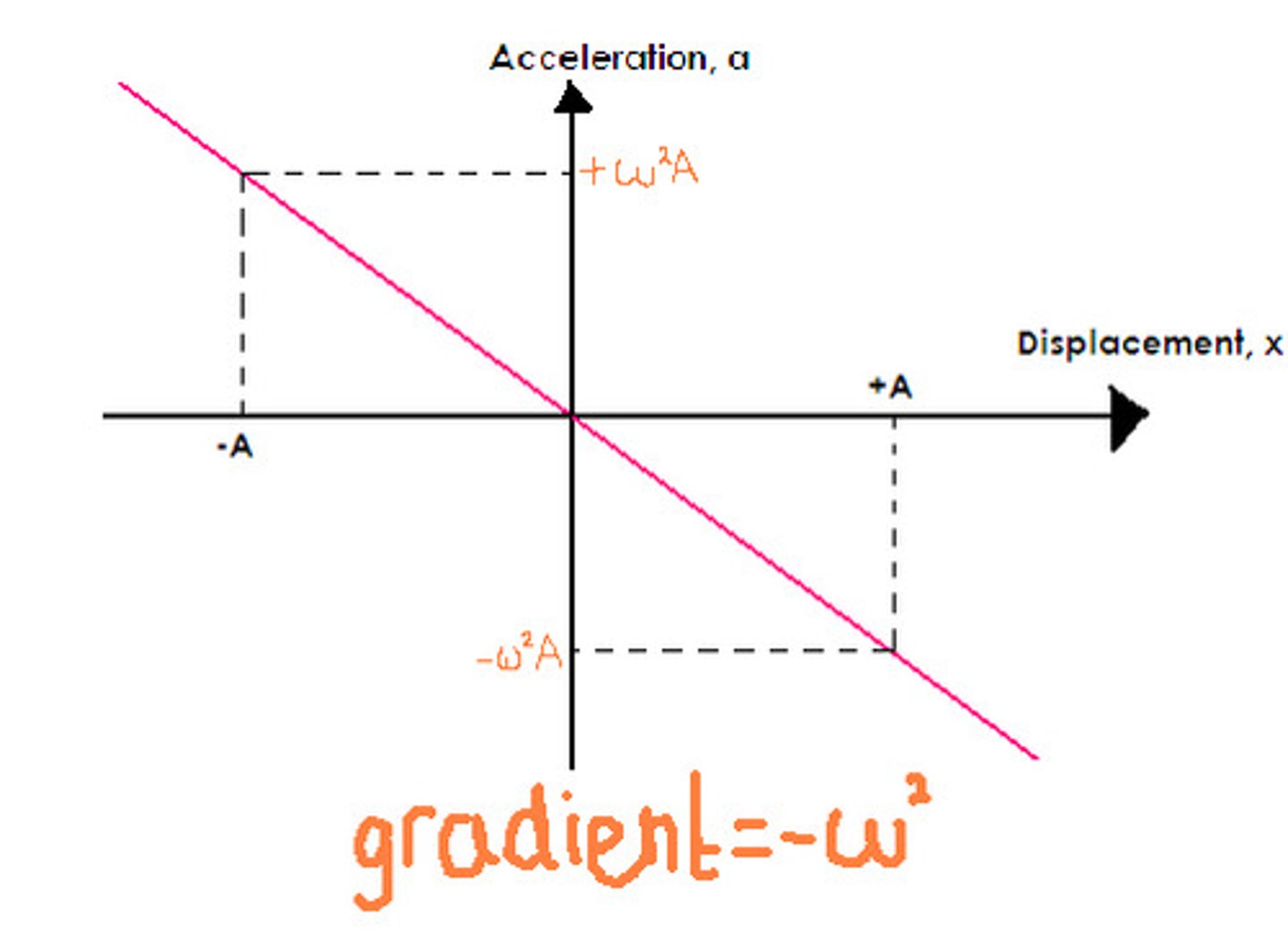
what two conclusions can we get if we graph acceleration and displacement from SHM?
- a∝𝑥
- the negative sign means that the acceleration acts in the opposite direction to the displacement (towards the equilibrium position)
- a gradient from the graph of this will be -ω²
- the period is independent of the amplitude
what does an isochronous osciallator mean
an oscillator where the time period of oscillation is constant and does not depend on the amplitude
what are two formulas to find displacement in SHM?
what is the difference between the two?
𝑥 = A sin ωt
𝑥 = A cos ωt
sine version is when oscillator begins at equilibrium
cosine version is if it begins at max amplitude position
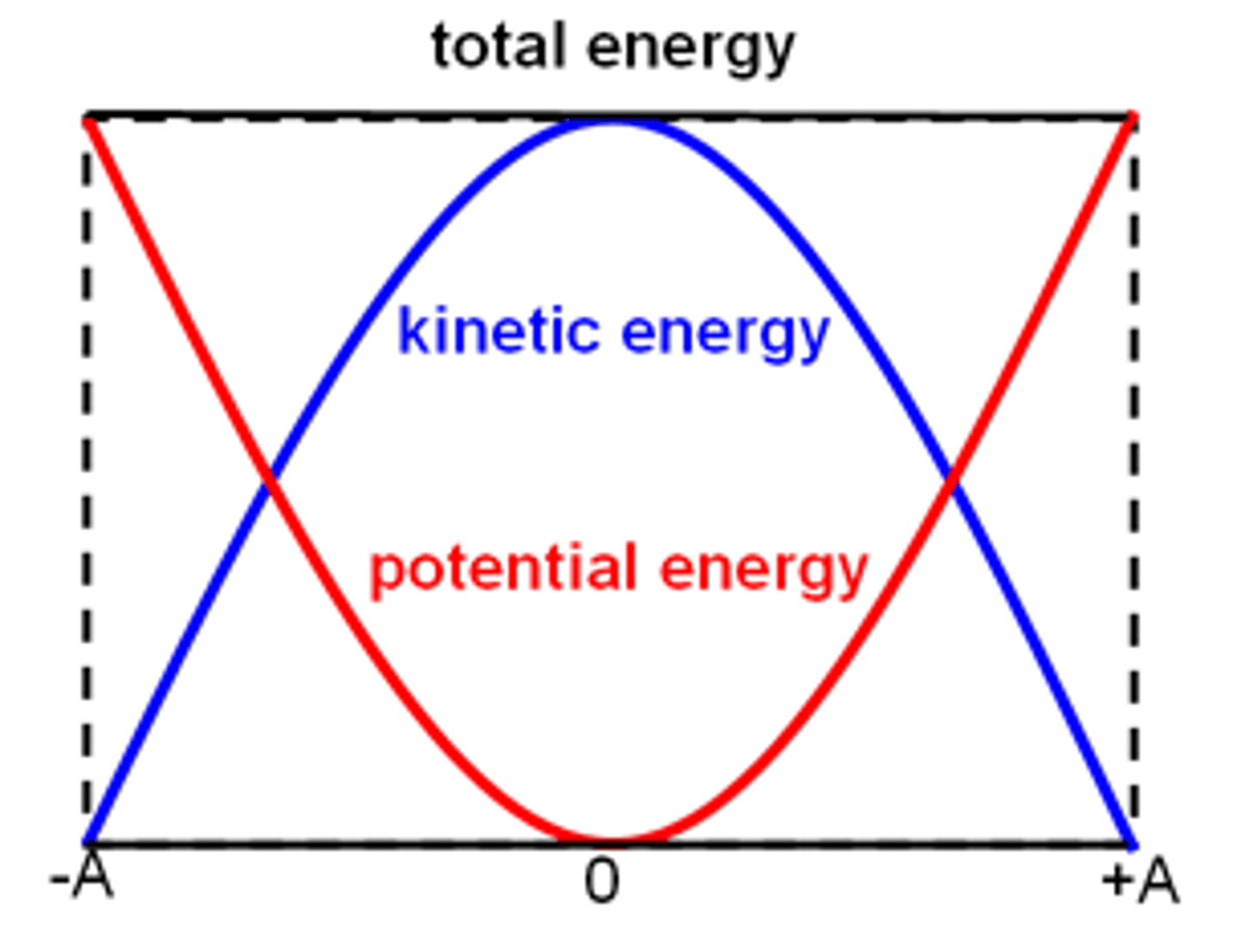
Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion
Energy is conserved between kinetic energy and potential energy.
- kinetic at max at the equilibrium point
- potential at max on amplitude where displacement is at maximum
damping (simple harmonic motion)
Damping is the process by which the amplitude of oscillations decreases over time due to energy loss
Light damping
Critical damping
Heavy damping
light damping - amplitude gradually dcreases over time