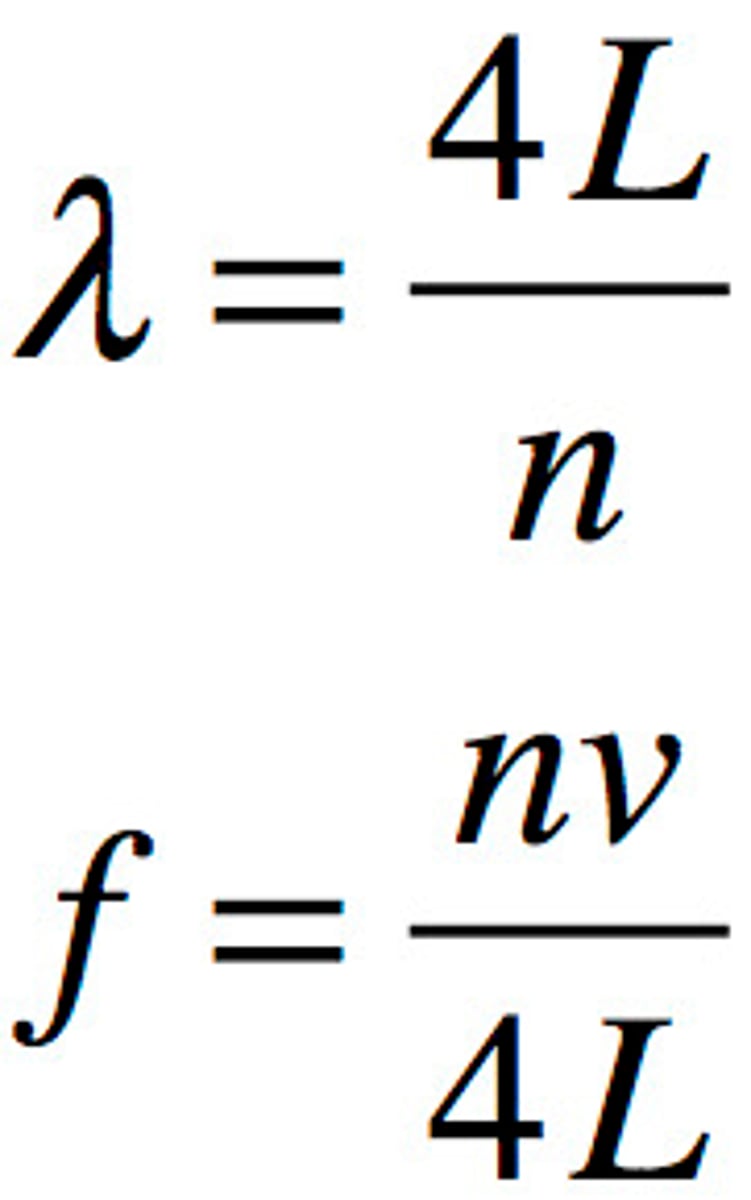Unit 3B Physics Mechanical Waves and Sound
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
wave
a traveling oscillation that transfers energy from one point to another
Wave characteristics
frequency, amplitude, wavelength, speed, energy
mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium through which to travel
electromagnetic waves
A form of energy that can move through the vacuum of space (does not need a medium)
transverse wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels
longitudinal wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction parallel to the direction in which the wave travels.
surface waves
A surface wave is a wave that travels along the surface of a medium
crest
a high point on a transverse wave
trough
the lowest point of a transverse wave
wavelength
Horizontal distance between points on wave (crests or trough or points of one cycle)
amplitude
total energy or height from equilibrium (rest position)
period
the time that it takes a complete cycle or wave oscillation to occur
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
rarefaction
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are far apart
reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass.
Doppler effect
A change in frequency caused by motion of the sound source, motion of the listener, or both.
Interference
the combination of two or more waves that results in a single wave
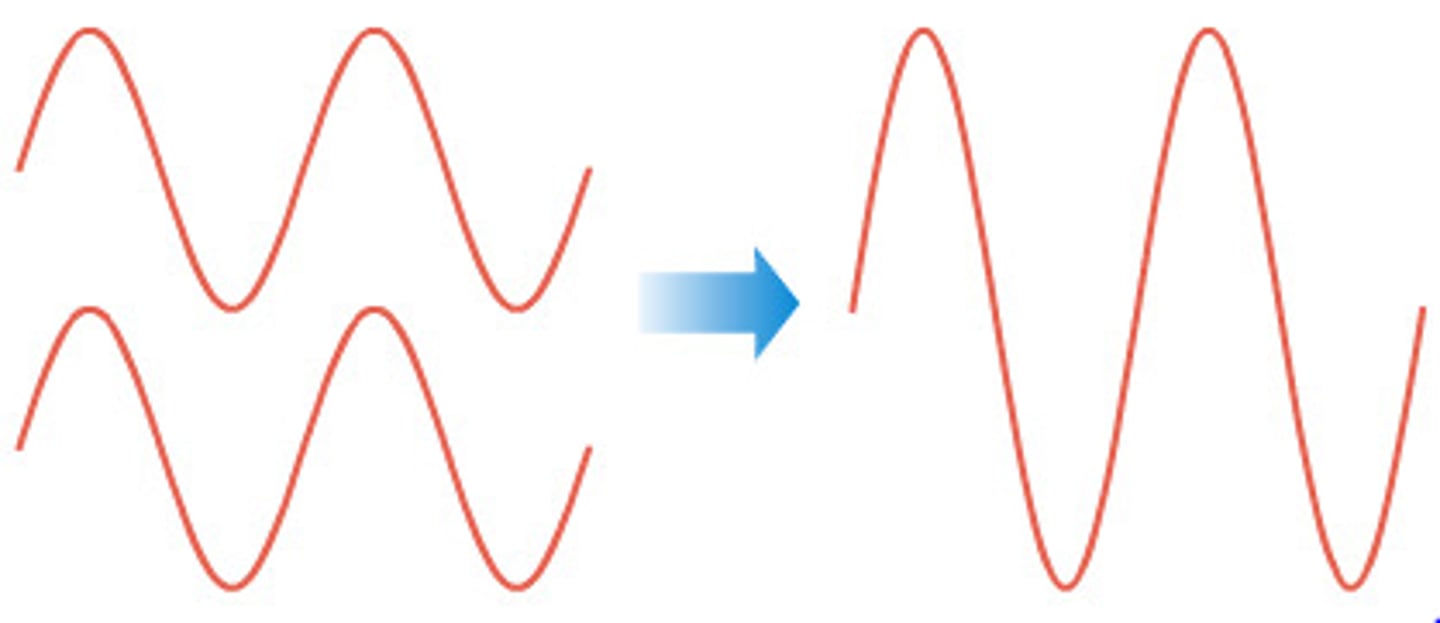
constructive inference
the interference that occurs when two waves combine to take a wave with a larger amplitude
destructive inference
occurs when waves add up to make a smaller amplitude (compressions align w rarefactions)
standing wave
a wave that appears to stand in one place, even though it is really two waves interfering as they pass through each other
node
A point on a standing wave that has no motion aka amplitude (resting)
antinode
A point of maximum amplitude on a standing wave
pitch
a tone's experienced highness or lowness; depends on frequency
volume
loudness of sound depending on sound waves amplitude
infrasound
Sound waves with frequencies below 20 Hz.
ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
How does air temperature affect the speed of sound?
when warm: more vibrations occur (more energy)
when cold: less vibrations occur (less energy)faster
inwarm air
speed of sound
depends on tension of medium and elasticity (ability to snap back into shape after disturbance)
why is sound a wave
has all properties of a wave (ie: frequency, amplitude, wavelength, speed, transfers energy)
harmonics
different patterns of nodes and antinodes created by multiples of frequency fundamentals
Law of Superposition
the amplitude of the resulting wave is always equal to the sum of the amplitude of the individual waves
units of frequency
Hertz (Hz)
units of period
time (seconds)
parts of a transverse wave
crest, trough, wavelength, amplitude
parts of a longitudinal wave
compression, rarefaction, wavelength
relationship between wavelength and frequency
Inversely related--as one increases, the other decreases
amplitude and energy
directly related (higher the amplitude, the greater the energy)
frequency and energy
directly related (higher the frequency, the greater the energy
speed of sound in solids
fastest
speed of sound in liquid
faster than in air
speed of sound in gas
depends on temperature of the gas and mass of particles
speed of sound in air
increases as air temperature increases
Wave speed equation
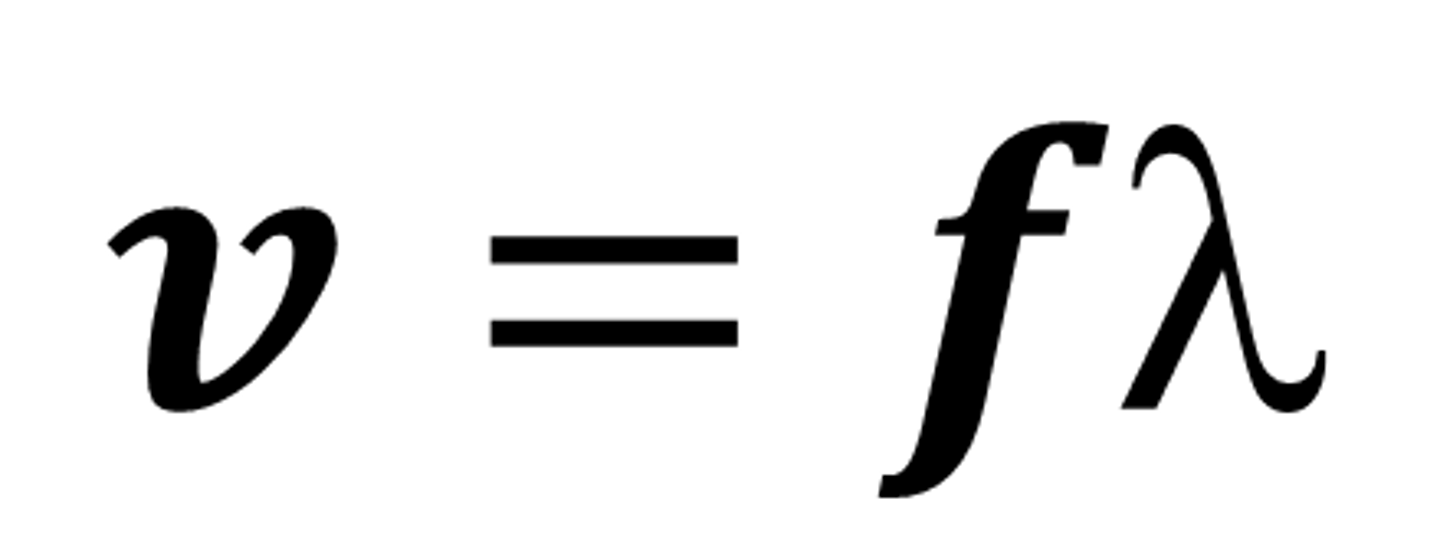
Doppler equation
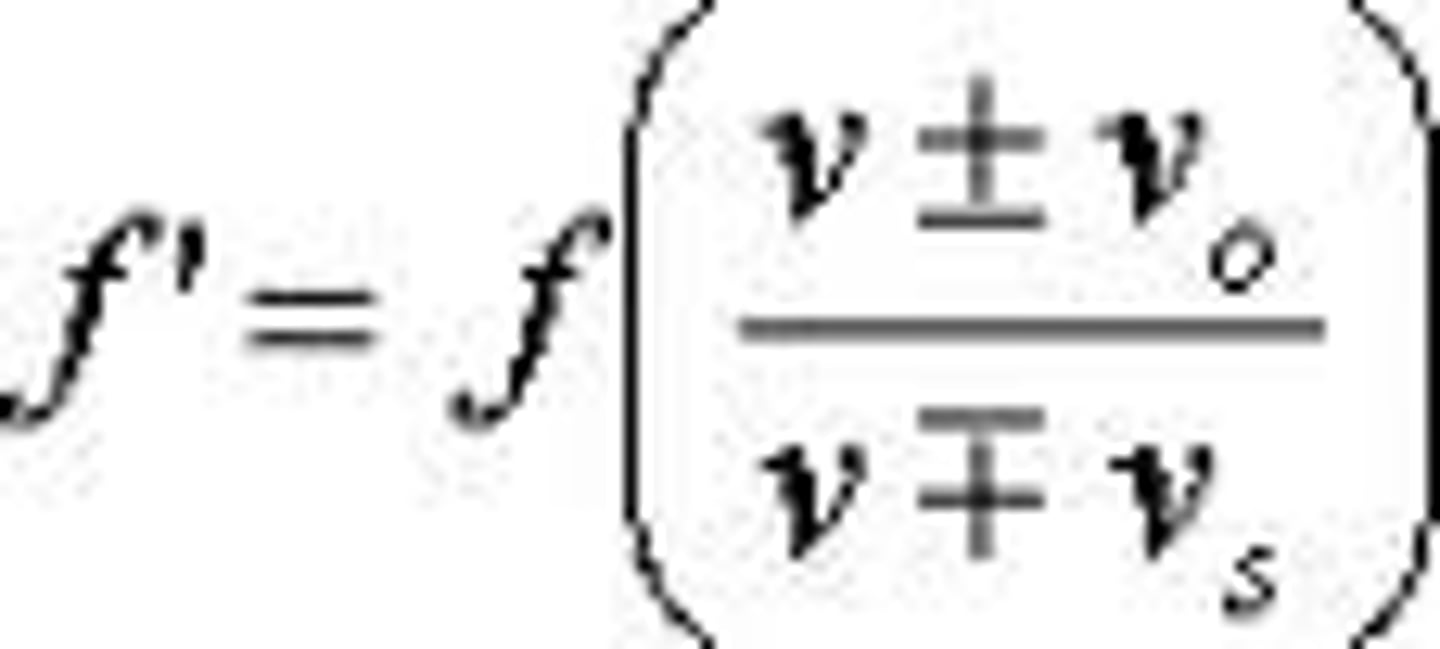
simple harmonic motion
vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium
Period of a pendulum equation
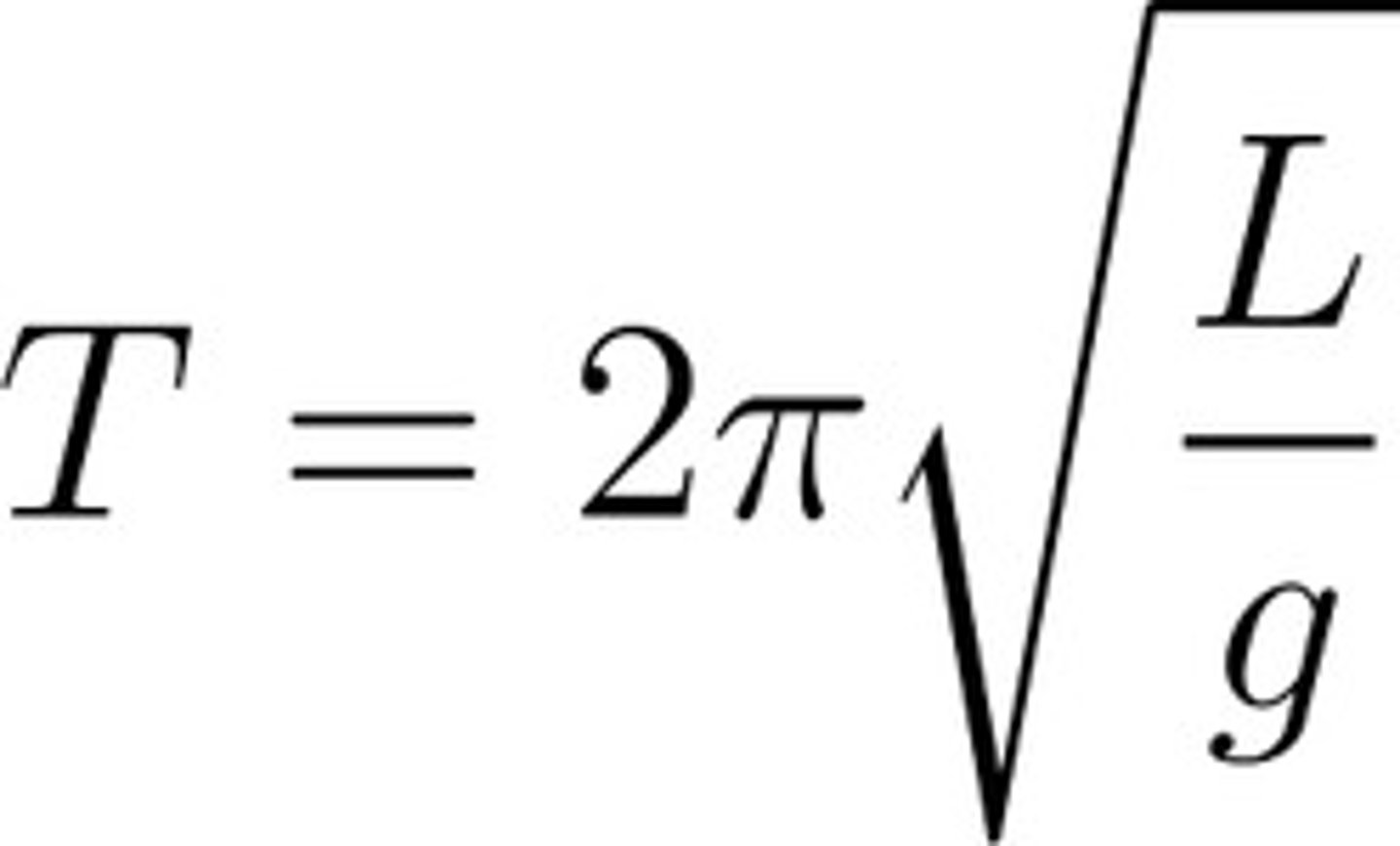
Period-Frequency Relationship
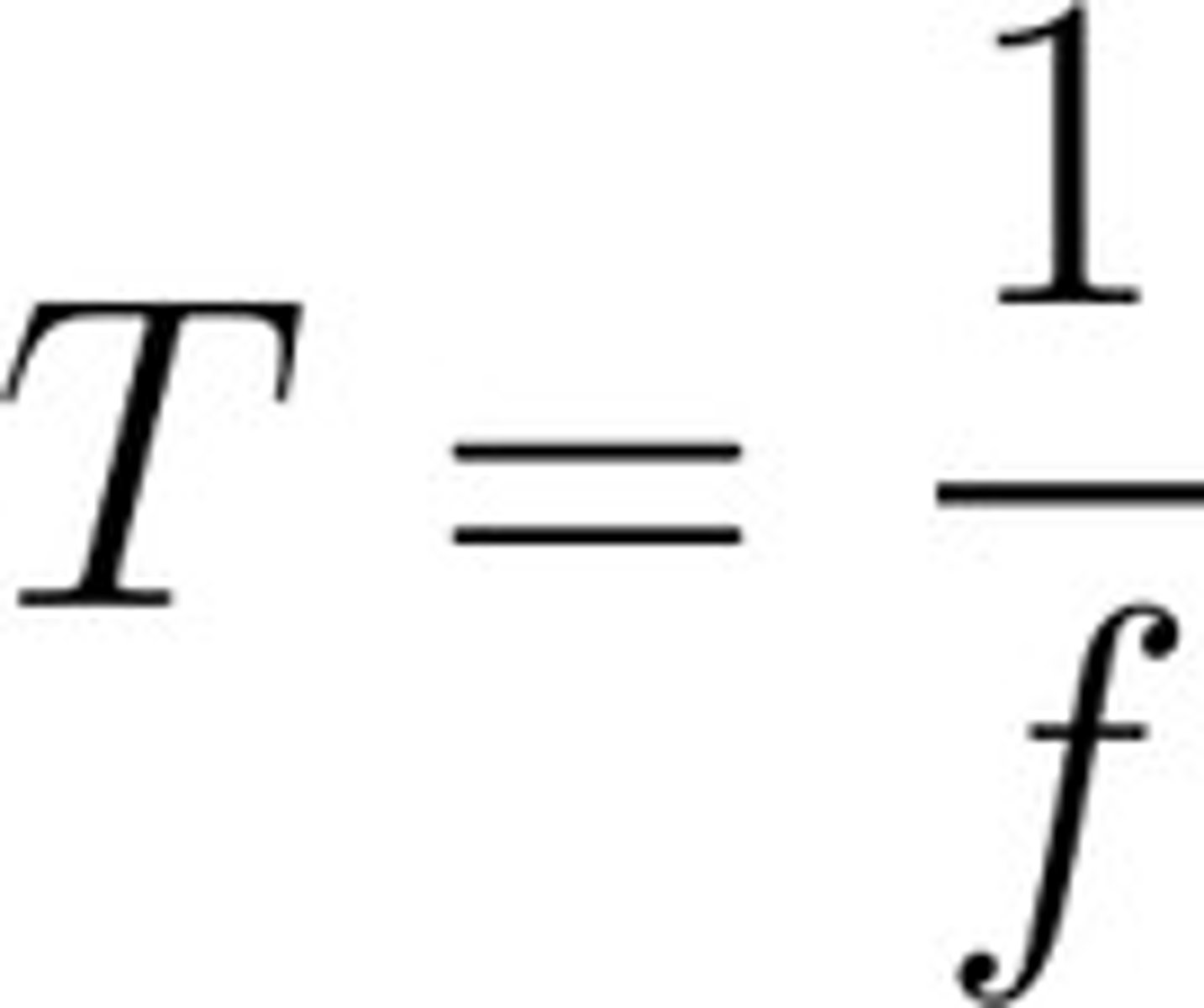
speed of sound in air equation

harmonic frequency - two open or two closed ends

harmonic frequency - one open, one closed end