Chapter 24: Speciation in Biological Science
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Speciation
Creation of distinct species from an ancestral species.
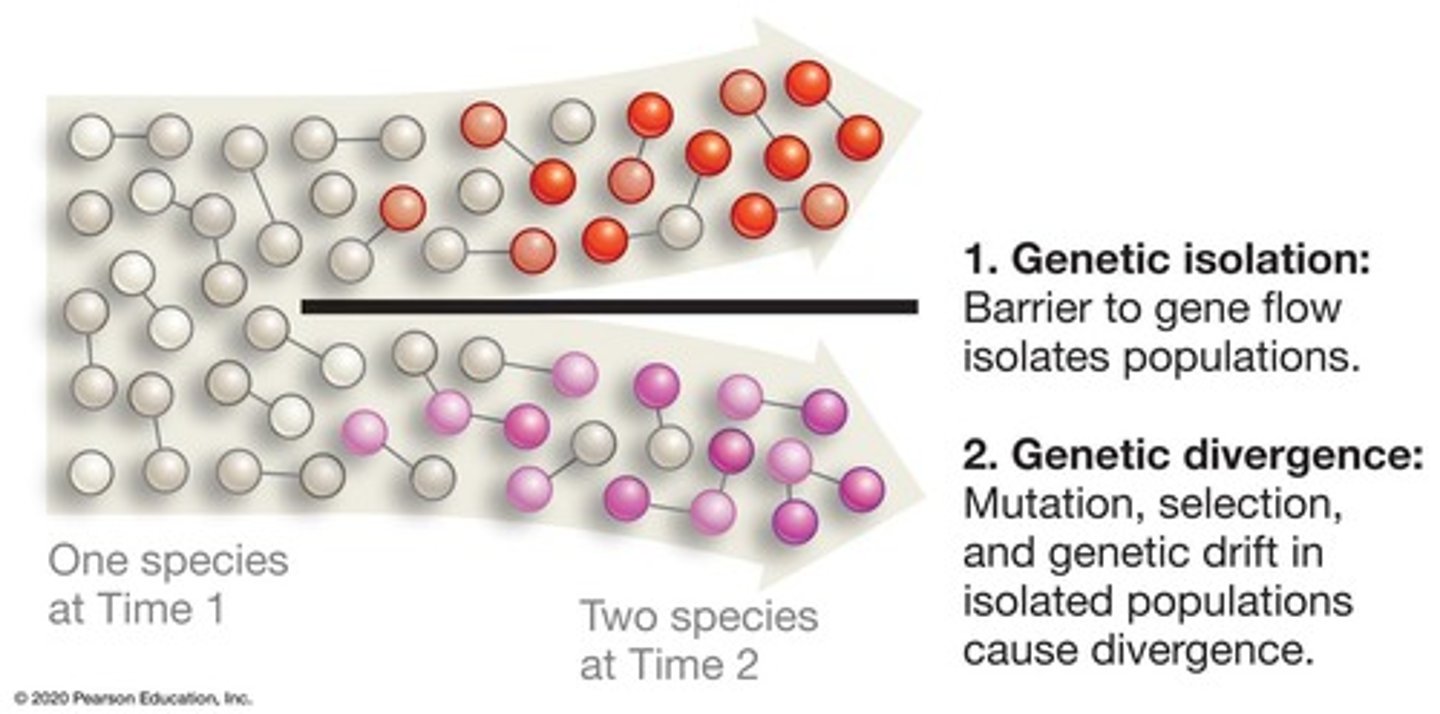
Gene flow
Movement of alleles between populations.
Genetic isolation
Barrier preventing gene flow between populations.
Genetic divergence
Evolutionary changes in isolated populations.
Mutation
Random changes in DNA sequence.
Natural selection
Differential survival and reproduction based on traits.
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies over time.
Allele frequencies
Proportion of different alleles in a population.
Divergence
Process where populations evolve independently.
Species
Evolutionarily independent population or group of populations.
Biological Species Concept
Identifies species based on reproductive isolation.
Reproductive Isolation
Prevents gene flow between populations.
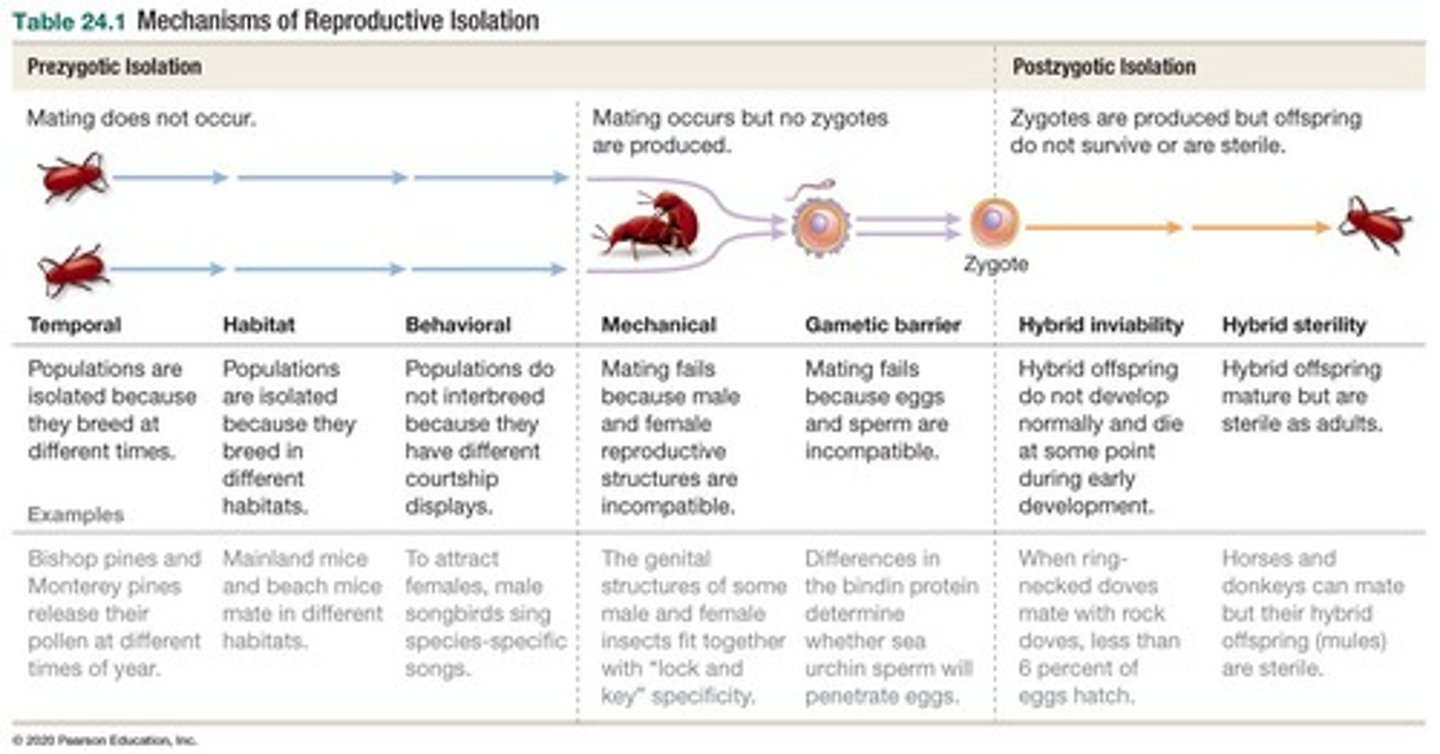
Prezygotic Isolation
Prevents mating between different species.
Postzygotic Isolation
Hybrid offspring fail to survive or reproduce.
Morphospecies Concept
Defines species by morphological differences.
Morphological Features
Size, shape, or other physical characteristics.
Polymorphic Species
One species appearing as multiple due to variation.
Cryptic Species
Species that differ in non-morphological traits.
Phylogenetic Species Concept
Identifies species based on evolutionary history.
Monophyletic Group
Ancestral population and all its descendants.
Synapomorphies
Unique traits shared by a common ancestor.
DNA Sequence Data
Used to identify synapomorphies in species.
Independent Evolution
Species evolve separately due to lack of gene flow.
Phylogenies
Evolutionary trees representing relationships among species.
Species Diversity
Variety of species recognized by different concepts.
Fossil Species
Species identified from fossil records.
Asexual Species
Species that reproduce without sexual reproduction.
Geographical Overlap
Necessary for evaluating reproductive isolation.
Disadvantages of Biological Concept
Not applicable to fossils or asexual species.
Application of Species Concepts
Researchers use all three concepts in practice.
Elephant Species Example
Illustrates application of species concepts in nature.
Systematics
Biology discipline classifying organism relationships.
Taxonomy
Describing, naming, and classifying species.
Taxonomist
Scientist answering species classification questions.
Species
Basic unit of biological classification.
Morphological comparisons
Analyzing physical traits to distinguish species.
Biological species concept
Species defined by interbreeding capability.
Morphospecies concept
Species defined by anatomical similarities.
Phylogenetic species concept
Species defined by genetic relationships.
Genetic isolation
Separation of populations due to geography.
Allopatry
Populations living in different geographic areas.
Allopatric speciation
Speciation due to geographic isolation.
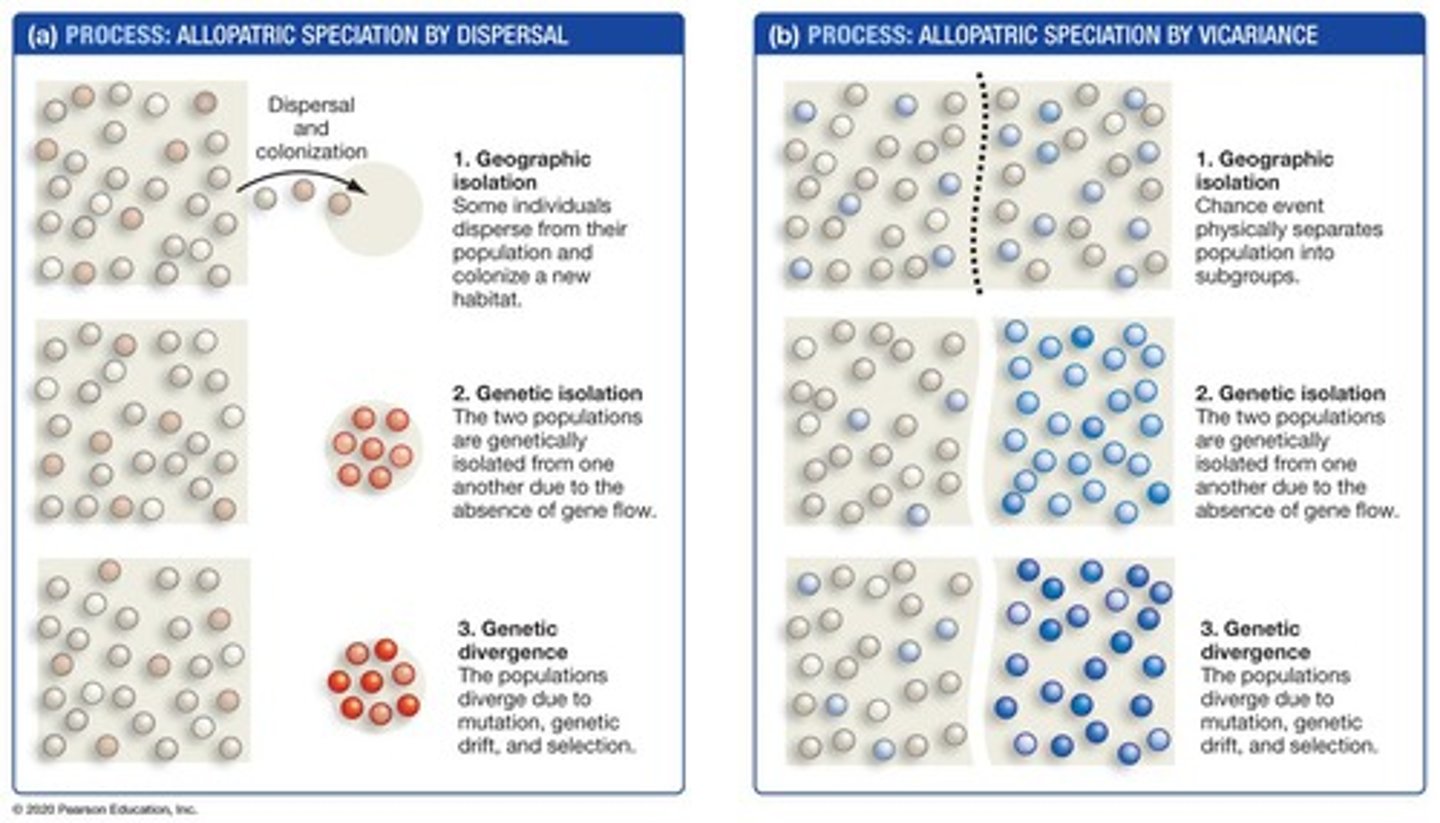
Dispersal
Movement of individuals to new locations.
Vicariance
Physical barrier splits a population.
Biogeography
Study of species distribution across geography.
Colonization events
Initial population establishment in a new area.
Speciation
Formation of new and distinct species.
Hybrid offspring
Offspring from interbreeding different species.
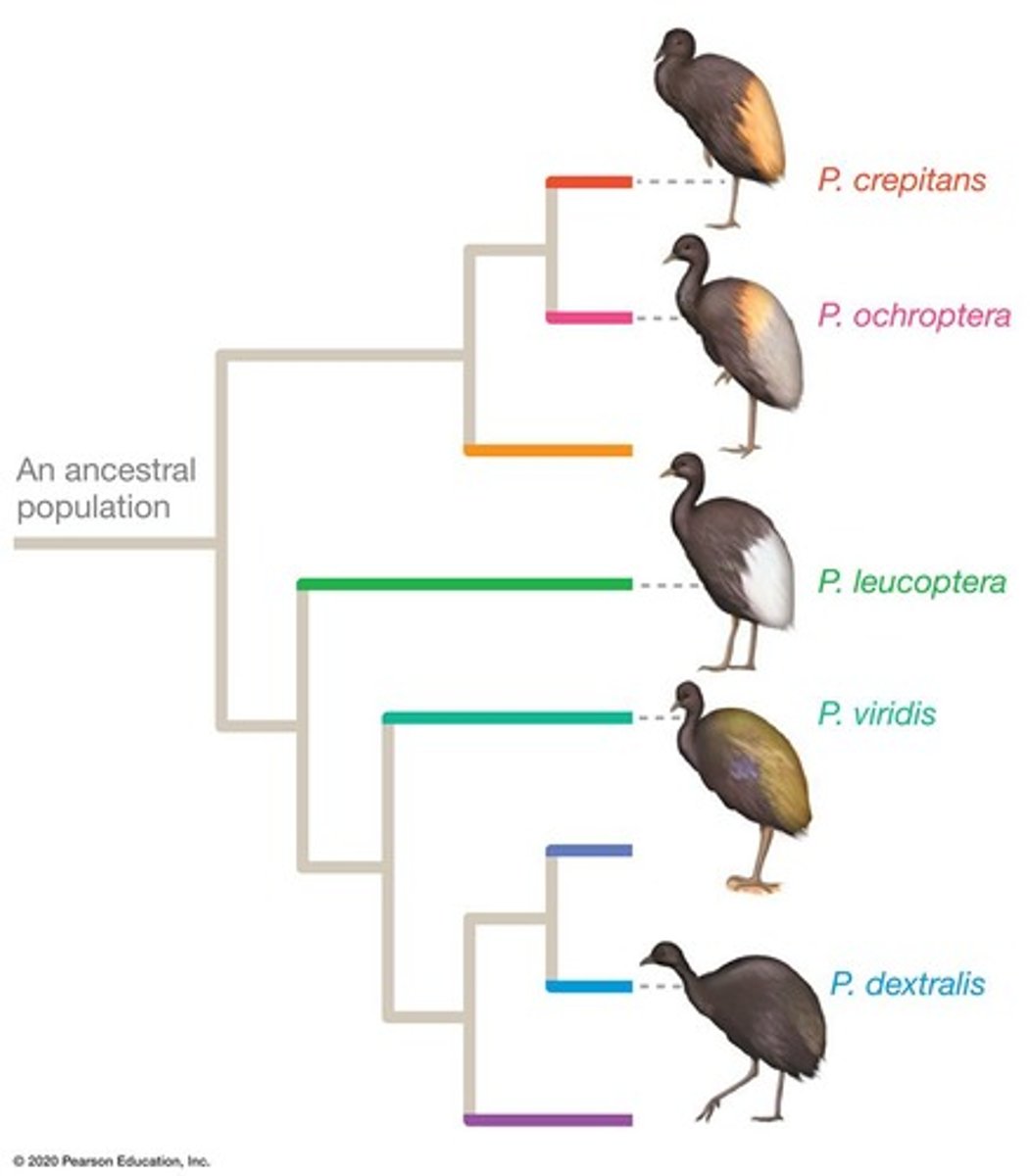
Monophyletic group
Group consisting of a common ancestor and descendants.
Savanna elephants
Larger eared elephants from Africa.
Forest elephants
Smaller eared elephants from Central Africa.
Three-species hypothesis
Theory proposing three distinct elephant species.
Allopatric Speciation
Speciation due to geographic separation of populations.
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in populations.
Natural Selection
Process favoring advantageous traits for survival.
Vicariance
Speciation caused by physical barriers splitting populations.
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation occurring within the same geographic area.
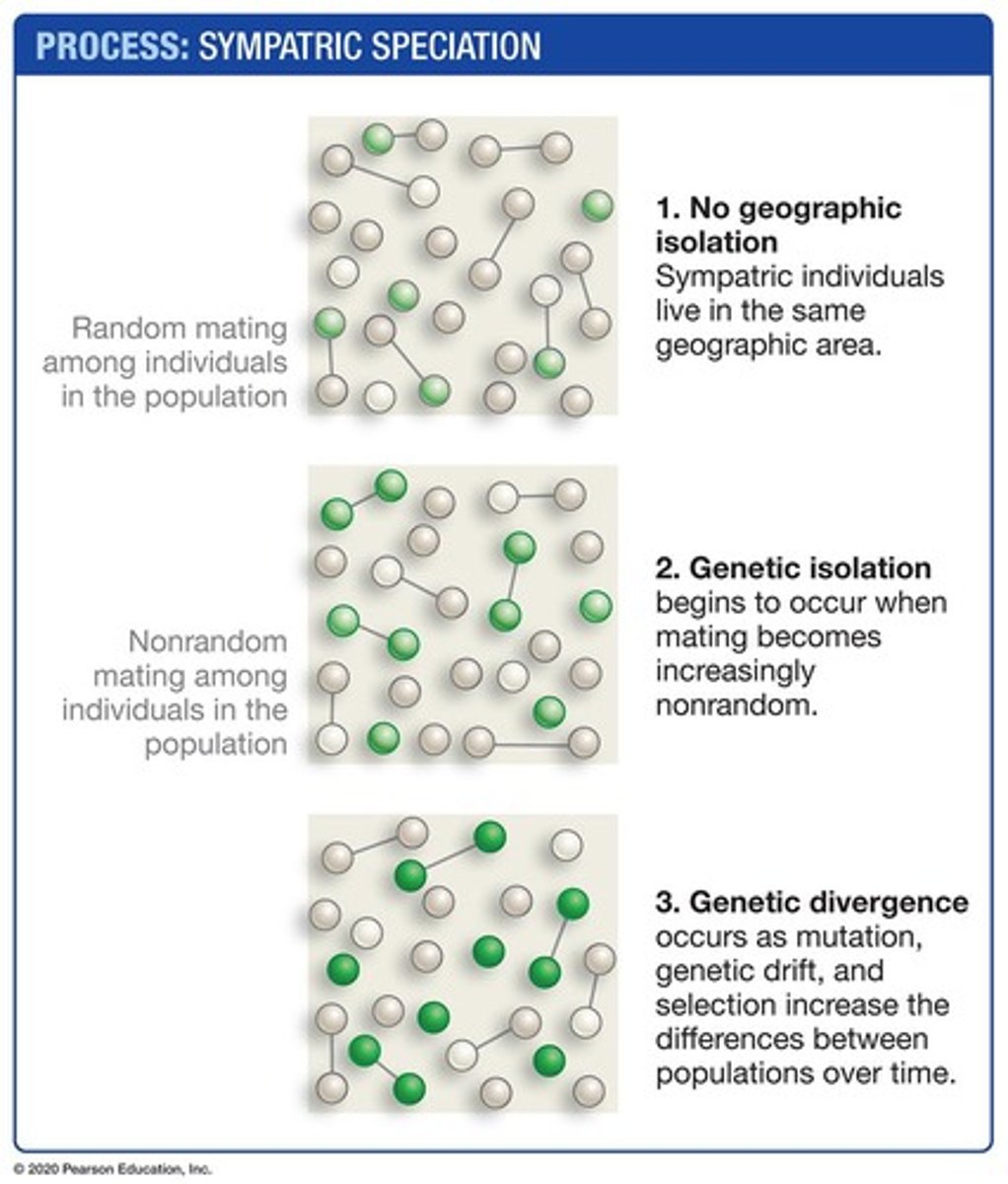
Disruptive Selection
Selection favoring extreme traits over intermediate traits.
Ecological Niche
Range of resources and conditions a species uses.
Killer Whale Ecotypes
Different groups of killer whales with distinct traits.

Resident Group
Larger, stable groups of killer whales.
Transient Group
Smaller, traveling groups of killer whales.
Mate Choice
Selection of partners based on specific traits.
Chromosomal Mutations
Genetic changes affecting chromosome structure or number.
Dorsal Fin Shape
Characteristic used to identify killer whale individuals.
Saddle Patches
Distinct markings on killer whales' backs.
Feeding Cultures
Behavioral differences in hunting and eating among ecotypes.
mFAS Gene
Gene influencing mate choice in fruit flies.
Ecological Selection
Survival based on adaptation to environmental conditions.
Gene Flow
Transfer of alleles between populations through migration.
Isolation Mechanisms
Factors preventing interbreeding between populations.
Divergence
Process where populations evolve different traits.
Behavioral Isolation
Differences in mating behaviors preventing interbreeding.
Environmental Adaptation
Changes in traits to better suit the environment.
Ancestral Population
Original population from which species diverge.
Killer Whale Ecotypes
Distinct groups based on behavior and morphology.
Resident Killer Whales
Larger groups with stable feeding habits.
Transient Killer Whales
Smaller groups with different hunting strategies.
Chromosomal Mutations
Genetic changes that can initiate speciation.
Gene Flow
Transfer of alleles between populations.
Dorsal Fin Shape
Characteristic used to identify killer whale ecotypes.
Saddle Patches
Unique markings on killer whales for identification.
Ecological Selection
Survival based on environmental adaptations.
Behavioral Isolation
Prevention of mating due to differing behaviors.
Isolation by Distance
Reduced gene flow due to geographic separation.
Niche Differentiation
Process where species adapt to different niches.
Disruptive Selection for Feeding
Selection favoring specific hunting methods in killer whales.
Speciation Evidence
Data supporting mechanisms of species divergence.
Amazon Basin Vicariance
Geological events isolating populations in the Amazon.
Disruptive Selection
Natural selection favoring extreme traits over intermediates.
Prezygotic Isolation
Prevents mating between different species before fertilization.
D. serrata
A species that no longer mates with D. birchii.
Pheromone
Chemical signal used for communication between mates.
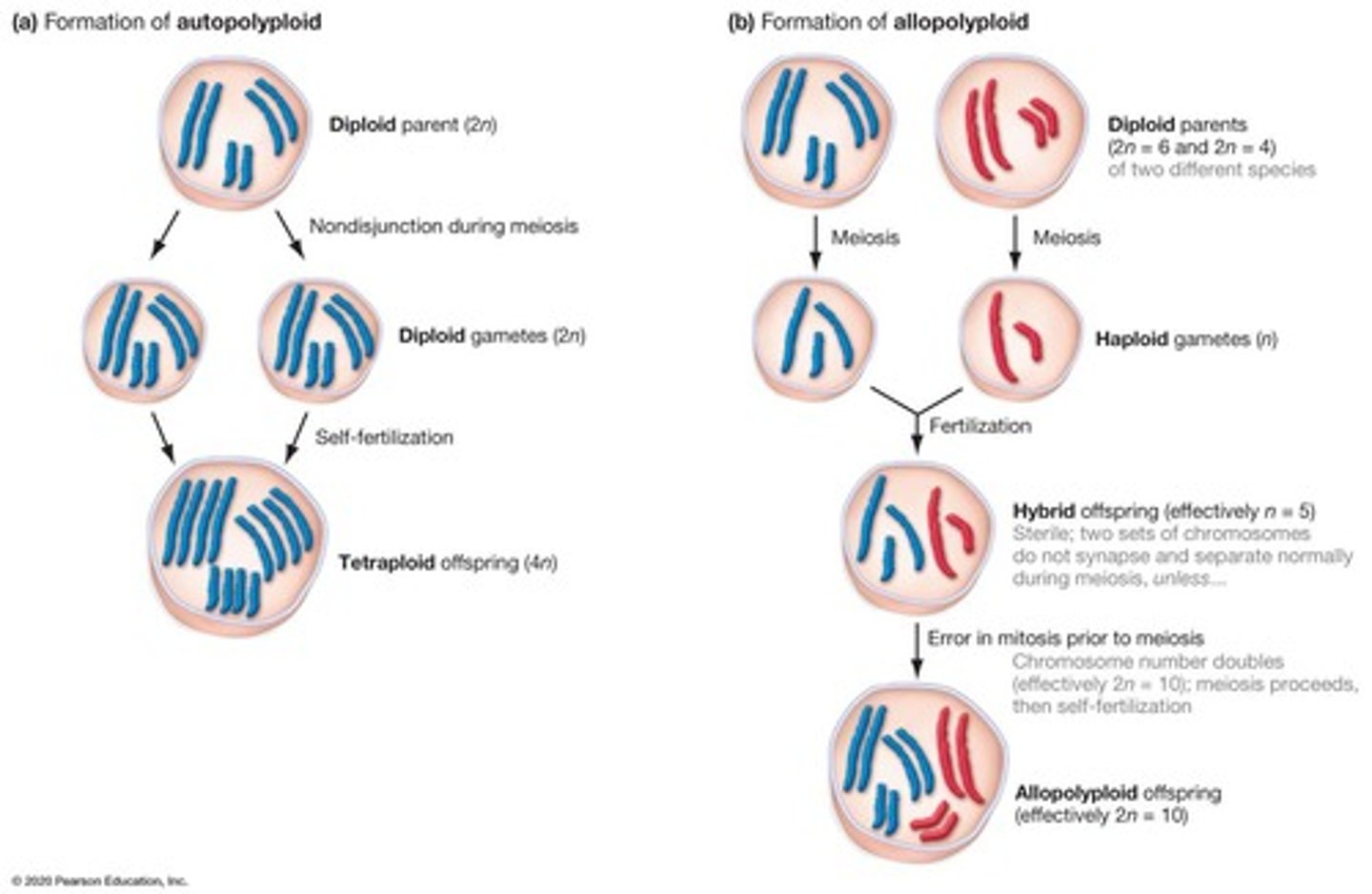
Polyploidy
Condition of having more than two chromosome sets.
Autopolyploid
Organism with doubled chromosome number from the same species.
Allopolyploid
Organism with chromosome sets from different species.
Tetraploid
An organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n).
Reproductive Isolation
Inability of different species to produce fertile offspring.
Inbreeding Depression
Reduced fitness due to breeding between closely related individuals.
Heterozygosity
Presence of different alleles at a gene locus.