Evolution Exam 3
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
Natural selection states that increases in ___ and ____ _____, which is key, can be small.
Survival
Reproductive success
Natural selection states that ___ in a trait cannot be easily detected by humans.
Variations
Natural selection states that ____ ____ is really key.
Reproductive success
Individuals in a population are different
Variation
The differences in a population are heritable.
Inheritance
The differences in individuals in populations increase fitness.
Reproductive success
The ability to survive and reproduce in a given environment.
Fitness
The study of the branching relationships of populations as they give rise to multiple descendent populations over evolutionary time.
Phylogenetics
Historical/evolutionary relationships between all living organisms
Tree of life
Taxon related to the others but branched off earlier in evolutionary history
Outgroup
Theory of evolution by ___ ___ does not try to explain how life on earth began, but does offer a tested theory of how subsequent life developed.
Natural selection
Last universal common ancestor. Was likely a population of organisms, not a single organism.
LUCA
What are the properties of life?
Homeostasis
Structural organization
Metabolism
Growth & reproduction
Response to environmental conditions
___ is the ability to adjust internal environment to maintain a stable equilibrium.
Homeostasis
___ is the ability to maintain distinct parts of their connections.
Structural organization
__ is the ability to control internal chemical reactions.
Metabolism
All life is subject to and has evolved by the process of ___ ___.
Natural Selection
Prebiotic Earth was likely __ than current earth by as much as 30 degrees celsius.
The ___ was different: Reducing (CH4 + N2, NH3 + H2O, or CO2 + H2 + N2) to neutral (CO2 + N2 + H2O), but no O2.
___ relations were different, like bombardment by asteroids.
Warmer
Atmosphere
Space
What was one primary theory Oparin and Haldane made?
Prebiotic soup hypothesis
Who came up with the prebiotic soup hypothesis?
Oparin and Haldane
In absence of oxygen, UV light and lightning were energy sources that converted atmospheric gases into molecules. (Energy + pre-biotic chemicals = earliest life forms).
This is what theory?
Prebiotic soup hypothesis
What are other energy sources that could have converted atmospheric gases into molecules?
Cosmic rays, volcanoes (sea & land), hydrothermal vents, earth’s internal heat
Molecular “soup” may have been enriched by extraterrestrial matter like ___ and ___ which harbor __ , ___ , and ___.
Meteorites and comets
Amino acids, purines, pyrimidines
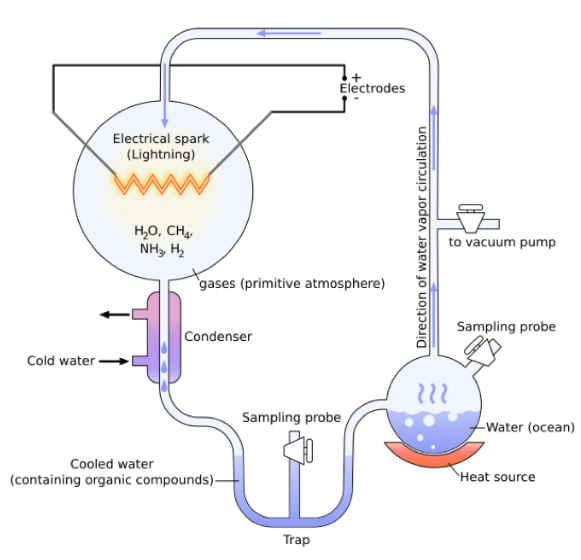
Who did the “synthetic ocean” experiment called “Organic Compound Synthesis on the Primitive Earth” ? Electric source + gases = amino acids: glycine, alanine, valine.
Miller & Urey 1959
Who did the experiment “Thermal Synthesis of Natural Amino Acids from a Postulated Primitive Terrestrial Atmosphere.”
Methane + NH4OH + Sand at 1000 degrees C = 12 amino acids.
Also, what is NH4OH?
Harada and Fox 1964
NH4OH Is ammonium hydroxide.

Who first answered Can amino acids join into chains? with the paper titled “A theory of Macromolecular and Cellular Origins?”
Combined amino acids at high temp (120 dg C) and placed mixture into water = peptide chain (weak)
Fox in 1965, then with a later paper Fox and Dose in 1977
Another to answer the question can amino acids join into chains was ___ by writing the article “ A Possible Primordial Peptide Cycle.”
Combined amino acids at high temp (120 dg C) in presence of CO2 and placed mixture into water = stable peptide bonds.
(CO was thought to exist in prebiotic atmosphere).
Huber et al. 2003
The breakdown of HCN to the next member of the series is called ___ ___ of hydrogen cyanide and its derivatives?
It showed that precursors of amino acids, lipids, and ribonucleotides can all be derived by this.
Reductive homologation
This study shows that Miller-Urey experiments produce ___ ____ in discharges and ___-driven plasma impact simulations carried out in a simple prototype of reducing atmosphere containing ammonia and carbon monoxide.
A.K.A. Meteor like impacts with early earth atmosphere can create all 4 __.
RNA nucleobases
Laser
Nucleobases
__ and colleagues showed that RNA molecules, alone, are affected by natural selection.
Spiegelman 1970
Spiegelman’s experiment was adding primer replicase nucleotides in __ consecutive transfers and incubating led to mutated strands of moderate length.
75
__ did the same experiment as Spiegelman but in a different way. Added __ __ (inhibits replication) which produced also mutated strands of moderate length but they evolved to function in __ __.
Sumper 1975
Acridine Orange
How can RNA replicate without replicase (enzyme)?
Ribozymes
__ are RNA molecules that can act as replication enzymes. (Initial system was very limited in terms of replication).
Ribozymes
Who discovered the system of ribozymes acting as replication enzymes in 2002?
The article title is “ A self-replicating ligase ribozyme.”
Paul and Joyce in PNAS journal
What does ligase do?
Sticks things together
Later on, what two people wrote “Self-Sustained Replication of an RNA Enzyme” that extended to show that 4 oligonucleotides could produce 2 enzymes that __-__.
Self-amplify
Lincoln and Joyce
We moved from RNA to DNA because natural selection would have favored ___ and more ___ systems than RNA and ribozymes. DNA is one such system.
Stable
Efficient
What are ways DNA is more stable than RNA? (Deoxyribose vs ribose)
Double-strand protects bases from interference
DNA replication allows proofreading
DNA has built in repair mechanisms (DNA has higher fidelity = lower mutation = bigger, more complex genomes)
DNA has higher __, which means lower mutation, and lower mutation means bigger, more complex genomes.
Fidelity
Once we moved to the DNA world, how did cells form?
Mutualism, molecular mutualism, hypercycle model
__ is when 2 or more individuals interact in ways which benefit each.
Mutualism
__ is when 2 or more molecular substrates contribute to the replication of each other in a positive way.
Molecular mutualism
The __ model applies to replicators (self-replicating entities). Replicators are found in the same environment and can interact in a cycle ( More A makes more B makes more C makes more D makes more A).
An increase in the rate that A self-replicates is selectively favored, NOT an increase in the beneficial effect that A has on B’s rate of replication, unless the components are enclosed in a membrane and share a collective replication rate.
Hypercycle
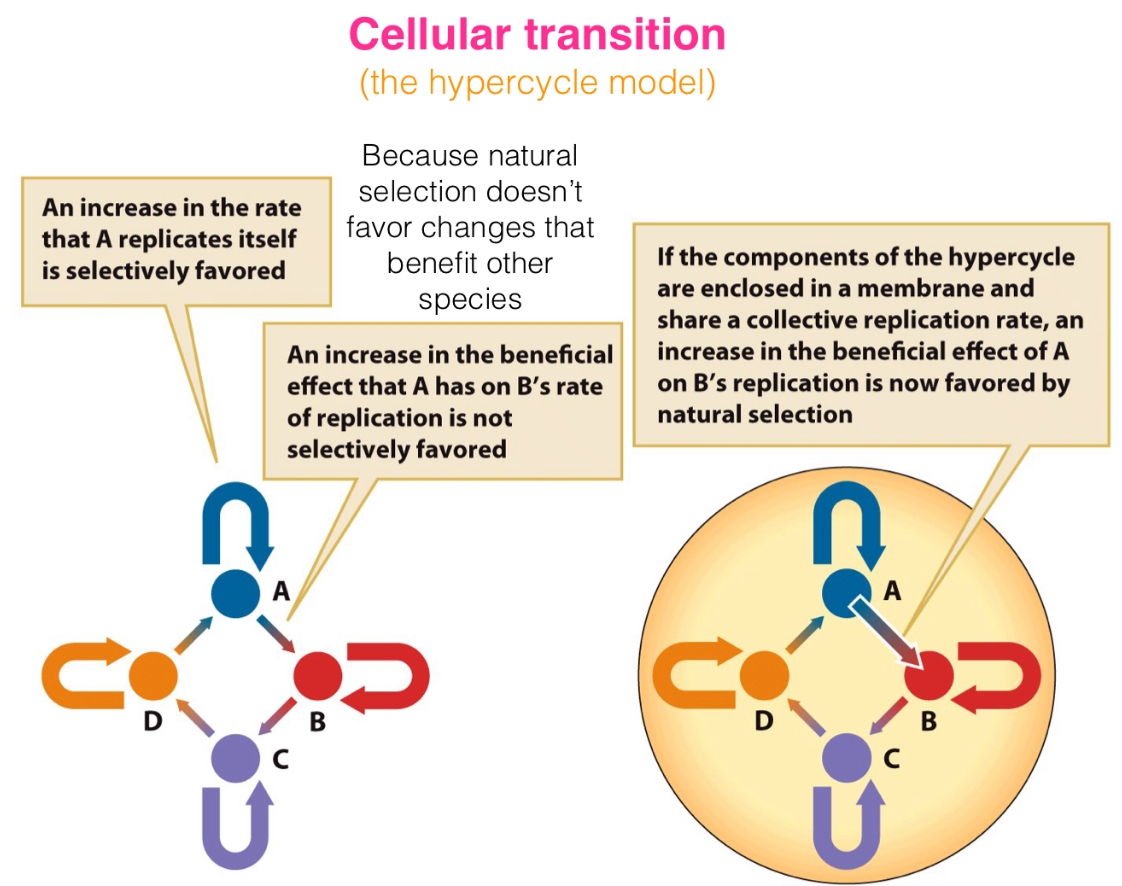
Natural selection does or doesn’t favor changes that benefit other species?
Doesn’t
Leading theory of how cell division arose is that replicators may also have been selected to produce some fatty acids for cell membrane, and increased efficiency led to ___ of cell membrane parts.
Doubling ___ __ more than doubles __, which eventually leads to cell instability and splitting.
Overproduction
Surface area and volume
__ is the transfer of genetic material from one organism to another organism that is not its offspring. Can be different species.
Horizontal gene transfer (lateral gene transfer)
What explains how cells became more complex?
Horizontal gene transfer
Darwin’s insight: All species descended from 1 or a few common ancestors. Species with a recent common ancestor share more features bc they share common ancestry. This explains the ___ of ___ and ___.
Origins of diversity
Heritability
What was the title of the article Darwin wrote about species?
The origin of species
The disagreements over how to define species are referred to as the ___ ___
Species problem
Usually, we define species using a ___, which defines what species are or what makes a species a species. There are many, 20+, but we look at 4.
Concept
What are the species concepts?
Evolutionary species concept
Phenetic species concept
Phylogenetic/cladistic species concept
Biological species concept
Which species concept is this?
A species is a single lineage of populations which maintain its identity from other such lineages and which has its own evolutionary tendencies and historical fate.
Evolutionary species concept
Who came up with the evolutionary species concept?
Simpson and Wiley
What are keys and problems with the evolutionary species concept?
Keys: shared evol. History, common future fate.
Problems: not clear how to identify or define species.
What species concept is this?
A species is a cluster of phenotypically similar individuals or populations.
Phenetic species concept
Who came up with the phenetic species concept?
Michener and Sokol
What species concept do these keys and problems correspond to?
Keys: measure traits, group similar individuals.
Problems: not clear how to weight importance of characteristics, can incorrectly group, (organisms could look similar due to convergent evolution).
Phenetic
Phenetics species concept is also called ___ concept?
It is used when trying to define species of fossil organisms. Also used in microorganisms to determine species.
Morphological
(Fossils: little/no DNA
Microorganisms: lateral gene transfer)
The ___ concept is “A species is the smallest diagnosable cluster of individual organisms within which there is a parental pattern of ancestry and descent beyond which there is not, and which exhibits a pattern of phylogenetic ancestry and descent among units of like kind”
Phylogenetic/cladistic
Eldredge and Cracraft came up with the ____ species concept?
Phylogenetic/cladistic
Phylogenetic species concept: Use phylogeny to define species. Species barriers are drawn using ___, ___ characters that are unique to one ___ group and absent from all other populations in the phylogeny.
Shared, derived
Monophyletic
___ are the smallest monophyletic group distinguished by a shared, derived, character.
Species
What species concept do these keys and problems describe?
Keys: shared evol. History, focus on diagnosable differences.
Problems: differences can be small/arbitrary, traits may not be ecologically significant, ignores gene flow btw species, species can fuse again (doesn’t guarantee evol trajectory in future)
Phylogenetic/cladistic
Since humans are unique and all look different, what species concept would not work to classify humans as one species?
Phylogenetic
Problems: differences are small, traits may not be ecologically significant
What species concept is this?
A species is a group of actually or potentially interbreeding populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
Biological species concept
Who came up with biological species concept?
Mayr
Problems and keys with biological species concept?
Keys: group of populations, reproductively isolated, gene flow.
Problems: hard to apply to extinct species, confusing within hybridization, doesn’t apply to asexual species.
Most common species concept is___. Uses patterns of gene flow to define species. Either no cross-breeding or hybrid sterility. If there IS gene flow… it is NOT a different species.
Biological
Most species concepts agree on species ____ (phenotypic differences, no gene flow, and monophyletic groups).
Delineations
Why are corner cases so hard?
Hard to classify all populations at all stages of evol history.
Trying to make a ___ process __.
Many forces, such as ___ and ___, affect speciation.
Continuous, discrete
Selection, drift, founder effects, inbreeding
What species concept would you apply to “ “ scenario.
What are the 3 models of speciation?
Allopatric, parapatric, sympatric
In __ speciation, reproductive isolating mechanisms evolve in populations that are geographically isolated.
Allopatric
In allopatric speciation, ___ in this model is due to drift, mutation, and selection.
Divergence
In allopatric speciation, often divided into __ and __ __ models.
Dumbbell
Peripheral isolate
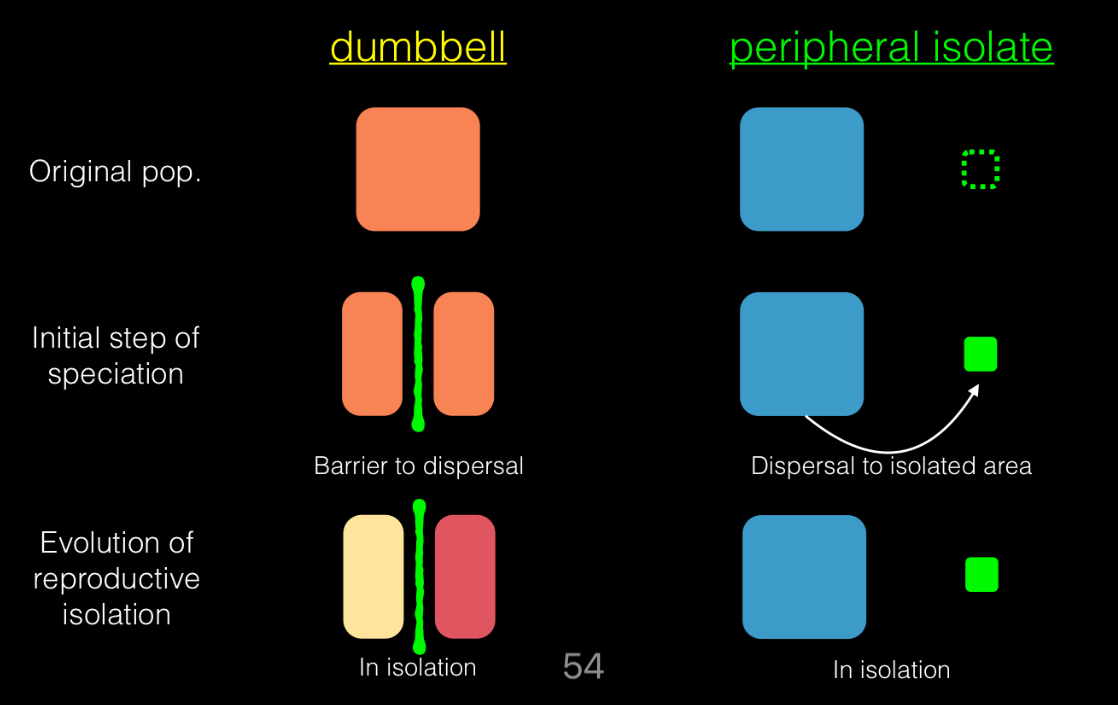
__ speciation occurs when 2 adjacent populations diverge into separate species without a barrier to dispersal. In most of these models, its assumed the hybrid zone will eventually disappear, completing speciation. This assumes that hybrid offspring are at a selective disadvantage across the cline.
Parapatric

__ is a spatial gradient in selective pressures and resulting genotypes and phenotypes.
Cline
The __ __ is an area in which divergent populations encounter each other, mate, and produce hybrid offspring.
Hybrid zone
__ __ is the case where individuals that live in a series of populations connected in a ring-like fashion and gene flow occurs btw adjacent populations. But, where populations come back into contact, there is no gene flow due to significant divergence.
Ring species
(Allopatric + parapatric speciation)
Example of a ring species?
Ensatina salamanders
In __ speciation, populations diverge when no geographic boundary exists between them.
Possible mechanisms: __ __ and __ __.
Sympatric
Resource competition & reproductive competition
Example of sympatric speciation?
Cichlids.
Many ecological niches in lake.
__ __ is the absence of gene flow btw populations.
Reproductive isolation
What are the 2 classes of mechanisms of reproductive isolation?
Pre-zygotic isolating mechanisms
Post-zygotic isolating mechanisms
Habitat isolation, temporal isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, and gametic incompatibility are __-__ isolating mechanisms.
Pre-zygotic
Zygote mortality, hybrid inviability, and hybrid sterility are ___-___ isolating mechanisms.
Post-zygotic
What 4 genetic mechanisms are responsible for reproductive isolation?
Changes in ploidy.
Chromosomal re-arrangement.
Dobzhansky-Muller incompatibility.
Sex-linked effects (Haldane’s rule).
Changes in __ ( chromosome number ).
Ploidy
Which genetic mechanism of reproductive isolation is this?
Many plants can tolerate changes in ploidy, adapting readily to new environments. Differences in ploidy btw individuals lead to infertile offspring (cannot do meiosis). This leads to reproductive isolation btw ploidy levels
Ex: One population had a fusion of chromosomes.
Changes in ploidy
Which genetic mechanism of reproductive isolation is this?
Over time, as populations isolated, genes & chromosomes may re-arrange (by __ or __). These re-arrangements can cause reproductive isolation btw individuals in a population or btw populations, bc individuals of one arrangement + individuals of the other = dysfunctional gametes.
Chromosomal re-arrangement
(Inversion or translocation)
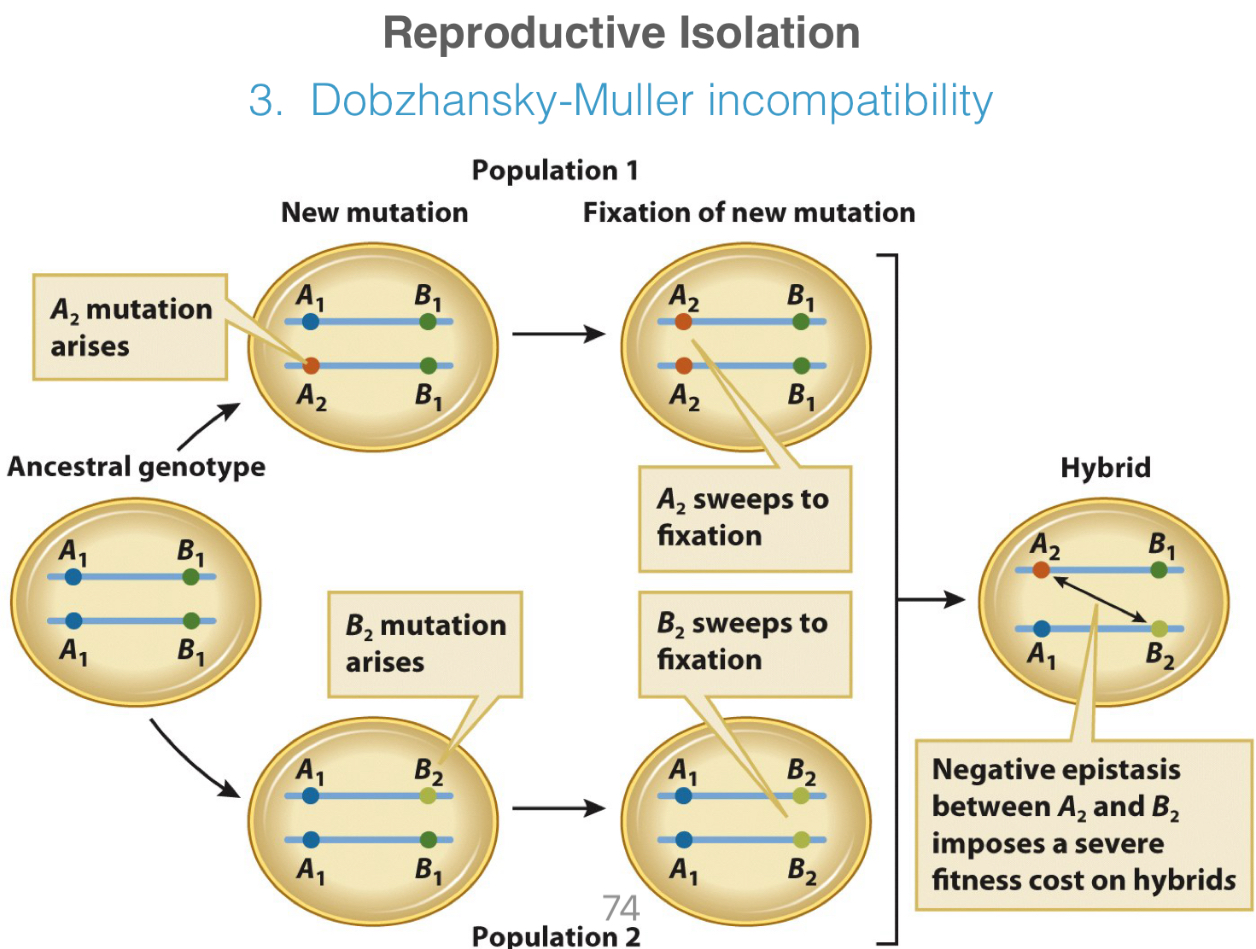
Which genetic mechanism of reproductive isolation is this?
Dobzhansky-Muller incompatibility
Which genetic mechanism of reproductive isolation is this?
JBS Haldane noted that among hybrids, when 1 sex is absent, it is the heterozygous one, & decreased fitness of heterogametic individuals leads to reproductive isolation.
Sex-linked effects (Haldane’s rule)
Regarding the genetic mechanism for reproductive isolation: sex-linked effects (Haldane’s rule),
Why heterogametic sex? ___ __ is if a recessive gene on X-chromosome has negative effect, it is masked in XX females but not in CY males (this works in opposite for ZW sex determination).
Dominance theory
__ __ are regions of DNA of unknown function that are located in non-coding regions of genes. Dr. Faircloth studies these in his lab. They also use these loci to study evolutionary relationships among different species.
Ultraconserved elements
A __ __ is a visual representation, in the form of a bifurcating __, of the evolutionary relationships between species, genera, families, etc…
Phylogenetic tree
Tree
Linnaeus developed the Linnaean __. It is NOT phylogenetics. It is arranged into hierarchical categories: order, family, genus, species, subspecies. Linnaeus had no clue why these similarities existed and some classifications were wrong.
Taxonomy
Who wrote Systema Naturae?
Carl Linneaus
At a ___-scale, phylogenetics allows us to reconstruct the ___of____ - those historical/evolutionary relationships btw all living organisms.
Tree of life