Economics HL all units
1/314
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
315 Terms
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced in an economy within a given period of time
Gross National Income (GNI)
the total income of nation’s people and businesses; GDP - net income from abroad
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the population number; gives the average income per citizen
Circular flow of income
a model that illustrates the interaction between the economic agents in an economy
the output method (of measuring GDP)
consists of counting the total output of firms in a certain period of time
the income method (of measuring GDP)
consists of adding up the incomes of all workers in a country
the expenditure method (of measuring GDP)
consists of adding up the total sales of goods and services in an economy: consumption expenditure + investment spending + government expenditure + net exports
business cycle
the boom-bust cyclical nature of the economy
World Happiness Report
an annual survey of the state of global happiness that ranks 156 countries based on where citizens place themselves on the Cantril ladder
OECD Better Life Index
a measure of 11 indicators (housing, income, jobs…) of 35 countries
Gross National Happiness
a measure of progress in a country considering ecological diversity, health, education, etc.
Happy Planet Index
a composite indicator that shows how well countries are doing at achieving a long, happy sustainable life through well-being, life expectancy, inequality of incomes and Ecological Footprint indicators.
Aggregate Demand
the total demand for goods and services produced in an economy; consists of consumer expenditure, investment spending, government expenditure and net exports.
determinants of aggregate demand: consumption
confidence, unemployment, interest rates, wealth, taxes, indebtedness
wealth
the asset accumulation that retains value and can change value; e.g. property and financial investment
determinants of aggregate demand: investment
confidence, interest rates, taxes, technology, indebtedness
investment
expenditure by firms on capital stock; it is planned investment for expansion.
determinants of aggregate demand: government
change in priorities, change in political parties, health of the economy
determinants of aggregate demand: net exports
income of trading partner, exchange rates, changes in trade policies (quotas and tariffs)
exchange rates
the value of a currency in terms of another
tariff
a tax on imports; it encourages consumers to purchase more domestic goods and move away from foreign goods.
quota
a physical limit to the volume of a particular good entering from abroad.
protectionism
a set of policies designed to protect domestic firms from the competition of foreign firms in the domestic market (quotas, tariffs, subsidies).
Aggregate Supply
the total quantity of goods and services produced in an economy over a specific period of time when resource prices stay relatively constant.
determinants of aggregate supply
resource prices, government intervention (regulation, subsidies, taxes), supply shocks
Monetarists
a school of thoughts that believes that money supply is the most effective and direct way of regulating the economy.
Keynesian
a school of thought that believes that government intervention and policies to manage aggregate demand is the best method of addressing the economy and preventing economic recessions.
Long-Run Aggregate Supply
a country’s potential capacity in terms of factors of production; determined by the quantity and quality of the factors of production.
determinants of LRAS
land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship, improvements in technology, efficiency and changes in institutions (degree of private and public ownership of resources, degree of competition, quantity and quality of government regulations, bureaucracy).
equilibrium in the short-term
intersection of the short-term aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve
deflationary gap
where aggregate demand falls, creating a negative output gap, meaning that the output is below full employment level of output.
inflationary gap
when aggregate demand increases, the economy overheats and produces above full employment.
stagflation
when the economy experiences high unemployment, rising inflation and lower real GDP; this is caused by a fall in SRAS
equilibrium in the long-run
when all resources are being employed and the economy is operating at a natural rate of unemployment; LRAS, SRAS and AD intersect.
recessionary gap
where the economy slows down and operates below full employment; this creates unemployment
human capital
the skills, knowledge, and experience of the workforce
monetary policy
where the central bank uses money supply and interest rate to manage the economy.
money supply
the total amount of money in circulation
interest rates
the cost of borrowing money
minimum reserve requirement
a minimum amount of the deposits that commercial bank must keep in its vault; decided by the central bank
minimum lending rate
the rate at which the central bank charges commercial banks for charging money; it influences the interest rate offered by commercial banks.
quantitative easing
where the central bank creates digital money to buy bonds.
real interest rate
interest rate adjusted for inflation
demand for money
the ability and willingness to hold money at certain interest rates at a certain moment in time
MPC - marginal propensity to consume
the proportion of the addition to income that consumers spend
MPS - marginal propensity to save
the proportion of the addition to income saved
MPM - marginal propensity to import
the proportion of the addition to income that is spent on imports
MPT - marginal propensity to tax
the proportion of the addition to income that is taxed
economic growth
an increase in real GDP
short-term growth
an increase in the actual output of an economy
long-term growth
an increase in the quality or quantity of the factors of production; an increase in the production possibility of the economy
unemployment rate
percentage of people who are of working age, actively seeking for work and unemployed relative to the labour force (employed + unemployed)
cyclical/demand-deficient unemployment
when a lack of aggregate demand forces the economy to make workers redundant
real-wage unemployment
a gap between the people willing and able to work for a certain wage and the number of jobs available a surplus in the labour market
natural rate of unemployment
the percentage of people who are unemployed because of a frictional, seasonal or structural reason
frictional unemployment
those who are between jobs or between schooling and a job and therefore unemployed
seasonal unemployment
those who are unemployed because their skills are needed only at certain times of the year
structural unemployment
a mismatch between the demand and supply for the labour caused by industrial changes or labour market rigidity
inflation
a sustained increase in the general price level over a period of time
deflation
a sustained decrease in the general price level over a period of time
disinflation
a decrease in the rate of inflation of a certain country
hyperinflation
when the inflation rate exceeds 50% a month
demand-pull inflation
inflation caused by a shift rightward of the AD curve
cost-push inflation
inflation caused by the shift leftward of the SRAS curve (usually increase in cost of production)
CPI - consumer price index
a weighted basket of goods and services that are bought in an economy by a typical family; used to measure inflation
Phillips curve
a diagram that plots the unemployment rate against the inflation rate in an economy
supply-side policies
policies which aim to increase the quantity and quality of the factors of production through increased efficiency and competition in the economy
market-based supply-side policies
policies that aim to increase the competition in the economy by encouraging the forces of the free market
interventionist supply-side policies
policies involving the government directly intervening in the economy to increase the quantity or quality of the factors of production
deregulation
removing rules and restrictions to production
privatization
the transfer of ownership from the public to the private sector
trade liberalization
the removal of trade barriers to increase trade with other nations
anti-monopoly regulation
regulation to increase competition in the economy by avoiding the dominance of one single firm
labour unions
an organized association of workers that aims to protect and further the rights and interests of workers
minimum wage
a price floor, where the government intervenes in the labour market and sets wages above equilibrium level
crowding out
when increased public sector borrowing and spending causes a decrease in loanable funds and an increase in interest rates; this can lead to lower investment in the economy
average tax rate
the share of income that a household pays in tax
marginal tax rate
the tax rate imposed on the last dollar earned by a household
international trade
the transnational exchange of goods and services which involves the sale of exports and purchase of imports
factor endowment
the quantity and quality of FOPs available in a country
benefit of trade - increased competition
domestic firms find greater competition as overseas firms can produce goods and services of higher quality and quantity at lower prices
local firms are forced to become more efficient and innovative which brings benefits to the consumer
benefit of trade - lower prices
more competition, efficiency, economies of scale due to the market being larger → lower average cost of production
domestic producers can buy FOPs from overseas which can be cheaper reducing the cost of production thus the final price
benefit of trade - greater choice
trade makes the market bigger, more goods and services from more firms are available
benefit of trade - acquisition of resources
different factor endowments mean different countries have resources suited to different FOPs
international trade can allow countries access to more natural and/or capital resources which would otherwise not be available thus bettering their production processes
benefit of trade - foreign exchange earnings
export earnings in the form of foreign currencies
exporting country can purchase goods and services from other countries (this is import expenditure)
benefit of trade - access to larger markets
greater quantity of consumers increases the quantity supplied which enables economies of scale
integration of economies through trading blocs further enables this
benefit of trade - economies of scale
increase in output lowers average costs of production
cost savings can be passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices
larger scale enables domestic businesses to utilise division of labour and specialisation, invest in capital machinery
benefit of trade - efficient resource allocation
international trade encourages an efficient allocation of scarce resources globally
relatively free international trade makes domestic firms increase the quality of their output due to overseas competition which improves resource allocation in the domestic economy
benefit of trade - efficient production
domestic and foreign firms engage in price and non-price competition
domestic consumers can access a greater quantity of goods and services at lower prices
inefficient and unproductive firms become uncompetitive so when competition increases they are forced to become more efficient in their production process
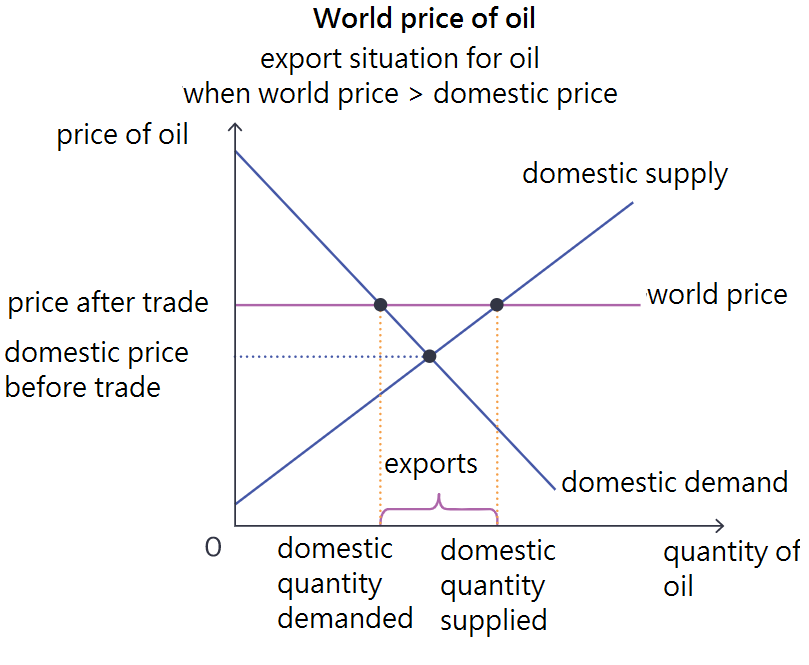
export situation diagram
when the world price is greater than the domestic equilibrium before trade occurs, producers benefit from free trade as they can export goods for higher prices and thus make more revenue and profits
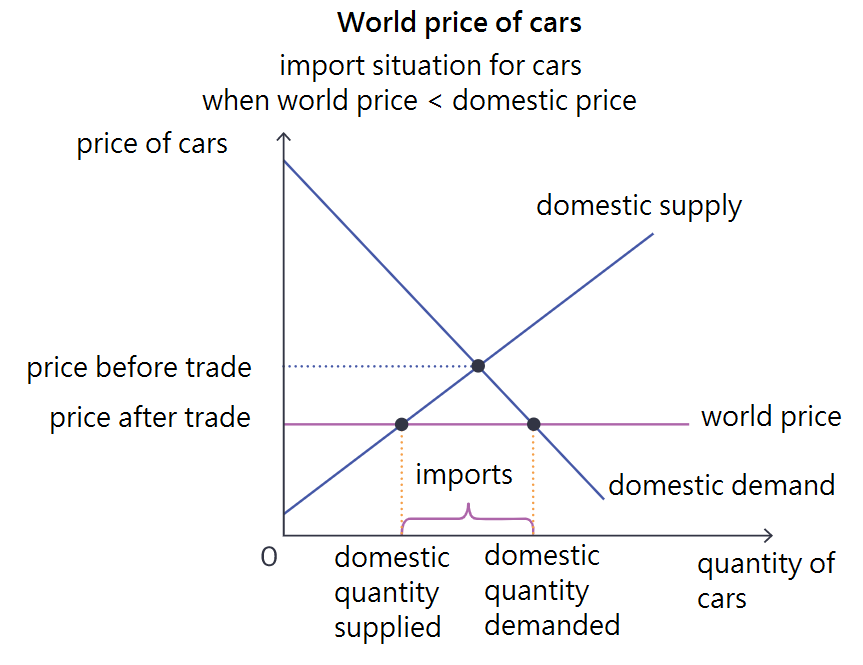
import situation diagram
when the world price is less than the domestic equilibrium before trade occurs, consumers benefit from free trade as lower priced goods are imported and thus reduce the domestic equilibrium price
the world price
the world price is horizontal meaning that the world will supply/demand any quantity of the good at one price
it assumes that the country has no influence over the world price — is a price taker
the World Trade Organisation
only global organisation dealing with rules of trade between nations
help producers and importers conduct their business
representatives from 150 nations
formed in 1995
positive = globalising the economy, allowing more trade to happen more smoothly
negative = developed countries increasing trade with developing countries without considerations for labour and environmental practices
protectionism
the use of barriers to trade to safeguard an economy from excessive international trade and foreign competition
barriers to trade
obstacles to international trade imposed by a government to safeguard national interests by reducing the competitiveness of foreign firms
comparative advantage
economies should specialise in the goods and services which they have a relatively low opportunity cost for when producing
increases efficiency and expands production capacity
tariffs
specific tax on imported goods and services
implemented unilaterally or as part of a trading bloc
increase the costs of production for foreign firms which raises the price of imported goods, so makes domestic products relatively cheaper
most common form of trade protection
quotas
quotas = quantitative limits on the importation of a good into a country
implemented unilaterally or as part of a trading bloc
restrict supply at the expense of foreign firms
quota creates more scarcity so increases the price
domestic supply shifts with the quota, additional amount is is the imported quantity
export subsidies
form of financial assistance to domestic firms which lowers their costs of production to help them compete against foreign firms
production subsidies = help reduce costs of production, most common
export subsidies = targeted at protecting specific export orientated firms
consumers pay Pw but producers receive Ps
reduces the quantity imported as the shortage in the domestic market is mitigated