StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.1.5 Nucleic acids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are nucleotides? (1)
The monomers that make up RNA and DNA
How are ribosomes formed? (1)
RNA and proteins are joined together
What is the basic function of DNA (1)
Stores genetic information
What is the basic function of RNA (1)
RNA transfers genetic material from DNA to the ribosomes
Draw the general structure of a nucleotide present in DNA and RNA (3)
- Phosphate group
- Pentose sugar
- Nitrogen-containing base
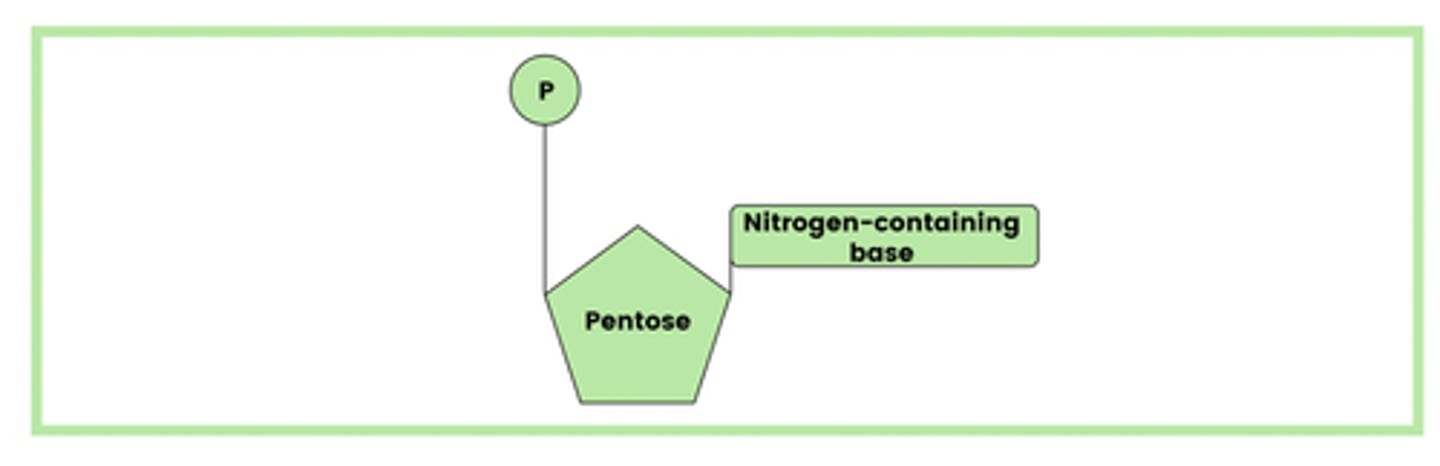
What are two ways in which the nucleotides in DNA are different from the nucleotides in RNA? (2)
- DNA contains thymine whereas, RNA contains uracil
- DNA contains deoxyribose whereas, RNA contains ribose
Compare the structure, properties and function of DNA and RNA (7)
NOTE: Please make sure that you use comparative terminology when answering an exam question like this!
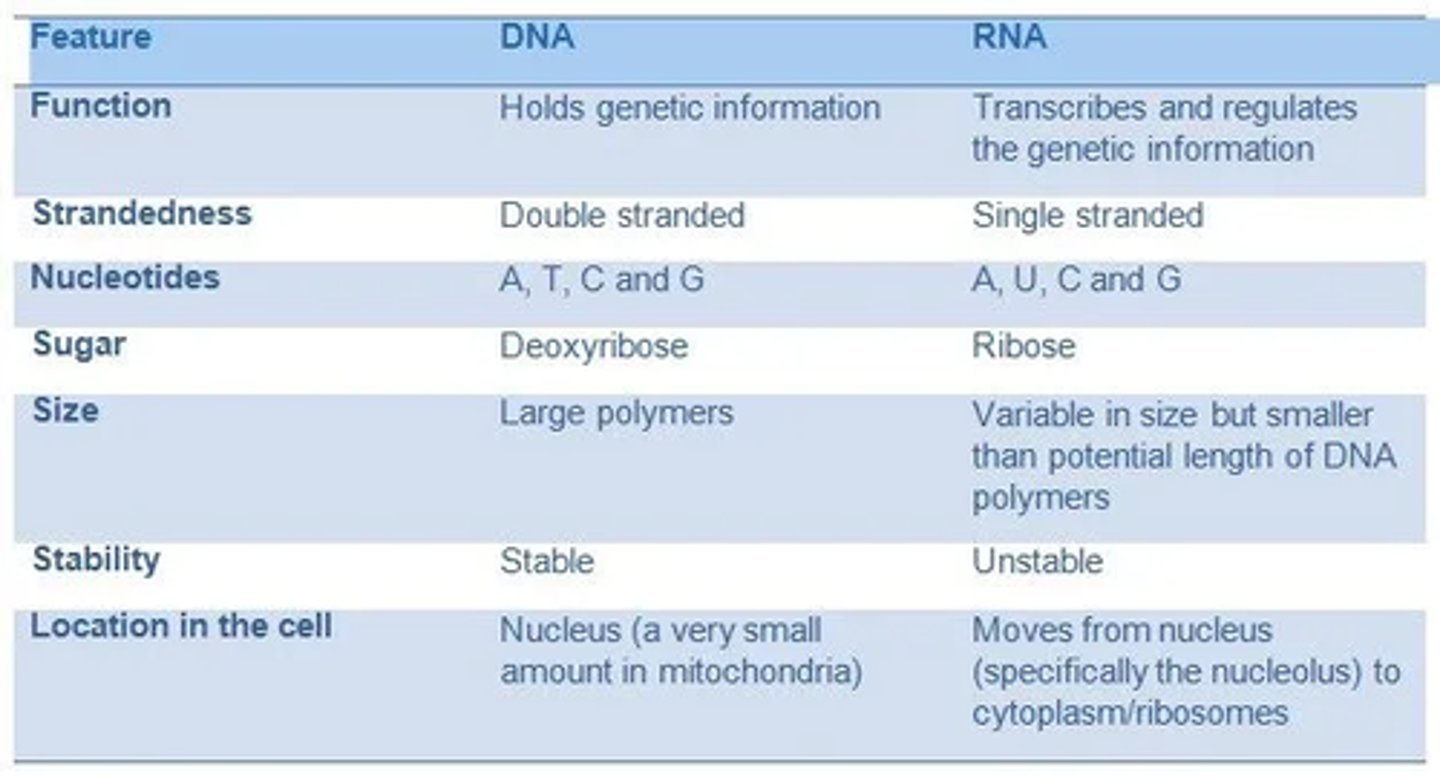
Describe the structure of RNA (5)
- Single stranded
- Short polynucleotide strand
- Contains a ribose sugar
- Contains the bases: uracil, guanine, cytosine, adenine
- Contains phosphodiester bonds between its nucleotides
Describe the structure of DNA (5)
- DNA is composed of two long polynucleotide strands
- It has a double helix structure, which is held together by hydrogen bonds
- Hydrogen bonding occurs between adenine and thymine, and between cytosine and guanine (complementary base pairing)
- Each nucleotide is made up of deoxyribose (a sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
- Phosphodiester bonds link the nucleotides within each strand
Explain how the structure of DNA is related to its functions (6)
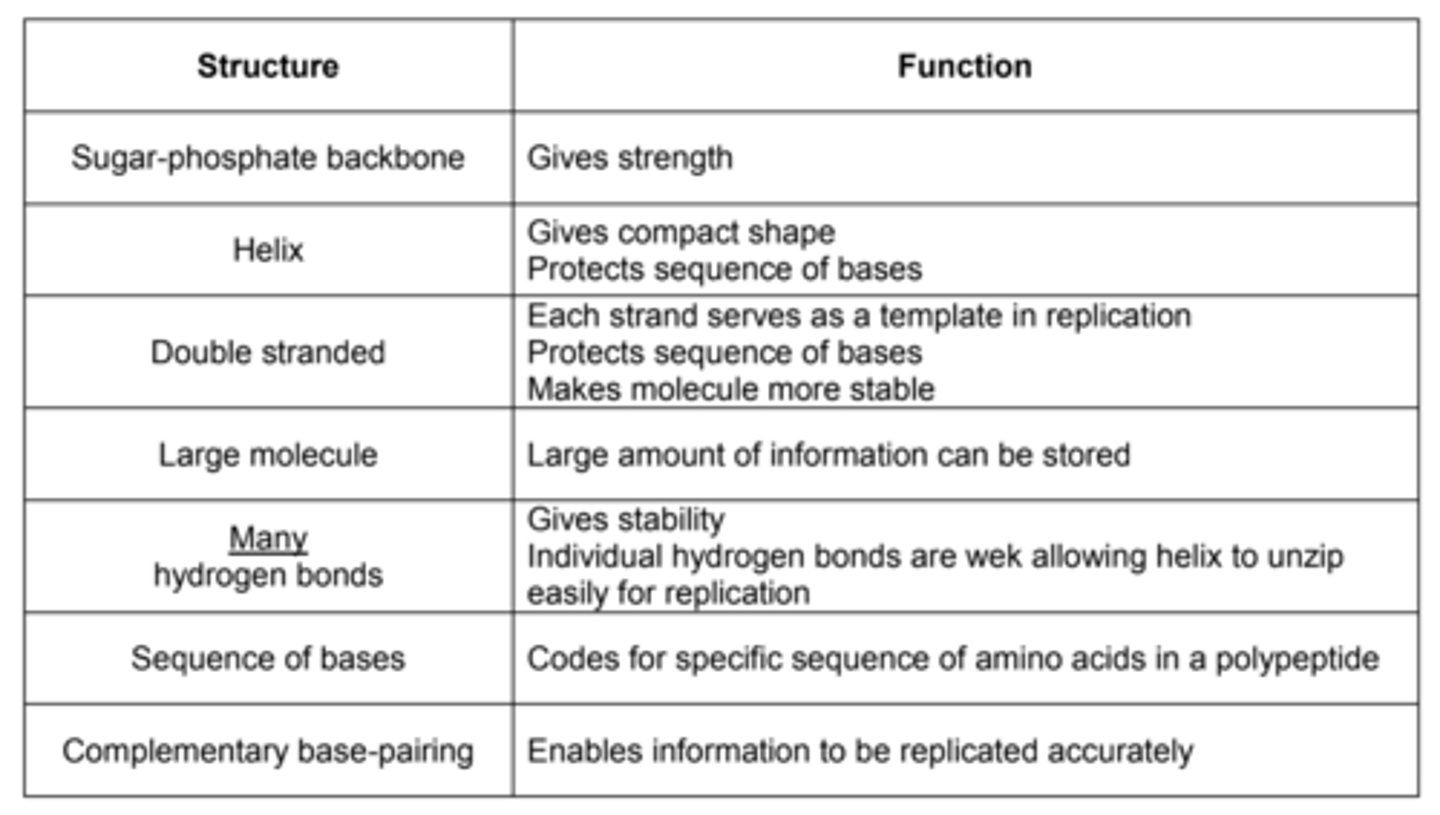
Explain how organic bases help to stabilise the structure of DNA (2)
- Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs holds two strands together
- Many hydrogen bonds provide strength
Name the two scientists who proposed models of the chemical structure of DNA and of DNA replication (2)
Watson and Crick
Describe how a phosphodiester bond is formed between two nucleotides within a DNA molecule (3)
- A condensation reaction occurs
- Between phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar
- Which is catalysed by DNA polymerase
Describe the process of the semi conservative replication of DNA (5)
1. DNA helicase unwinds the double helix and breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases of the two polynucleotide strands
2. Each strand acts as a template for the formation of two new complementary strands
3. Individual DNA nucleotides align and attach by hydrogen bonding to the exposed bases of each template strand according to specific complementary base pairing (A-T and C-G)
4. DNA nucleotides in each new strand are joined together by phosphodiester bonds during a condensation reaction catalysed by DNA polymerase
5. This process results in the formation of complementary strands to the original DNA molecule
Describe the function of DNA helicase (2)
- Unwinds DNA
- Breaks the hydrogen bonds between the strands
Describe the function of DNA polymerase (2)
- Joins nucleotides together
- By forming phosphodiester bonds
Describe and explain how the structure of DNA results in accurate replication (4)
- Two strands and therefore, replicates semi conservatively
- Base pairing is held by hydrogen bonding
- A pairs with T & C pairs with G
- Hydrogen bonds are weak so can easily be broken allowing the strands to separate
How does DNA polymerase arrange itself around a new DNA strand? (2)
- New strands are made from 5' to 3'
- Because DNA polymerase's active site is only complementary to the 3' end of a DNA strand
What directions do DNA strands run? (1)
- Opposite directions
- Antiparallel
Why is the replication of DNA referred to as "semi-conservative"? (1)
Half the strands in each new DNA molecule are from the original DNA molecule