radioactivity
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what are the three things in an atom
proton
neutron
electron
what is the atomic number in an atom
shows number of protons in an atom
what is the atomic mass show in the atom
shows number of protons and neutrons in an atom
define isotope
version of an atom that has same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
what are the three ionising radiations
Alpha radiation
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
what is alpha radiation, what does it take out of an atom, what is the penetrating power and what is the ionising affect
in alpha radiation it takes out two protons and two neutrons, the penetrating power is low and the ionising affect is high.
in beta radiation, what does it take out of an atom, what is the penetrating power and what is the ionising affect
beta radiation takes out an electron, the penetrating power is medium and the ionising affect is medium.
in the gamma radiation what doe it take out, what is the penetrating power and what is the ionising affect
gamma radiation takes out gamma waves, the penetrating power is high and the ionising affect is low.
what is the ionising affect
the ability of radiation to knock out electrons causing a charged ion
using the penetrating power data, what material blocks alpha
paper
using the penetrating power data, what material blocks beta
aluminium
using the penetrating power data, what material blocks gamma
lead
what is the atomic and mass change for alpha
atomic number decreases by two
atomic mass decrease by four
what is the atomic and mass change for beta
atomic number decreases by one
mass doesnt change
atomic number changes since atomic number protons have the same number of electrons, and beta takes out an electron meaning a proton will do as well.
what is the atomic and mass change for gamma
none only loses energy
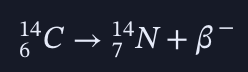
in beta radiation how can you balance the equation of
since beta releases an electron and it is negative, the atomic number has to be 6 + 1 = 7 to balance it.

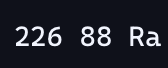
for alpha radiation how can you balance the equation of
since we know that alpha radiation releases two protons and two neutrons that must be the atomic number is 2 and the atomic mass is 4, so we do 88-2 and 226-4 to balance it

how does neutron emission change the atomic number and atomic mass
doesn’t change atomic mass but changes atomic mass by decreases one.
how can you detect ionising radiation
photographic film - darkens when exposed to radiation
geiger muller detector - produces a click sound when radiation ionises
what is the sources of background radiation
rocks (natural radiation)
high energy particles from sun (cosmic rays)
plants (bananas)
what is background radiation
ionising radiation that is always present in our environment
in ionising radiation, what is the unit for when a nucleus is unstable and emits something then decays
becquerels (Bp)
explain over time would becquerels decrease or increase
decrease because its unlikely for the nuclei to stay unstable for a period of time
define half life
half life is the time that it takes for half the nuclei to decay OR for activity to half
define activity half
the number of nuclei to decay in ever period of time.
A radioactive source has an initial activity of 960 Bq. The half-life of the isotope is 4 minutes. What is the activity after 12 minutes?
960, 480, 240, 120
what is the use of radioactivity medically
radiotherapy (high does of gamma rays that kill cancer cells)
medical tracers (radioactive isotope that is swallowed, then it emits gamma rays to give an diagnosis image)
sterilisation (sterilise medical equipment without using heat)
what is the use of radioactivity in the industries
thickness control- beta particles used in paper/metal to monitor thickness (thickness of the material that is between the beta particles and the detector
leak detection (can detect leaks in pipelines)
define contamination
when a radioactive material moves to another object or substance.
define irradiation
being exposed to a radioactive material without being in contact with the radioactive material.
what are the dangers of ionising radiation
damage living organisms DNA → causing mutations
damage cells and tissue
if radioactive material/waste stays radiactive for 1000 of years causing environmental contamination