Chemistry Nuclear Reactions flashcards
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What type of reaction
_________ > _________ + _________
Emission/decay
What type of reaction
___________ + ___________ > ___________
Capture (opposite of emission)
What type of reaction
_________ + _________ > _________+__________
Bombardment (number of products can very)
What reaction often contains Alpha (4/2 He) or Beta (0/-1 e)
Emission/decay
What reaction only uses Electron (0/-1 e)
Capture
What reaction often contains neutron (1/0 n) or Alpha (4/2 He)
Bombardment
What is the only particle that is a reactant and goes before the arrow?
An electron (electron capture)

What is the top number?
Mass number

What is the bottom number?
Atomic number (number of protons)
What law is this: Like charged particles repel, opposite charged particles attract.
Electrostatic law
What does hold the nucleus together?
Strong force: force between quarks holds protons and neutrons together.
What are responsible for the strong force for distances of 10^-15 meters?
Quarks
Which kinds of transformation does emission include
Alpha decay, Beta decay, Gamma decay, and Positron decay
Which kinds of transformation does bombardment include
Fission and fusion
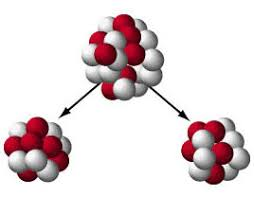
What kind of bombardment is this
Fission
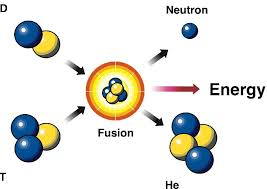
What kind of bombardment is this
Fusion

Alpha decay

Beta decay or Electron capture
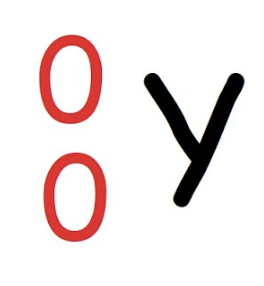
Gamma decay

Positron emission
Which kind of decay:
Isotope 4/2 He is produced
Mass number is reduced by four
Atomic number is reduced by two
Alpha decay
Which kind of decay:
An electron is produced
Mass number stays the same
Atomic number increases by one
Beta decay
Which kind of decay:
A gamma ray is produced
Mass number stays the same
Atomic number stays the same
Gamma decay
What kind of transformation:
A positron is produced
Mass number stays the same
Atomic number decreases by 1
Positron emission
What kind of transformation:
An electron is a reactant
Mass number stays the same
Atomic number decreases by 1
Electron capture
What kind if bombardment:
Atomic bombs, and Nuclear power plants.
Fission
What kind of bombardment:
Hydrogen bombs, no nuclear power, reactions being tested right now, and the sun.
Fusion
What is the least dangerous type of radioactive decay
Alpha
What is the most dangerous type of radioactive decay
Gamma
The time it takes for half of the original value of a radioactive isotope to decay
Half Life
The release of energy after a heavy nucleus splits after impact with another particle is known as…
Nuclear fission
______ is a process in which the nucleus changes the number of protons to produce an atom with a different atomic number
Transmutation
An electron that is emitted during radioactive decay is a ____
Beta particle
The element is changing into another element and the nucleus is becoming unstable
The element is radioactive
Very large nuclei tend to be unstable because of the_______
Repulsive forces between protons