Anatomy and Physiology Honors | UNIT 2: Support and Motion|
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between a tendon and a ligament?
Tendon - cords of dense connective tissue that connects muscles to bones
Ligament - short bands of tough but flexible connective tissue that connects two bones and stabilize joints
Ligament - short bands of tough but flexible connective tissue that connects two bones and stabilize joints
2
New cards

What are the bones that make up the ankle?
Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges, Talus, and Calcaneus

3
New cards
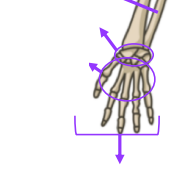
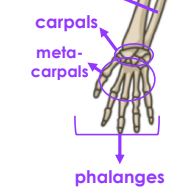
What are the bones that make up the wrist?
Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
4
New cards
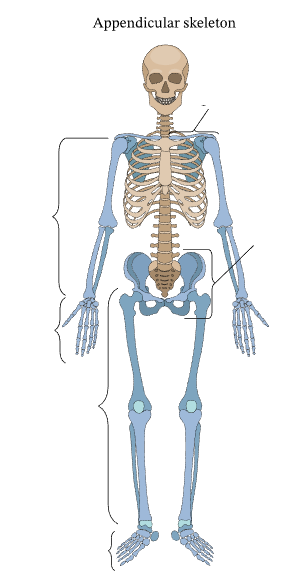
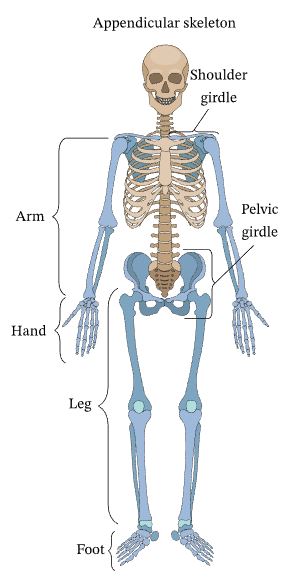
What are the bones that make up the appendicular skeleton?
Shoulder girdle, Arm, Pelvic girdle, Hand, Leg, Foot
5
New cards
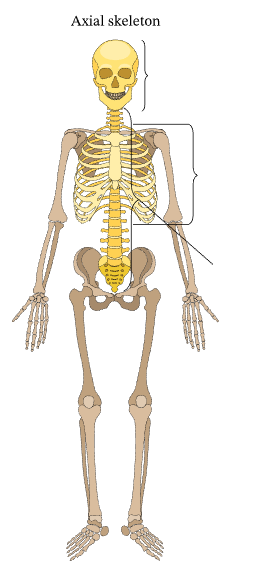
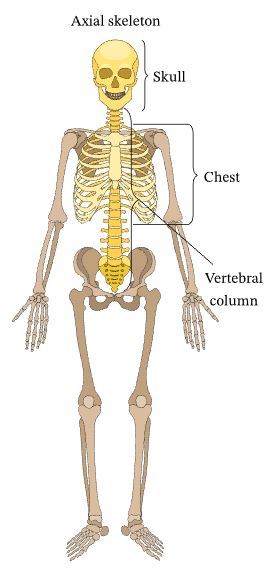
What are the bones that make up the axial skeleton?
Skull, Chest, Vertebral column
6
New cards
What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeletons?
The axial skeleton makes up our central axis and consists of the following bones: skull, vertebrae, ribs and sternum. The appendicular skeleton consists of the limbs and girdles.
7
New cards
What are the five (5) regions of the vertebral column (in order from top to bottom)?
Cervical (C1-C7), Thoracic (T1-T12), Lumbar (L1-L5), Sacral (5 fused vertebrae), Coccyx (4 fused vertebrae)
8
New cards
What is the difference between the pelvic and pectoral girdles?
Pectoral girdle -> upper limbs (clavicles and scapulae)
> clavicles attach to the sternum on one end, scapulae on the other
> each scapula -> humerus (upper limb) to the clavicle
> scapulae attach to the rib cage and vertebral column w/ muscle (gives the pectoral girdle mobility and flexibility
Pelvic Girdle -> lower limbs (sacrum and hip bones)
> extremely strong ligaments
> sturdy less mobility
> protects reproductive organs, bladder, and lower digestive tract
> clavicles attach to the sternum on one end, scapulae on the other
> each scapula -> humerus (upper limb) to the clavicle
> scapulae attach to the rib cage and vertebral column w/ muscle (gives the pectoral girdle mobility and flexibility
Pelvic Girdle -> lower limbs (sacrum and hip bones)
> extremely strong ligaments
> sturdy less mobility
> protects reproductive organs, bladder, and lower digestive tract
9
New cards
The pectoral girdle is attached to the?
Upper limbs to the body's trunk
10
New cards
The pelvic girdle is attached to the?
Lower limbs to the body's trunk
11
New cards
How and why are the pelvic girdles of females differ from males?
Females have much wider birth canals and pubic arches in order to accommodate for growing a fetus and the birth of an infant.
12
New cards
What are the different classes of levers?
First, Second, and Third
13
New cards
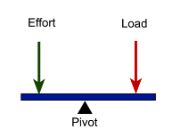
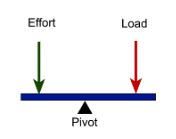
This type of lever is like a seesaw wherein the effort is applied at one end of the lever and the load is at the other, with the fulcrum in between.
First-class lever
14
New cards
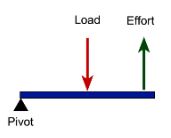
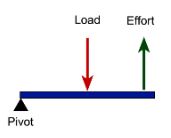
This type of lever is like a wheelbarrow wherein the effort is applied at one end of the lever and the fulcrum is at the other end, with the load in between.
Second-class lever
15
New cards
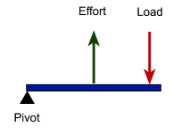
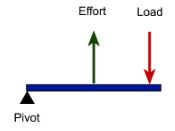
This type of lever is like catapult wherein the effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum.
Third-class lever
16
New cards
What are prime movers?
They are also known as agonists and are muscles that are most responsible for producing a certain movement.
17
New cards
What are antagonists?
They are muscles that oppose or do the reverse of a certain movement.
18
New cards
It is the connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber?
Endomysium
19
New cards
It is the connective tissue that surrounds each fascicle?
Perimysium
20
New cards
It is the connective tissue that surrounds each muscle?
Epimysium
21
New cards
What are the four (4) classifications of bones?
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular
22
New cards
This type of bone acts as levers to aid in movement.
Long bones
23
New cards
This type of bone provides support and stability with little movement.
Short
24
New cards
This type of bone has a large surface area for muscle attachment.
Flat bones
25
New cards
These bones are highly specialized shape and thus function.
Irregular bones
26
New cards
What are the six (6) overall functions of the skeletal system?
Support, Protection, Movement, Storage, Blood cell formation, Hormone production
27
New cards
Why are ribs floating?
The lower 11th and 12th pairs are usually referred to as “floating ribs.”. Because your 8th, 9th, and 10th ribs aren't directly connected to your sternum, they are prone to excess movement. It's this hypermobility that exposes your false ribs to the likelihood of slipping.
28
New cards
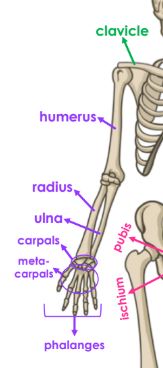
Label the bones of the arms and hands? (include the back)
Scapula, Clavicle, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
29
New cards
What is the general steps in bone remodeling?
1. Resting
2. Resorption
3. Reversal
4. Formation
5. Mineralization
2. Resorption
3. Reversal
4. Formation
5. Mineralization
30
New cards
What is the actual process in bone remodeling?
> OSTEOCYTES release chemical signals that send OSTEOCLASTS to the site of damage
> They then RELEASE ENZYMES that allows calcium phosphate to be digested; calcium and phosphate resorbed into blood
> MACROPHAGES promote bone tissue remodeling and osteoblasts come in an builds new bone
> They then RELEASE ENZYMES that allows calcium phosphate to be digested; calcium and phosphate resorbed into blood
> MACROPHAGES promote bone tissue remodeling and osteoblasts come in an builds new bone
31
New cards
What are the six (6) configurations of joints?
Gliding, Hinge, Pivot, Condylar, Saddle, and Ball and Socket
32
New cards
This joint configuration is known as a "plane" joint.
Gliding
33
New cards
This joint configuration only moves in one direction (like a door).
Hinge
34
New cards
This joint configuration allows rotation as well as twisting movements back and forth.
Pivot
35
New cards
This joint configuration allows movements like flexion/extension, as well as abduction and adduction.
It is like a pedestal with a joint in top.
It is like a pedestal with a joint in top.
Condylar
36
New cards
This joint configuration allows opposition movements as well as flexion/extension, abduction/adduction
Saddle
37
New cards
This joint configuration has lots of maneuverability, and allows for rotational movements such as abduction/adduction and flexion/extension.
Ball and Socket
38
New cards
What are the three (3) functional classifications of joints?
Synarthroses (non-moving)
> serves to protect internal structures such as the brain or heart
> ex. cranium
Amphiarthroses (slightly-moving)
> bind bones together tightly while allowing a small degree of flexibility
> ex. where pubic bones meet in the pelvis
Diarthroses (freely moving)
> allowing fluid and safe movement of the body
> knee and elbow joints (limbs)
> serves to protect internal structures such as the brain or heart
> ex. cranium
Amphiarthroses (slightly-moving)
> bind bones together tightly while allowing a small degree of flexibility
> ex. where pubic bones meet in the pelvis
Diarthroses (freely moving)
> allowing fluid and safe movement of the body
> knee and elbow joints (limbs)
39
New cards
What are the three (3) structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial
40
New cards
What are fibrous joints?
They are joints that connect bones with collagen fibers of dense connective tissue.
> Mostly immoveable (synarthroses)
> Mostly immoveable (synarthroses)
41
New cards
What are cartilaginous joints?
They are joints that connect bones with cartilage
> Can be rigid but also slightly movable (amphiarthroses)
> Can be rigid but also slightly movable (amphiarthroses)
42
New cards
What are synovial joints?
They are joints that connect bones with dense connective tissues and a fluid filled joint cavity
> All of them are diarthroses (freely moving)
> All of them are diarthroses (freely moving)
43
New cards
Homeostasis
It is a self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions.
44
New cards
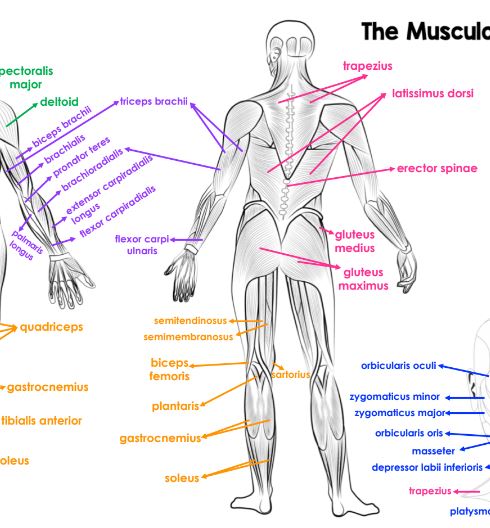
Label the posterior view of the muscular system.
45
New cards
What needs to happen for muscle contraction to occur?
Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. The signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron.
46
New cards
Why is the nervous system important for muscle contraction?
The motor neurons release a chemical, which is picked up by the muscle fiber. This tells the muscle fiber to contract, which makes the muscles move. Neurons carry messages from the brain via the spinal cord. These messages are carried to the muscles which tell the muscle fiber to contract, which makes the muscles move.
47
New cards
Summarize the sliding filament model and explain what happens when muscles contract.
Muscles contract because sarcomeres contract when the myofilaments slide past each other. This happens when the heads of the thick myosin filament heads grab on to the thin actin filaments and pull the thin filaments to slide past the thick ones. This causes the filaments to overlap more and the sarcomere to shorten.
48
New cards
List three (3) ways that muscles can increase the force of their contraction.
1. Increasing or decreasing the number of motor units active at any one time changes the amount of force produced by a muscle.
2. Exercise-induced muscle damage
3. An increase in the level of circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system also increases the force of contraction.
2. Exercise-induced muscle damage
3. An increase in the level of circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system also increases the force of contraction.