PCE Multisystems
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Morning stiffness lasting at least 1 hour, swelling in at least 3 joints, at least one area swollen is wrist, MCP or PIP, symmetrical arthritis, rheumatoid nodules, abnormal amounts of RF, erosions or bony decalcification on radiographs of hand and wrist
7 criteria for the classification of acute RA
Piano key sign
May occur in RA patients
Volar subluxation of the wrist and hand on the radius
May cause extensor tendon rupture
DIP flexion, PIP hyperextension, MCP flexion
Swan neck deformity
Brunnel-Littler Test
Passive PIP flexion with MCP held in flexion, repeat with MCP held in extension
Positive = PIP joints limited in flexion when MCP held in extension = intrinsic muscle tightness
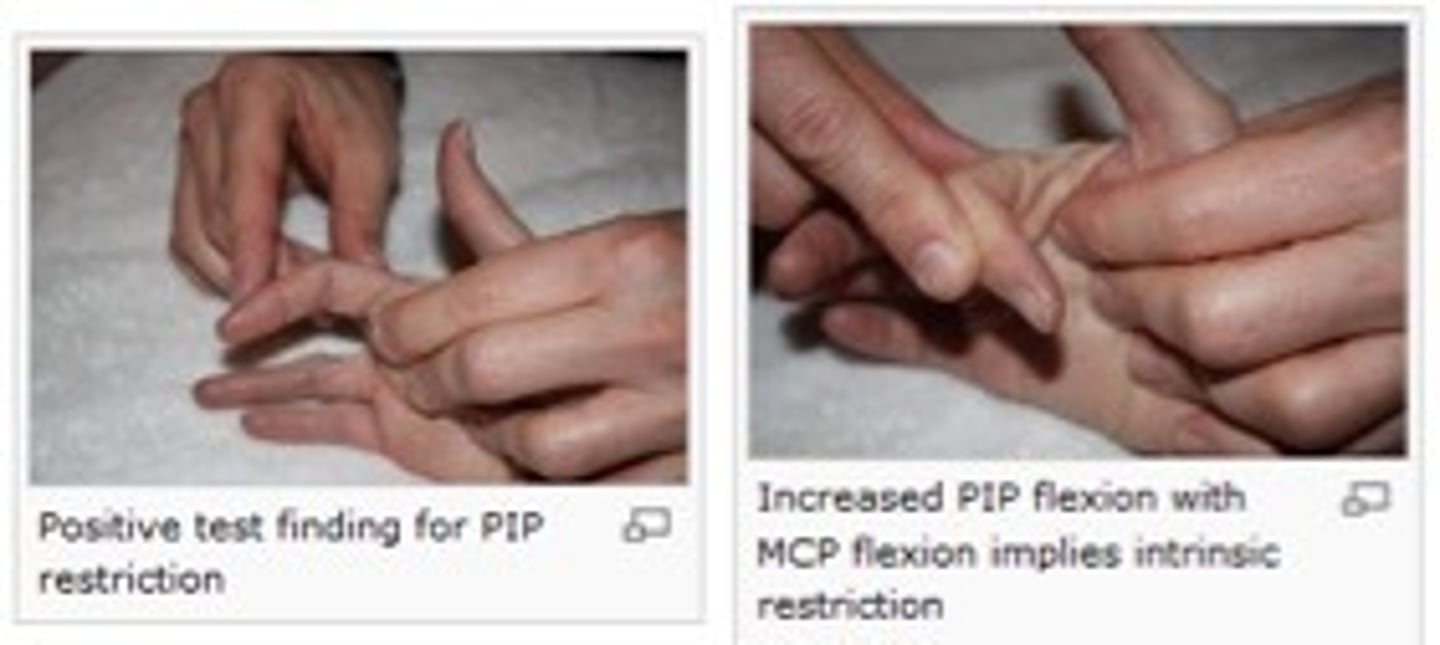
Flexor digitorum profundus
Swan neck deformity typically involves...
DIP extension, PIP flexion, MCP extension
Boutonniere deformity
IP hyperextension, MCP flexion
Z-deformity
Knee ballottement, brush tests
Tests to see if there is excess fluid in the knee
Hammer toe
Claw toe
Mallet toe
Rheumatoid cachexia
Loss of body mass (predominantly skeletal muscle) due to RA
Tenosynovitis
Inflammation of a tendon sheath
Wrist flexors, thumb flexors, patella, achilles tendon
Common sites for tenosynovitis in RA
Olecranon bursae, extensor surface of forearms, achilles tendon
Common sites for rheumatoid nodules in RA
Duration of morning stiffness, bilateral grip strength testing, number of active joints, ESR
4 components of SAJI
Vasculitis, peripheral neuropathy, spinal cord compression, cardiovascular disease, episcleritis
Vascular, neurological, CV and ocular complications of RA
Effusion, joint line tenderness, stress pain
1 of the following (3) means a joint is "active"
Subluxation or deformity, bone on bone crepitus, loss of more than 20% of PROM, ligament instability
1 of the following (4) means a joint is "damaged"
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
An autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of autoantibodies
Can affect any organ
Presents with episodes of remission and relapse
Heat, stretching, strengthening
Contraindicated in inflamed, hot or swollen joints
Serositis, oral ulcers, arthritis, photosensitivity, blood disorders, renal disorder, ANA +ve, abnormal immune tests, seizures or psychosis, malar rash, discoid rash
Name as many criteria for the Dx of SLE that you can think of...
Malar rash
Seen in SLE
Erythema over the cheeks, tending to spare the nasolabial folds
Symmetrical, tenderness, effusion, commonly in peripheral joints, spine and hips usually spared
Describe the nonerosive arthritis seen in SLE
Discoid rash
Seen in SLE
Erythematous raised patches, may cause scarring
Ankylosing spondylitis
A chronic inflammatory arthritis of the axial skeleton
May progress to complete spinal fusion
Associated with HLA-B27
Low back and glute pain, loss of ROM, postural abnormalities, tenderness of muscle insertion sites, insidious onset
Signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
Increased thoracic kyphosis, decreased lumbar lordosis, eye upward gaze, fixed thoracic cage, hip and knee flexion
Postural changes in advanced ankylosing spondylitis
Cervical rotation, tragus to wall, modified Schober, finger to floor side flexion, intermalleolar distance
5 components of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI)
LBP >3 months, Lsp ROM limitation, chest expansion limitation, sacroilitis on x-ray
Modified New York Criteria for Dx of AS - 4 criteria (3 clinical + 1 radiographical)
Osteoporosis
A metabolic bone disease that presents with decreased bone mass (density) and microarchitectural deterioration (quality)
Osteomalacia
A metabolic bone disease which results in softening of bones due to decalcification of bones
Paget's disease
A metabolic bone disease involving abnormal osteoclast and osteoblast activity followed by disorganized remodeling
Leads to enlarged and misshapen bones
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation within bone caused by an infection
Osteogenesis imperfecta
A genetic bone disorder characterized by fragile bones
Superficial burn (1st degree)
Pink or red, no blisters, dry, mild pain
Damage to epidermis only
Healing takes 2-3 days, no scarring
Superficial partial thickness burn
Bright pink or red, intact blister, moderate edema, very painful
Damage into papillary dermis
Healing takes 7-10 days, minimal scarring
Deep partial thickness burn
Broken blisters, wet surface, insensitive to light touch or light pinprink
Damage into the reticular dermis
3-5 weeks healing time
Scar formation (heterotrophic or keloid)
May require skin grafting
Full thickness burn
White, charred, black or red
Eschar formation, no blanching with pressure
Painless
Damage to dermis, and partially into subcutaneous tissue
Subdermal burn
Subcutaneous tissue visible
Large exit wound and smaller entry wound
Always considered severe
Extensive surgery, debridement and grafting
18
Head and neck % in children
14
Each leg is which % in children
Facial burns, singed eyebrows and nasal hairs, harsh cough, hoarseness in voice, carbonaceous sputum, abnormal breath sounds, respiratory distress, hypoxemia
Signs of inhalation injury
Infection, increase in metabolic activity, inhalation injury, fluid loss, heterotopic ossification, peripheral neuropathy, amputation, scars
Complications of burn injuries
Heterotopic ossification
The presence of bone in soft tissue where bone normally does not exist
Complication of burn injury
Etiology unknown, usually in areas with full thickness burns
Fluid loss, decreased CO
Cardiovascular complications associated with burn injuries
CO poisoning, tracheal damage, upper airway obstruction, pulmonary edema, pneumonia
Inhalation injury complications
Hypertrophic scar
Excessive scar formation that raises above the level of the adjacent skin
Raised, red and rigid
Keloid scar
Scar that extends beyond the boundary of the OG wound
More common in people with dark pigmentation
Autograft
Graft from patient's own skin (taken from unburned area)
Common donor sites = thighs and back
Sheet graft
A skin graft which is applied without alteration
Better cosmetic appearance (face, neck, hands)
Mesh graft
A skin graft processed through a device that makes tiny incisions to allow the skin graft to expand
Used when there is limited donor skin
Greater SA but poorer cosmetic appearance
Allograft
Temporary graft from the same species (usually from a cadaver)
Xenograft
Temporary graft from another species (usually a pig)
Flexion
Anterior neck position of contracture in burn injury
Adduction, IR
Shoulder position of contracture in burn injury
Flexion, pronation
Anterior elbow position of contracture in burn injury
Wrist flexion, thumb adduction, intrinsic minus position (claw hand)
Wrist and hand position of contracture in burn injury
Flexion, adduction
Hip and groin position of contracture in burn injury
Flexion
Knee position of contracture in burn injury
PF
Ankle position of contracture in burn injury
Neutral or extension
Anterior neck suggested positioning in burn injury
Abduction, flexion, ER
Shoulder suggested positioning in burn injury
Extension, supination
Anterior elbow suggested positioning in burn injury
Wrist extension, intrinsic plus position, thumb abduction
Wrist and hand suggested positioning in burn injury
Extension, abduction, neutral rotation
Hip and groin suggested positioning in burn injury
Extension
Knee suggested positioning in burn injury
Neutral
Ankle suggested positioning in burn injury
Sweating, nausea, tremors, warmth, anxiety, palpitations, hunger, headache, blurred vision, confusion, weakness, fatigue, difficulty speaking, seizures, coma
Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia
Polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria, fatigue, blurred vision, delayed healing
Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia
Symmetrical, distal > proximal
Diabetes, HIV, Guillain-Barre peripheral neuropathy distribution
Autonomic neuropathy
Seen in diabetes
Impaired function of the peripheral nerves of the ANS
Blunted HR and BP response to activity
High resting HR
Poor thermoregulation
Increased incidence of orthostatic hypotension, post-exercise hypotension
HIV
A virus which attacks the immune system, specifically T-cells with CD4 receptors
Progressively weakens the hosts immune system
Increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections and cancers
Feces, urine, saliva, sweat and tears
Body fluids not infectious for HIV
Fibromyalgia syndorme (FMS)
A syndrome characterized by widespread chronic pain and increased pain response to pressure with no other cause
Pain, allodynia, headache, fatigue, sleep disturbance, cognitive dysfunction, anxiety and/or depression, IBS
S&S of fibromyalgia syndrome
Pitting, brawny, weeping
3 types of lymphedema from least to most severe
Deep heating agents, electrical stimulation (local), traction, local ultrasound
Contraindicated during pregnancy...
Greater potential for ambulation, decreased energy expenditure
Transtibial amputation advantages
Not a weight bearing end, bony prominences are at increased risk for skin breakdown
Transtibial amputation disadvantages
Greater healing
Transfemoral amputation advantage
Not a weight bearing end, lower potential for ambulation, greater energy expenditure
Transfemoral amputation disadvantages
Rigid dressings
Can be removable (RRDs) or non-removable (IPOP)
Excellent for edema and pain control
Excellent for protection
Enhances healing
May help prevent knee flexion contractures
Disadvantages = expensive
Semi-rigid dressings
i.e. Unna's paste
Good edema control, can remove and reapply easily to inspect incision, superior to soft dressing in enhancing healing
However, may loosen easily, needs frequent changing, and takes time to dry
Soft dressings
i.e. elastic wraps and elastic shrinkers
Easy to remove and apply, inexpensive
But poorer edema control and protection