9- retention and relapse, iatrogenesis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is relapse?
Any change from the final position achieved at the end of treatment- loss of correction
Usually moves toward original malocclusion
What is retention?
holding the newly moved teeth in place long enough for the correction to stabilise
Who dictated the 4 thoughts of school?
Occlusion- Kinsley
Apical base- Lundstrom
Mandibular incisor- Grieve and Tweed
Musculature- Roger’s
What are the 4 schools of thought that help prevent relapse?
Occlusal- achieve proper intercuspation and interdigitation- cusp to fossa relationship
Apical base- avoid changes to intercanine/intermolar widths and increase arch length minimally
Mandibular incisor- placed upright and over basal bone
Musculature- proper balance
What are 5 causes of relapse?
Periodontal and Gingival Factors
Occlusal Factors- better quality occlusal finish- less relapse
Soft Tissue Pressures- if teeth moved far out of neutral zone, bigger change in arch form, old age- more unstable
Growth
Pressure from 3rd molars- not much evidence
How do periodontal and gingival factors contribute to orthodontic relapse? (4)
Periodontium must remodel after tooth movement
Most collagen fibers reorganise in 3–4 months
Dentogingival and interdental fibers take 8 months
Must be held in correct place until remodelling- especially after rotational correction
How can you reduce rotational relapse?
Pericision- surgically sever supracrestal fibres (fibreotomy)- removes elastic forces that cause the tooth to rotate back
How can late mandible growth cause relapse?
Late lower incisor crowding due to forward mandibular growth.
Mandible displaced distally- rare, may relate to myofascial pain/TMJ dysfunction
Flaring/spacing of upper incisor- least common
Distal displacement and crowding of lower incisors with a decrease in intercanine width
How can you identify patients who will suffer replace?
Impossible- must treat all patients as if they can relapse
Informed consent before- unpredictable nature, life long retention to reduce risk
For what 6 cases do we need semi/permanent retention?
Midline diastema
Severe rotations
Arch expansion achieved without ensuring good occlusion
Some class II div 2 deep bite cases
Have abnormal musculature or tongue habits
Expanded arches in cleft palate patients
How long is Harley’s retainer worn for?
6 months full time then part time at night
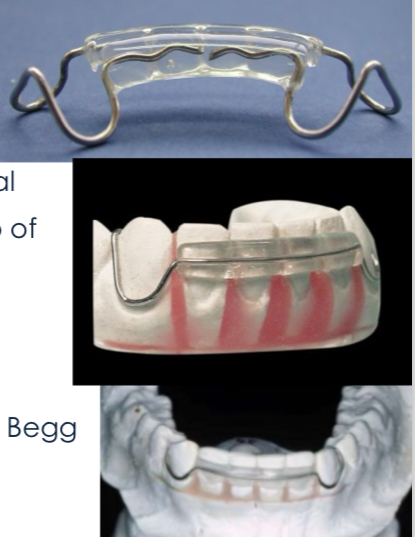
When is Begg’s retainer used?
Need to settle occlusion- no wire framework across teeth
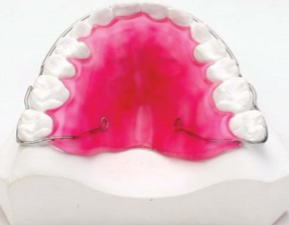
Which removable retainer corrects rotations?
Clip on/spring retainer
Runs labial and lingual
Wrap around retainer is an extended version- covers all teeth
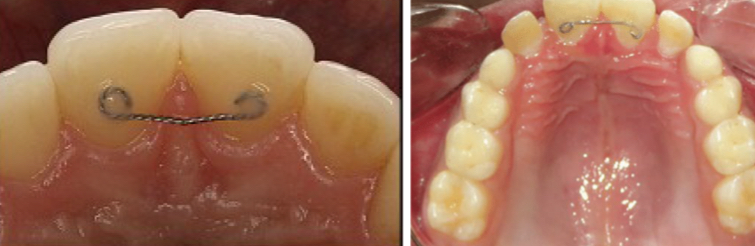
When is a fixed retainer indicated? (5)
Hold diastema closed- bonded to selected teeth
when final position unstable due to-
Periodontally compromised support
Malocclusions with spacing
Severe rotations
Lower labial segment moved during treatment
Adverse Iatrogeny effects of orthodontic treatment include… (6)
Root effects
Coronal effects
Malpositions
Bonding
Periodontal effects
Post-surgical effect
TMJ effects
Psychological effects
What are some adverse root effects caused by ortho treatment?
Pulp effected- vitality loss due to traumatic occlusion or excessive (intrusive) force or uncontrolled coronary lingual torque
Mobility and pain- some mobility normal
Root resorption- apex rounding
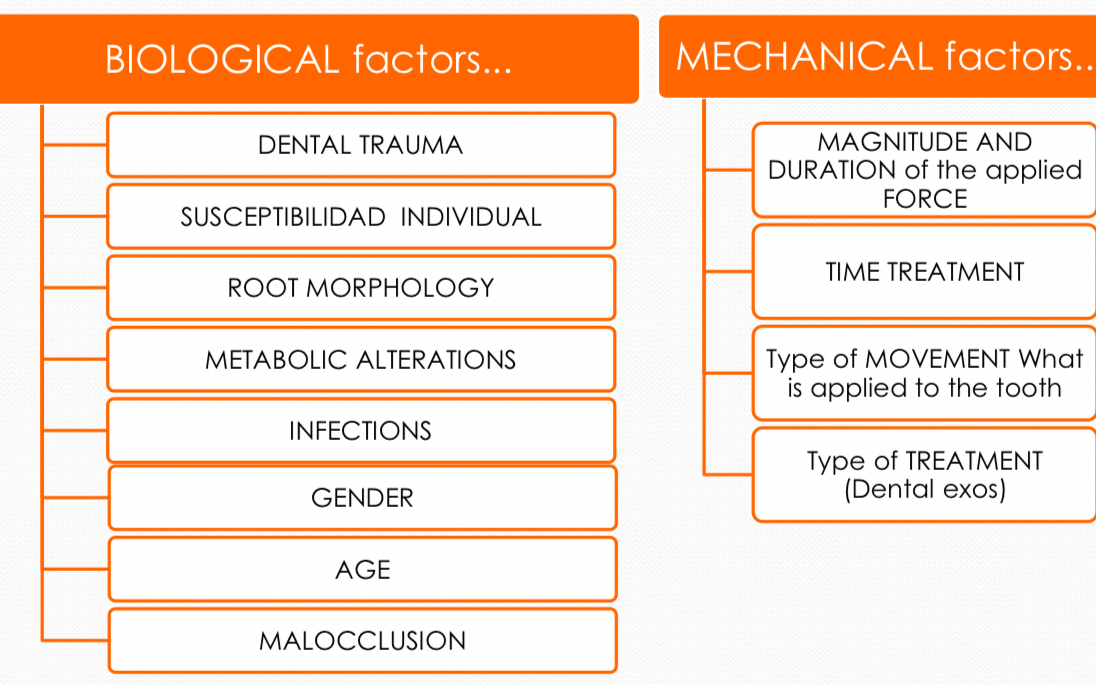
Biological (7) vs mechanical factors (4) causing root resorption
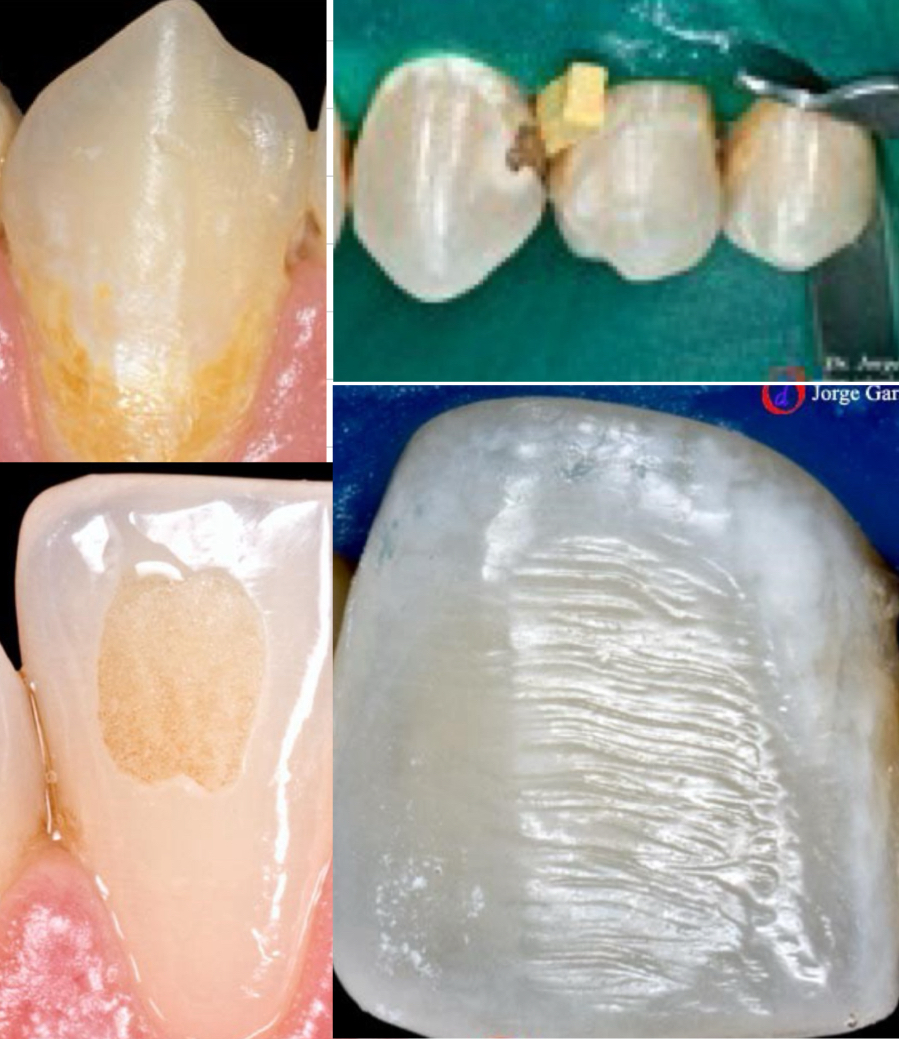
What are 3 adverse crown effects of orthodontic treatment?
Caries
Accumulation of plaque
Premature contacts
How can effect of debonded braces in enamel adversely effect crown? (4)
White / yellow spots
Cavitations
Bonding material remains
Effect of the bur on the enamel when removing brackets
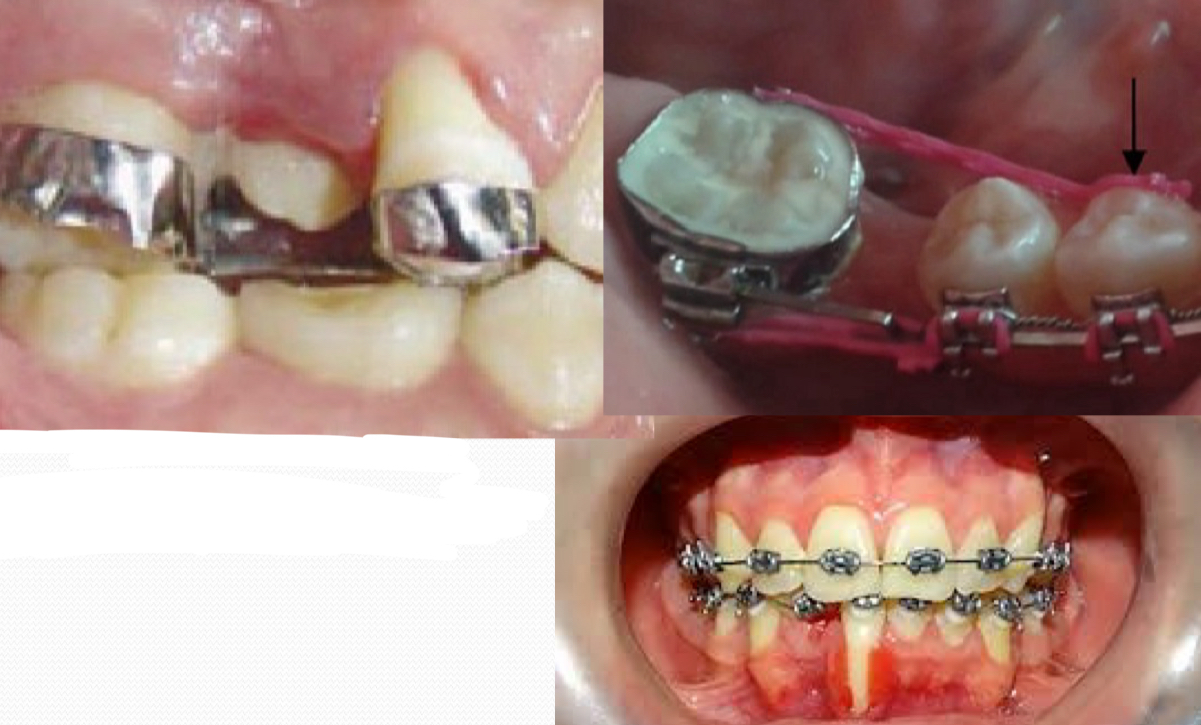
What can cause adverse periodontal effects? (4)
Badly adjusted bands
Bands with gingival overflowing bond
Periodontal effect
Recessions
What are 5 adverse mucous effects of orthodontic treatment?
Traumatic ulcer-
Acute
Chronic reactive
Traumatic granuloma
Frictional or focal hyperkeratosis