Biology 1010 - Unit 2
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
genetics
study of the inheritance of observable traits from one generation to the next, and their effect on populations and species
molecular biology
the study of the molecular processes involved in the transfer of genetic information from genotype to phenotype of an organism
expression of a gene may be affected by…
environment
genotype determines…
phenotype
phenotype
an organism’s physical and biochemical traits
genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup, the genetic information contained in genes
_____ backbone forms the “ribbons” of DNA?
sugar-phosphate
_____ form the “rungs of the ladder”
nitrogenous bases
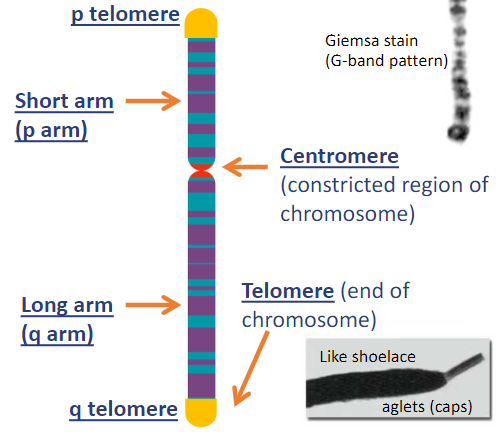
structure of DNA
double helix
each chromosome is…
one long DNA molecule
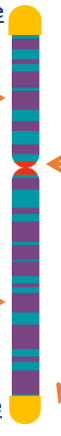
name the parts of the chromosome
homologous chromosomes
2 chromosomes, same size, same shape, same genes — but not identical
locus
a specific place along the length of a chromosome where a given gene is located
eg. gene for eye colour in fruit flies
alleles
alternative versions of the same gene
eg. each chromosome can have a different version of the eye colour gene
red or white eye allele
when do homologous chromosomes exist?
G1 (before DNA starts to replicate)
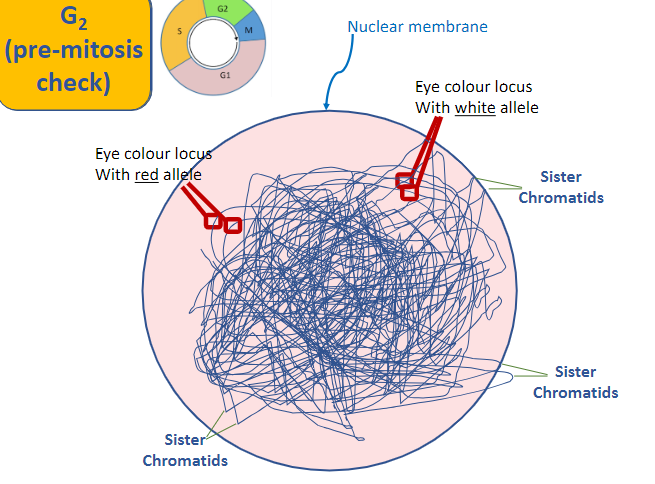
sister chromatids
2 DNA strands with identical nucleotide sequence, one copied from the other to prepare for mitosis, joined at the centromere
homologous chromosomes are not to be confused with…
sister chromatids
when are sister chromatids not present? when are they?
Not- G1
Are- when the cell prepares to divide
S-phase
DNA replication
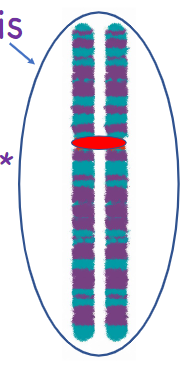
what is this
a single replicated chromosome (aka mitotic chromosome), consisting of 2 sister chromatids
G2
pre-mitosis check
what happens during G2 - pre-mitosis check
sister chromatids scrambled everywhere
chromosomes (duplicated and uncondensed)
what happens during mitosis prophase
nuclear membrane starts to break apart
2 replicated chromosomes (2 sister chromatids) condense
centrosomes move apart
what happens during mitosis prometaphase
nuclear envelope disappears
spindles interact with chromosomes
what happens during mitosis metaphase
alignment of chromosomes on metaphase plate
what happens during mitosis anaphase
daughter chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell
homologous chromosomes separate (sister chromatids stay together)
what happens during mitosis telophase
nuclear envelope reforms
chromosomes condense
mammalian somatic cells ___ sets of homologous chromosomes. They are _______ (they have ___ chromosomes)
2
diploid
2n
only _____ _________ have only one set of homologous chromosomes. they are _________ (they have ___ chromosomes)
sex cells
haploid
n
human karyotype
display of condensed chromosomes arranged in pairs
application of human karyotype
identification of chromosomal abnormalities
abnormal number, abnormal arrangements
these abnormalities are associated with certain congenital disorders
trisomy 21/ down syndrome
histones
the proteins that complex DNA
DNA + protein = __________
chromatin
several conformations (types) of chromatin exist in the…
nucleus
hierarchical structure of a chromosome
“naked” DNA
nucleosomes
chromatin fiber
chromatin loops
sister chromatid
metaphase chromosome
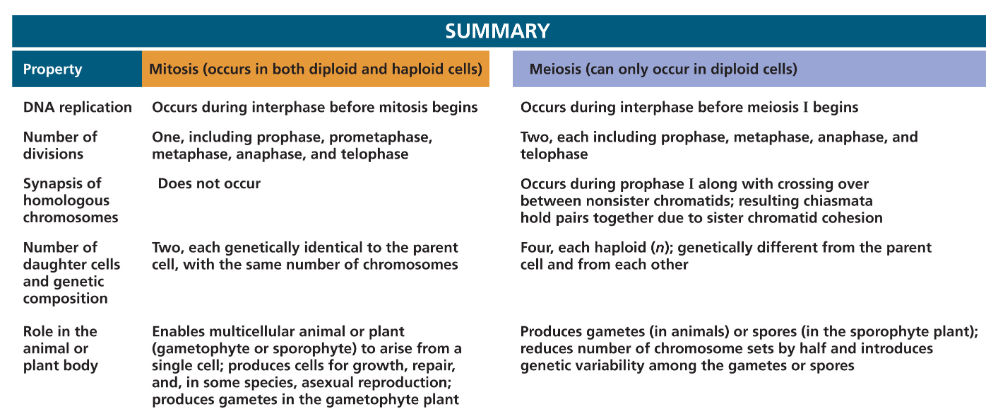
purpose of mitosis
to ensure that an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA is passed on to the 2 new daughter cells
mitosis is a ________ process
continuous
humans decided to separate that process into ‘phases’ because we like
to categorize things
there are actually several inter-dependent
processes occurring in parallel
what is mitosis
cells split into 2 daughter cells with equivalent DNA
types of asexual reproduction
budding (hydra)
fragmentation (plants, some non-vertebrate animals)
If all the cells in an organism have the same genes, can the nucleus from a differentiated animal cell be used to create a new organism (a clone)
The potential of a cell nucleus to produce a whole organism decreases as the cell becomes more differentiated, presumably due to changes in the nucleus
gametes (eggs & sperm) of an organism contain a single basic complement (______) of chromosomes
haploid
fusion of haploid gametes to form a new diploid cell is…
fertilization
fertilization
the fusion of haploid gamete to form a new diploid
what is produced by fusion of egg and sperm
zygote
what does a zygote contain?
in each cell 2 copies of each chromosome (diploid)
what is meiosis?
the cellular process of reducing the diploid complement of chromosomes to a haploid complement of chromosomes to produce sex cells (gametes), an essential process for sexual reproduction
diploid: 2n or 1n
2n
haploid: 2n or 1n
1n
what are is the key difference between mitosis and meiosis?
mitosis: separation of the sister chromatids
meiosis 1: separation of the homologous chromosomes
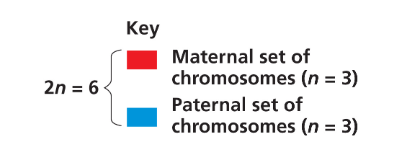
2n = 6 → breakdown
n = 3 (maternal)
n = 6 (paternal)
synapsis
pairing of homologous chromosomes
crossing over may occur
crossing over
exchange of alleles
number of genes in each chromosome stays the same
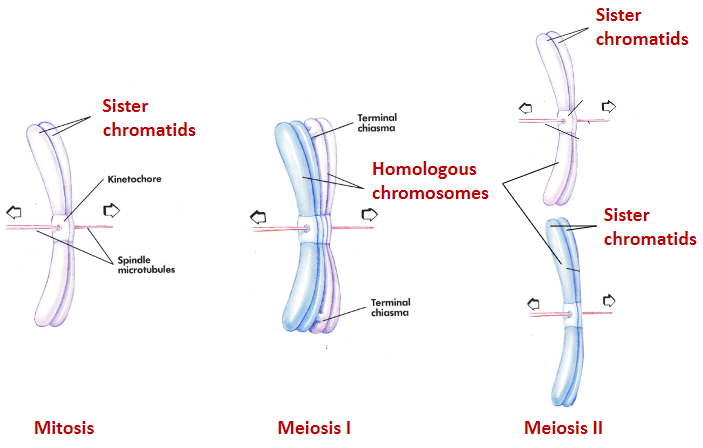
what are the different chromosome arrangements in mitosis, meiosis l, and meiosis ll
mitosis - sister chromatids
meiosis l - homologous chromosomes
meiosis ll - sister chromatids x2
why sex and not just asexual reproduction?
new alleles and new combination of alleles
what is the purpose of meiosis
divide the number of chromosomes in half
still want one copy of all the genes
diploid (2n = 2 sets)
haploid (n = 1 set)
variation: new alleles or new combinations of alleles
gametes randomly receive one chromosome of each homologous pair
crossing over shuffle genes within homologous chromosomes
lecture 1 summary
hybridization
crossing of 2 true-breeding varieties
Mendel’s first law: Segregation of Alleles
2 alleles for a heritable characteristic segregate (separate from each other) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
___________ __________ of genes account for variations in inherited characters. Mendel’s Observations For each character, an organism inherits ____ _____ (that is, two alleles) of a gene, one from each parent. If the two alleles at a locus differ: ______ _____ determines the organism’s appearance ______ _____ has no noticeable effect
Alternative versions
two copies
dominant allele
recessive allele
genotype determines…
phenotype
heterozygous
an organism with two different alleles for a character
homozygous
an organism with a pair of identical alleles
Mendel’s second law: Independent Assortment of Genes
during gamete formation, a pair of alleles for one gene will segregate independently of a pair of alleles for another gene
deviations from Mendel’s Laws
some traits not on nuclear chromosomes
eg. mitochondrial or chloroplast chromosomes
traits on the same chromosome
traits carried on sex-chromosomes
eg. mammals XX female, XY male
other deviations from Mendel’s Laws
incomplete dominance
multiple alleles
co-dominance
lethal alleles
incomplete dominance
red + white = pink
multiple alleles & co-dominance
blood types
A allele produces the enzyme __________, which catalyzes the transfer of…
GaINAc residues
B allele encodes the enzyme __________, which catalyses the transfer of…
galactose residues
the i allele ______ both enzymatic activities
lacks
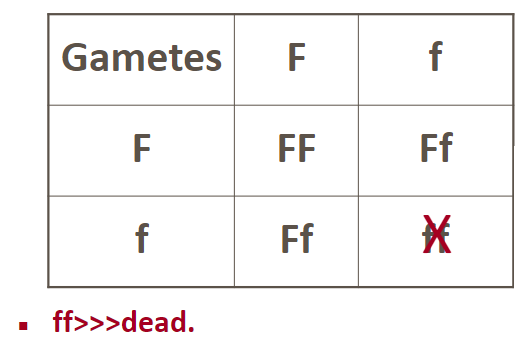
lethal alleles
ratio of offspring is not 3:1, but 2:1
what is giemsa stain?
nucleic acid stain that attaches preferentially to A-T bonds
There are way more genes on a chromosome than there are Giemsa stain bands
autosomes
22 pairs of homologous chromosomes exactly the same in both male and female karyotypes
sex chromosomes
one pair of chromosomes (mammals)
female - XX / male - XY
classifications of genetic disorders
multifactorial
chromosomal
single gene
multifactorial disorders
congenital malformations
cancers
coronary artery disease
chromosome or cytogenetic disorders examples
down syndrome
trisomy 21
XYY syndrome
extra Y
nondisjunction
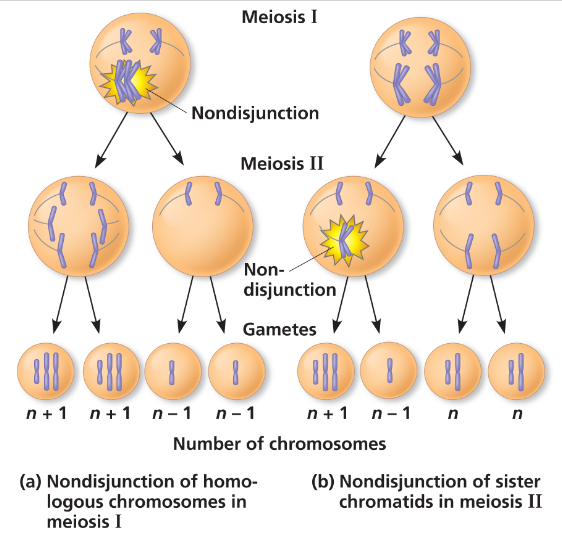
nondisjunction gives rise to:
monosomics
trisomics
monosomy
lack a single copy of a chromosome
trisomy
carry an additional copy of a chromosome
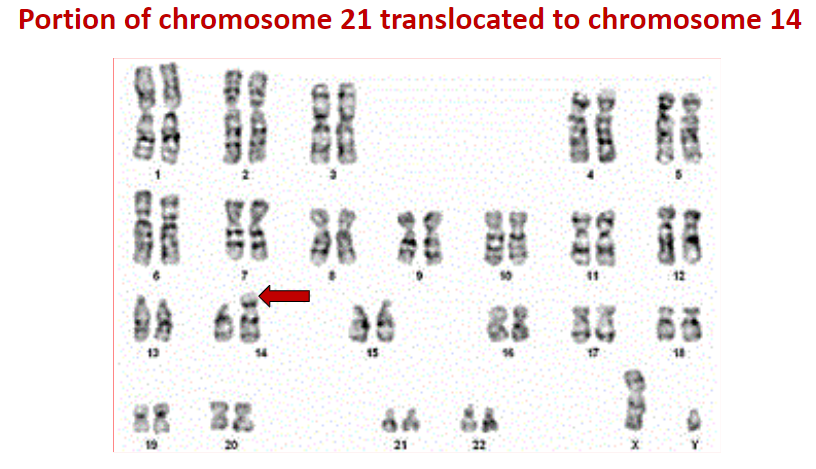
what does a down syndrome karyotype look like?
portion of chromosome 21 translocated to chromosome 14
Incidence of Down Syndrome (and other trisomies) ________ dramatically with the age of the mother
increases
nondisjunction of sex chromosomes
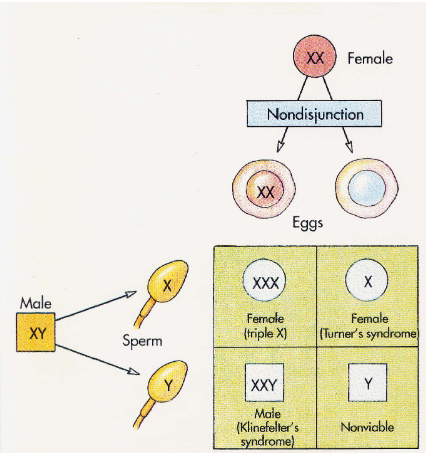
sex chromosome disorders
Klinefelter syndrome - sterile - male w/female characteristics
turner syndrome - sterile - female, short, immature sex organs
XXX syndrome - learning difficulties
XYY syndrome - behavioural difficulties
single gene disorders
caused by a mutant gene allele
in single gene disorders, where is the mutant allele found?
may be present on only one chromosome of a homologous pair (dominant) or on both chromosomes (recessive) to exhibit the disease
usually obvious pattern of inheritance in a pedigree. most defects are rare
single gene disorder examples
cystic fibrosis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Huntington’s disease
sickle cell anemia
cystic fibrosis
common autosomal recessive disease
very rare in aisians
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
common X-linked recessive disorder
rare in females
Huntington’s disease
autosomal dominant, late onset
much higher in small isolated populations
sickle cell anemia
autosomal recessive
~1/400 african americans affected
male

female
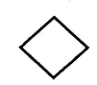
sex unspecified
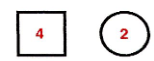
number of children of sex specified

affected

heterozygotes for autosomal trait
aka carriers
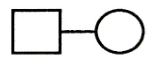
extramarital mating
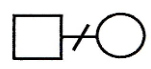
divorce