Unit 3: Cellular Energetics
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Bioenergetics
Ex.
Gibbs Free Energy
Ex.

Enzymes
Ex.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
Ex.

Enzyme Regulation
Ex.

Reaction Coupling
Ex.

Photosynthesis
Ex.
Light Reactions
Ex.
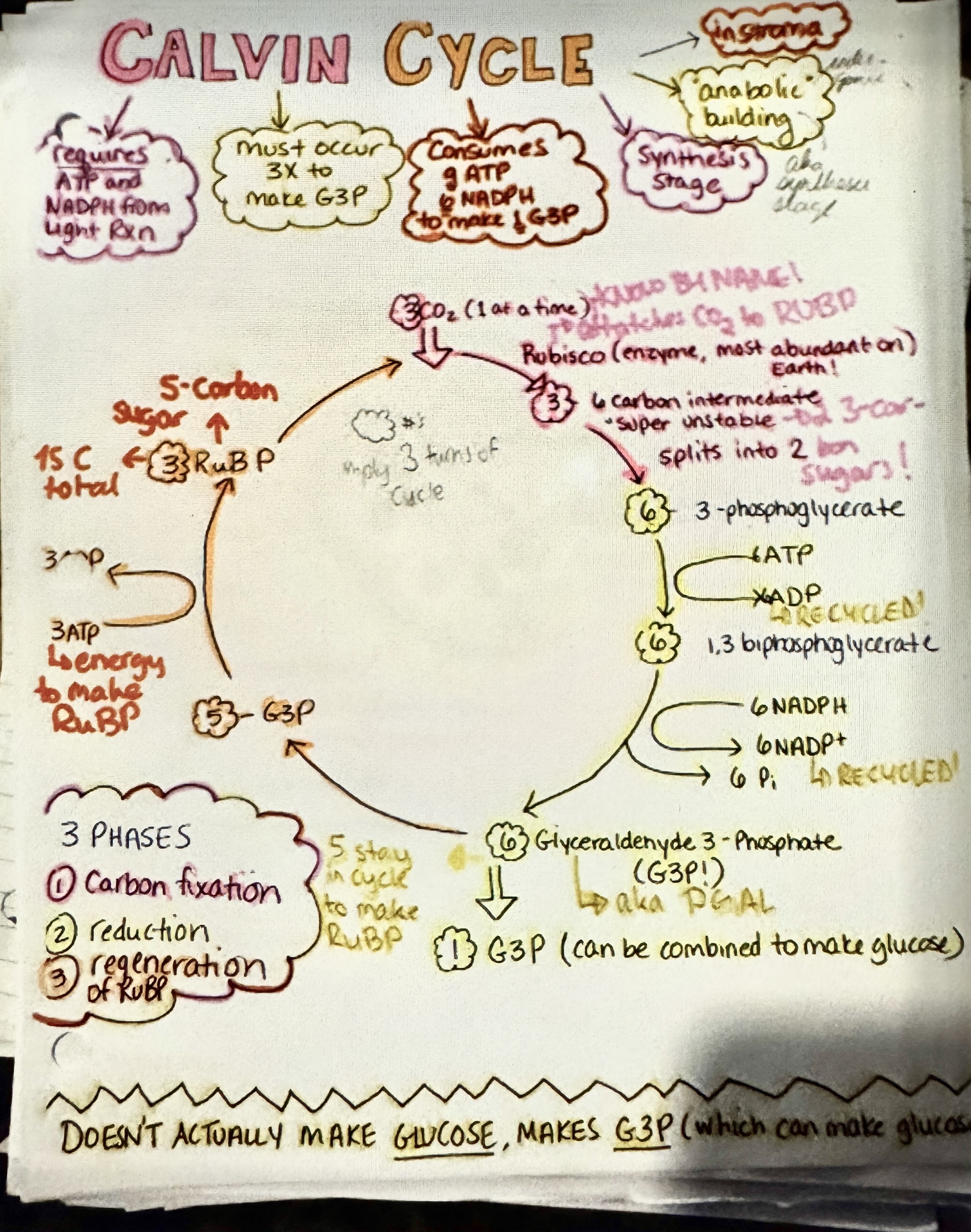
Calvin Cycle Notes
Ex.
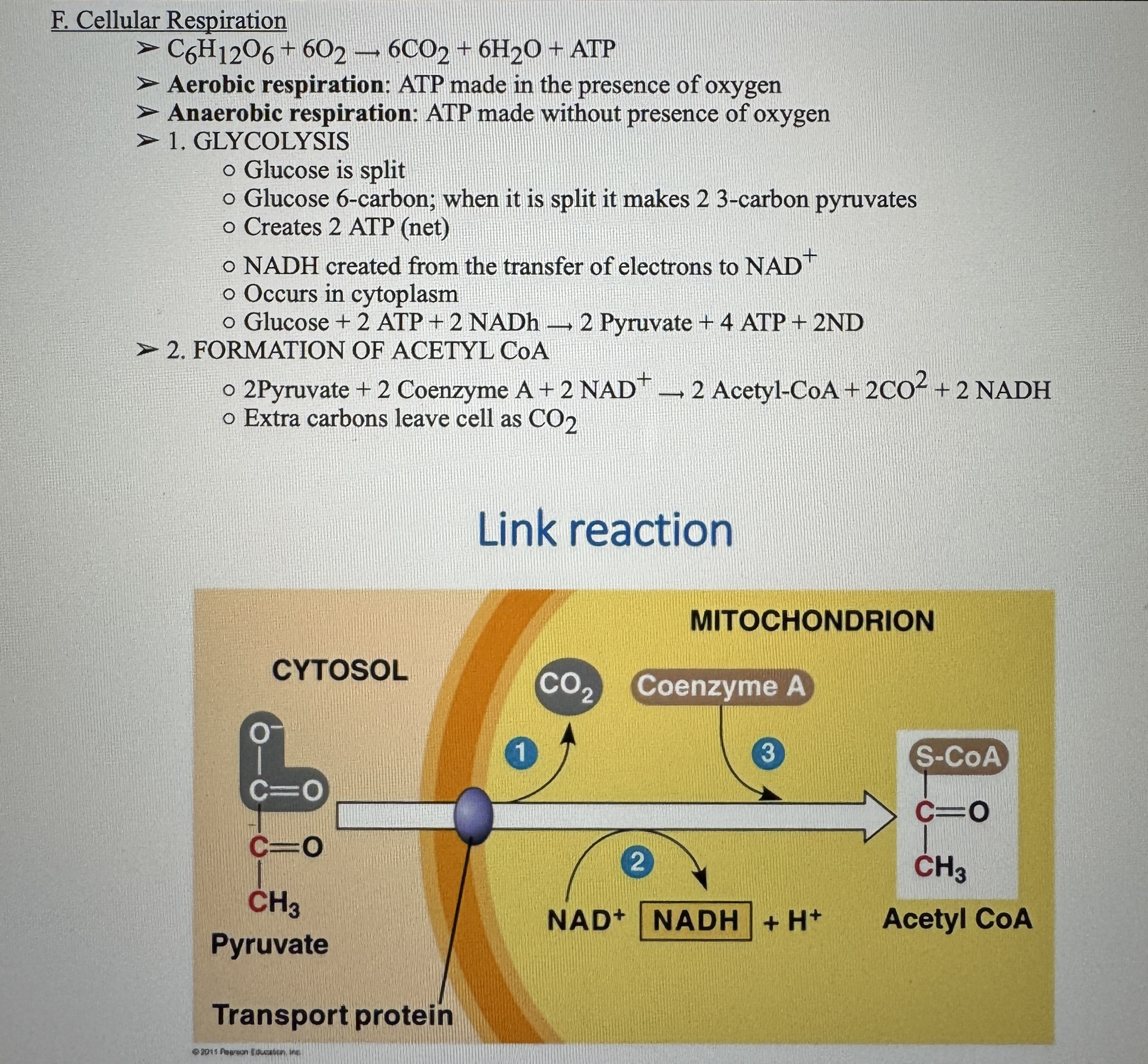
Glycolysis and Acetyl CoA (+Cellular Respiration Info)
Ex.
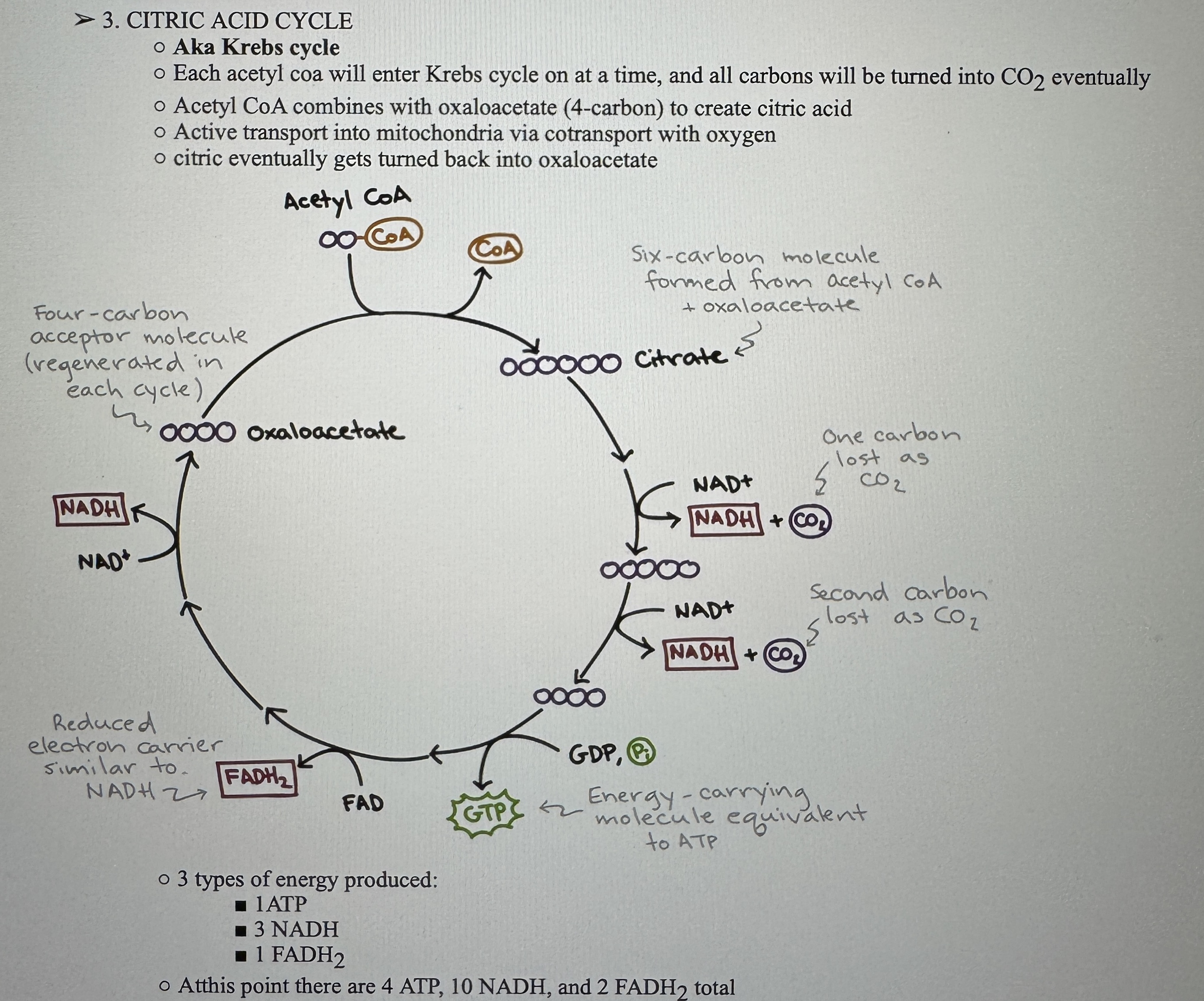
Citric Acid Cycle
Ex.
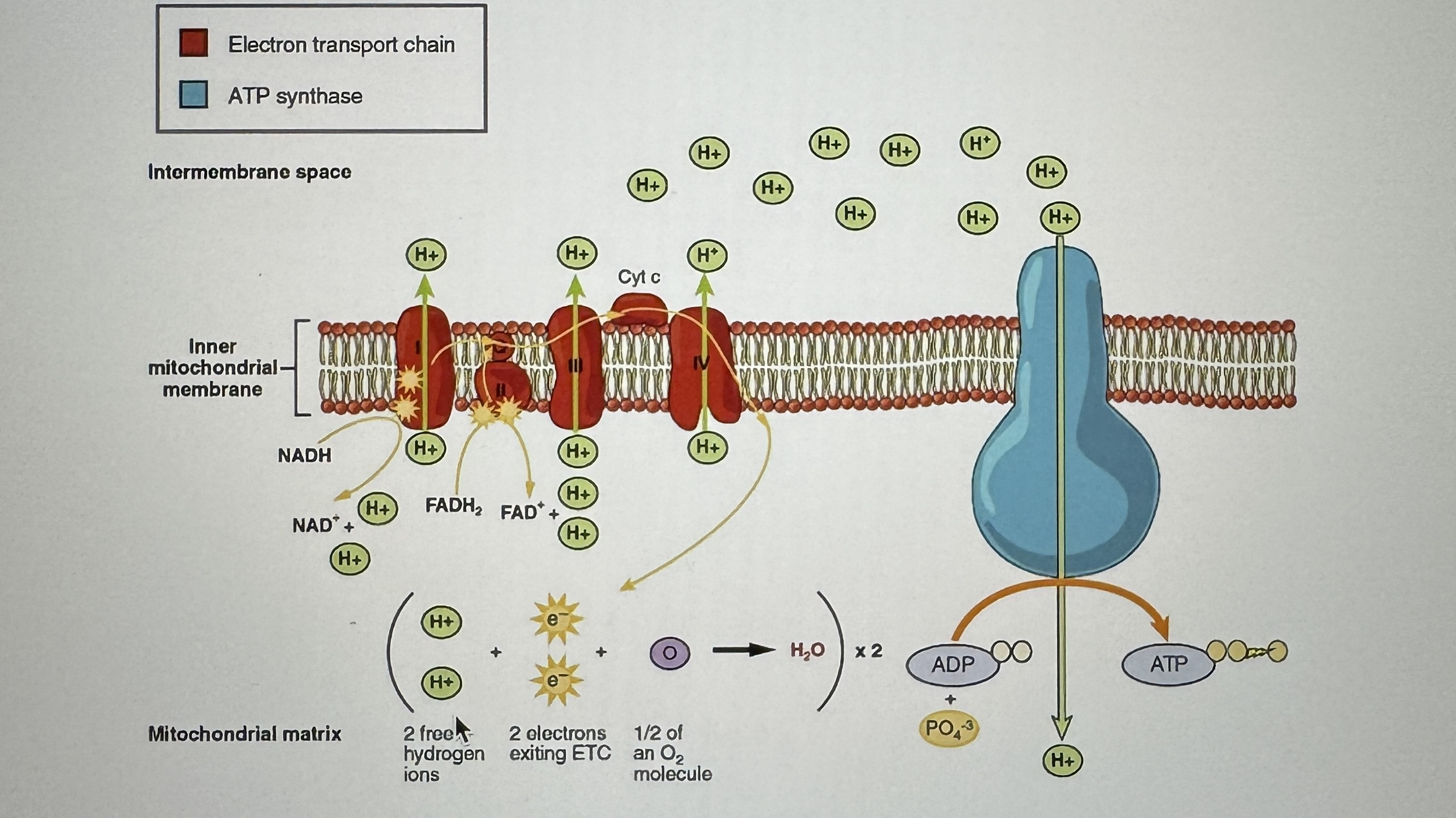
Oxidative Phosphorylation/ The Electron Transport Chain
Ex.

Oxidative Phosphorylation/ The Electron Transport Chain Diagram
Ex.
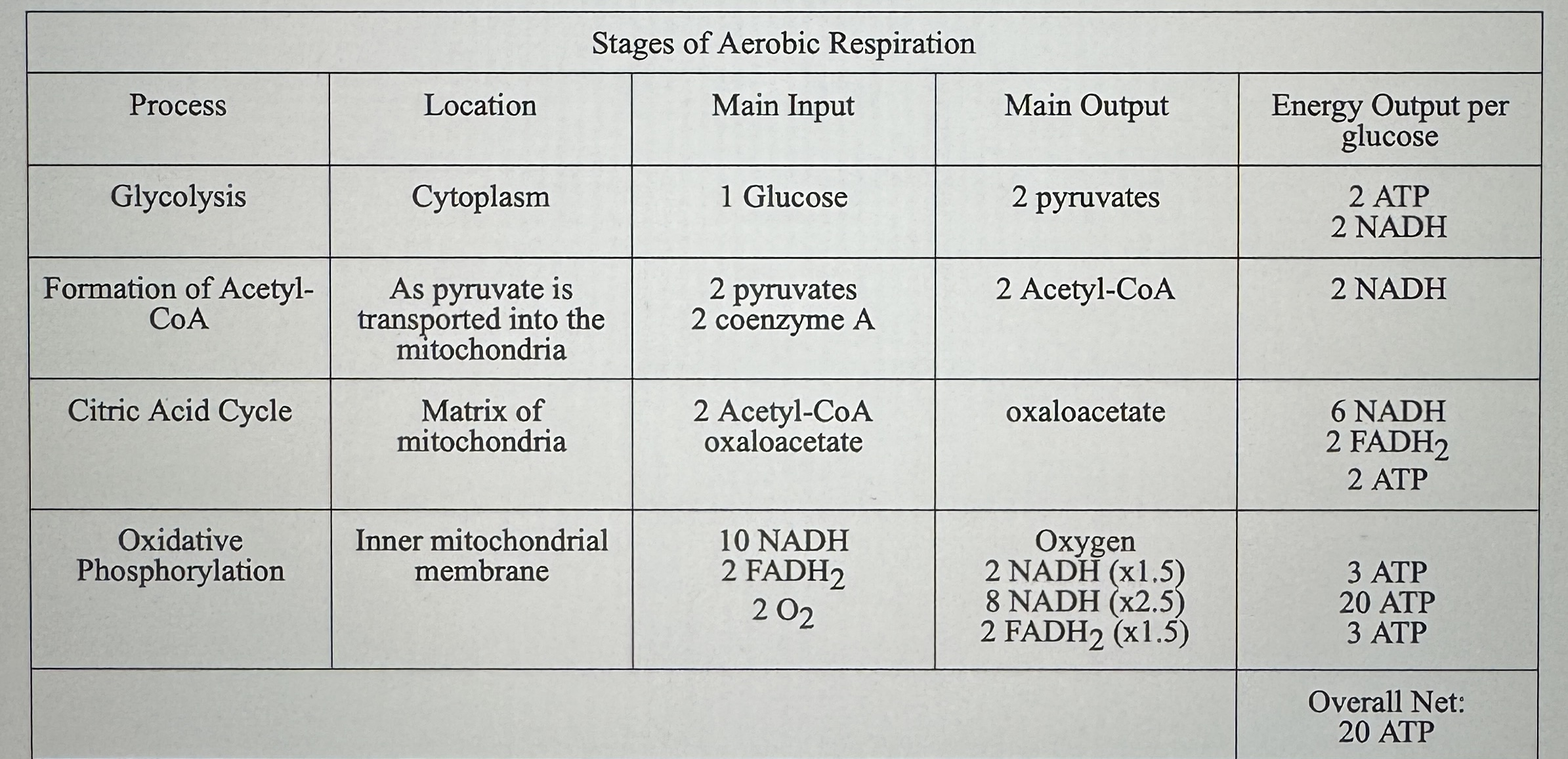
Stages of Aerobic Respiration
Ex.
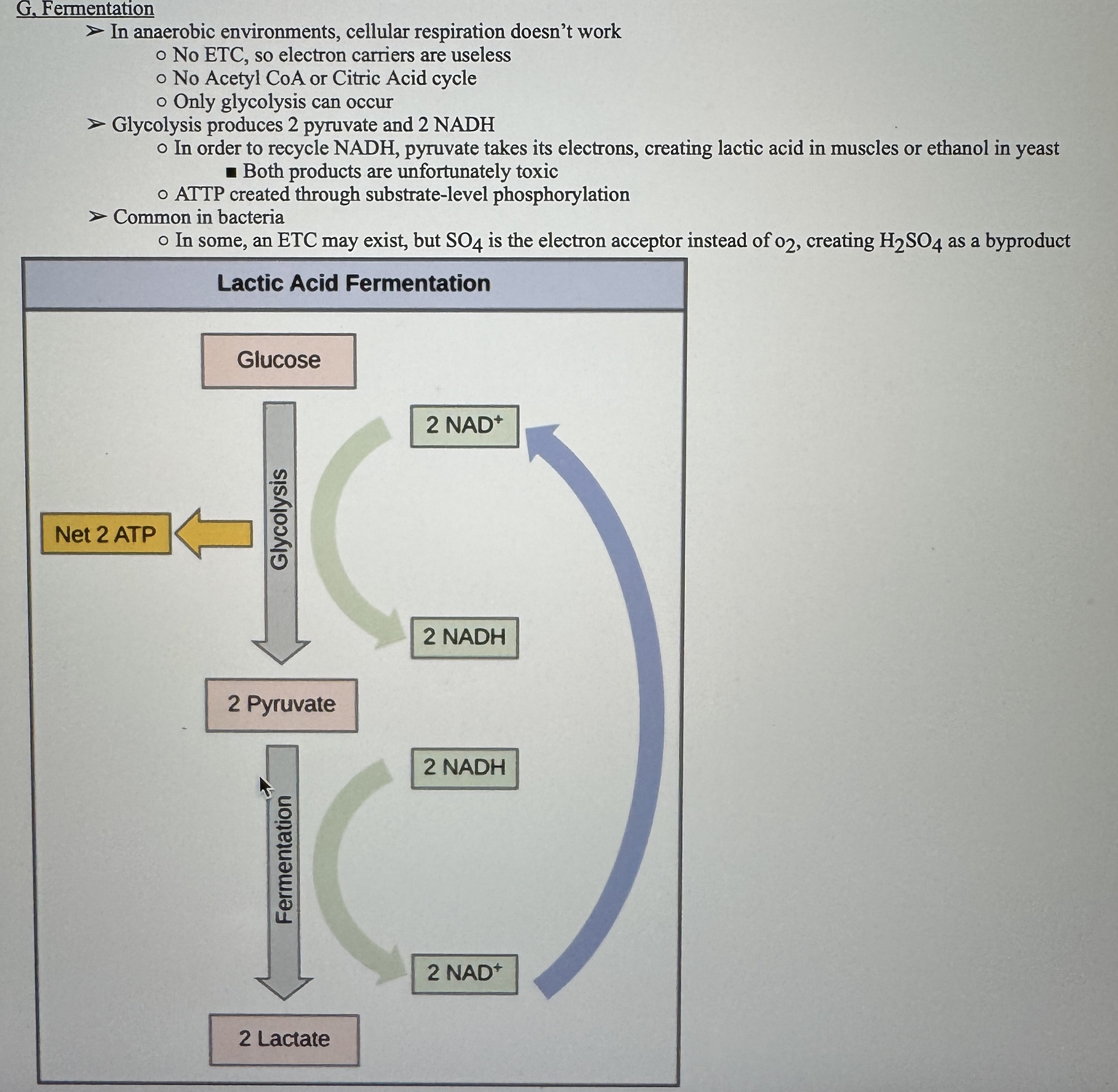
Fermentation
Ex.
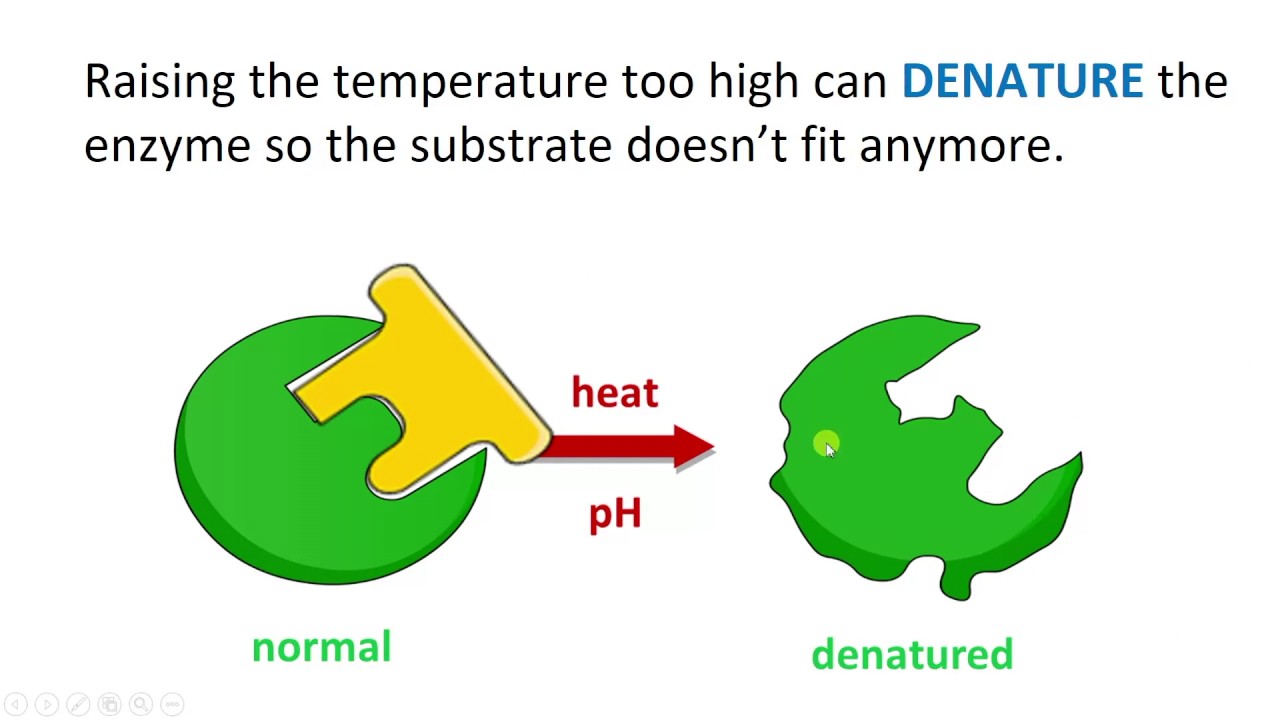
Extra - Denaturing
Ex.
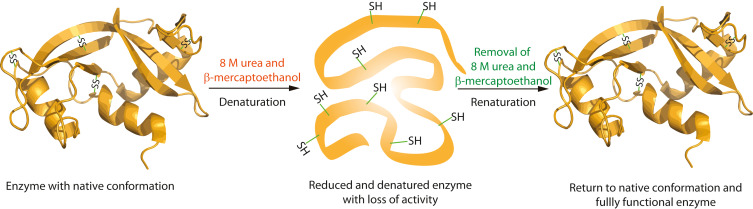
Extra - Is denaturing reversible?
Yes
Extra - Results of Light Dependent Reaction s and Calvin Cycle.
Ex.
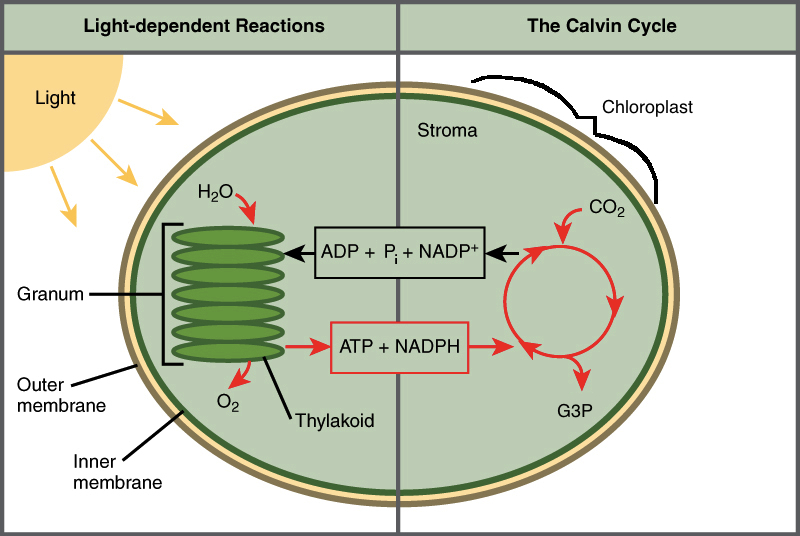
Extra - Better Light Reactions Photo
Ex.
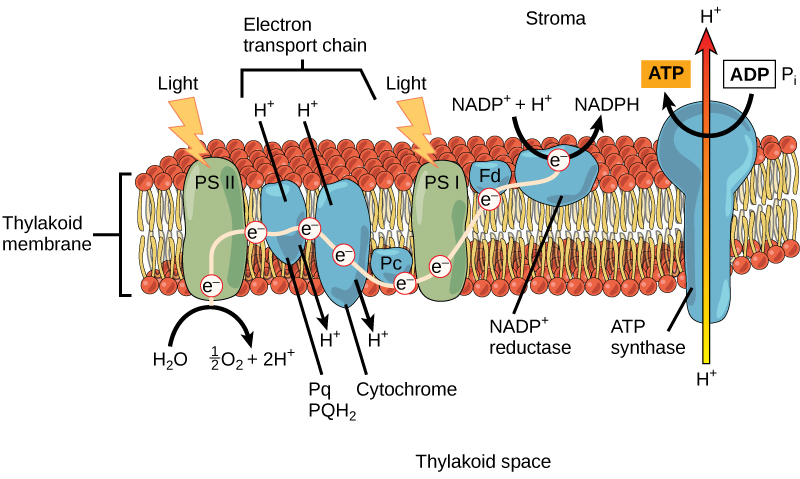
Extra - Better Calvin Cycle Photo (Know Three Stages)
Ex.
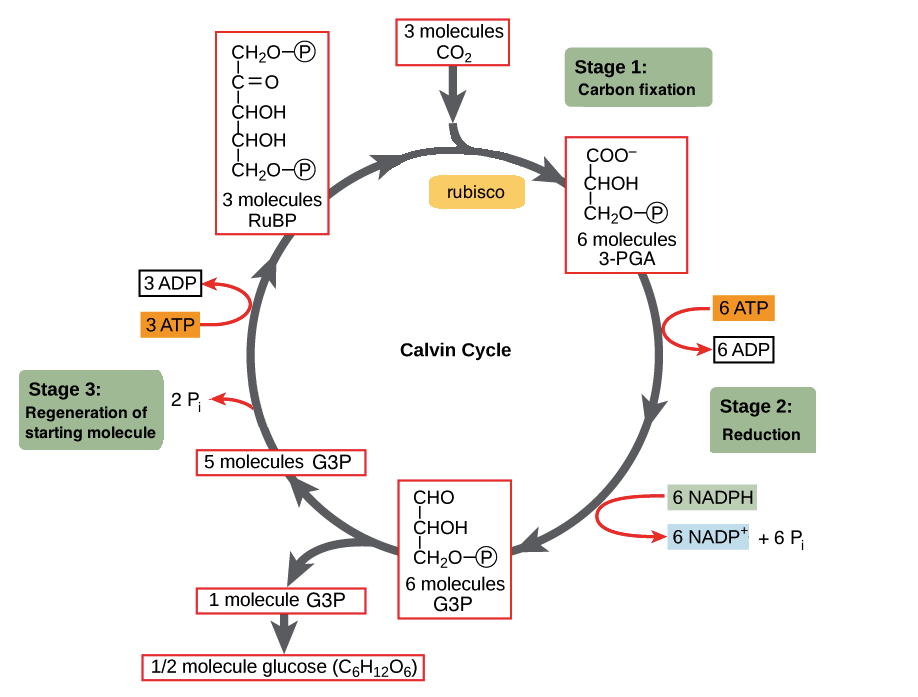
Extra - Results of Cellular Respiration
Ex.
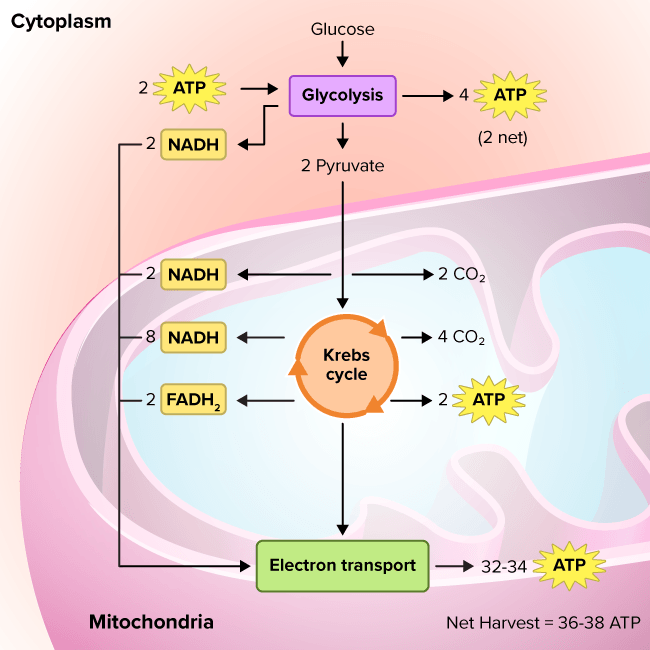
Extra - The Electron Transport Chain in Prokaryotes
In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain (ETC) is located within the plasma membrane, where it facilitates the transfer of electrons and generates a proton gradient for ATP synthesis.
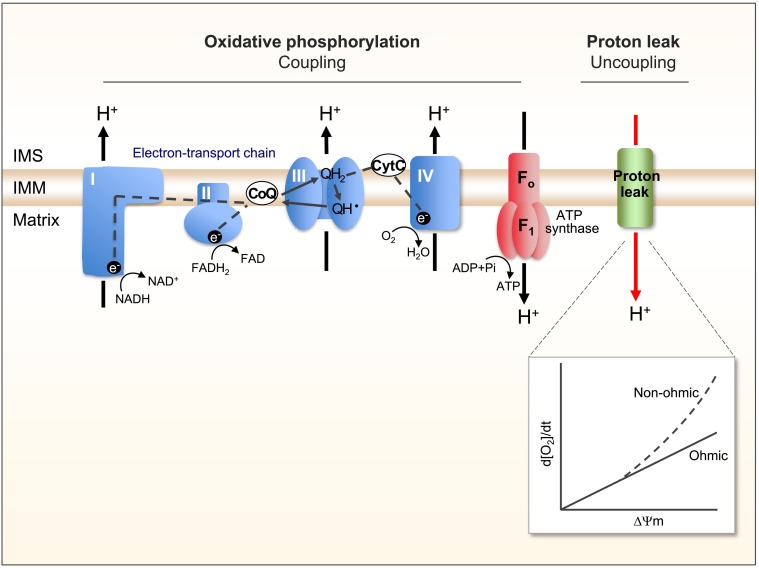
What is Decoupling Oxidative Phosphorylation and how does it create heat?
Oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling refers to the process where the energy generated from substrate oxidation in mitochondria is released as heat instead of being used to produce ATP, due to the leakage of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane independently of ATP synthase.
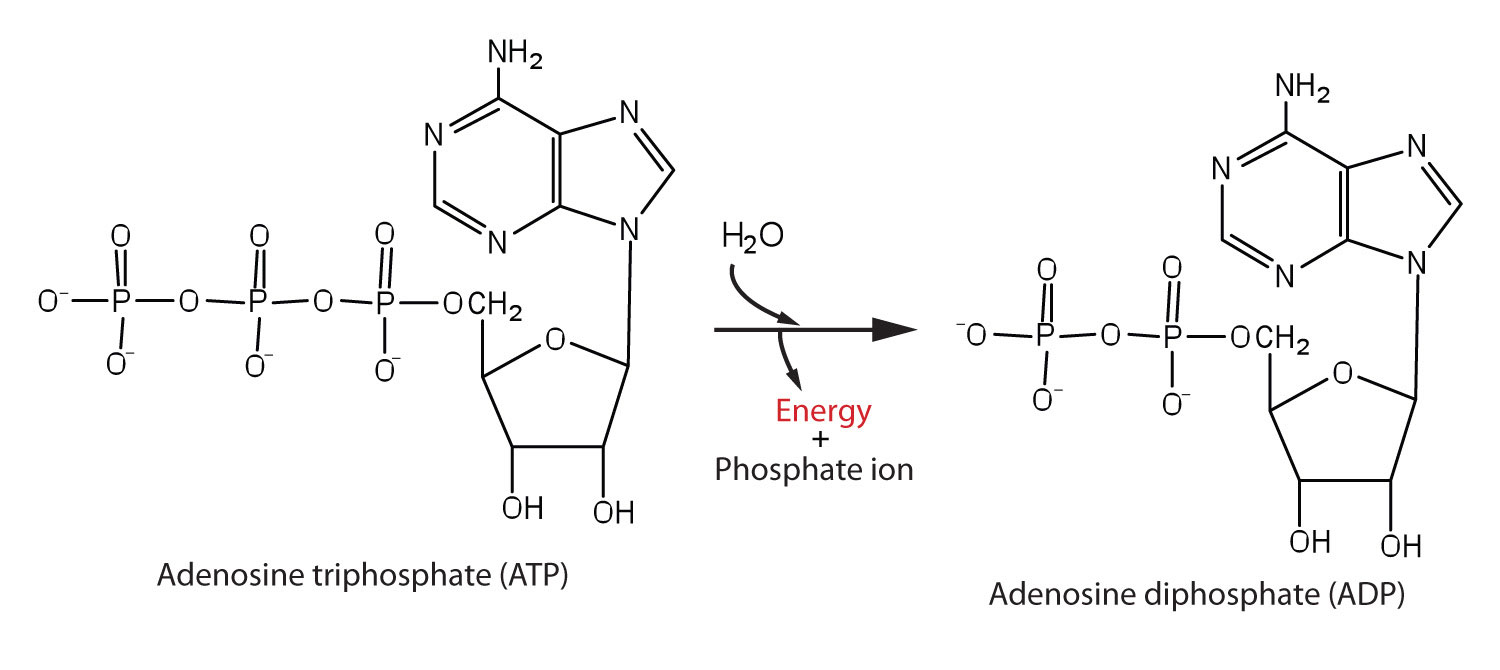
Extra - What is ATP Hydrolysis?
Ex.
Extra - Can variation at a molecular level effect an organisms fitness?
Yes, variation in the number of molecules, particularly at the genetic level, can indeed affect selective advantage, as this variation can lead to different traits, some of which may be advantageous for survival and reproduction, thus influencing the process of natural selection.