ID - Bacterial Infections
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
1
Less than ___% of bacteria cause disease
3 multiple choice options
circular
Diplo, strepto and staphylo are examples of ___ bacteria
rod
Coccbacilli, streptobacilli and mycobacteria are examples of ___ shaped bacteria
curved
Vibrio, spirilla, and spirochete are examples of ___ shaped bacteria
- direct invasion
- toxin formation
- blood clotting (from toxins)
How do bacteria damage tissue?
Diptheria
Which organism produces toxins that damage the heart muscle by inhibiting protein synthesis?
Staph, strep, and clostridium
Which three bacteria are most common causative agents of disease?
25
Staph aureus is present in about ___% of the population on the skin/nares
staph
A skin and soft tissue infection with associated purulence is likely caused by ___
non-purulent
Erysipelas, cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis are ___
purulent
Abscesses, furuncles and carbuncles are ___
- oral cephalexin, clindamycin or dicloxacillin
Tx of mild cellulitis, erysipelas or necrotizing infection?
- IV Cloxacillin, cefazolin, clindamycin, penicillin or ceftriaxone
Tx of moderate cellulitis, erysipelas or necrotizing infection?
- empiric Rx (vancomycin + piperacillin/tanzobactam)
Tx of severe cellulitis, erysipelas or necrotizing infection?
- I&D
Tx of mild furuncle, carbuncle, or abscess?
- I&D w/ C&S
- cephalexin or doxy PO or cefazolin IV
Tx of moderate furuncle, carbuncle, or abscess?
- I&D w/ C&S
- IV vancomycin
Tx of severe furuncle, carbuncle, or abscess?
mild symptoms with associated systemic symptoms
What makes a SSTI moderate?
failed abx, failed I&D, systemic symptoms, immunocompromised (DM/HIV), signs of deeper infection, extremes of age, difficulty of complete drainage
What makes an SSTI severe?
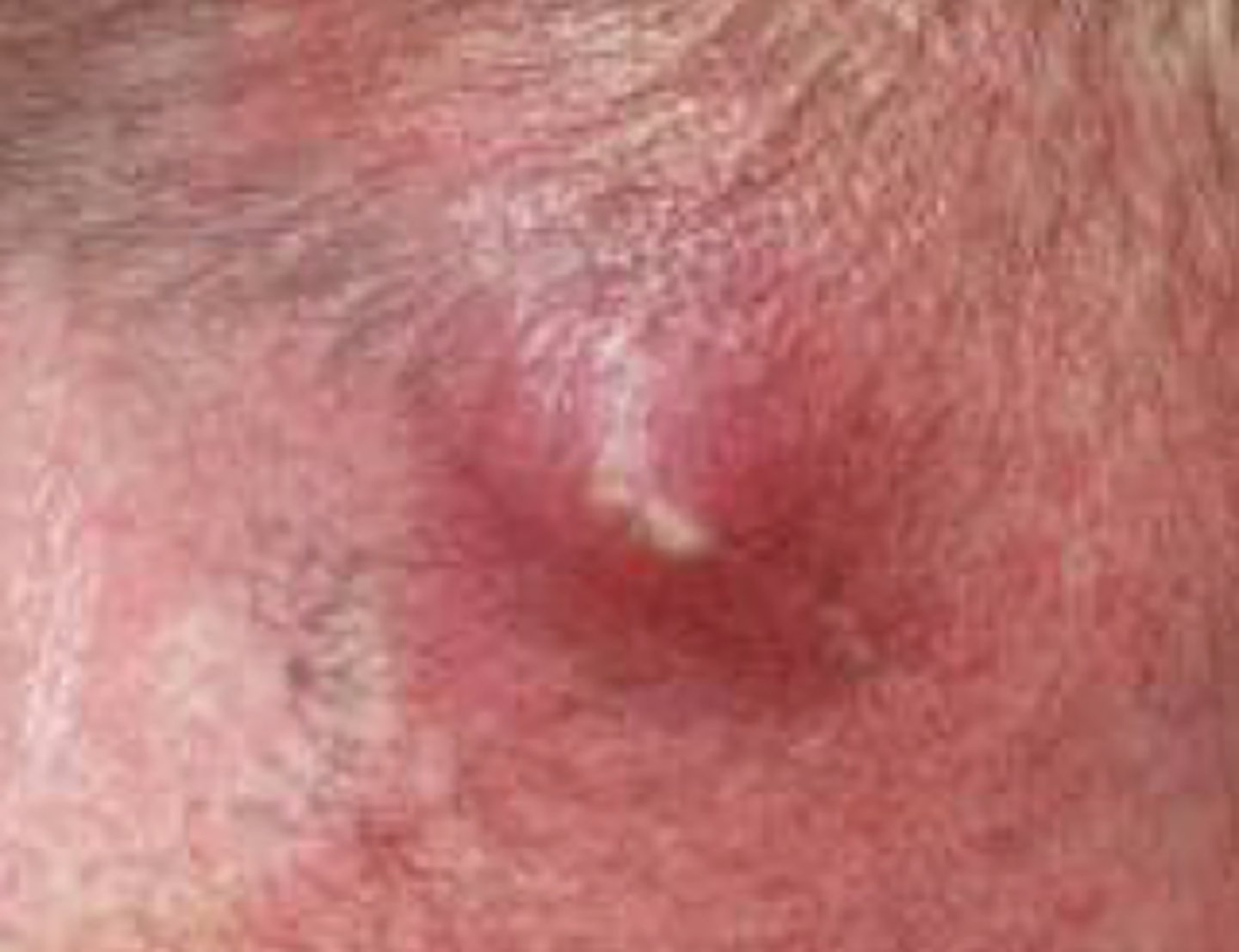
Furuncle
What is the diagnosis?
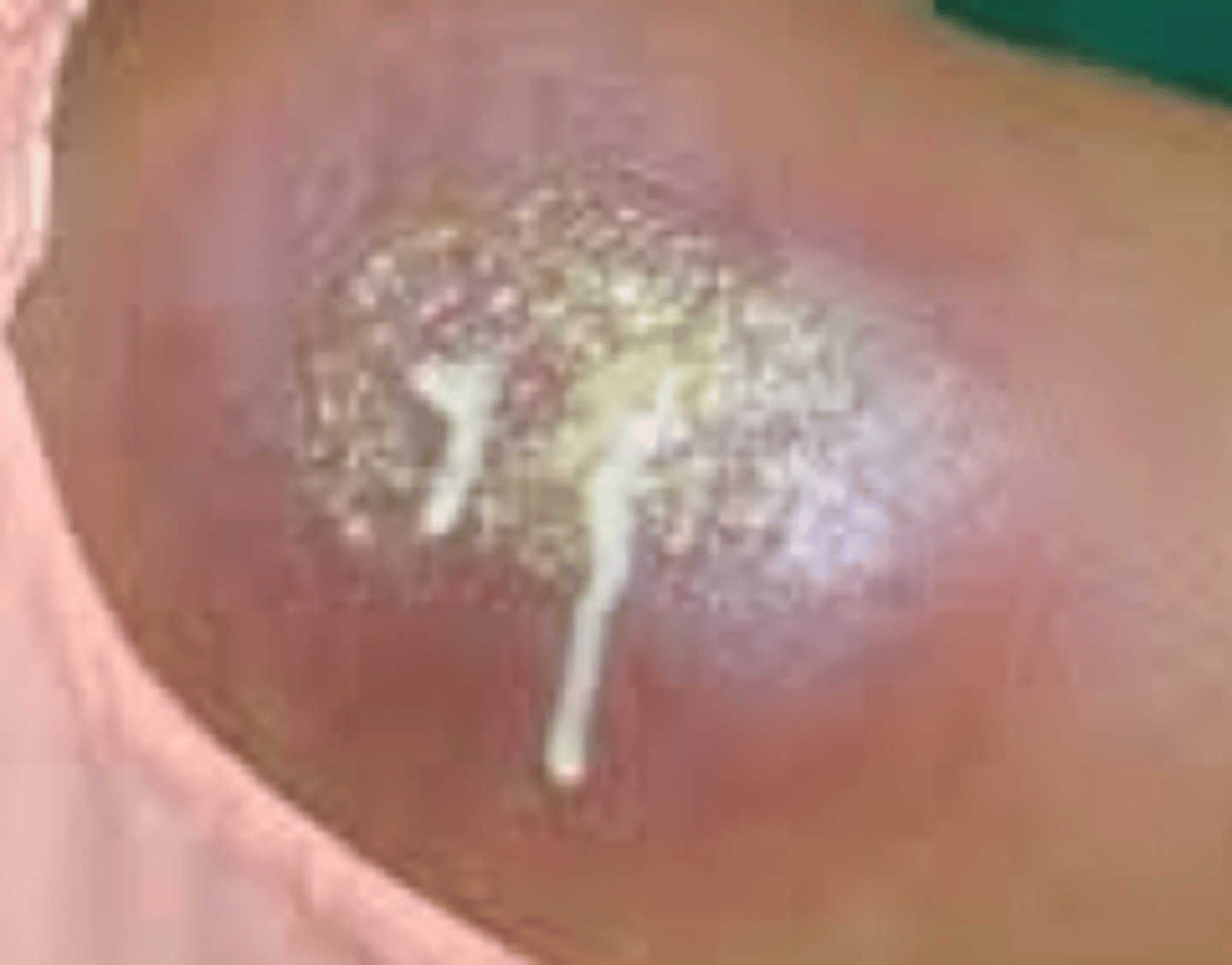
Carbuncle
What is the diagnosis?
CBC w/ diff and blood cultures
What should always be ordered in patients with systemic symptoms?
- Purulence
- penetrating trauma
- IV drug use
- open wound/hardware
- evidence of MRSA elsewhere
- lack of response to beta-lactam
- severe systemic involvement
When should MRSA coverage be added in cellulitis?
- Clindamycin
- TMP-SMX DS
- Doxycycline
What meds have MRSA coverage?
vancomycin and linezolid
Which IV abx are recommended for MRSA?
ceftriaxone (Rocephin) or Cefazolin (Ancef)
IV option for non-MRSA moderate infection
bilateral
Cellulitis is rarely ___ and this can help distinguish it from stasis/contact dermatitis
staph
Pneumonia, infective endocarditis, sepsis and osteomyelitis are other conditions caused by ___
Fournier gangrene
___ is most commonly seen in diabetic males aged 20-50 and presents in the perineal area
E coli, bacteroides, staph, strep, and clostridium
Which microbes can cause fornier gangrene?
- wide emergent I&D
- IV nafcillin or vancomycin
Tx of Fournier gangrene?
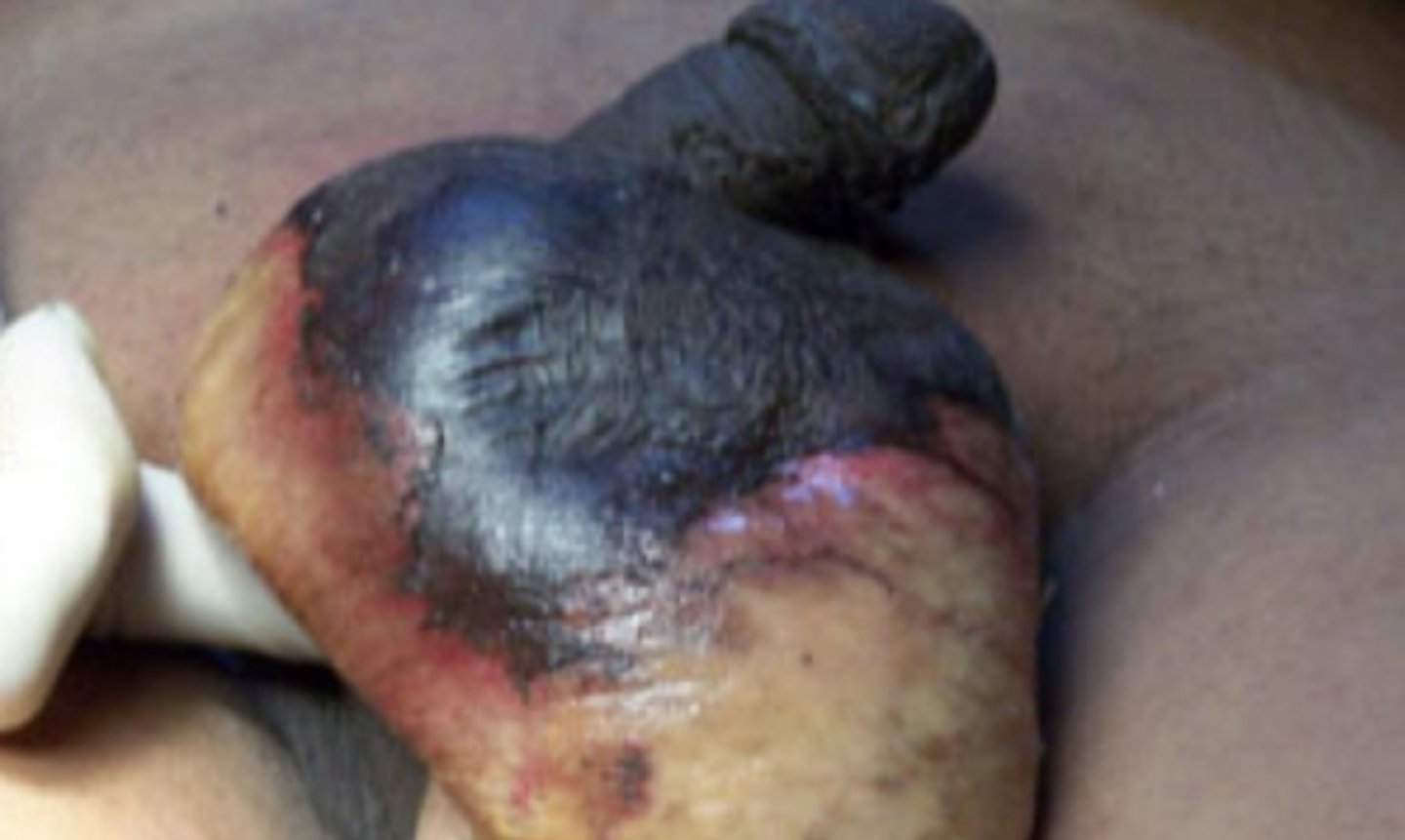
Fournier gangrene
What is the diagnosis?
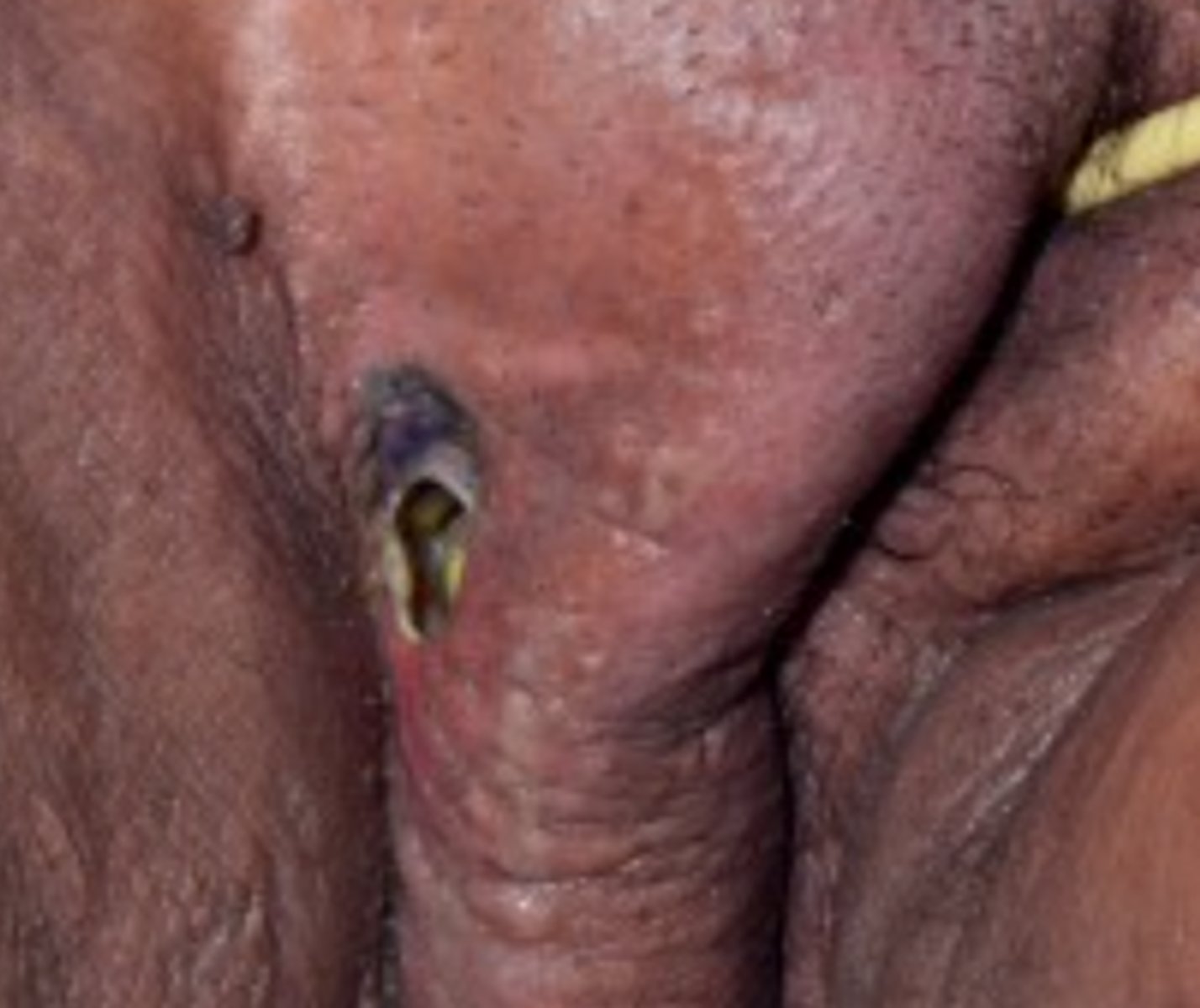
Fournier gangrene
What is the diagnosis?
Staph (60%)
What is the most common causative agent of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis
___ usually involves long bones or vertebrae
Staph aureus
SSSS, enterotoxin food poisoning and TSS can all be caused by
suppression of all immune responses
In TSS staph produces toxins that stimulate T-cells producing cytokines that cause ___
symptoms are due to toxins not an infection
Blood cultures for TSS are often negative because ___
alpha hemolytic
Pneumoniae and viridian are included in ___ strep
Beta hemolytic
Pyogenes and agalactiae are included in ___ strep
Streptococcus pyogenes
Group A beta-hemolytic strep is synonymous with ___
strep pyogenes
Which bacteria is the most common cause of pharyngitis and can cause scarlet fever and impetigo
Erysipelas
Painful superficial cellulitis (usually of the face) with well demarcated borders and a rapid progression
Erysipelas
What is the diagnosis?
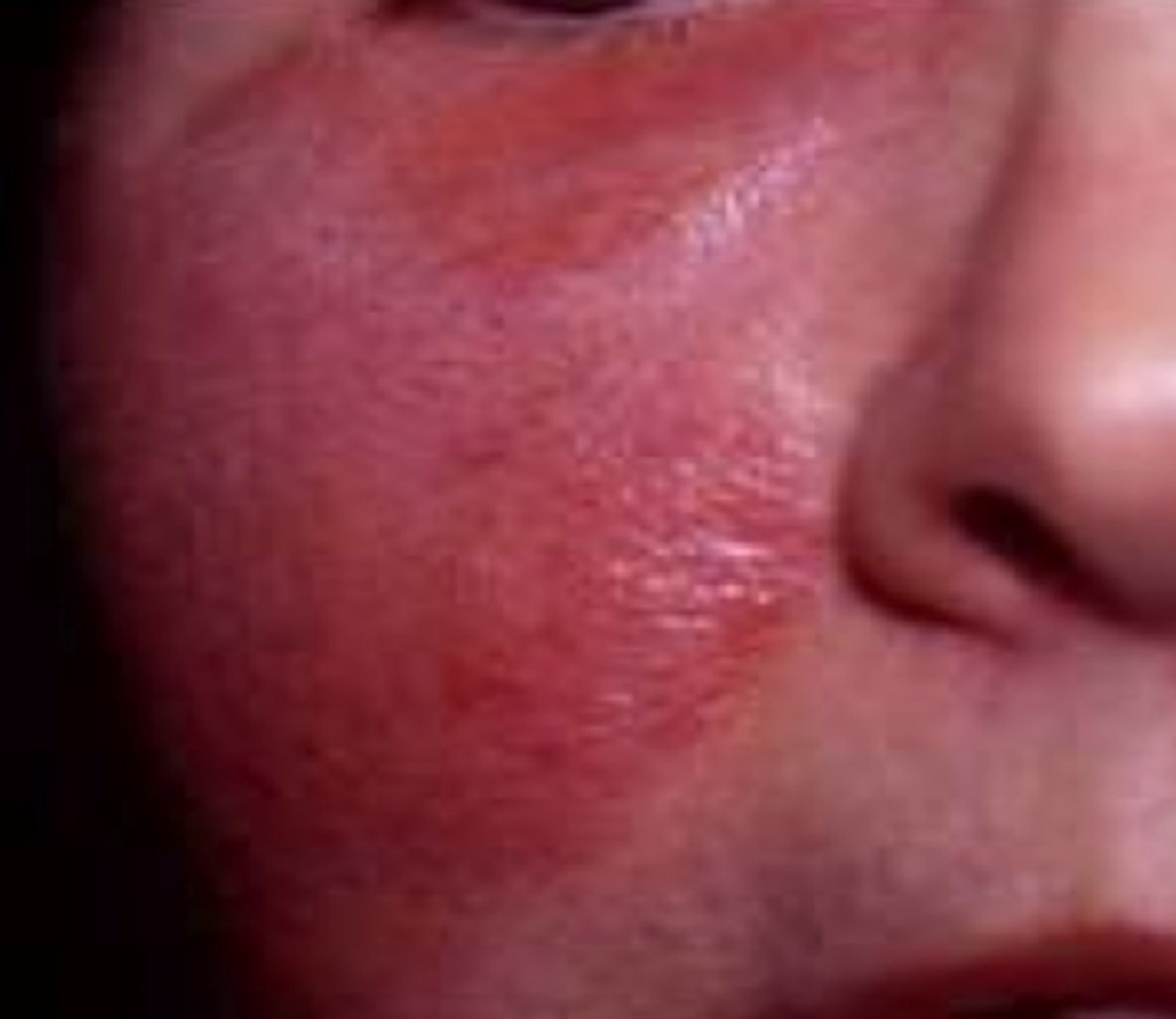
Strep pyogenes
Which organism likely caused this condition?
Empyema
What is a pus filled pocket within the pleural space called?
Necrotizing fascitis
Severe rapidly progressing life threatening soft tissue infection with blisters, purple discoloration and crepitus
Necrotizing fascitis
What is the diagnosis?
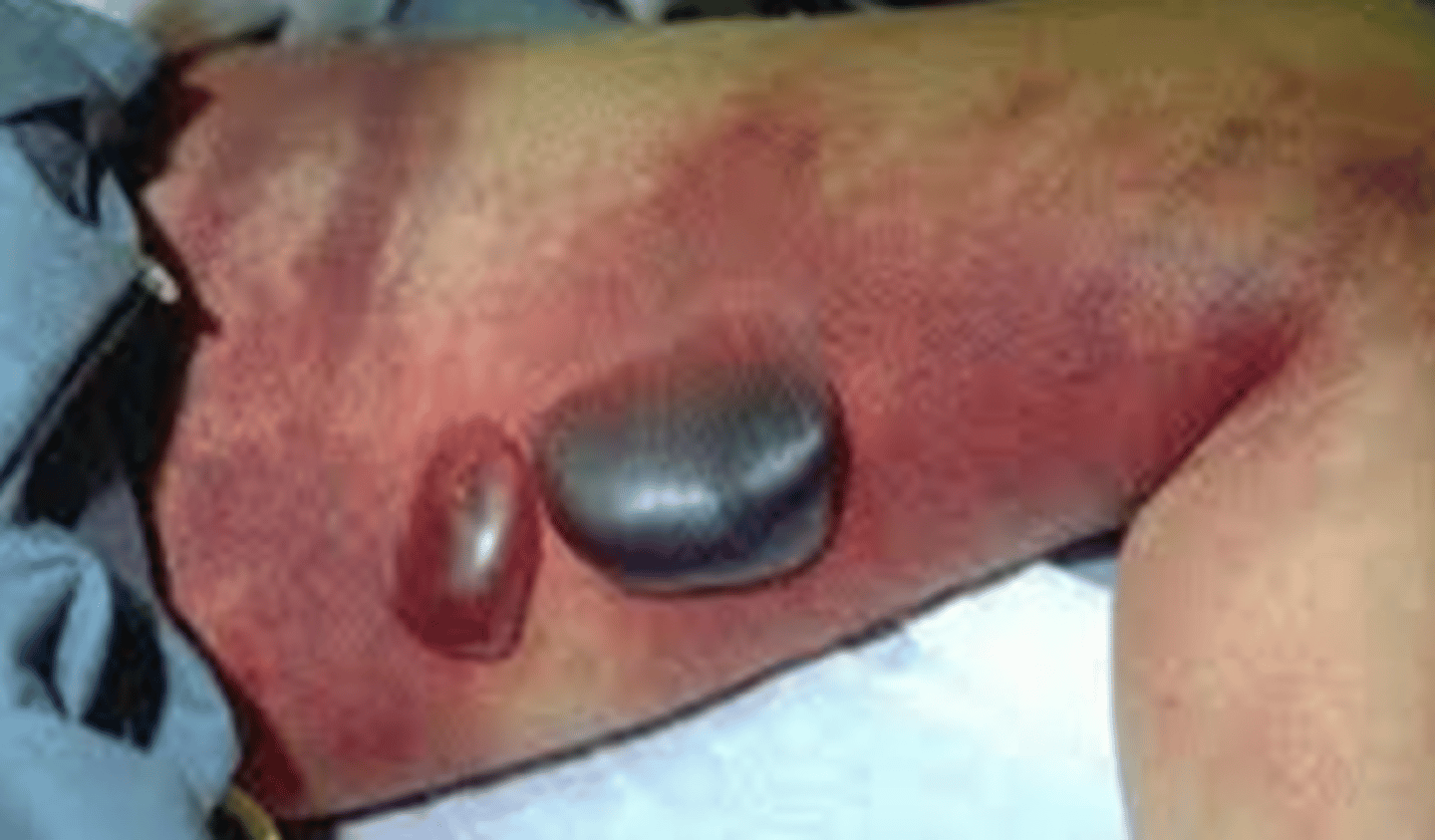
Necrotizing fascitis
What is the diagnosis?
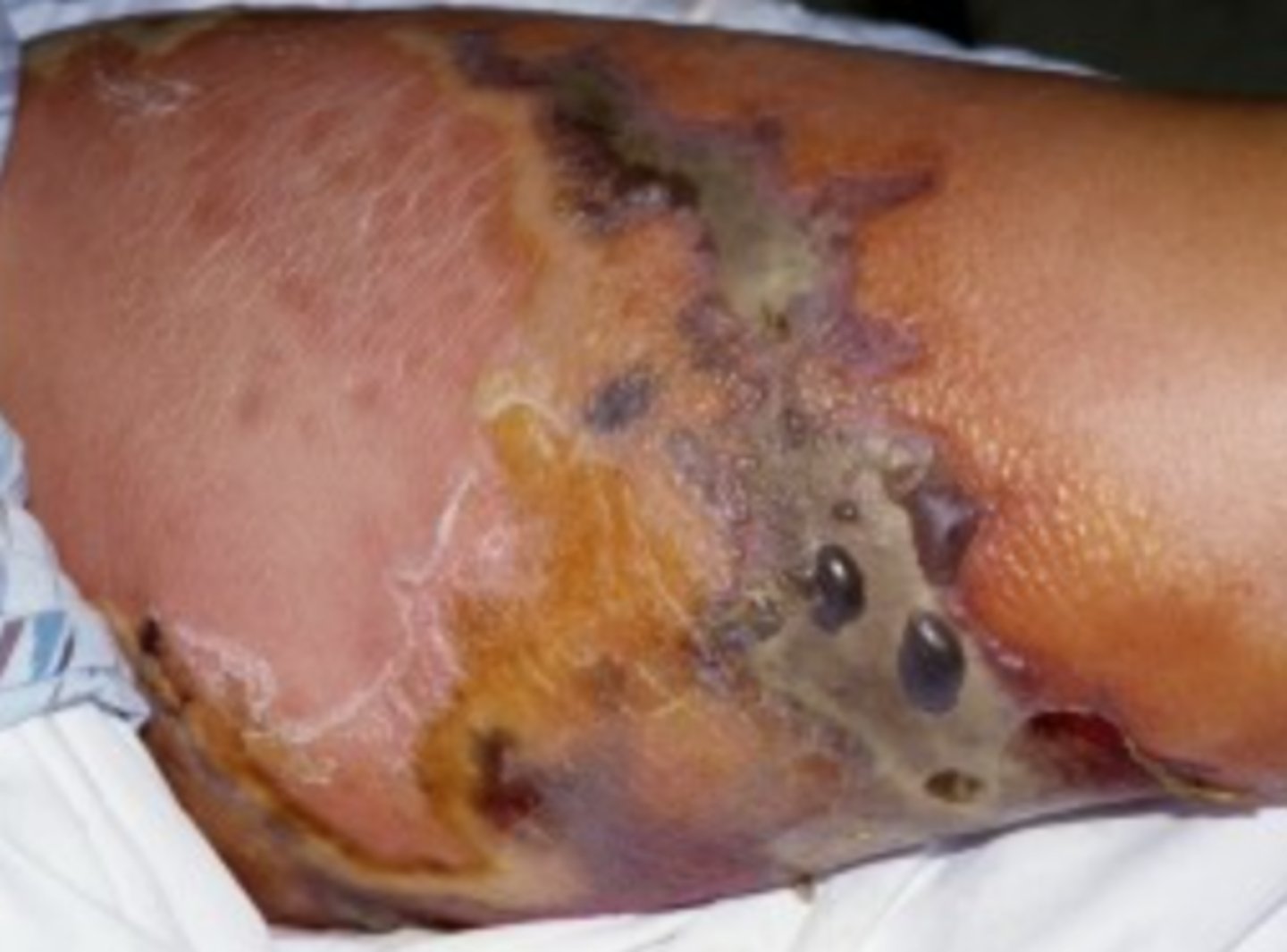
Type II monomicrobial (Strep pyogenes or staph a)
Which type of NF typically does not form gas?
Type I Polymicrobial
Which type of NF typically affects patients with comorbidities?
Type III Clostridium
Which type of NF occurs after surgery or a penetrating wound?
- broad spectrum abx
- penicillin and clindamycin
- urgent surgical debridement
Tx for suspected NSTI (necrotizing soft tissue infection)
strep pneumoniae
What is the m/c cause of community acquired bacterial pneumonia
strep pneumoniae
what is the most common cause of meningitis in adults
Clostridium botulinum
___ anaerobic spore-forming bacillus found in soil that inhibits the release of acetylcholine if ingested
- food
- infant
- wound
What are the three ways in which botulism occurs?
botulism
Poorly packaged or stored canned, smoked, or vacuumed packed meat fish or vegetables are at risk of ___
honey ingestion
What causes infant botulism?
IV drug use
Wound botulism is rare but occurs most commonly in ___
early findings of botulism
Dry mouth, double vision, ptosis, CN palsy, fixed and dilated pupils, symmetrical cranial nerve impairment with dysphagia, nausea, and vomiting
late findings of botulism
Descending peripheral muscle weakness and respiratory failure
- equine serum heptavalent botulism antitoxin
- contact CDC
- within 24 hours of symptom onset
Tx for botulism?
Clostridium tetani
Spores found in the soil that germinate in open woulds and produce neurotoxins that lead to uncontrolled muscle spasms and exaggerated reflexes
8-12 days
What is the incubation period for tetanus?
Tetanus
Pain and tingling at injury site with spasticity of muscles, neck and jaw stiffness (tismus), dysphagia and tonic convulsions
strychnine poisoning
Tetanus can be confused for ___ and toxicology should rule it out
Tetanus
Risus sardonicus, or peculiar grin, is associated with
- sedation, paralysis and mechanical ventilation
- penicillin 20 million units IV
- human tetanus immune globulin 500 units IM
- immunize after acute phase
Tx for acute tetanus?
clostridium perfringens
Which organism is most associated with gas gangrene?
less than 24 hours
Typical incubation period of gas gangrene?
gas gangrene
Toxins of ___ produce shock, hemolysis, and myonecrosis under anaerobic conditions
Posttraumatic (auto accidents m/c)
Which type of gas gangrene is most common?
Gas gangrene
Sudden onset of pain and heaviness in extremity, low fever, apathetic mental state after a car accident with localized swelling, crepitus, bronze skin, pain, and tachycardia
- penicillin and clindamycin (sub metronidazole for allergies to pcn)
- aggressive surgical debridement
Tx of gas gangrene?
occult malignancy of the GI tract
Spontaneous gas gangrene has a strong association with ___
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Sore throat, nasal discharge, hoarseness, malaise and fever which can involve the skin cause by exotoxins. Can lead to myocarditis and neuropathy
C. Diphtheriae
Exotoxins of ___ cause myocarditis (arrhythmias, heart block and failure) as well as neuropathy (diplopia, slurred speech and dysphagia)
C. Diphtheriae
What is the diagnosis?
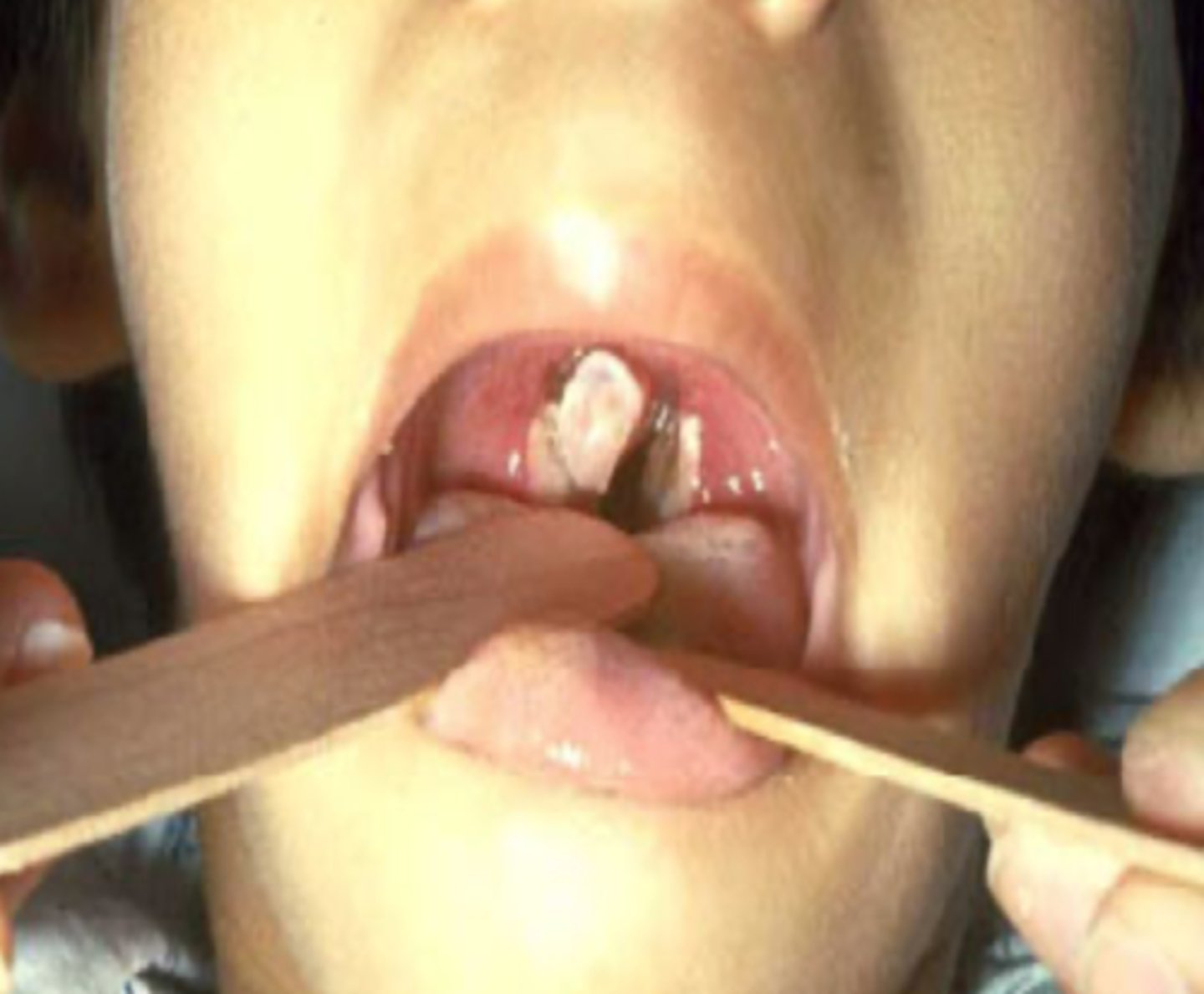
Diphtheria
Gray pseudo membrane covering the tonsils and pharynx is concerning for ___
Diphtheria
Culture of mucosal lesions or nasal discharge using tinsdale agar can be helpful in diagnosing
- antitoxin (diphtheria equine)
- keep airway clear
- penicillin or erythromycin
- respiratory isolation
Tx for diphtheria?
pregnant, immunocompromised, neonates and elderly
Listeria monocytogenes most commonly affects which populations?
Listeria
___ is a food borne organism that can be isolated from soil, water and decaying vegetation and is transmitted to humans via mammals, fish, birds and insects.
diarrhea (resembles a GI illness)
Most common clinical manifestation of listeria is ___
Bacteremia and meningitis
What are the more serious manifestations of Listeria?
- suspicion = IV ampicillin (+/- gentamicin) bactrim if allergic to pcn
- diagnose w/ culture of blood or CSF (tumbling motility)
- isolation not necessary no horizontal transfer
Tx for listerosis?
Enteric typhoid fever
M/c form of salmonellosis
5-14 days
Incubation period of typhoid fever?
Salmonella
___ is an intracellular pathogen which invades and replicates in macrophages, lymph nodes and the spleen
Typhoid fever
Gradual onset malaise, headaches, sore throat, cough, fever, and constipation OR pea soup diarrhea
7-10
After ___ days of typhoid fever infection, fever plateaus patient appears very ill and rose spots develop as well as hepatosplenomegaly, abdominal distention, and occasional bradycardia
Typhoid fever
What is the diagnosis?
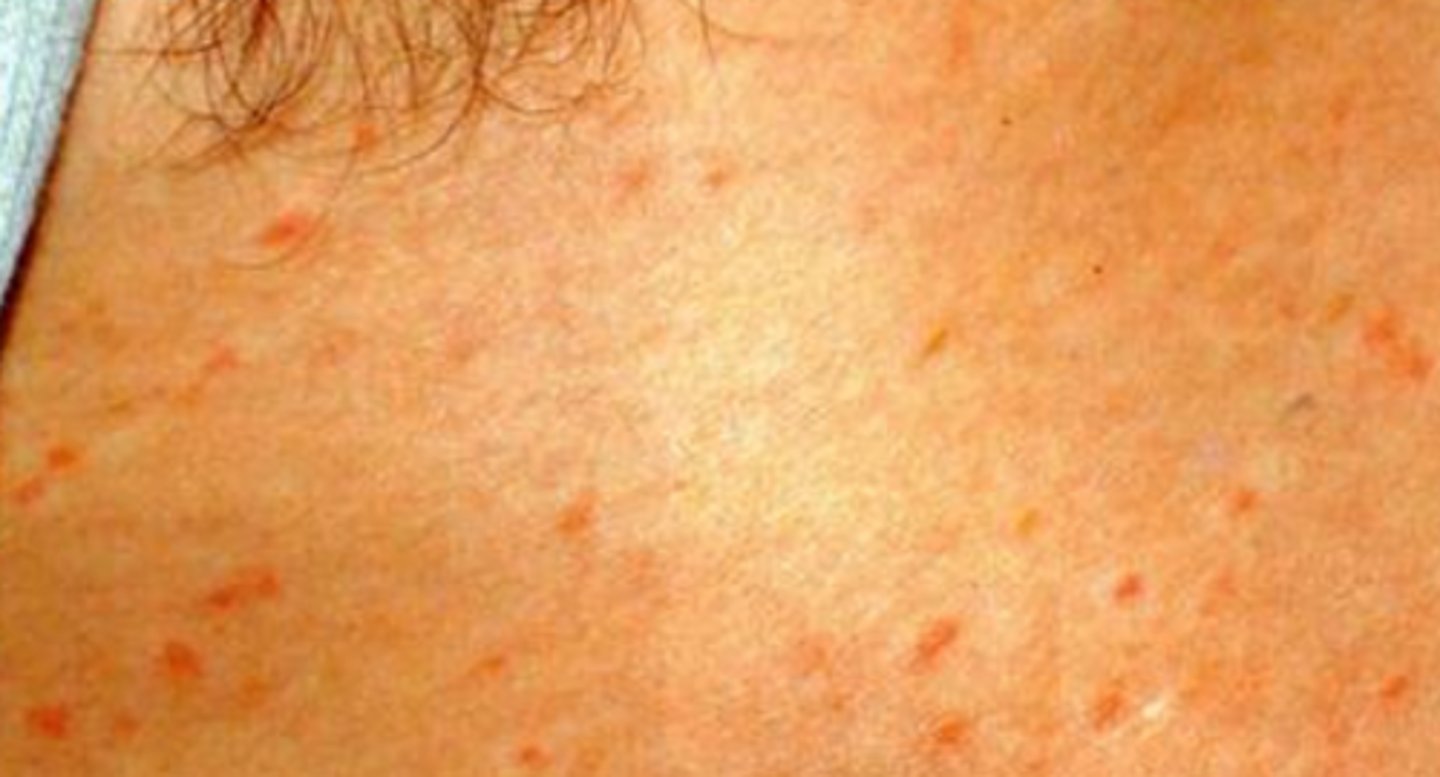
- (+) blood culture to diagnose
- abx (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin and ceftriaxone IV)
- hydration
Tx of typhoid fever?
bacillus anthracis
Anthrax is caused by ___ a gram (+) spore forming aerobic rod
Anthrax
Naturally occurring disease of several domestic farm animals that is transmitted to humans via contaminated animal products, soil inoculation, or IV drug use/inhalation
cutaneous, GI, and inhalation
What are the three main types of anthrax
Cutaneous anthrax
2-12 days after exposure an erythematous papule ulcerates and becomes necrotic to form a painless black eschar. Is fatal within 48 hours if not treated
- PCN
- immunization
- immune serum
Tx of cutaneous anthrax
Inhalational anthrax
Onset of illness within 10 days with 2 stages of severity