Lesson 5.3. Anti-Angina and Coronary Artery Disease Drugs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Angina
Not a disease, but a symptom of inadequate oxygen delivery (ischemia) to the heart muscle.
Characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the myocardium
Stable angina
Types of Angina
predictable, triggered by stress, lasts for a short time and can be relieved by rest
Unstable Angina
Types of Angina:
unpredictable, not triggered by stress, lasts for a long time and is not relieved by rest
Prinzmetal / Variant angina
Types of Angina
unpredictable, sometimes triggered by stress, worsens overtime and is not relieved by rest
Coronary Artery Disease
characterized by narrowing or blockage due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup)
results in reduced oxygen supply to the myocardium → angina, myocardial ischemia, or infarction
nitro compounds and ranolazine
anti angina drugs
Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide Mononitrate, Isosorbide Dinitrate
Drugs under nitro compounds
increases nitric oxide
MOA of Nitro Compounds:
_________________________ which results in vasodilation and relieve chest pain
Monday’s Disease
Nitro compounds causes _______________. Once tolerance is lost, re-exposure to nitro compounds causes fast HR, dizziness, and headache
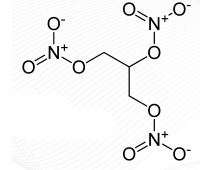
Nitroglycerin Structure
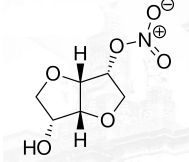
Isosorbide Mononitrate Structure
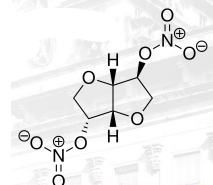
Isosorbide Dinitrate (ISDN) Structure
late Na + current
MOA of Ranolazine:
selectively inhibits ______________ leading to decreased intracellular Na + levels and Na + overload, modifying contractility leading to cardioprotective effects.
Angina (combined with CCBs, β-blockers, or nitrates)
Use of Ranolazine
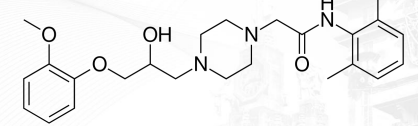
Ranolazine Structure