FINAL REVIEW ALL DOPPLER /WAVEFORM STUFF
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
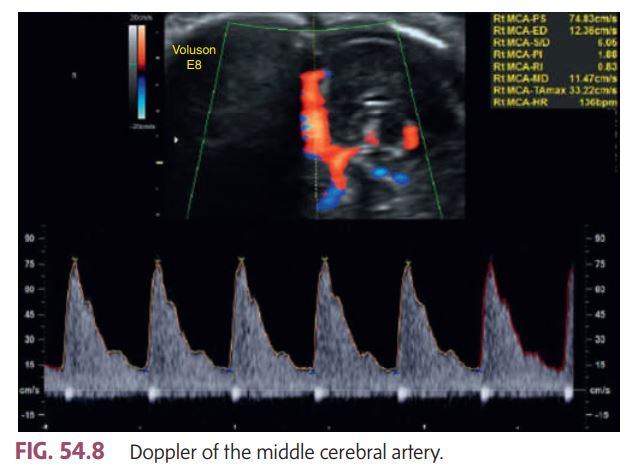
The waveform pattern looks normal — sharp systolic peaks with clear forward diastolic flow.
The peak systolic velocity (PSV) shown in the image is 74.83 cm/s, which is within the normal range for most gestational ages.
According to book: a PSV greater than 1.5 multiples of the median (MoM) suggests severe fetal anemia. Since this velocity does not exceed that threshold, it indicates no evidence of fetal anemia.
This MCA Doppler image demonstrates a __________
Normal flow pattern and normal velocity, suggesting no signs of fetal anemia.
Doppler of the middle cerebral artery
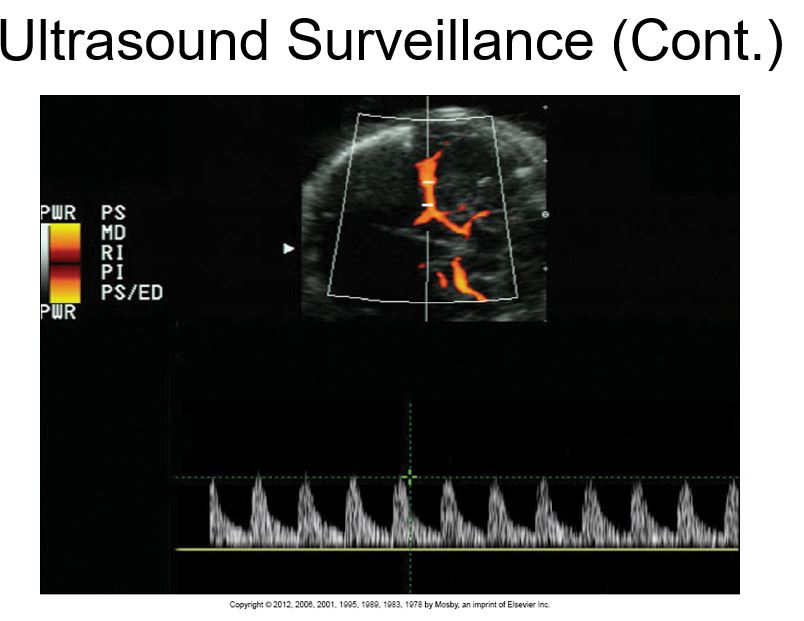
Two-dimensional and M-mode image demonstrating
pericardial effusion.
most common in women of childbearing age
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect almost all organ systems in the body. I
3-5 times higher rate of preeclampsia
increased spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and growth-restricted fetuses.
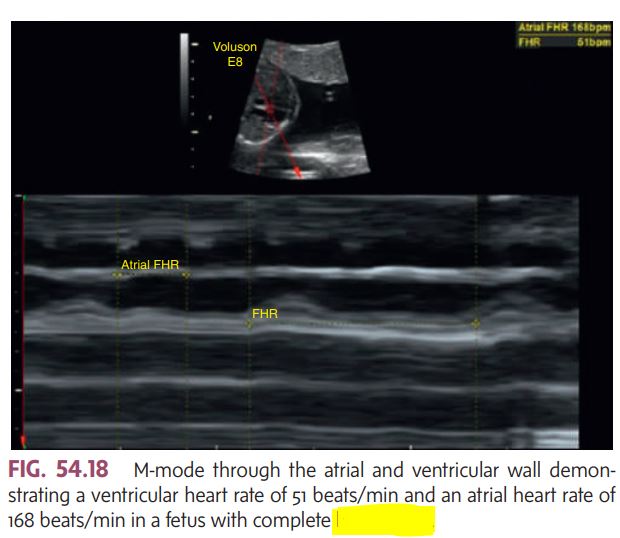
The fetal heart must be monitored to rule out congenital _________ (Fig. 54.18) and pericardial effusion.
heart block
During the fetal cardiac cycle, there is umbilical blood flow during both the pumping (systole) and filling (diastole) phases of the heartbeat.
No flow (absent end-diastolic flow) and_______ during diastole .
signs of fetal jeopardy and may prompt the obstetrician to do further fetal well-being testing or even to deliver the fetuses.
Reversal of diastolic flow in a twin gestation with twin-totwin transfusion syndrome.
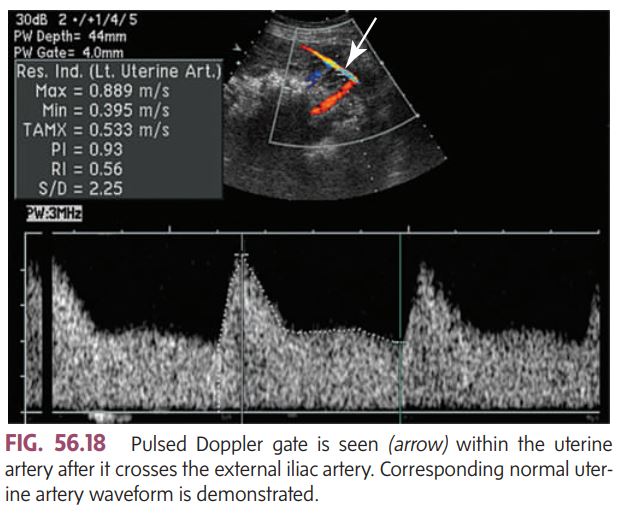
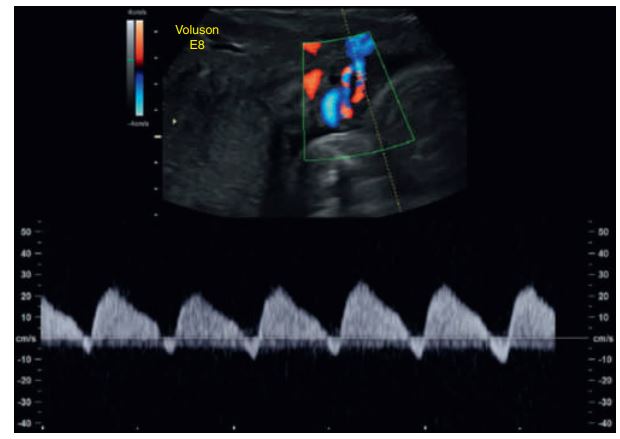
The uterine arteries are the main blood supply to the placenta.
By assessing them with color Doppler, we can see if enough oxygen and nutrients are reaching the placenta and fetus.
It helps detect problems like placental insufficiency (when the placenta isn’t getting enough blood), which can lead to fetal growth restriction or preeclampsia.
In a healthy pregnancy, the __________ shows _____ (good continuous flow throughout diastole), meaning the placenta is well perfused and active.
If there’s high resistance or notching in the waveform, it can suggest poor placental development or function.
normal placenta: uterine artery shows low-resistance flow
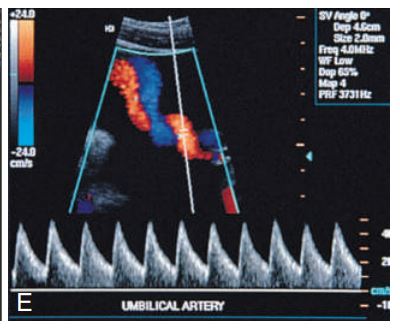
Spectral Doppler shows____ umbilical artery flow in a fetus with a two-vessel cord.
normal
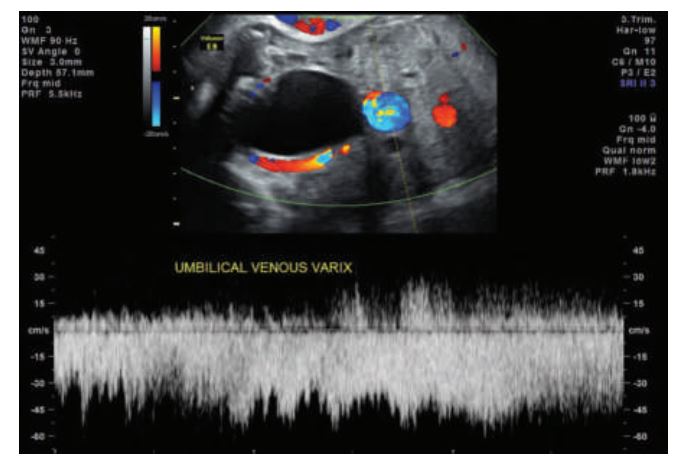
_________ the umbilical vessels affecting the umbilical artery and vein, respectively. Focal dilation of the umbilical vein is nearly always intraabdominal, but extrahepatic in location.
A varix appears on sonography as a dilated intraabdominal, extrahepatic portion of the umbilical vein. Color Doppler shows continuity with the umbilical vein.
Aneurysm and varix are focal dilations
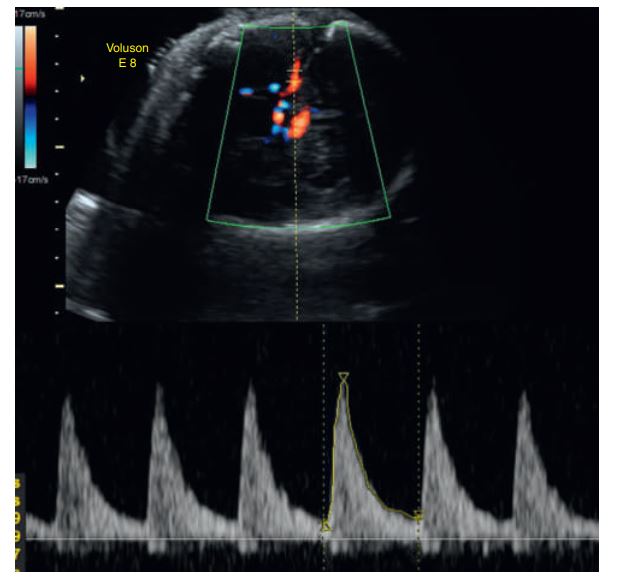
If the peak velocity is 50 cm/sec after 30 weeks of gestation, fetal anemia is mostly indicated (related to IMMUNE HYDROPS)
🧠 Vessel:
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
📈 Finding:
Peak systolic velocity (PSV) = ~50 cm/s after 30 weeks
💬 Interpretation:
That value is too high for gestational age, meaning increased MCA blood flow velocity.
🚨 Diagnosis indicated:
Fetal anemia — commonly due to immune hydrops (Rh isoimmunization) or other causes like parvovirus infection.
So:
🔹 The waveform shape looks normal (no reversed flow, etc.)
🔹 But the measured velocity makes it abnormal and clinically significant
Bottom line:
👉 The Doppler waveform is abnormal because of elevated MCA peak velocity → consistent with fetal anemia.
Middle cerebral artery color and spectral Doppler analysis in this anemic fetus indicates abnormal peak velocities.
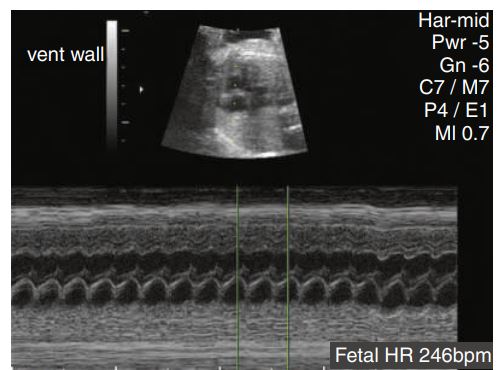
Tachycardia was identified in this patient with a heart rate of 246 beats/min.
___________ caused by cardiac insufficiency is one of the most common causes. Cardiac insufficiency can result from cardiac anomalies or arrhythmias .
Nonimmune hydrops
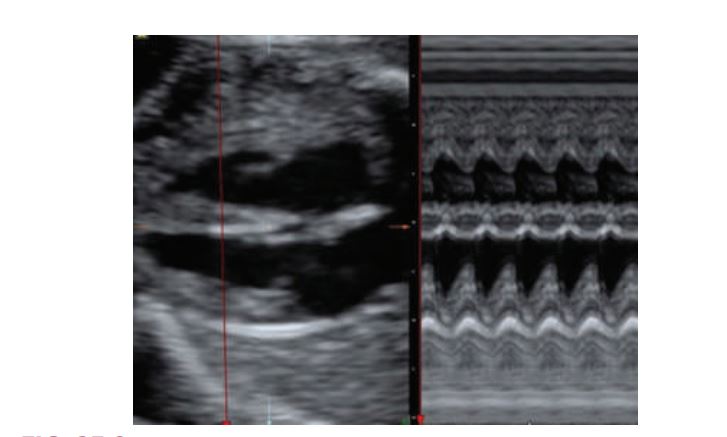
Two-dimensional and M-mode of the ventricular cavities. On the motion mode, time is depicted along the horizontal axis (dots along the top of the image). The distance between two dots represents 1second. Distance is located along the vertical axis. The aorta is shown as the two parallel lines moving as a “unit” through systole (pumping) and diastole (resting).
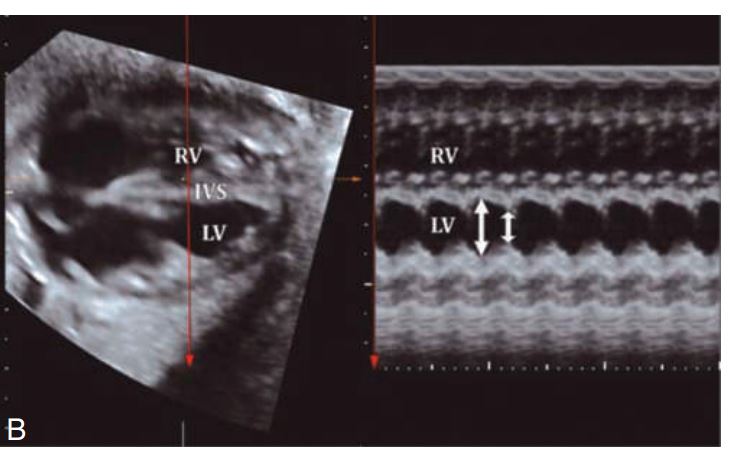
M-mode measurement of the fetal heart.IVS =
Intraventricular septum

The atrioventricular valves have a ______ of blood flow on the Doppler tracing. The first peak, e, is termed the passive filling phase. This peak is smaller than the second peak because the fetal heart is less compliant than the nenatal heart.
The second, taller peak, a, is termed the active atrial phase. In later pregnancy, the e point equals or exceeds the a point on the Doppler tracing as the pressure on the left side exceeds the right-side pressure. The mean tricuspid valve velocity is 65 cm/sec; the mean mitral valve velocity is 60cm/sec.
“double peak”
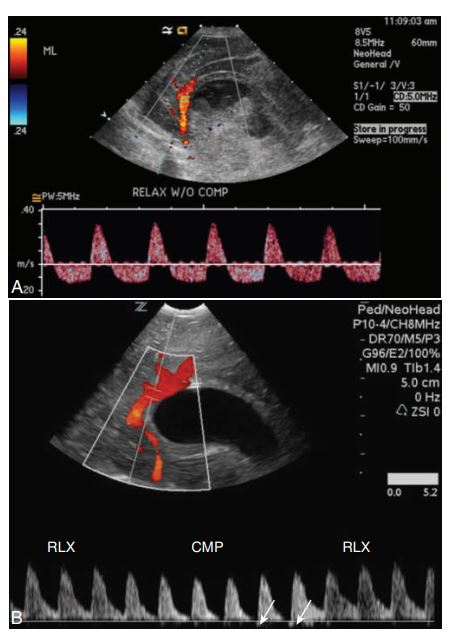
Spectral Doppler of the pericallosal artery in the presence of hydrocephaly to evaluate for intracranial pressure (ICP). (A) Neonate with bilateral grade IV hemorrhage and a diffusely echogenic and swollen brain demonstrates reversal of diastolic flow without compression, indicating elevated ICP.
(B) Premature infant with bilateral periventricular leukomalacia shows an absence of diastolic flow with compression on the anterior fontanel. The small bit of reversal of flow shown with arrows indicates ICP is increasing. CMP, With transducer compression; RLX, with relaxation.
Spectral Doppler to evaluate for increased intracranial pressure.
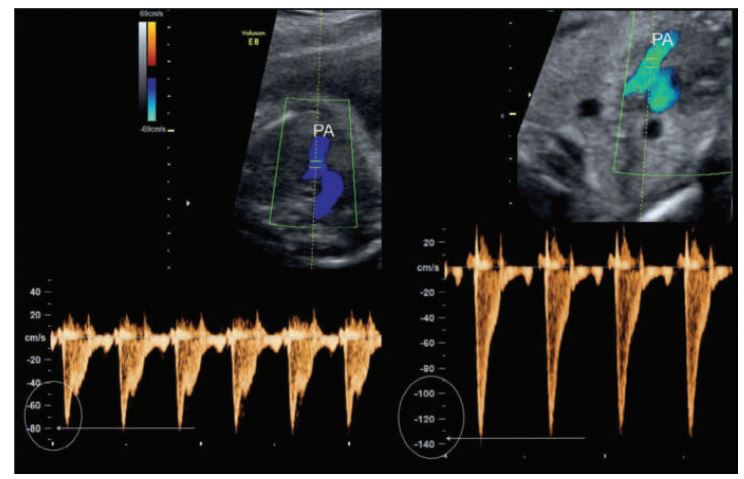
Pulmonic flow patterns are obtained parallel to flow in the high short-axis plane with the Doppler cursor at the level of the pulmonic cusps. The cursor is moved into the main pulmonary artery to map any changes in the flow pattern.
The mean velocity in the pulmonary artery ranges from 60 to 80cm/sec. Note the high-velocity pulmonic flow on the right which could be from. ________PA, Pulmonary artery.
pulmonary stenosis
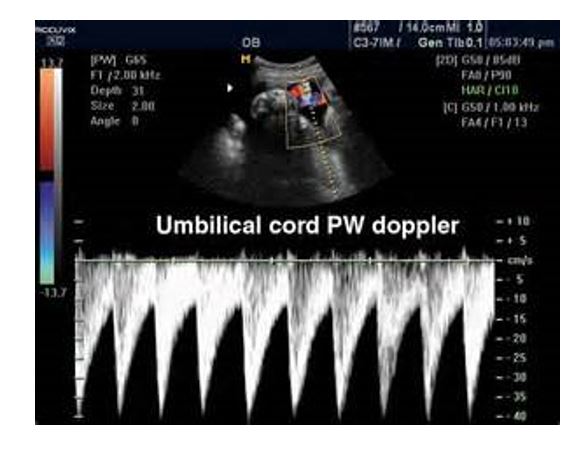
is this normal
normal 3 vessel cord Pw Doppler
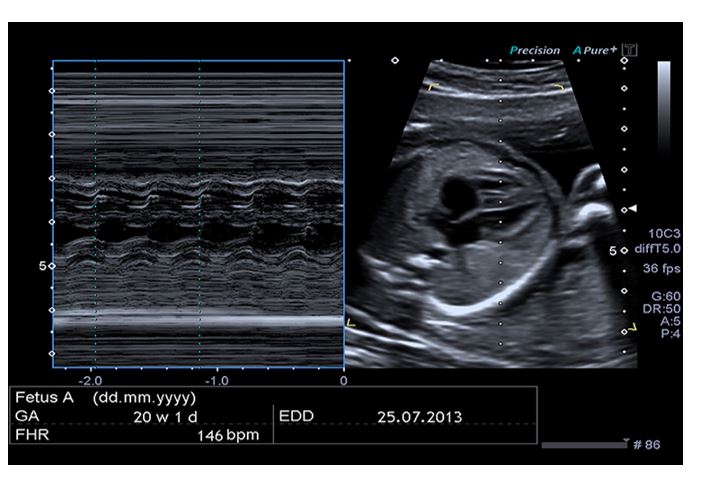
Four-Chamber View: M-Mode
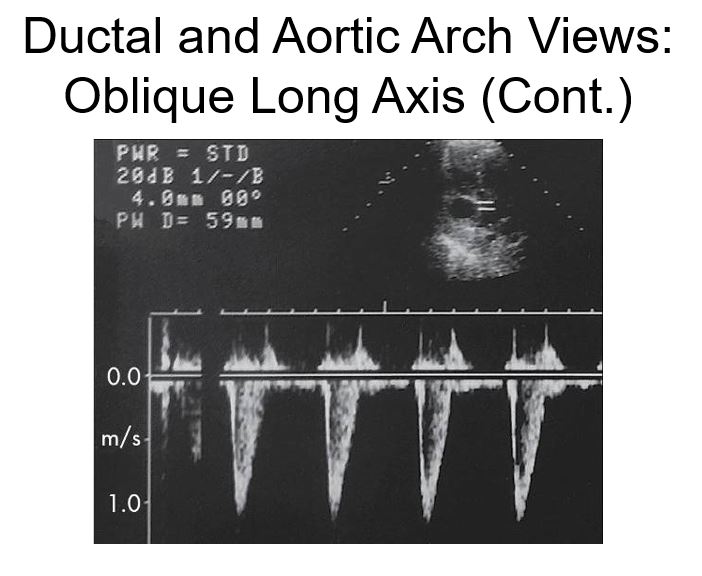
Normal velocity in the aorta.