Lesson 4.2. CNS Depressants
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Anxiety Disorders
group mental illness described as having significant levels of anxiety and fear that interfere with social and occupational functioning, but should not be associated to an exogenous factor or medical condition
Generalized anxiety disorder
Example of Anxiety disorders:
a. chronic abnormally high levels of anxiety
b. other examples
a = ?
Phobias, Social phobia, OCD, and PTSD
Example of Anxiety disorders:
a. chronic abnormally high levels of anxiety
b. other examples
b = ?
genetic
Anxiety disorder are not a._________ nor caused by b.____________, mostly it is associated with c.______________________.
a = ?
neural damage
Anxiety disorder are not a._________ nor caused by b.____________, mostly it is associated with c.______________________.
b = ?
GABA transmission
Anxiety disorder are not a._________ nor caused by b.____________, mostly it is associated with c.______________________.
c = ?
Gamma aminobutyric acid
meaning of GABA
GABA
major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the Central Nervous System (GABA A and GABA B)
heteropentameric
GABA Receptors is ______________ in structure that provides binding sites to different drug molecules.
Benzodiazepines and Non-Benzodiazepines GABA Agonist
Anxiolytic Drugs
Benzodiazepine ring allosteric site
Benzodiazepines Mechanism of Action:
a. Benzodiazepine binds to the ___________________ to modulate Cl- conduction.
b. Benzodiazepine increases the binding rate of GABA to __________________.
c. Cl- hyperpolarizes the membrane, decreasing __________________.
a = ?
GABA A receptors
Benzodiazepines Mechanism of Action:
a. Benzodiazepine binds to the ___________________ to modulate Cl- conduction.
b. Benzodiazepine increases the binding rate of GABA to __________________.
c. Cl- hyperpolarizes the membrane, decreasing __________________.
b = ?
membrane firing
Benzodiazepines Mechanism of Action:
a. Benzodiazepine binds to the ___________________ to modulate Cl- conduction.
b. Benzodiazepine increases the binding rate of GABA to __________________.
c. Cl- hyperpolarizes the membrane, decreasing __________________.
c = ?
Flumazenil
Treatment for overdose of Benzodiazepines which is a competitive molecule for Benzod
CYP 3A4 and 2C19
Metabolism of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
a. Phase 1 metabolism
b. diazepam and flurazepam
c. N-desmethyldiazepam, C1methyl, C4methylene of Class B BZDs
a = ?
N-dealkylation
Metabolism of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
a. Phase 1 metabolism
b. diazepam and flurazepam
c. N-desmethyldiazepam, C1methyl, C4methylene of Class B BZDs
b = ?
C3 aliphatic hydroxylation
Metabolism of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
a. Phase 1 metabolism
b. diazepam and flurazepam
c. N-desmethyldiazepam, C1methyl, C4methylene of Class B BZDs
c = ?
Benzodiazepine Pharmacophore
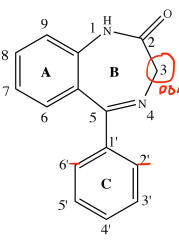
Ring A
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
aromatic ring essential for binding and activity
electronegative group (Cl, F, Br)
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring A
At C7, the presence of _________________________, increases drug activity
C6, C8, C9 substitution
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring A
_______________________ significantly decreases drug activity
Ring B
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
7 sided ring
small alkyl (Hydrogen and methyl) group at N1
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring B
promotes receptor affinity and activity
proton-accepting group (O/S)
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring B
At C2, the presence of _______________________ is required for ligand binding
-OH
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring B
At C3, _______ (hydrophilic) promotes faster excretion = short DOA
Ring C
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
C5-phenyl ring not required for activity
receptor binding
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring C promotes hydrophobic and steric interaction for __________________
increases
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring C
The presence of electron-attracting groups at ortho (C2’ or C6’) and diortho position (C2’ and C6’) _________ activity
decreases
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Ring C
The presence of substitutions at para position (C1’ or C4’) __________ activity
Electron-rich ring (s-triazole/imidazole)
Benzodiazepine Structure-Activity Relationship
Annelation
____________________at C1-C2 of Ring B increases Benzodiazepine affinity
-epam/-epates
suffix for Class A Benzodiazepine
-olam
suffix for Class B Benzodiazepine
Class A and B
Structure-Activity Relationship of Benzodiazepine:
a. Ring A, B, C are applicable for ______________
b. Annelation is applicable for ____________
a = ?
Class B
Structure-Activity Relationship of Benzodiazepine:
a. Ring A, B, C are applicable for ______________
b. Annelation is applicable for ____________
b = ?
Structure of Diazepam
Diazepam
Examples of Benzodiazepines Anxiolytics:
prototype Class A drug
long-acting
has the greatest affinity
Structure of Lorazepam
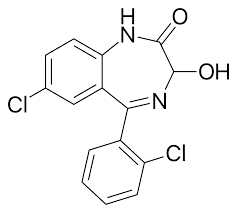
Lorazepam
Examples of Benzodiazepines Anxiolytics:
prototype Class A drug
presence of C3-OH
short-acting
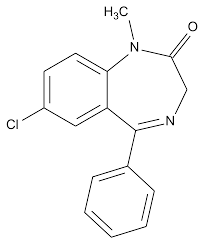
Structure of Alprazolam
Alprazolam
Examples of Benzodiazepines Anxiolytics:
prototype Class B drug
contains a triazole ring
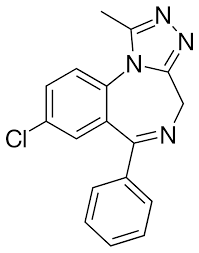
Structure of Midazolam
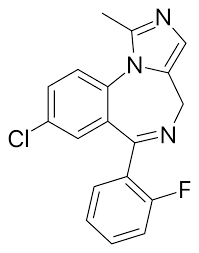
Midazolam
Examples of Benzodiazepines Anxiolytics:
prototype Class B drug
contains an imidazole ring
Non-BZD GABA Agonist
drugs that do not possess the BZD pharmacophore but exhibits anxiolytic and sedative/hypnotic activity thru other mechanism
zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon
Non-BZD GABA Agonist Drugs
highly selective for alpha-GABA A receptor subtype
Mechanism of Action for Non-BZD GABA Agonist
Insomnia
Use of Non-BZD GABA Agonist
CYP 3A4, 1A2 and 2D6
Metabolism of Non-BZD GABA Agonist:
a. Phase 1 metabolism
b. Happens in zaleplon
a = ?
first-pass effect
Metabolism of Non-BZD GABA Agonist:
a. Phase 1 metabolism
b. Happens in zaleplon
b = ?
Structure of Zolpidem
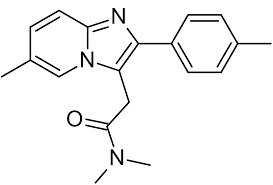
Zolpidem
Non-BZD GABA Agonist
prototype non-BZD
with an imidazopyridine ring
has 3 areas are essential for binding
R1
Zolpidem
electron-rich planar aromatic region
R2
Zolpidem
free rotating aromatic ring region
R3
Zolpidem
antiplanar region
electronegative group substitution
Structure-Activity Relationship of Non-BZD GABA Agonist (Zolpidem)
In R1/R3, _____________________ decreases activity.
Bulky N-substitution
Structure-Activity Relationship of Non-BZD GABA Agonist (Zolpidem)
In R3, _____________________ decreases activity.
Structure of Eszopiclone
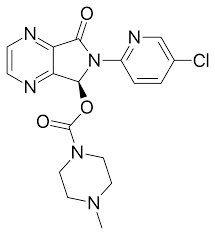
Eszopiclone
Non-BZD GABA Agonist
with cyclopyrrolone ring
binds at allosteric site of GABA A receptors
Structure of Zaleplon
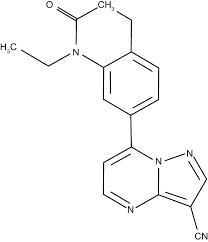
Zaleplon
Non-BZD GABA Agonist
with pyrazolopyrimidine ring
-CN group provides receptor selectivity
Sedative/Hypnotics
drugs which depress or slow down the body’s function
its activity can range from calming to sleep promotion
Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS)
Arousal input in the body regulated by Glutamate
Tuberomammalian nucleus (TBN) and Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
facilitate wakefulness via different mechanisms
GABA A receptor
Sedative/ Hypnotics work primarily as:
a. ____________ agonist
b. __________________ system modulator
a = ?
histamine/melatonin
Sedative/ Hypnotics work primarily as:
a. ____________ agonist
b. __________________ system modulator
b = ?
Sedative/Hypnotics Drugs
BZDs, non-BZD GABAA agonist, barbiturates, melatonin receptor agonist, H1-receptor agonist
Barbiturates
agents of choice as sedative/hypnotic until they developed tolerance, dependence and/or toxicity
ultra-short acting
Barbiturates can be:
a. less than 3 hours
b. 3-4 hours
c. 6-8 hours
d. 10-16 hours
a = ?
short-acting
Barbiturates can be:
a. less than 3 hours
b. 3-4 hours
c. 6-8 hours
d. 10-16 hours
b = ?
intermediate-acting
Barbiturates can be:
a. less than 3 hours
b. 3-4 hours
c. 6-8 hours
d. 10-16 hours
c = ?
long-acting
Barbiturates can be:
a. less than 3 hours
b. 3-4 hours
c. 6-8 hours
d. 10-16 hours
d = ?
sulfur
A barbiturates is ultra-short acting and is considered as an anesthetics which is characterized by the presence of:
alternating ketone (3) and nitrogen (2)
Structurally, barbiturates are characterized by:
binds to GABA A receptor
Mechanism of Action of Barbiturates:
a. __________________________ = increasing GABA binding
b. increased GABA binding increases _________________= reversible inhibition of excitatory neurons.
a = ?
Cl- ion transport
Mechanism of Action of Barbiturates:
a. __________________________ = increasing GABA binding
b. increased GABA binding increases _________________= reversible inhibition of excitatory neurons.
b = ?
liver metabolism
Metabolism of Sedative/Hypnotics:
a. significant ___________________
b. C5-substituent ____________
c. other metabolism
a = ?
oxidation
Metabolism of Sedative/Hypnotics:
a. significant ___________________
b. C5-substituent ____________
c. other metabolism
b = ?
glucuronidation and sulfation
Metabolism of Sedative/Hypnotics:
a. significant ___________________
b. C5-substituent ____________
c. other metabolism
c = ?
Barbituric Acid
Barbiturate pharmacophore
structure of Barbiturate pharmacophore
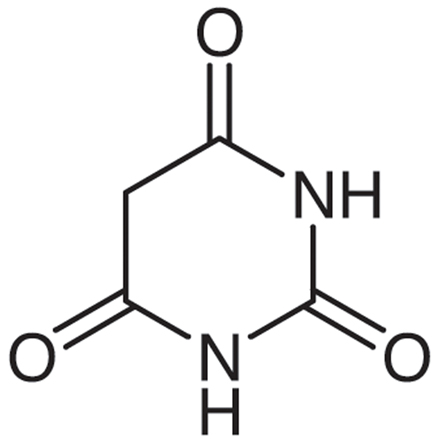
Acidic N and C5-H
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates
_____________________ results into inactivity
C5 substitution (except H)
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates
_____________ results to maximal activity
N1 and N3 alkyl substitution
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates
_______________ increases lipophilicity
anesthetics
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates
The replacement of =O with =S produces thiobarbiturates, ultra-short-acting agents, which is used for __________________.
ethyl and phenyl
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates (C5 di-substitution)
a. it is long acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
b. it is intermediate acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
c. it is short acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
a = ?
ethyl or phenyl
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates (C5 di-substitution)
a. it is long acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
b. it is intermediate acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
c. it is short acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
b = ?
neither ethyl or phenyl
Structure Activity Relationship:
Barbiturates (C5 di-substitution)
a. it is long acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
b. it is intermediate acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
c. it is short acting when the di-substitutions of C5 are:
c = ?
branched
Structure-Activity Relationship
The following shortens Barbiturates’ duration of action when:
a. presence of __________ chains
b. presence of _____________ side chains
c. side chain is larger than the _________________
a = ?
unsaturated
Structure-Activity Relationship
The following shortens Barbiturates’ duration of action when:
a. presence of __________ chains
b. presence of _____________ side chains
c. side chain is larger than the _________________
b = ?
ethyl group
Structure-Activity Relationship
The following shortens Barbiturates’ duration of action when:
a. presence of __________ chains
b. presence of _____________ side chains
c. side chain is larger than the _________________
c = ?
Structure of Phenobarbital
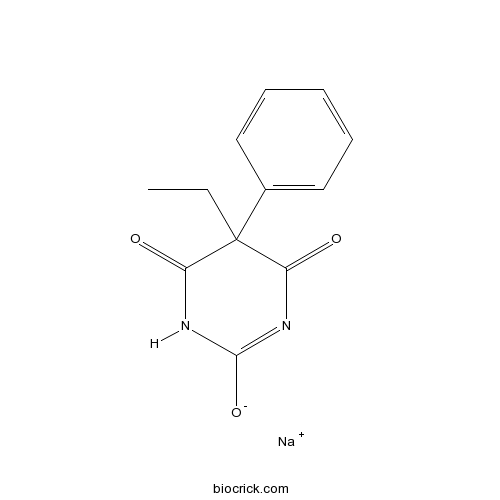
Phenobarbital
Examples of Barbiturates
long-acting agent due to the presence of ethyl and phenyl at C5
Structure of Butabarbital
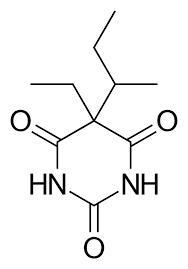
Butabarbital
Examples of Barbiturates
intermediate-acting agent due to the presence of ethyl at C5
Structure of Secobarbital
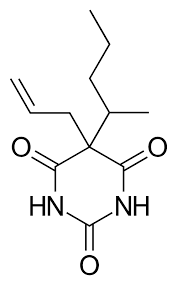
Secobarbital
Examples of Barbiturates:
short-acting agents due to the presence of double bonds and branching
Structure of Thiopental
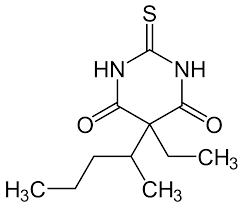
Thiopental
Examples of Barbiturates:
ultra short-acting agent used as an anesthetic due to the substitution of =S from =O
Melatonin Receptor Agonists
drugs which promotes sleep by binding into melatonin receptors in the brain (MT1R and MT2R)
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Mechanism of Action of Melatonin Receptor Agonists:
a. binds to MT1R decreasing ________________________ firing promoting sleep
b. binds to MT2R affecting __________________ (CNS clock)
a = ?
circadian rhythm
Mechanism of Action of Melatonin Receptor Agonists:
a. binds to MT1R decreasing ________________________ firing promoting sleep
b. binds to MT2R affecting __________________ (CNS clock)
b = ?