Quantitative Analytical Chemistry Exam 2 Terms
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Titrant
A standard solution of exactly known concentration used to analyze an analyte (in solution) using the method of titration
Primary Standard
A highly purified compound that is used as a reference material in titrimetric analysis; the mass of primary standard allows accurate calculation of moles of standard
Equivalence Point
The theoretical point in a titration when the volume of titrant added contains the stoichiometrically equivalent number of moles to the number of moles of analyte in the standard/unknown solution analyzed
Endpoint
The point in a titration when a physical/chemical change is observed in association with the equivalence point; used to estimate the equivalence point of a titration
Titration Curve
The plot of the negative log of the concentration of a titration reaction species as a function of titrant volume added
Titration Error
The difference between the titrant volume needed to reach an endpoint in a titration and the theoretical volume required to obtain the equivalence point, and the volume difference is very small (on the order of 10 μL)
Titration Volume
The volume of a titrant solution that has been added to a standard/unknown solution at the endpoint (symbol VEP)
Titrant Standardization
The process of determining the concentration of the titrant by titrating against a solution of accurately known concentration made using a primary standard
Indicator
A chemical species that interacts with one of the titration reaction species (either reactants or products) in order to visualize the change in concentration of that species in the titration
Back Titration
The process in which an excess of a titrant (e.g. strong acid) is deliberately added to a solution of a standard/unknown, and the excess is titrated with a second titrant (e.g. strong base) solution to obtain a sharper/clearer titration endpoint
Strong Acid
An acid that dissociates completely (100%) in water generating the same concentration of hydronium ion as the acid concentration
Strong Weak Acid
An acid that does not completely dissociate in an aqueous solution and generates a relatively high concentration of hydronium ions in solution; it has a high Ka value and produces a weak weak conjugate base
Weak Weak Acid
An acid that does not completely dissociate in an aqueous solution and generates a relatively low concentration of hydronium ions in solution; it has a low Ka value and produces a strong weak conjugate base
Strong Base
A base that dissociates completely (100%) in water generating the same concentration of hydroxide ion as the base concentration
Strong Weak Base
A base that does not completely dissociate in an aqueous solution and generates a relatively high concentration of hydroxide ions in solution; it has a high Kb value and produces a weak weak conjugate acid
Weak Weak Base
A base that does not completely dissociate in an aqueous solution and generates a relatively low concentration of hydroxide ions in solution; it has a low Kb value and produces a strong weak conjugate acid
Conjugate Acid
The ion formed by the gain of a proton by a weak base
Conjugate Base
The ion formed by the loss of a proton from a weak acid
Ka
Dissociation constant of a weak acid
Kb
Dissociation constant of a weak base
Kw
Dissociation constant of water
Analytical Concentration
The sum of the concentrations of all forms of a substance (all species that are derived from only it) in a solution
Buffer
A mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists a change of pH
Buffer Capacity
The number of moles of strong acid or base that 1 L of the buffer can absorb without changing the pH by more than 1
Buffer Region
The region (on a titration curve) where pH = pKa ± 1
pKa
The negative log of the acid dissociation constant
pKb
The negative log of the base dissociation constant
Alpha Diagram
A plot of the proportional amounts of chemical species, in one or more chemical equilibria, as a functional of pH
Alpha Value
Unitless number > 0 and < 1 representing the relative amount of a species to a total of all species related to the same source
Diprotic Acid
An acid that is able to donate two protons per mole of the substance
Triprotic Acid
An acid that is able to donate three protons per mole of the substance
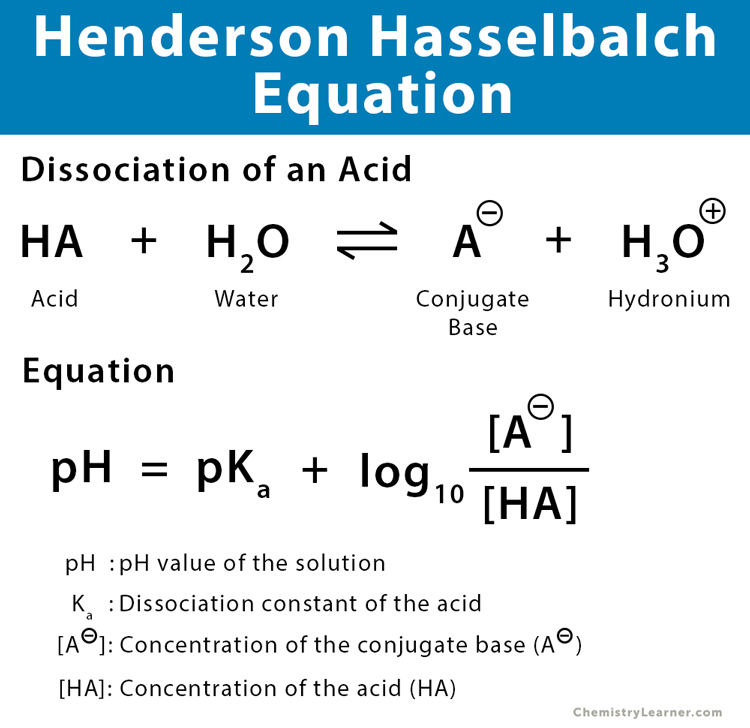
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Be able to define variables as well as write the equation