Exam 1 Mircobiology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Define Mircobiology
Study of organisms to small to see with the naked eye
prokaryotes
No nucleus, non bound organelles, circular DNA, older and less complex
Eukaryotes
Nucleus, membrane bound organelles linear DNA and more complicated
How do you see a virus
electron mircoscope
Imagine of Virus
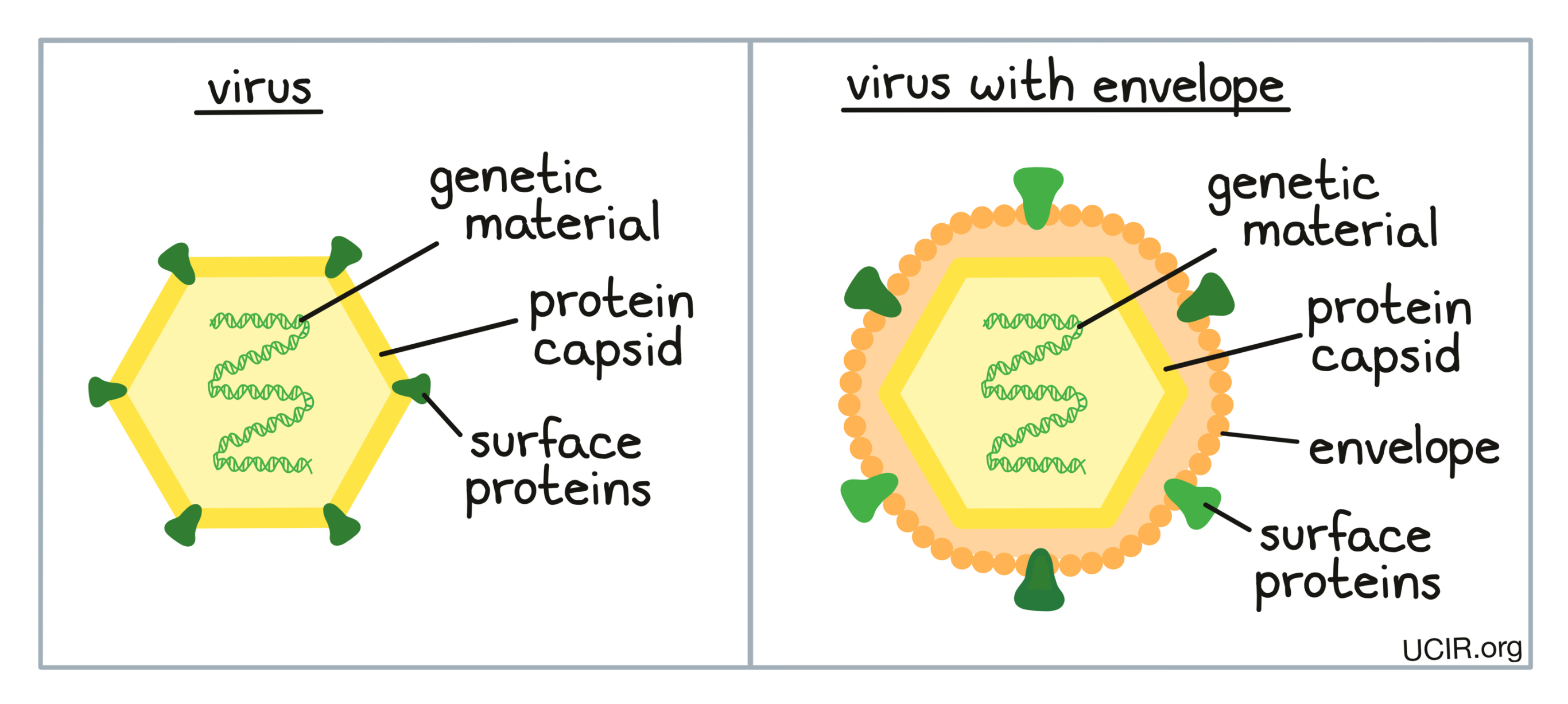
Virus structure description
Nucleic acid core (RNA or DNA) Covered by a protein called a caspin than covered with a nuclear envelope
Medical Microbiology
studies the effects of
microorganisms on human beings
Public Health Microbiology
understanding how these microorganisms cause diseases in populations, how they spread, and how to control or prevent these diseases.
Epidemiology
track how diseases spread across different populations and regions.
Biotechnology
study of living organisms, cells, or biological systems to develop products or processes for specific applications, often in fields such as medicine, agriculture, environmental science, and industry.
Genetic Engineering
process of altering the genetic material of an organism by directly manipulating its DNA
Industrial Microbiology
using microbes such as bacteria, fungi, and yeast to create commercially valuable products, like food, beverages, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels, on a large scale.
Immunology
Study of ways to prevent microorganisms from harming one’s body
Virologist
Study of viruses
Agricultural Mircobiology
Study between microbes and domesticated plants and animals
How long have microorganisms been on the earth?
3.5 billion years
Food Microbiologists
Study microorganisms relationship with food supply, including such areas
as food spoilage, food-borne diseases, and
production
Viruses
Acellular, parasitic particles
composed of a nucleic acid and protein (caspin)
Mutualism
Both species benefit
Commensalism
One species benefits while the other isn’t affected
Parasitism
One specie benefit at the expense of the other
Is bacteria prokaryote or eukaryote
Prokaryote
Is viruses prokaryote or eukaryote
neither
Is fungi prokaryote or eukaryote
eukaryote
Is Protozoa prokaryote or eukaryote
eukaryote
Is Algae prokaryote or eukaryote
eukaryote
Is Helminths (worms) prokaryote or eukaryote
eukaryote
What is protozoa nickname and why is it called eye
little eye, its because they are small unicellular animals
First plant in the see to make oxygen through photosynethesis
Algae
How does fungi get food
it absorbs nutrients
Photosynthesis
Light fueled conversion of
carbon dioxide to organic material
Decomposition
Breakdown of dead matter
and wastes into simple compounds
Decomposition
Breakdown of dead matter
and wastes into simple compounds
Which of the following does NOT describe a
fungus?
A. Contains a nucleus
B. Has 80S Ribosomes
C. Useful in Decomposition
D. Is photosynthetic
D
Bioremediation
Using living organisms to
remedy an environmental problem
Pathogens
Microbes that do harm
• Nearly 2,000 different microbes cause
diseases
Colony
Visible mass of cells that come from 1 cell
Spontaneous Generatiion
Old belief that living things can come from non-living things
Theory of biogeneis
the idea that living things can only come from other living things
Leeuwenhoek
Created the first microscope and called microorganisms animalcules
smallpox is caused by
mircorgansims goes inside through cuts and causes scars
Who created vaccine for small pox?
Dr. Edward Jennifer
pasteurization
Killing mircorganisms through boiling it (also increases shelf-life)
Endospores
heat-resistance bacteria
Sterility
Kill all life
Aseptic Technique
procedures used to decrease risk of infarctions
Joseph Lister
introduced aseptic techniques
to reduce microbes in medical settings and
prevent wound infections
Germ theory of disease
Diseases are caused by the growth of microorganisms in the body not by sins, or bad character
Dr. Ignaz Semmelweis
correlated
infections with physicians coming directly from
the autopsy room to the maternity ward
Dr. Oliver Wendell Holmes
observed that
mothers of home births had fewer infections
than those who gave birth in hospitals
Louis Pasteur
Created Germ theory
Louis Pasteur Achievents (4)
Showed microbes caused fermentation and
spoilage
• Disproved spontaneous generation of
microorganisms
• Developed pasteurization
• Demonstrated what is now known as Germ
Theory of Disease
Taxonomy
organizing, classifying, and
naming living things
Classification
orderly arrangement of
organisms into groups
Nomenclature
assigning names
Identification
determining and recording
traits of organisms for placement into
taxonomic schemes
Formal system originated
Carl von Linné
Levels of Classification
Domain - Archaea, Bacteria, & Eukarya
• Kingdom
• Phylum or Division
• Class
• Order
• Family
• Genus
• Species
Archaea
anything that lives in very intense climates
Eukarya
plants and animals (have a nucleus and organelles)
Bacteria
Bacteria (causes disease and eat decayed stuff)
Order of classification acrynoum
Domain King Phillip came over from Greece Stoned
Phylogeny
natural relatedness between
groups of organisms
Organisms in the Domain Archaea have more
DNA sequence similarity to:
A. Escherichia coli which is in the Domain
Bacteria
B. Humans which are in the Domain Eukarya
C. Archaea have no DNA sequence similarity to
any other organism
A
Neutrons + Protons =
Autonomic Mass/Weight
Protons =
Electrons
Neutrons =
Autonomic mass - protons
Isotopes
Same element just different neutrons
If two atoms have the same number of protons
and electrons but different numbers of neutrons,
they would be
A. Different elements
B. Isotopes of the same element
C. Ions of the same element
D. Orbitals of the same element
B
Molecule
a chemical substance that results
from the combination of two or more atoms
Compounds
molecules that are
combinations of two or more different
elements
Polar covalent bonds
Unequal Sharing
Ionic Bonds
one or more electrons from
one atom are removed and attached to
another atom, forming positively charged
cations and negatively charged anions
Oxidation
Loss of electrons
Reduction
Gaining Electrons
Exchange reaction
the reactants trade
portions between each other and release
products that are combinations of the two
Hydrophilic
dissolve in water
Hydrophobic
repel water
Amphipathic
have both hydrophilic and
hydrophobic properties
If solution A has a pH of 2 and solution B has a pH
of 4, which of the following is true?
A. Solution A has 2 times more H+ ions than
solution B
B. Solution B has 2 times more H+ ions than
solution A
C. Solution A has 10 times more H+ ions than
solution B
D. Solution B has 10 times more H+ ions than
solution A
E. Solution A has 100 times more H+ ions than
solution B
E
4 Biological Macromolecules
Carbohydrates,
Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids