AP Psychology: Cognition - Unit 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
2
New cards
information processing model
encode-->store-->retrieve
3
New cards
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information
4
New cards
Confabulation
the unintended false recollection of episodic memories
-memories match our expectations
-memories match our expectations
5
New cards
Encoding
the processing of information into the memory system—for example, by extracting meaning.
6
New cards
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
-studying, thinking
-studying, thinking
7
New cards
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings
8
New cards
parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously
9
New cards
methods of effortful processing
chunking, schemas, mnemonics, hierarchies
10
New cards
deep processing (semantic encoding)
encoding semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tends to yield the best retention
11
New cards
shallow processing
encoding on a basic level based on the structure or appearance of words
-maintenance rehearsal
-single repetition
-maintenance rehearsal
-single repetition
12
New cards
elaborative rehearsal
a method of transferring information from STM into LTM by making that information meaningful in some way
13
New cards
maintenance rehearsal
A system for remembering involving repeating information to oneself without attempting to find meaning in it
14
New cards
Chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
Ex: phone numbers
5103634558 becomes 510-363-4558
Ex: phone numbers
5103634558 becomes 510-363-4558
15
New cards
Schemas (Piaget)
mental frameworks that shape and are shaped by our experience
16
New cards
mnemonics
learning aids, strategies, and devices that improve recall through the use of retrieval cues
Ex: FTOP (frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal)
Ex: FTOP (frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal)
17
New cards
Hierarchies
Complex information broken down into broad concepts and further subdivided into categories and subcategories
18
New cards
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
19
New cards
distributed practice
spacing the study of material to be remembered by including breaks between study periods
20
New cards
massed practice
cramming the memorization of information or the learning of skills into one session
21
New cards
Overlearning
Continued rehearsal of material after one first appears to have mastered it.
22
New cards
storage
the process of retaining encoded information over time
23
New cards
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory
24
New cards
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
25
New cards
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
26
New cards
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; //if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
27
New cards
short term memory (STM)
the memory system in which information is held for brief periods of time while being used
-limited capacity (20 secs)
-can store 7 + or - 2 non-related items
-limited capacity (20 secs)
-can store 7 + or - 2 non-related items
28
New cards
working memory
(short term + long term)
29
New cards
long term memory (LTM)
all the information is placed to be kept more or less permanently
-unlimited capacity
-unlimited capacity
30
New cards
explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
- remembering a driving lesson and what happened during it
-hippocampus
- remembering a driving lesson and what happened during it
-hippocampus
31
New cards
implicit memory
retention independent of conscious recollection
- knowing how to drive as a result of the driving lessons
-Cerebellum, CC
- knowing how to drive as a result of the driving lessons
-Cerebellum, CC
32
New cards
episodic memory
memory of a specific event
-explicit
-explicit
33
New cards
semantic memory
memory for information/facts/ideas and their meaning
- Explicit
- Explicit
34
New cards
flashbulb memory
a clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event.
-(implicit)
-amygdala
- PTSD, remembering where you were during 9/11
-(implicit)
-amygdala
- PTSD, remembering where you were during 9/11
35
New cards
procedural memory
A type of long-term memory of how to perform different actions and skills.
-implicit
-riding a bike
-implicit
-riding a bike
36
New cards
context dependent memory
The theory that information learned in a particular situation or place is better remembered when in that same situation or place.
37
New cards
state dependent memory
Long-term memory retrieval is best when a person's physiological state at the time of encoding and retrieval of the information is the same.
- fight or flight
- fight or flight
38
New cards
constructive memory
memory that utilizes knowledge and expectations to fill in the missing details in retrieved memory traces
39
New cards
serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list
- primacy + recency
- primacy + recency
40
New cards
primacy effect
tendency to remember words at the BEGINNING of a list especially well
41
New cards
recency effect
tendency to remember words at the END of a list especially well
42
New cards
information processing theory
a perspective that compares human thinking processes, by analogy, to computer analysis of data
- shallow processing, deep processing, implicit memory
- shallow processing, deep processing, implicit memory
43
New cards
encoding specificity principle
we retrieve when we recreate a particular scene
44
New cards
mood congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood
- if you're sad you recall other sad memories more easily and vice versa
- if you're sad you recall other sad memories more easily and vice versa
45
New cards
eidetic memory
photographic memory
46
New cards
Framing
the way an issue is posed // how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.
47
New cards
misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event
- Elizabeth Loftus
- plays into the unreliability of eyewitness accounts in court
- Elizabeth Loftus
- plays into the unreliability of eyewitness accounts in court
48
New cards
long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. Believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory.
- Eric Kondel
- Eric Kondel
49
New cards
hippocampus (memory)
formation of new memories
50
New cards
cerebellum (memory)
forms and stores implicit memories
((classical conditioning))
- procedural memories
((classical conditioning))
- procedural memories
51
New cards
prefrontal cortex (memory)
habit learning
52
New cards
amygdala (memory)
emotional memories are involved here
-flashbulb memories
-flashbulb memories
53
New cards
Self-referencing
Thinking about new information and how it relates to you personally. Form of encoding
54
New cards
Tulving and Craik
levels of processing - self referencing- making connections for your memory to real life situations
55
New cards
forgetting curve
a graphic depiction of how recall steadily declines over time
- Ebbinghaus
- Ebbinghaus
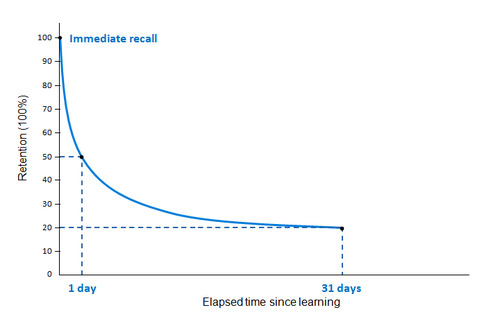
56
New cards
anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories
57
New cards
retrograde amnesia
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
-can't recall episodic memories
-can't recall episodic memories
58
New cards
proactive interference
old information interferes with the recall of new information
59
New cards
retroactive interference
new information interferes with the recall of old information
60
New cards
Repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
- Sigmond Freud
- Sigmond Freud
61
New cards
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
62
New cards
prototype
a mental image or best example of a category
63
New cards
convergent thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
64
New cards
divergent thinking
expands the number of possible problem solutions (creative thinking that diverges in different directions)
65
New cards
incubation
taking time to let thinking sit and come back with new solutions
66
New cards
functional fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions; an impediment to problem solving
67
New cards
Metacognition
thinking about thinking
68
New cards
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
69
New cards
algorithim
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.
70
New cards
Heuristic
shortcut thinking strategy
-Kohnemen, Traversky
-Kohnemen, Traversky
71
New cards
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind, we presume such events are common
- ariplanes vs. roadway travel example
- ariplanes vs. roadway travel example
72
New cards
representative heuristic
how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes
- truck driver vs. Ivy League professor example
- truck driver vs. Ivy League professor example
73
New cards
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
74
New cards
self-serving bias
the tendency to perceive oneself favorably
75
New cards
belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
-people are slow to detach from beliefs
-people are slow to detach from beliefs
76
New cards
cognitive dissonance
an unpleasant state that arises when a person recognizes the inconsistency of his or her actions, attitudes, or beliefs
77
New cards
Psycholinguistics
The study of how language is acquired, perceived, understood, and produced.
78
New cards
B.F. Skinner
believed in nurture side of psycholinguistics
79
New cards
Noam Chomsky
language development // disagreed with Skinner about language acquisition // stated there is an infinite # of sentences in a language, humans have an inborn native ability to develop language
(NATURE)
- LAD
(NATURE)
- LAD
80
New cards
Morphemes
The smallest units of MEANING in a language.
-suffixes and prefixes
-suffixes and prefixes
81
New cards
Whorf
hypothesized that language determines how reality is perceived
-linguistic determinism
-linguistic determinism
82
New cards
Phonemes
in language, the smallest distinctive SOUND unit
83
New cards
overregularization
Applying a grammatical rule too widely and thereby creating incorrect forms.
-children learning to apply grammar
-children learning to apply grammar
84
New cards
Genie case study
showed the damage that missing critical periods can do.
85
New cards
Semantics (grammar)
Meaning of words and sentences
86
New cards
syntax (grammar)
arrangement of words
87
New cards
Language Development Stages
babbling stage (4-12 months), one-word stage (12-24 months), two-word stage (24 months)
88
New cards
receptive language
ability to comprehend speech
89
New cards
productive language
ability to produce words
90
New cards
telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram—"go car"—using mostly nouns and verbs.
91
New cards
linguistic determinism
Whorf's hypothesis that language determines the way we think
92
New cards
Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
93
New cards
Broca's aphasia
inability to produce speech
94
New cards
Wernicke's aphasia
inability to comprehend speech
95
New cards
Lack of encoding
often, we don't even encode the features necessary to remember an object/event