Food Science Exam 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Categories of Lipids
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Sterols
Basic structure of a fatty acid
Chain of carbons with a carboxyl (hydrophilic) group on one end, methyl (hydrophobic) group on other end.
saturated vs monounsat vs polyunsat vs cis vs trans fatty acid structures
saturated: carbon chain with NO double bonds. Fully occupied by H atoms.
monounsaturated: one double bond
polyunsaturated: two or more double bonds
trans fatty acid: hydrogens are on opposite sides around the CC double bond
cis fatty acid: hydrogens are on the same side around CC bond (creates a kink in the chain)
common dietary sources of sat, unsat, trans fatty acids, and cholesterol
sat: beef, pork, dairy products, palm & coconut oil
unsat: vegetable oil, nuts, fish
trans fatty acid: dairy, milk, meat, margarine, cookies
cholesterol: only in animal products
effects of saturation on the physical state of fatty acids at room temperature
Hydrogenation makes trans fatty acids (adds hydrogen to unsat) solid at room temp
saturated is solid at room temp
mono and poly unsaturated is liquid at room temp
Two essential fatty acids and dietary sources
Omega-6 (Linoleic acid): canola oil, walnuts, soybeans
Omega-3 (Linolenic acid): flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts
Lipid function in body and in foods
Body: Organ protection, flavor and satiety, storage of energy as fat tissue, steroid hormone production, cell membrane structure, primary energy source for heart.
In foods: effects mouthfeel and texture, flavor compounds interact with fat molecules in food
fat and oil properties that impact function in products
Properties of fats and oils that impact their function in food products include their melting point, which determines a product's texture and mouthfeel, and plasticity, which affects spreadability. Other key properties are their role in emulsification, heat transfer, flavor enhancement
Apply what you know about the functions of fats and oils in foods to hypothesize how foods and beverages may change if fats and oils are eliminated or reduced in their formulation
The removal of fats and oils would profoundly impact the texture and mouthfeel of many foods: without fat foods are drier, less creamy, and have less flavor.
Food Processing vs Processed Food definition
Food Processing: use of methods and techniques involving equipment, energy, and tools to transform agricultural products into food products
Processed Food: food material has been changed in some way through a combo of ingredients together with processing steps to make food safe to eat, shelf-stable
Processed Foods: Pros vs Cons
Pros:
food safety
convenience
availability
food preservation
Cons:
higher levels of fats, sugars, salt
lower fiber
health risks
Main points for and against food processing
For:
help long term fuel/endurance(ex: gel for marathons)
plant based food can’t be made without processing
natural isnt always good (ex: folate vs folic acid)
Against:
excess calories, causing obesity
higher sugars, fat, and salts but lower fiber
Objectives of food processing
ensure food safety, extend shelf life,
improve convenience, affordability
Ultra-Processed food definition
foods comprised of industrially produced ingredients
Value added ingredients vs. processed/formulated foods
Value added ingredients: agricultural commodities that have been processed or modified for specific functional/nutritional benefits. EX: Flour, milk powder, liquid eggs
Processed foods: food that has been changed to preserve it for convenience, etc. EX: potato chips, cereals, cheese dip
Definition of pathogen, spoilage microorganism, D-Value, and temp danger zone
Pathogen: a microorganism that harms human health
Spoilage microorganism: microorganisms that cause spoilage or disease (some contain enzyme pectin esterase that rot fruits/veggies)
D-value: decimal reduction time, time required at given condition to achieve a log reduction (kill 90%) of microorganisms
Temp danger zone: temperatures that cause microorganisms to grow and multiply (foods stored warmer that 41F and reheated to cooler than 140F)
Conditions that affect bacterial multiplication in foods
Food - nutrients (carbs/protein)
Acidity (neutral to low acid)
Temperature ( 41-135)
Time, bacteria double every 20 mins
Oxygen (anaerobic vs aerobic)
Moisture (high water activity: adding salt or sugar)
How can you modify those conditions to slow bacterial growth?
store foods out of danger zone, keep water activity low
5 bacteria & viruses that cause most illness, hospitalizations and deaths in US each year
Norovirus, Salmonella, Campylobacter, E. coli, and Listeria
Different routes foodborne illness may occur
Contamination: -can occur during harvest or food prep
Incorrect Storage: allows for growth of bacteria or toxin production
Not processed/cooked right: allowing bacteria/toxin to survive before food is eaten
Bacteria and Virus table: food/bev association, incubation time, and prevention
see paper
Diff types of contaminants that make a food unsafe
Biological, Physical, and Chemical
Pop groups at highest risk of foodborne illness and why?
ages 65+
children less than 5 yrs old
ppl with weak immune systems
pregnant women
ALL DUE TO ALTERED IMMUNE SYSTEMS
Explain how groups at risk of foodborne illness can reduce their risk of foodborne illness through food selection, food preparation, and food storage
Groups at risk can reduce foodborne illness by selecting safer foods, practicing safe preparation, and following proper storage guidelines. When shopping, choose undamaged products and keep raw items separate from other groceries. thoroughly cook all food
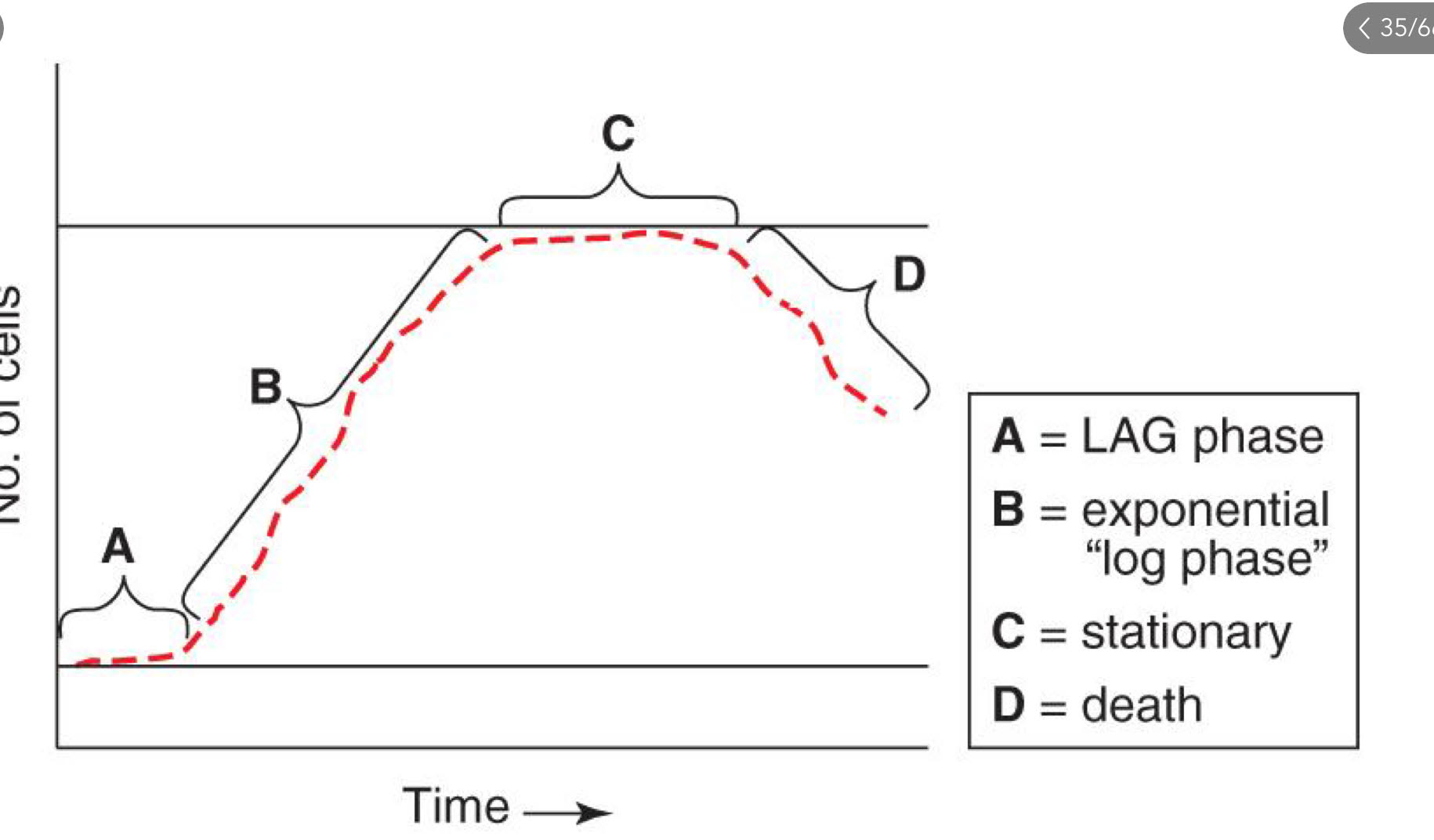
Label each phase of a microbial growth curve and describe what is occurring during each phase.
Quality vs Total Quality Management Definition
Quality: degree to which food product conforms to specifications and consumer expectations
Total Quality Management: company wide system aimed at continuous improvement to ensure regulatory compliance/customer satisfaction
elements of total quality management
Management responsibility, documented procedures, testing, sanitary design, HACCP plan, recall procedures, sustainability, consumer awareness
7 steps of HACCP Plan
Conduct hazard analysis
Identify critical control points
Establish critical limits
Establish monitoring procedures
Corrective actions
Verification procedures
Documentation/record keeping
3 diff types of food/bev recalls
Class I: health hazard w/ reasonable probability of health problems or death
Class II: remote probability of temporary/reversible health consequences
Class III: ingestion of food product is unlikely to cause any adverse health consequences
Market withdrawal: product has minor violation not subject to legal action
List factors/properties of a food product a quality assurance manager may test to
determine final product quality
They may perform physical, chemical, or microbiological (toxins, bacteria) tests. They can do a sensory evaluation (taste/flavor, texture) and test packaging and labeling accuracy.
Which points/unit operations in the ice cream making process may pose a hazard to the final safety level of the ice cream
The pasteurization of milk (being heated to kill bacteria, storage and ingredient sourcing bc of packaging, transport, aging/freezing
Are there any steps taken to control the level of the safety risk? If so, what are the
steps/actions
They perform good hygiene, continuous monitoring, sampling, and temperature management
Beyond food safety, what other factors are taken into consideration when assessing the
overall quality of ice cream? What tests could be performed by a quality assurance
scientist to evaluate the final quality of an ice cream product
Test the composition (butter fat, air percentage), microbial quality, texture, sensory like flavor and mouthfeel, and shelf life