Lab 2: Prokaryotes- Bacteria and Cyanobacteria Structure and Mitotic Division of Eukaryotic Cells
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Mitotic division
mitosis
Which organisms account for the earth’s biomass?
prokaryotes
Why do we study prokaryotes?
they form an important, neglected, unexplored, part of biodiversity
crucial role in ecosystems as decomposers
Heterophic
organisms that obtain their food from consuming other organisms
Decomposers
organisms that break down dead organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem (heterotrophic bacteria)
Primary producers
organisms that synthesize their own food, typically through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain (cyanobacteria)
Some of the first organisms to evolve the capacity for photosynthesis
Domain Bacteria
What do bacterial cells lack?
nuclear envelope, plastids, mitochondria, and other membrane bound organelles
What do bacteria cells consist of?
plasma membrane, cytoplasm with ribosomes, DNA(chromatin+associated proteins), and sometimes endomembranes
What do bacteria cell walls consist of?
peptidoglycan
Flagella
long, whip-like structures that enable locomotion in many prokaryotic organisms, allowing them to swim through liquids.
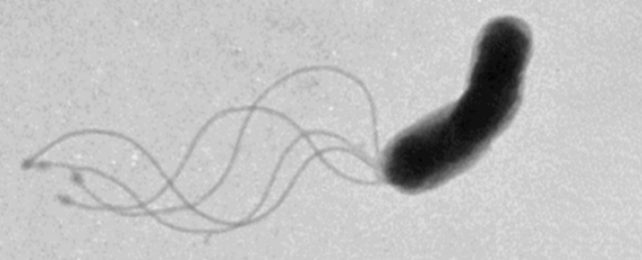
Unicellular
organisms that consist of a single cell, functioning independently
Are prokaryotes unicellular or multicellular?
unicellular, can form colonies
Filamentous
thread-like or consisting of long, thin filaments
Globular
spherical in shape
What are the shapes of colonies of bacteria/prokaryotes?
filamentous, globular, sheets/mats
Photosynthetic pigments of cyanobacteria
green chlorophyll a, yellow carotenoids, blue phycobilins
What does chlorophyll a do in cyanobacteria
photosynthesis
What do cartenoids and phycobilins do in cyanobacteria
help capture light in dark places and pass it to chlorophyll
What is all photosynthesis on Earth is done by?
chlorophyll a, aided by carotenoids
Heterocyst
specialized cell in cyanobacteria that is for nitrogen passing and storage
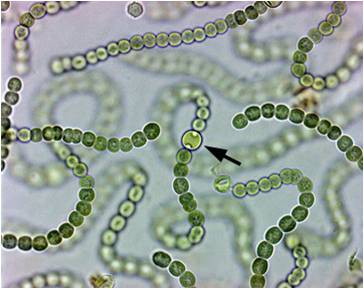
Why are heterocysts yellowish?
presence of cartenoids which help protect against UV damage
Why type of reproduction does bacteria have?
asexual (binary fission)
Binary Fission
asexual reproduction by the plasma membrane and cell wall grow inward, divides cell in half
Conjugation
asexual reproduction by portions of DNA exchanging between bacterial cells through a temporary connecting pilus (conjugation pilus)
What are critical functions of heterotrophic bacteria?
fixation of atmospheric nitrogen
nutrient cycling
Why is cyanobacteria important?
largest form of prokaryotes to produce oxygen
frequently confused with green algae
occur as symbionts frequently with fungi
Symbionts
organisms in a symbiotic relationship, often living closely with another species to benefit each other
In most cases the cell wall of bacteria contain
peptidoglycan
True or False: Only eukaryotes are motile
False
Are bacteria and algae with phycobilin pigments found in sunnier or shadier places, why?
shadier, phycobilin pigments capture light in dark places to pass to chlorophyll to do photosynthesis and also fall apart from light
What’s one way heterotrophic bacteria feed?
absorption on nutrient substances
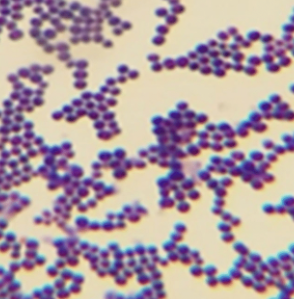
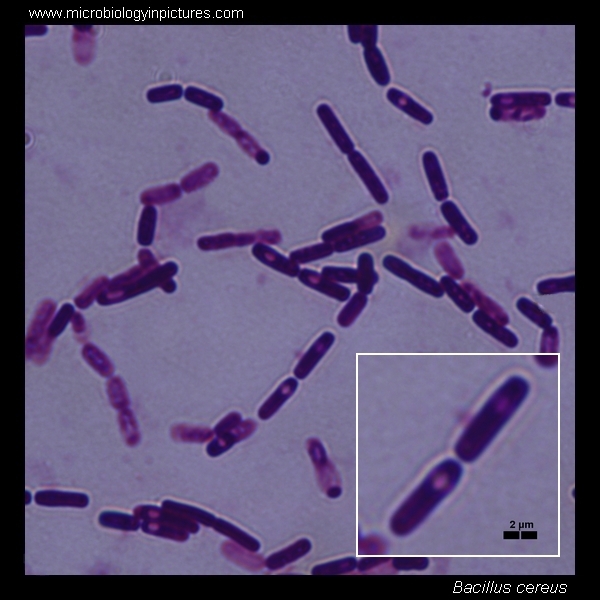
Three forms of bacteria cell shape
coccus, bacillus, and spirilla
Spheroid-shaped bacteria
coccus (pl. cocci)
Rod-shaped bacteria
bacillus (pl. bacilli)
Spiral-shaped bacteria
spirilla (pl. spirilli)
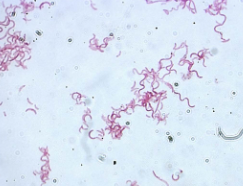
Two species of bacteria in yogurt
Lactobacillus bulgaricus (rod-shaped) and Streptococcus thermophilus (spherical)
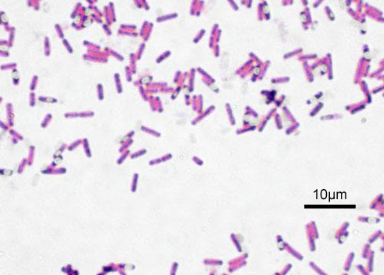
What shape is this bacteria?
Bacilli
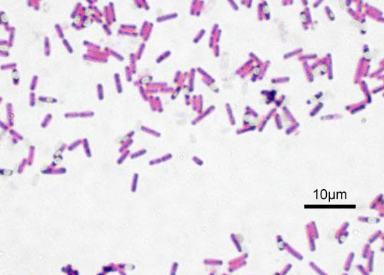
Are these eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
prokaryotes
What shape is this bacteria?
cocci
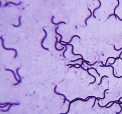
What shape is this bacteria?
spirilli
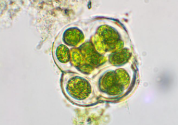
What domain of life does Gloeocapsa belongs to?
Domain Bacteria
What type of colonies do Gloeocapsa form?
globular colonies
Filamentous colonies
filaments; strings of cells

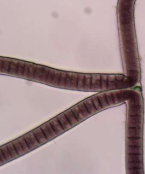
False branching
two filament ends continuing to grow at an angle and away from the rest of the main filament
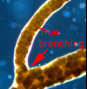
True branching
formed by lateral divisions in cells of the main filament and occurs in different planes all around the main filament
True or False: Only members of the Domain Eukarya are autotrophic
false, prokaryotes can also be autotrophic
Chlorophyll a evolved in Domain
bacteria, prokaryotes
Name one way in which cyanobacteria are important to forests
symbiotic relationship with fungi
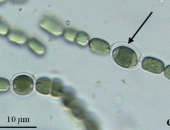
Name the structure at the pointer under the microscope, what is it’s function, and what domain is the organism in?
Heterocyst
Nitrogen fixation
Domain Bacteria
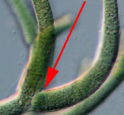
Is the example under the microscope pointer true or false branching?
false branching
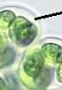
What is the name of the structure at the pointer under the microscope? What is it’s purpose?
extracellular sheaths. they
attach to substrate to each other
help cells communicate to one another
protect them from the environment
What do plant cells consist of?
nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, cellulose, protoplast
Protoplast
delimited by cell(plasma) membrane, contains the cytoplasm and the nucleus
Nuclear envelope
2 membranes that surround the nucleus and contains 1+ dense regions of nucleoli
Nucleoli (pl. nucleolus)
centers of ribosomal RNA production
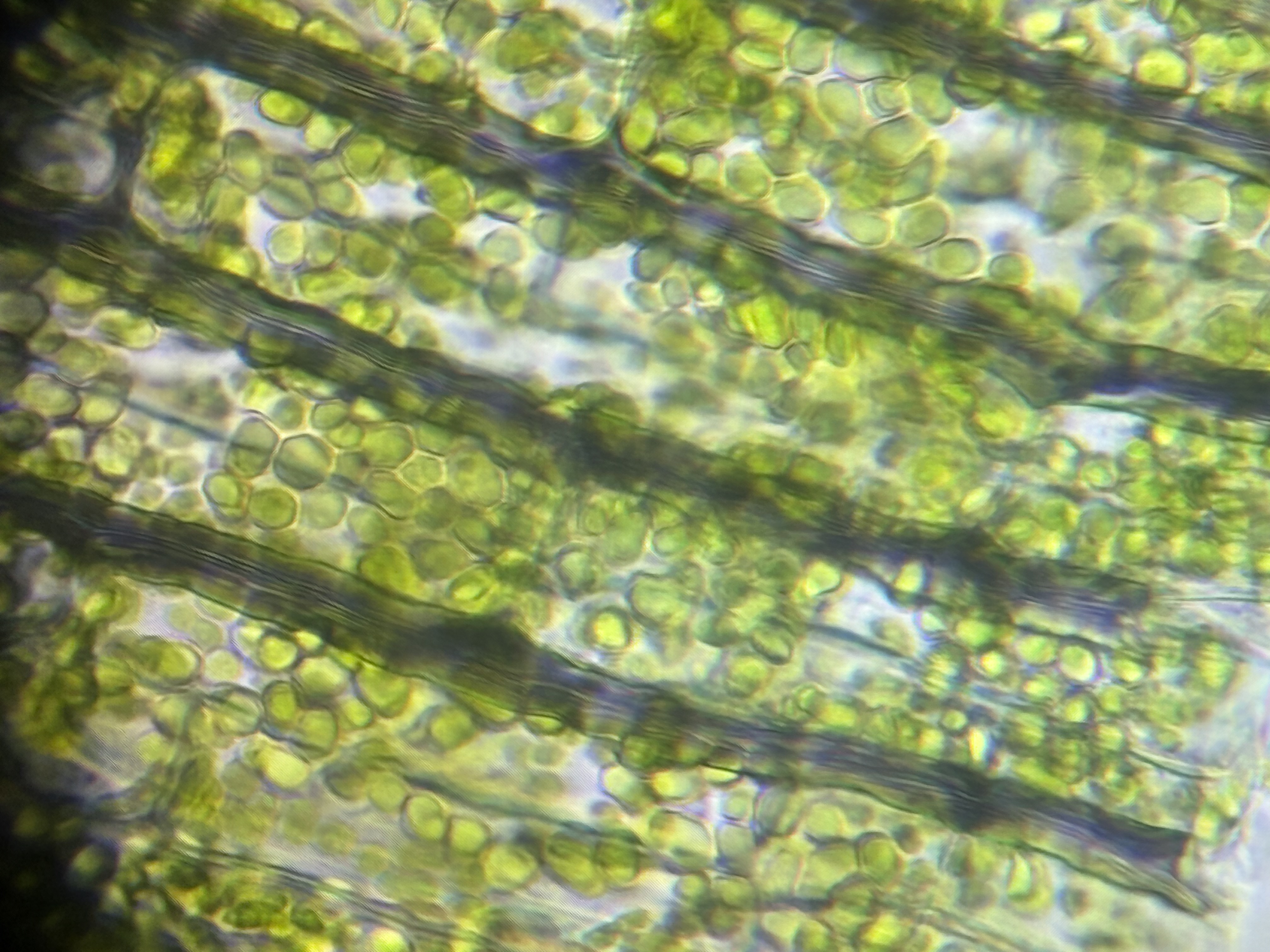
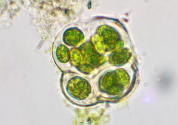
Name the green organelles inside this cell
chloroplasts
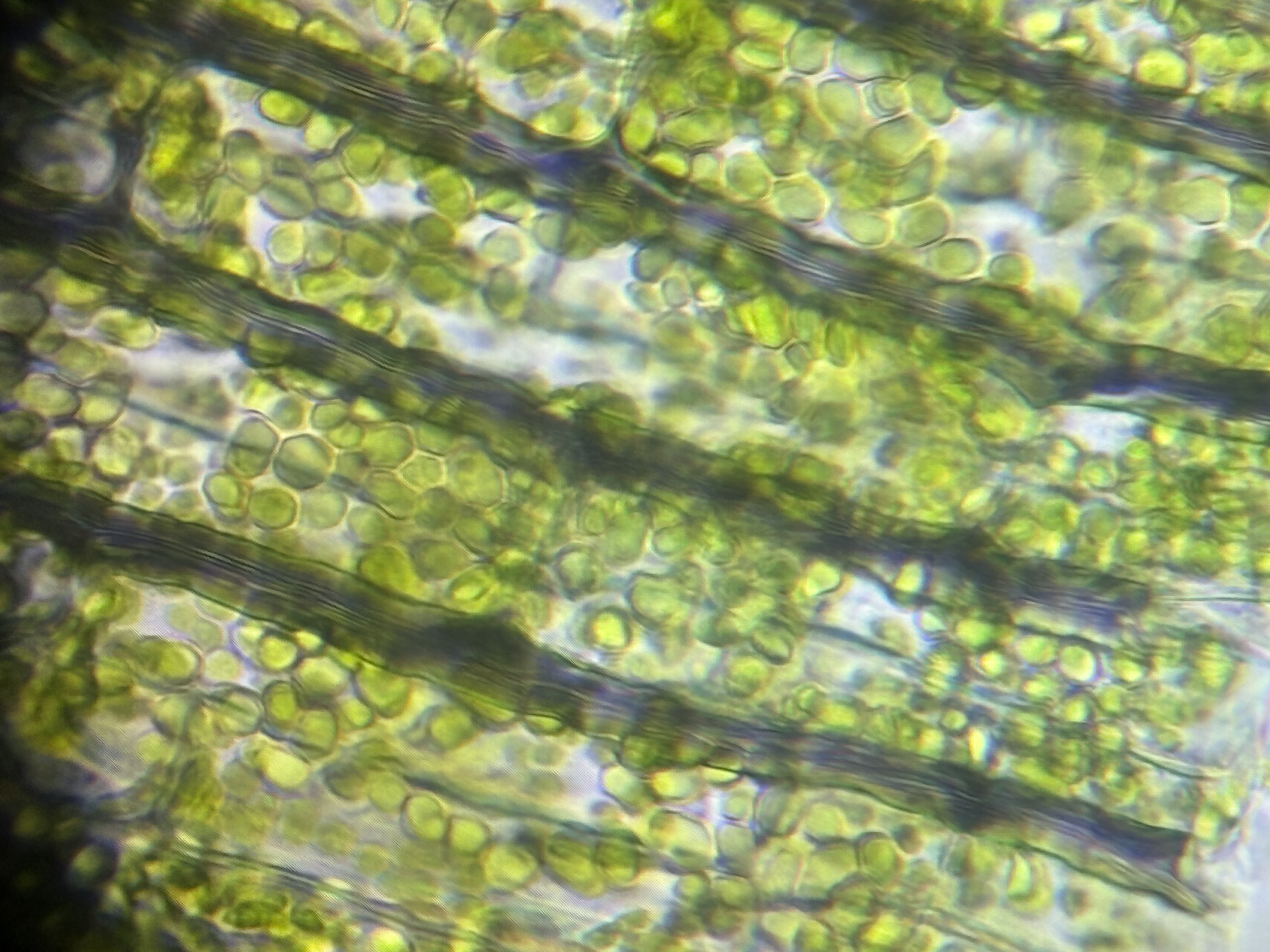
What is the function of these organelles?
photosythesis
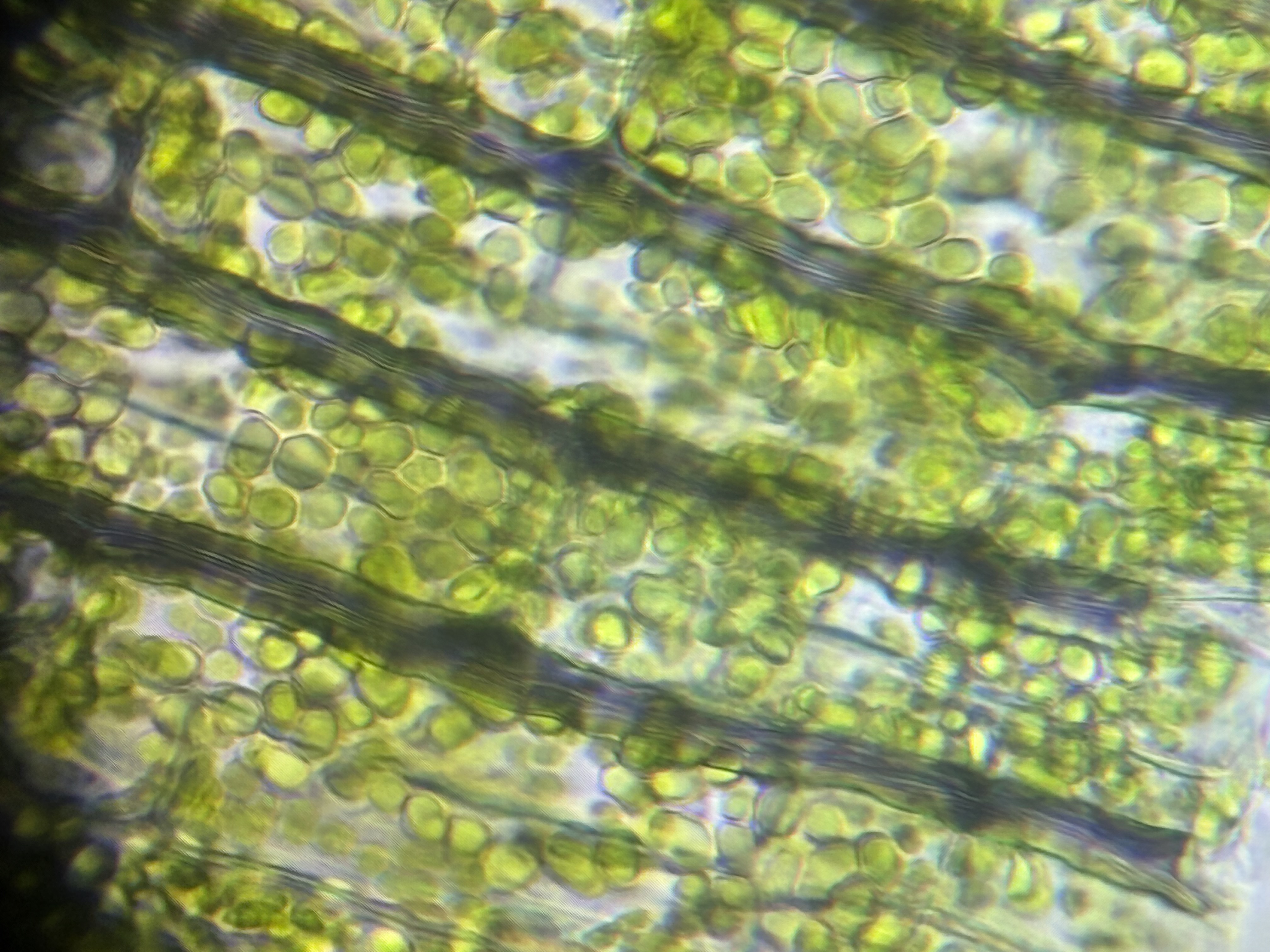
What is the kingdom of this organism?
Plantae
Cytoplasmic streaming
in general, not static, constant movement
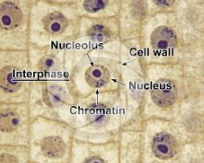
Dark spot of the cell?
nucleoli
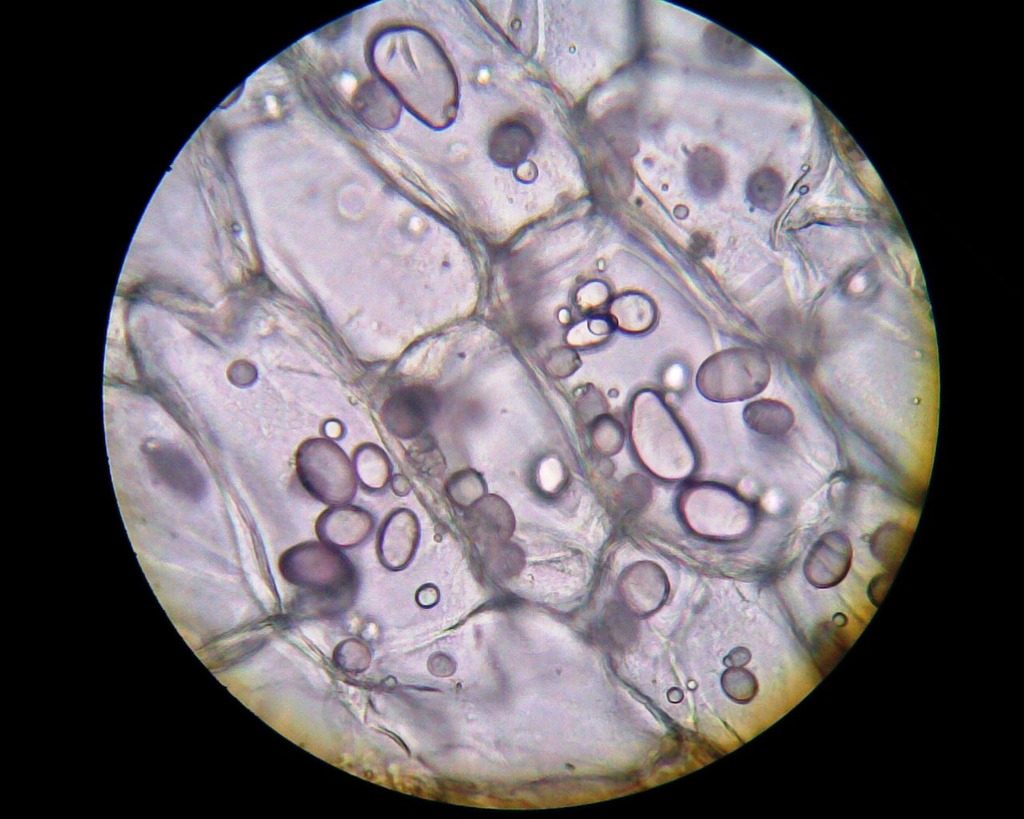
Name the organelle indicated by the pointer
amyloplast

What’s the function of this organelle?
Stores starch
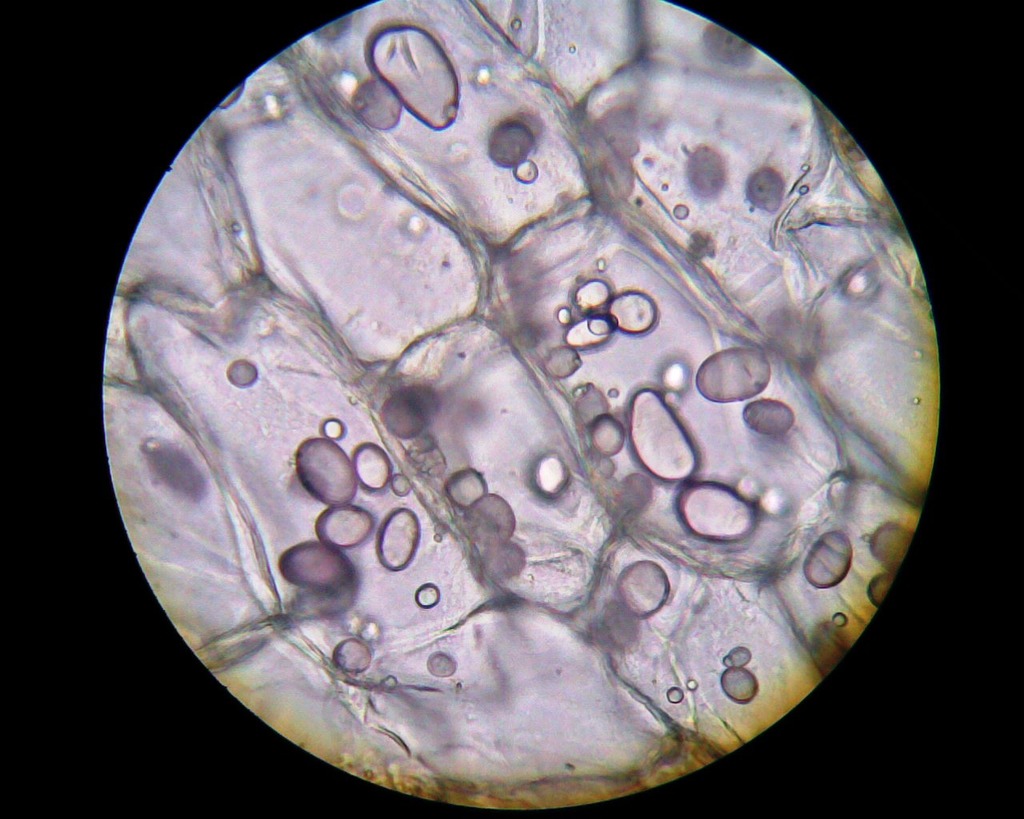
Name the domain of life that this organism belongs to
Plantae
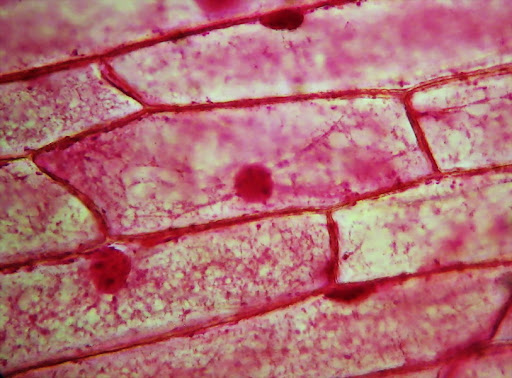
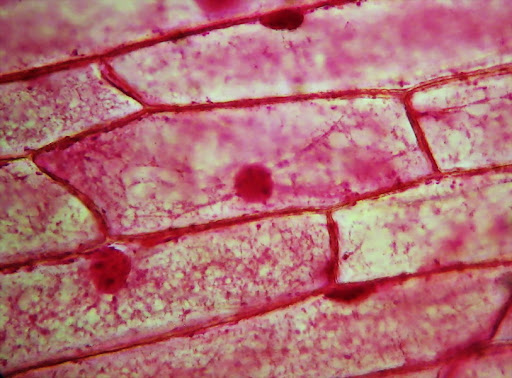
What is the round red object in the cells?
Nucleus
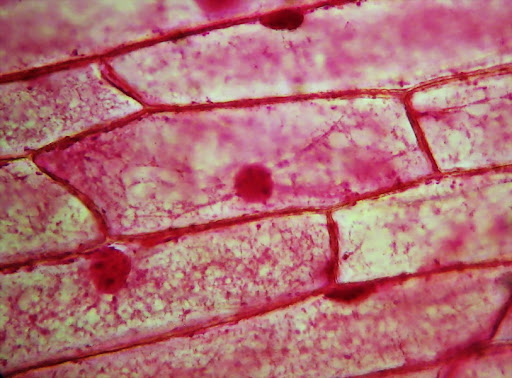
What are the dark spots in it?
Nucleoli
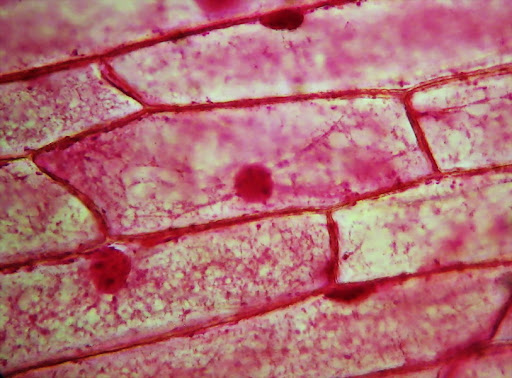
Is this a eukaryote or prokaryote? How do you know?
eukaryote, by the nucleus
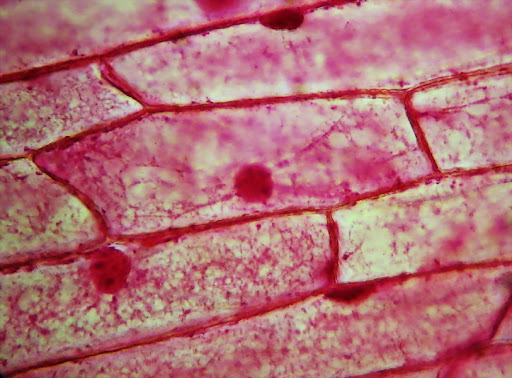
What is the mode of nutrition of this organism?
autotroph
What Kingdom does this organism belong to?
Plantae
True or False: All unicellular organisms are prokaryotes
false
Equatorial plane
where the chromosomes align in metaphase
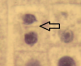
What is the structure at the pointer
Cell plate
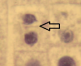
The presence of this structure indicates that the process of __ has started
cytokinesis
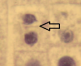
What phase of division is this cell in? Name of division that occurs after this phase?
telophase and cytokinesis
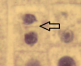
What is the Domain of this organism? What kingdom? How do you know?
Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Plantae, we know this because the presence of a nucleus (eukaryote) and the cell walls are glued together (plantae)