Economic ISL Year10
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Want
A want is a desire however not an essential for survival
Need
A need is an essential for survival
Economic choice
A decision to purchase certain goods instead of another
List of preference
A list used to state the urgency and importance of resources
Basic Economic Problem
There are unlimited wants and needs however the number of resources are scarce/limited
Economics
Economics is the study of using limited resources to satisfy unlimited needs and wants
Free Goods
Free goods are goods with no price, plenty and have no opportunity cost
Economic Goods
Economic goods are goods that have a value, scarce, require an economic choice and have an opportunity cost
Factors Of Production(FOPs)
Land, Labour, Capital, Enterprise
LAND
All natural resources found on, above and below the earth’s surface used in production
Land Mobility
Occupationally mobile and not geographically mobile
LABOUR
Mental and physical efforts put in by workers or labourers
Labour Mobility
Occupationally mobile and highly geographically mobile
CAPITAL
All man-made resources available in an economy
Capital mobility
Occupationally mobile and geographically mobile
Enterprise
The ability to take risks and run a business
Reward for Land
Rent
Reward for Labour
Wage
Reward for Capital
Interest
Reward for Enterprise
Profit
Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is the nest best alternative forgone/option
Define PPC
PPC is used to show the maximum combination of two goods that can be produces at a particular time using available resources
Expand PPC
Production Possibility Curve
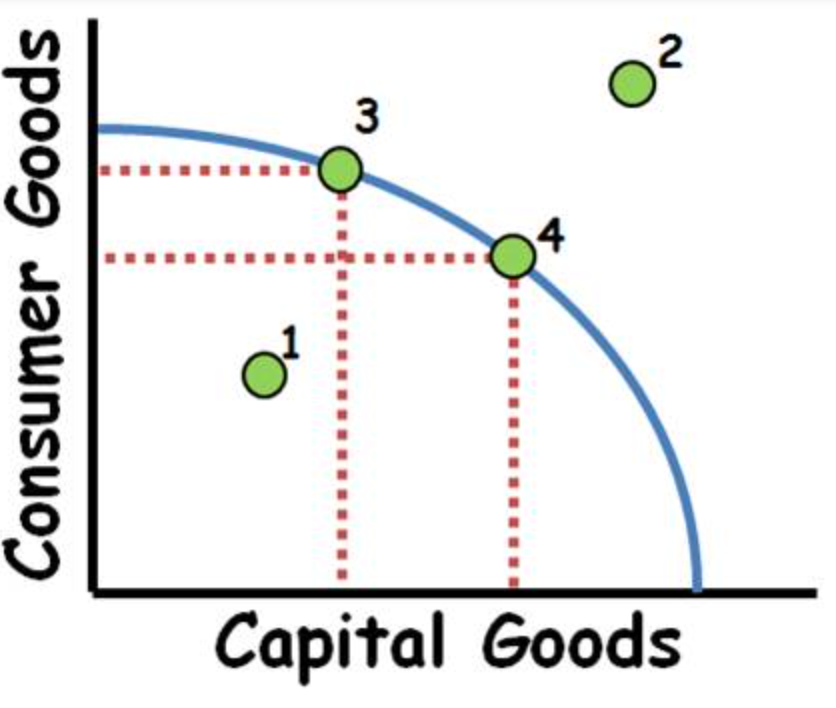
Point 1
Under efficient use of resources
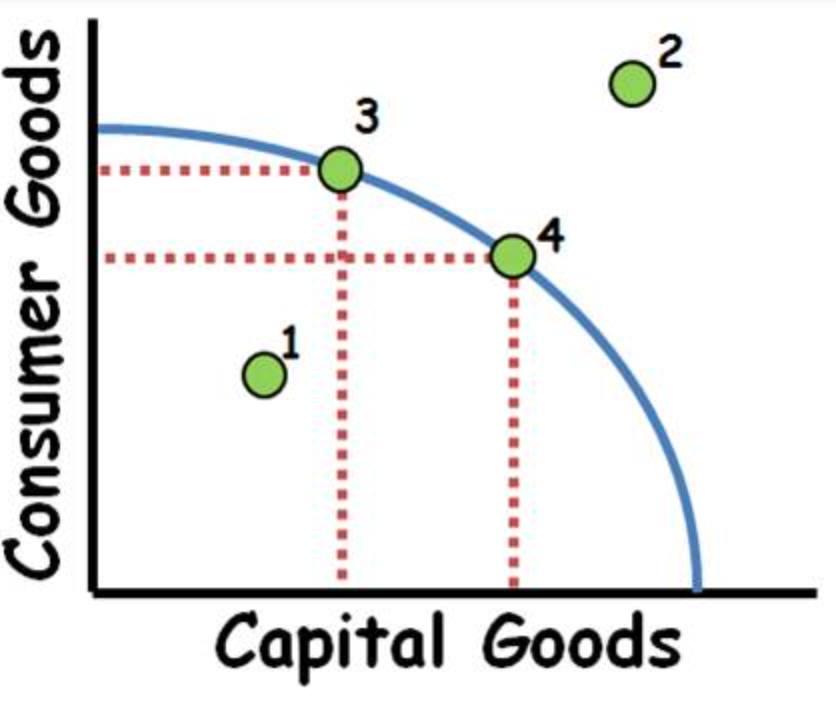
Point 4
Efficient use of resources
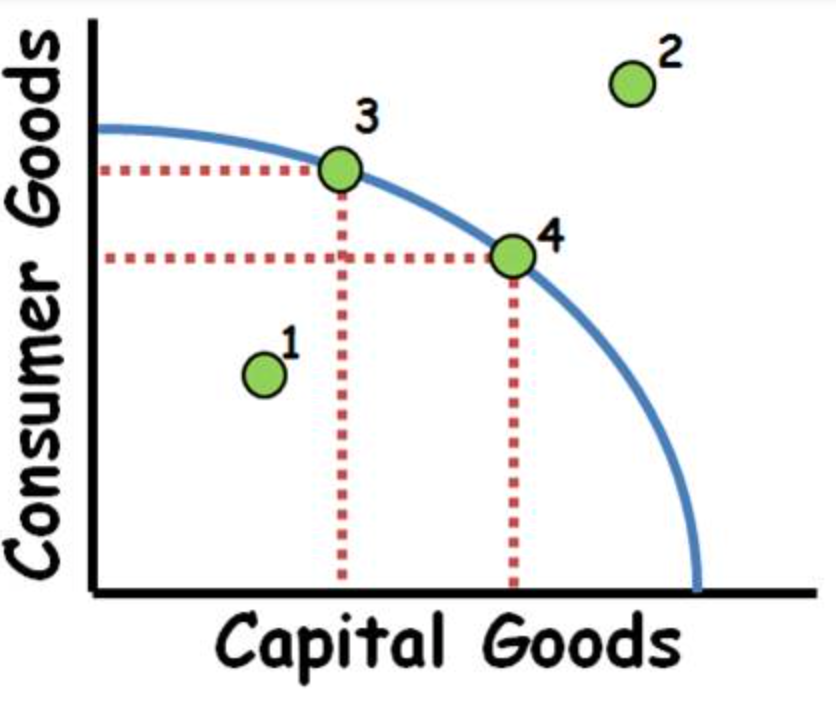
Point 2
Unattainable point
Microeconomics
The study of individual markets, microeconomic decision makers are the producers and consumers
Macroeconomics
The study of an entire economy, macroeconomic decision makers are the government
Economy
An area where people and firms produce, trade and consume goods
Market
An arrangement that enables buyers and sellers to exchange goods and services
Demand
Demand is the quantity of goods and services consumers are willing able to buy at a given price
Demand Curve
The demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between quantity demanded and the price
Law Of Demand
The higher the price the lower the quantity demanded and the lower the price the higher the quantity demanded
Non-Price determiners of Demand
Population, Price of other related goods, Income, Government, Fashions, Advertisement, Future price expectations
Non-Price determiners of supply
Cost of production, Government, Price of other related goods, Technological advancement, Quantity and Quality of factors of production
Equilibrium
Occurs when demand is equal to supply
Disequilibrium
Disequilibrium occurs when demand is not equal to supply
Price Elasticity
Price elasticity is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to the changes in price
Types of Elasticity
Elastic and Inelastic
Elastic demand
Changes in price lead to a more than proportionate change in quantity demanded
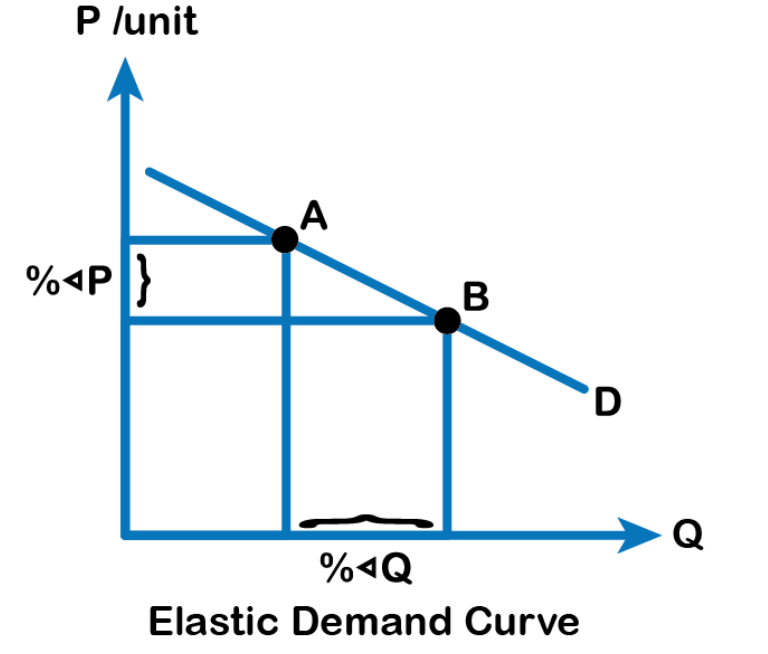
Inelastic demand
A change in price leads to a less than proportionate change in quantity demanded
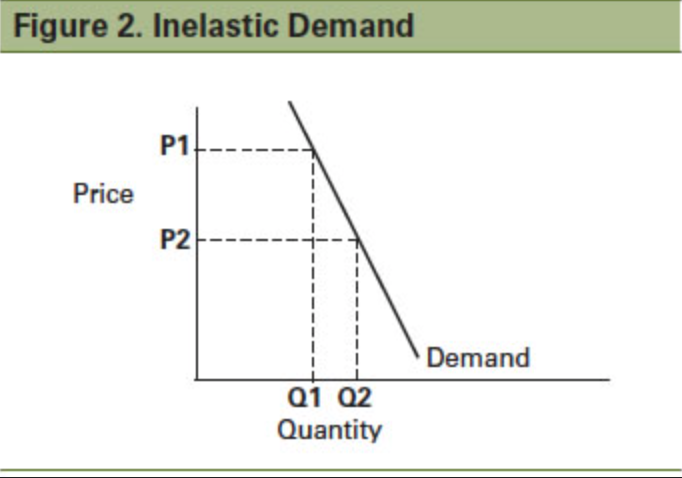
Perfectly Inelastic
PED is zero
Perfectly Elastic
PED is infinite
Calculaton of PED
Percentage change in quantity/ percentage change in price
Unitary
A change in price leads to an equal change in quantity demanded
Factors determining PED
Degree of necessity, amount of income spent on product, number or closeness of substitutes, Time period
Factors determining PES
Time period, availability of resources
Price Mechanism
Price mechanism occurs as a result of changes in price in order to have equilibrium
Revenue
Revenue is the amount of money made from sales
Revenue Formula
Price x Quantity
Market failure
Market failure occurs when a market does not efficently allocate resources
Pubic Goods
Goods that cannot be produced when left to the forces of demand and supply
Merit Goods
Goods that can be under produces hence under consumed when left to the forces of demand and supply(e.g education, healthcare)
Demerit goods
Goods that can be over produced hence over consumed when left to the forces of demand and supply(e.g cigarettes)
Monopoly
A farm that is the only supplier in the market
External cost
The negative impacts on society due to production or consumption of goods and services
Private goods
Goods that are purchased before consumption
Clearance price
When surplus and shortage are equal
Causes of market failure
Social cost exceeding social benefits, over production of demerit goods, under production of merit goods, Lack of public goods, Immobility of resources, Information failure, Abuse of monopoly powers
Mixed economic system
Public and private sector co-existing together
Public sector
A company owned by the government