Special Senses I – Vision
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
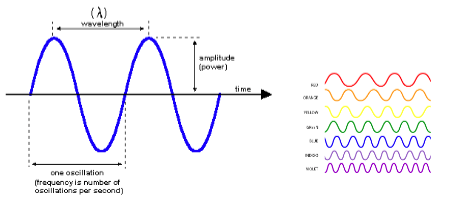
Light has a dual nature. It is both a:
- Particle (photon)
- Wave (electromagnetic spectrum)
Each photon is a packet of _______
energy
photons travels with a specific _______ and ________
wavelength and frequency
Light activates cells in the retina called
photoreceptors
how does the brain transform light into perception?
Light activates cells in the retina called photoreceptors.
Shape, motion, and color create differences in activation of photoreceptors in the retina.
The visual cortex turns these differences in activation into the visual world we perceive.
The retina is part of the which nervous system?
central NS (called "island in the periphery” beacuse it’s part of the CNS but outside of the brain)
the retina develops from which embryologic structure during development?
ventral diencephalon
The purpose of all this elegant anatomy of the eye is to project a version of the outside world onto the
retina

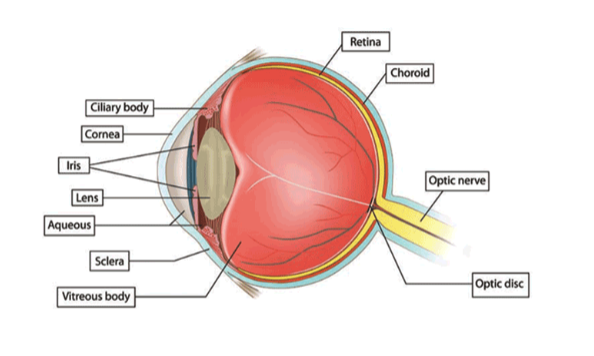
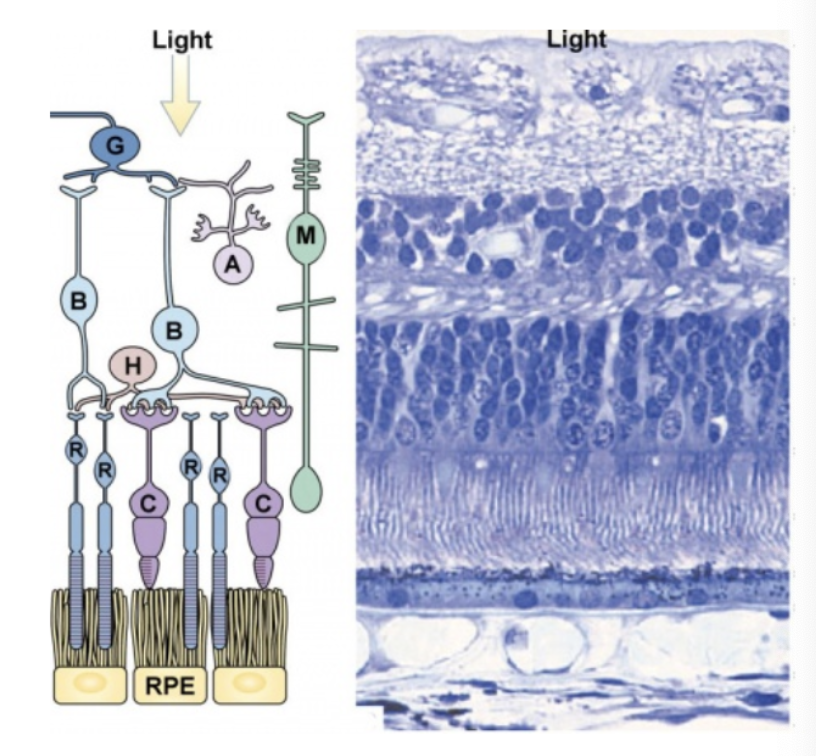
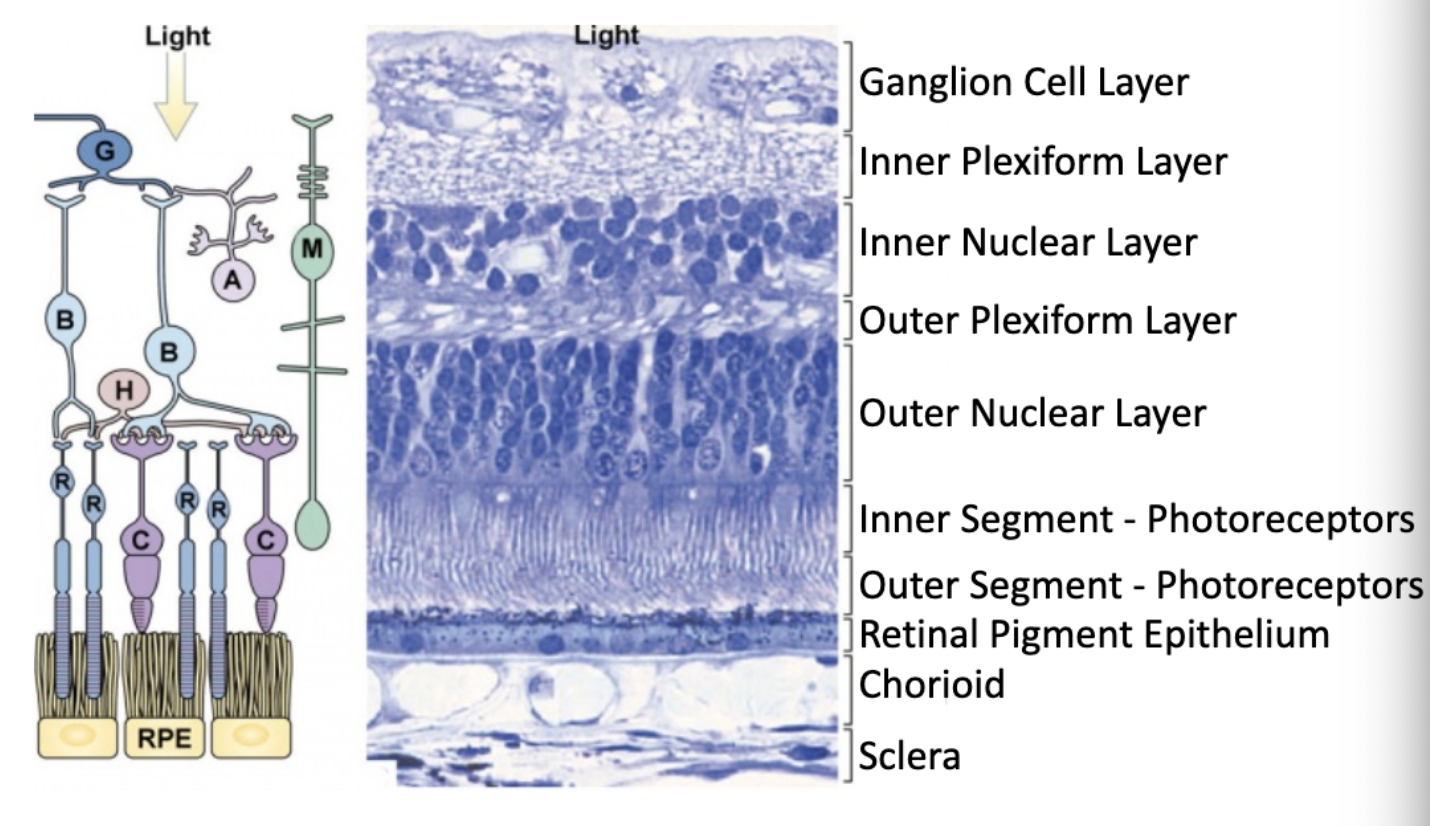
what are each of these figures depicting?
what is the order of the types of cells found in the retina epithelium structure?
ganglion cells (first thing light hits)
bipolar cells
nuclei of rods/cones
outer segments of rods/cones
pigmented layer
choroid
sclera (innermost)
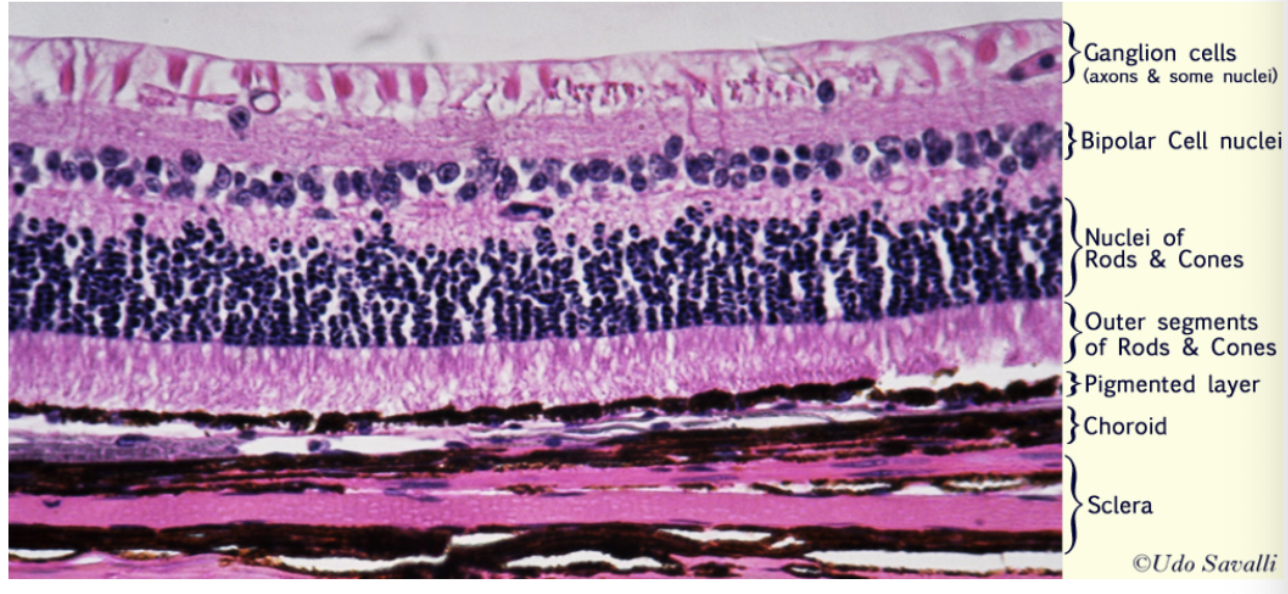
what is the function of the pigment epithelium?
absorb scattered light which:
improves quality of visual system
diminishes photo-oxidative stress
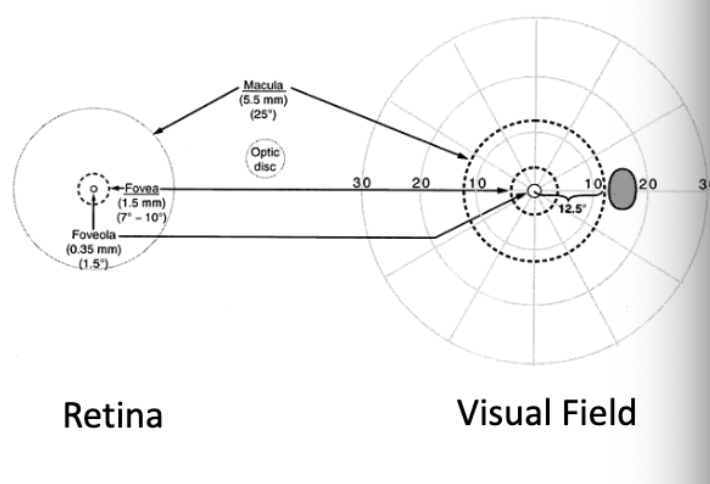
what is the area of the retina most densely packed with rods and cones and is the area of highest visual acuity?
macula
what lies at the center of the macula and is the center of the visual field?
fovea
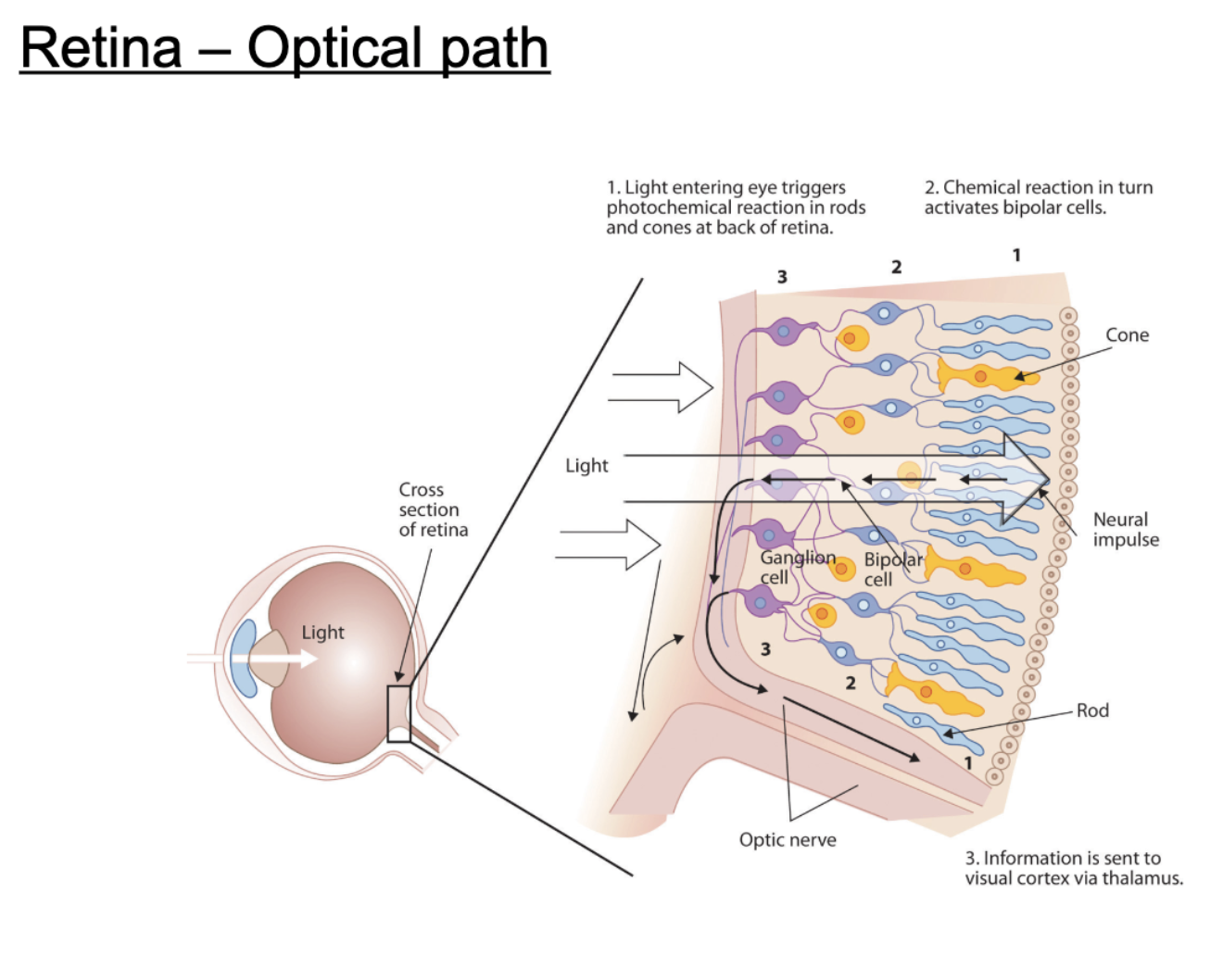
describe the optical path light takes to the retina?
light entering eye triggers photochemical reaction in rods/cones at back of retina
chemical reaction activates bipolar cells
information sent to visual cortex via thalamus
what are the neurons of the retina?
G = Retinal Ganglion Cells
B = Bipolar Cells
A = Amacrine Cells
H = Horizontal Cells
R = Photoreceptor - Rods
C = Photoreceptor - Cones
M = Müller Glia Cell
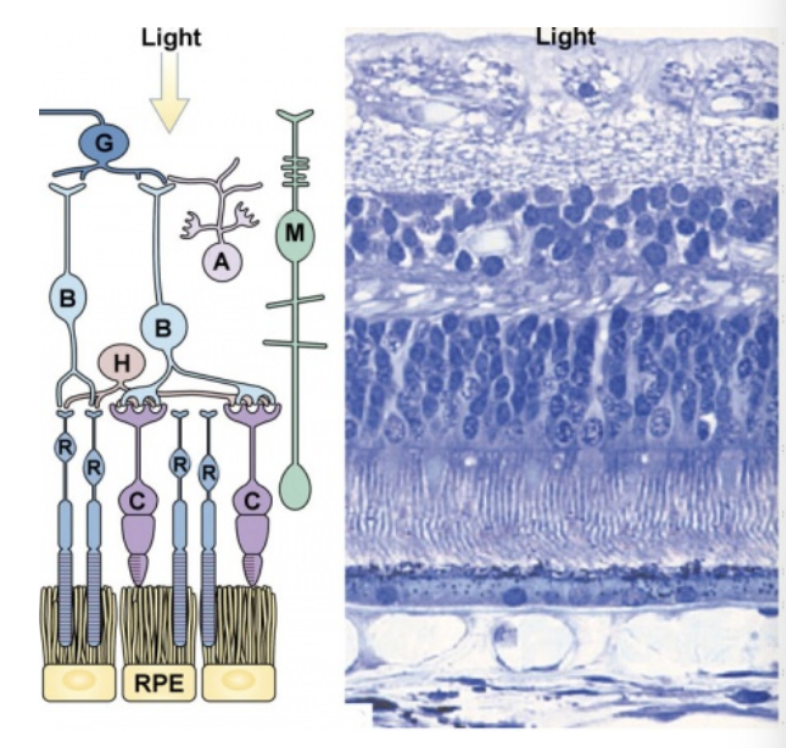
which cells are the output of the retina that take info from the retina up to optic nerve and then to thalamus?
retinal ganglion cells (last point in retina before info goes to optic nerve)
what are the layers of the retina?
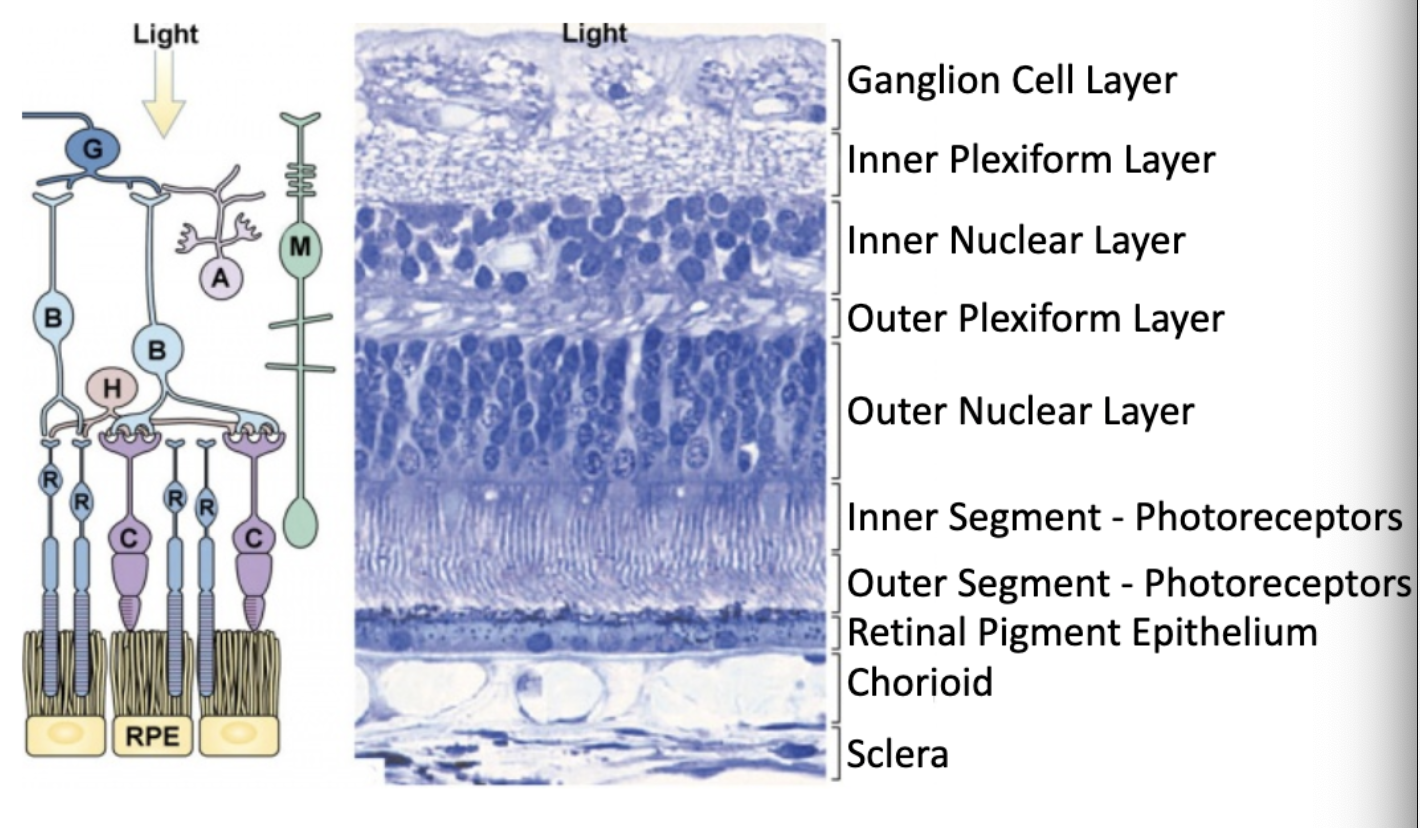
which layer of the retina contains axons of the ganglion cells and nuclei of the ganglion cells?
ganglion cell layer

which layer of the retina contains synaptic connections between ganglion cells and bipolar cells?
inner plexiform layer
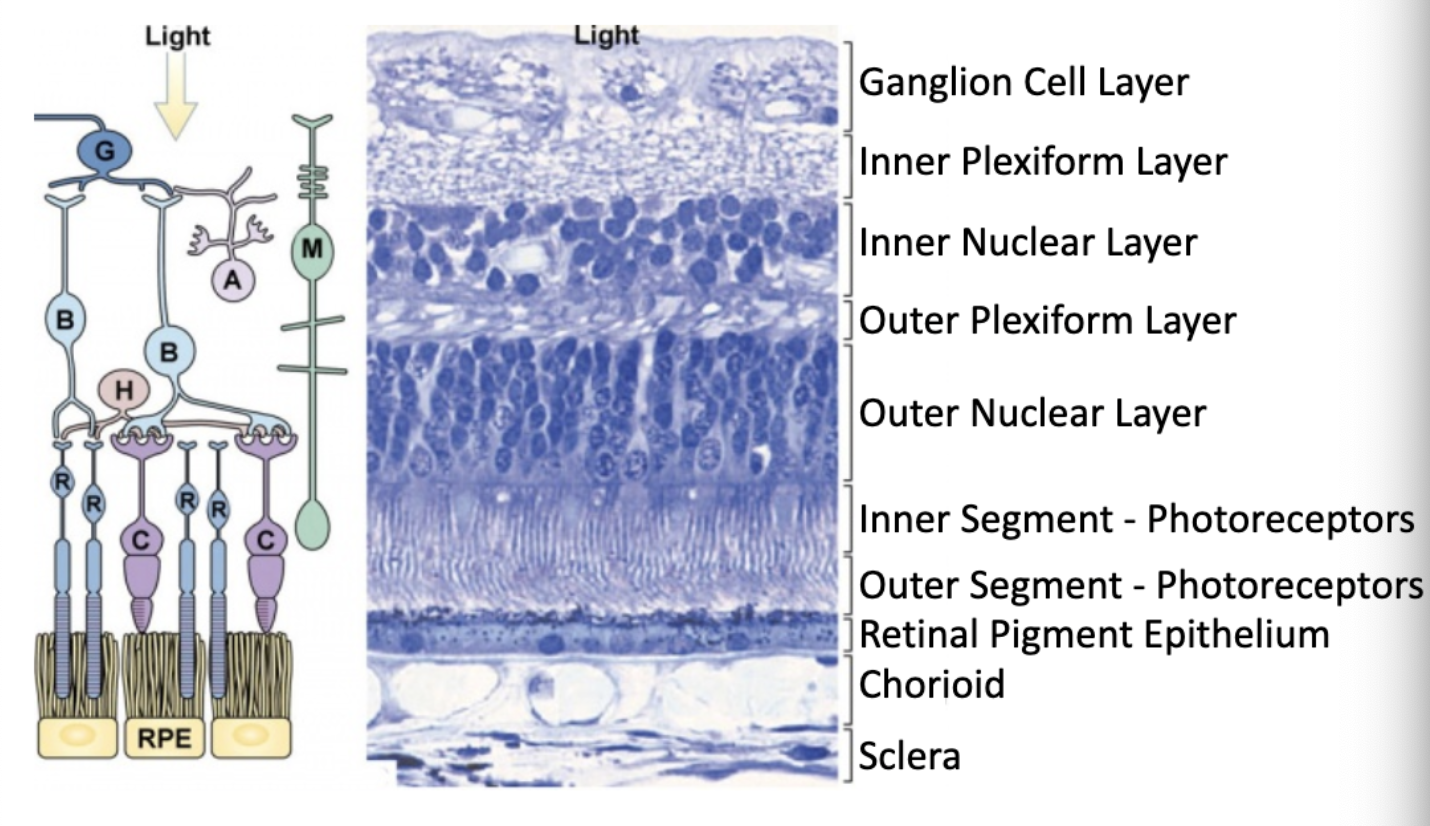
bipolar, horizontal, amocrine cells are located in which layer of the retina?
inner nuclear layer
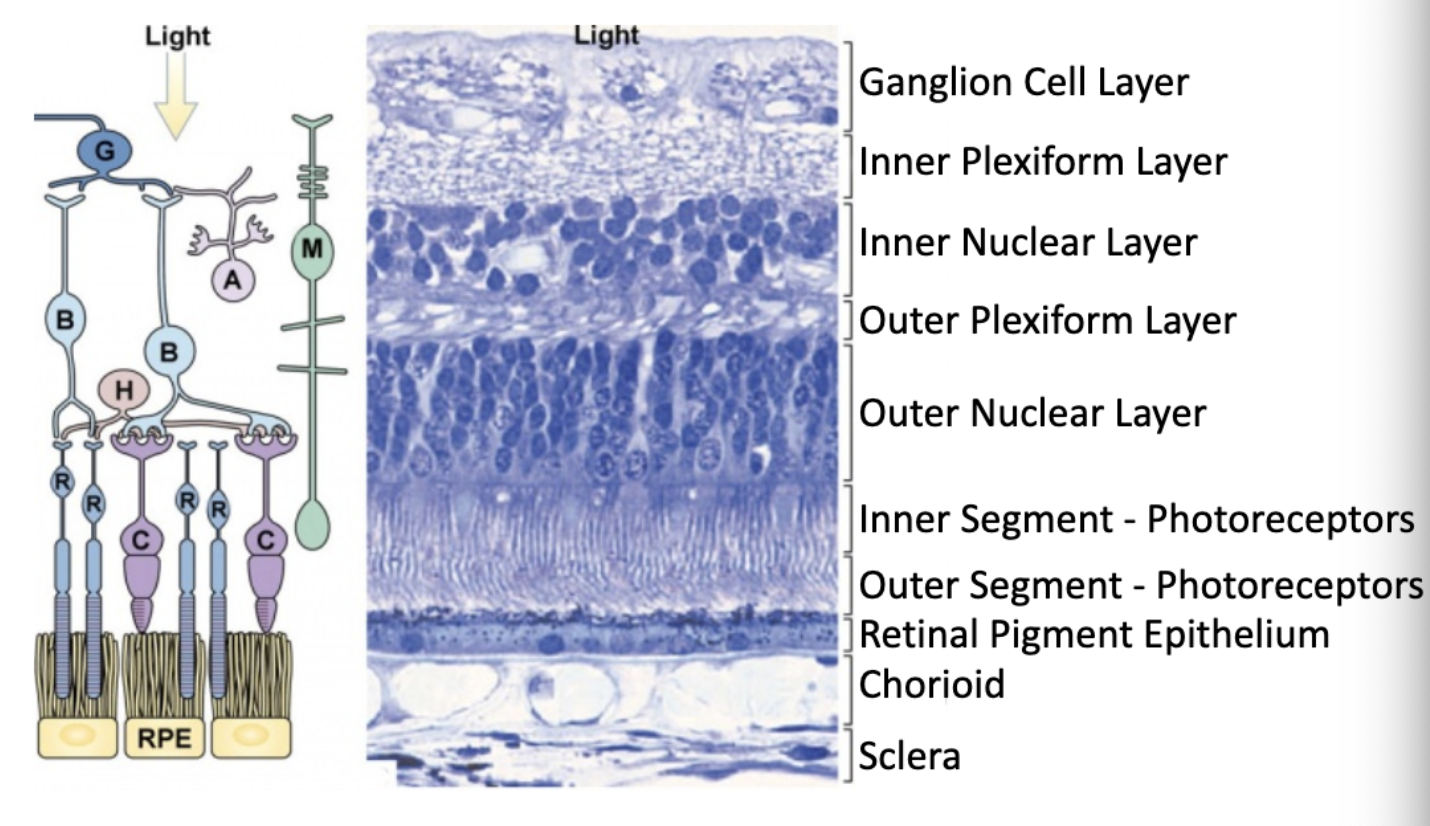
synapses from photoreceptor cells onto horizontal and bipolar cells are located in which layer of the retina?
outer plexiform layer
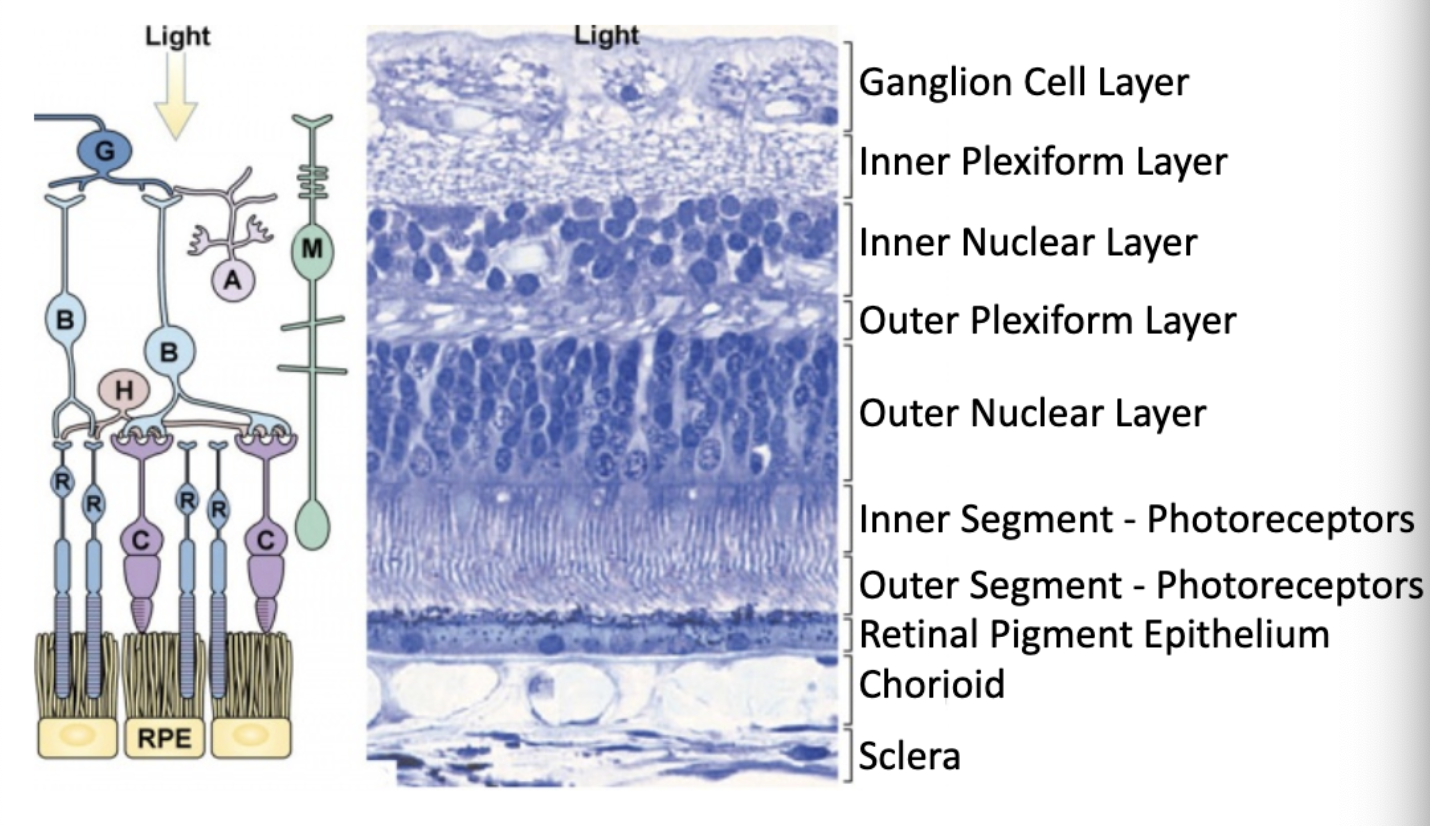
where are the nuclei of photoreceptor cells located?
outer nuclear layer

the inner and outer segments of photoreceptors are important for…?
detecting light
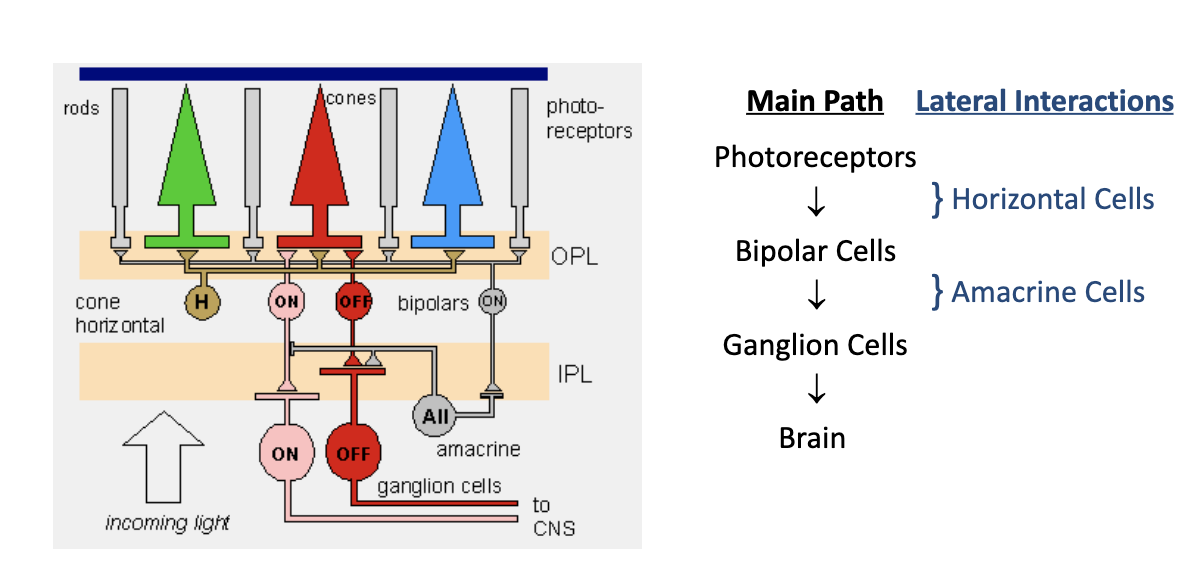
what is the main pathway of retina-neuronal connectivity?
photoreceptors → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → brain
(modulated lateral interactions with horizontal and amacrine cells as well)

describe the process of phototransduction.
Photopigments (rhodopsin in rods, opsins in cones) absorb photons, causing a conformational change in the retinal molecule from 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal.
This change activates G-protein transducin, which then stimulates phosphodiesterase (PDE).
PDE breaks down cGMP, leading to closure of Na⁺ channels.
With Na⁺ channels closed, the photoreceptor cell hyperpolarizes, reducing the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate at the synaps (less active cell)
The reduction in glutamate release modulates bipolar cells, which in turn affect ganglion cells, sending visual information via the optic nerve to the brain.
what is the opsin protein containing retinal molecule involved in phototransduction?
rhodopsin
signals during phototransduction are transduced by …?
G-proteins
during phototransduction, when at rest, are sodium channels kept open or closed?
open (by high levels of cGMP)

Light activates signal transduction leading to …? (during phototransduction)
decreased cGMP and closing of Na+ channels.
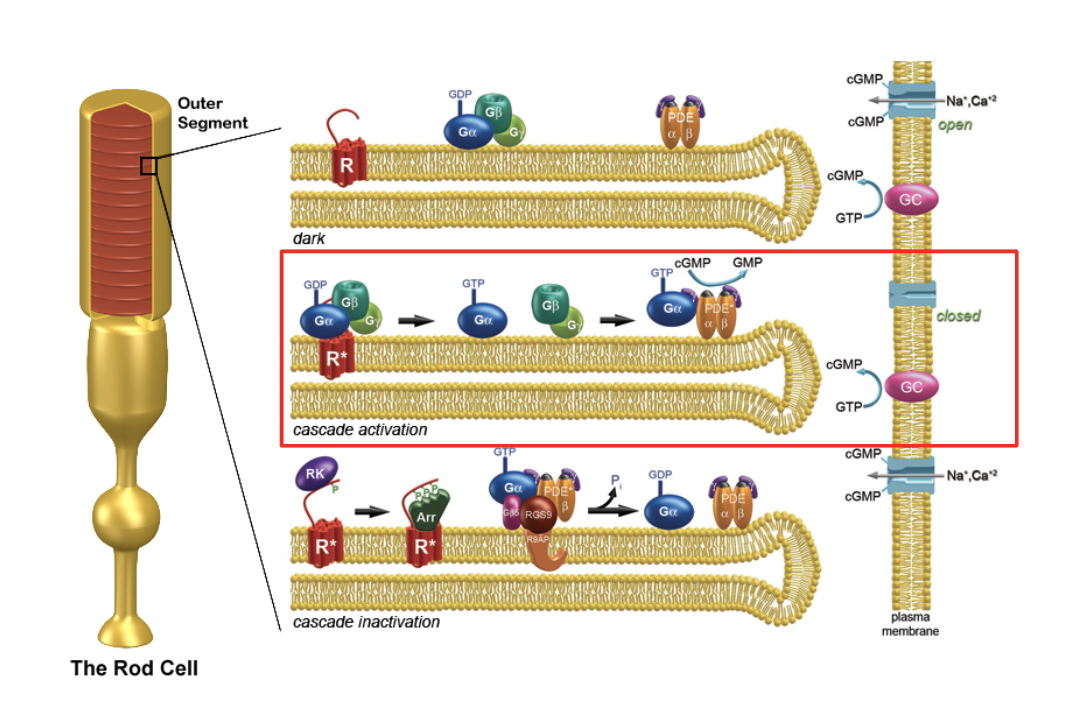
t/f: a single photon can activate multiple phosphodiesterases which can each break down cGMP. This is called signal amplification via G-proteins.
true
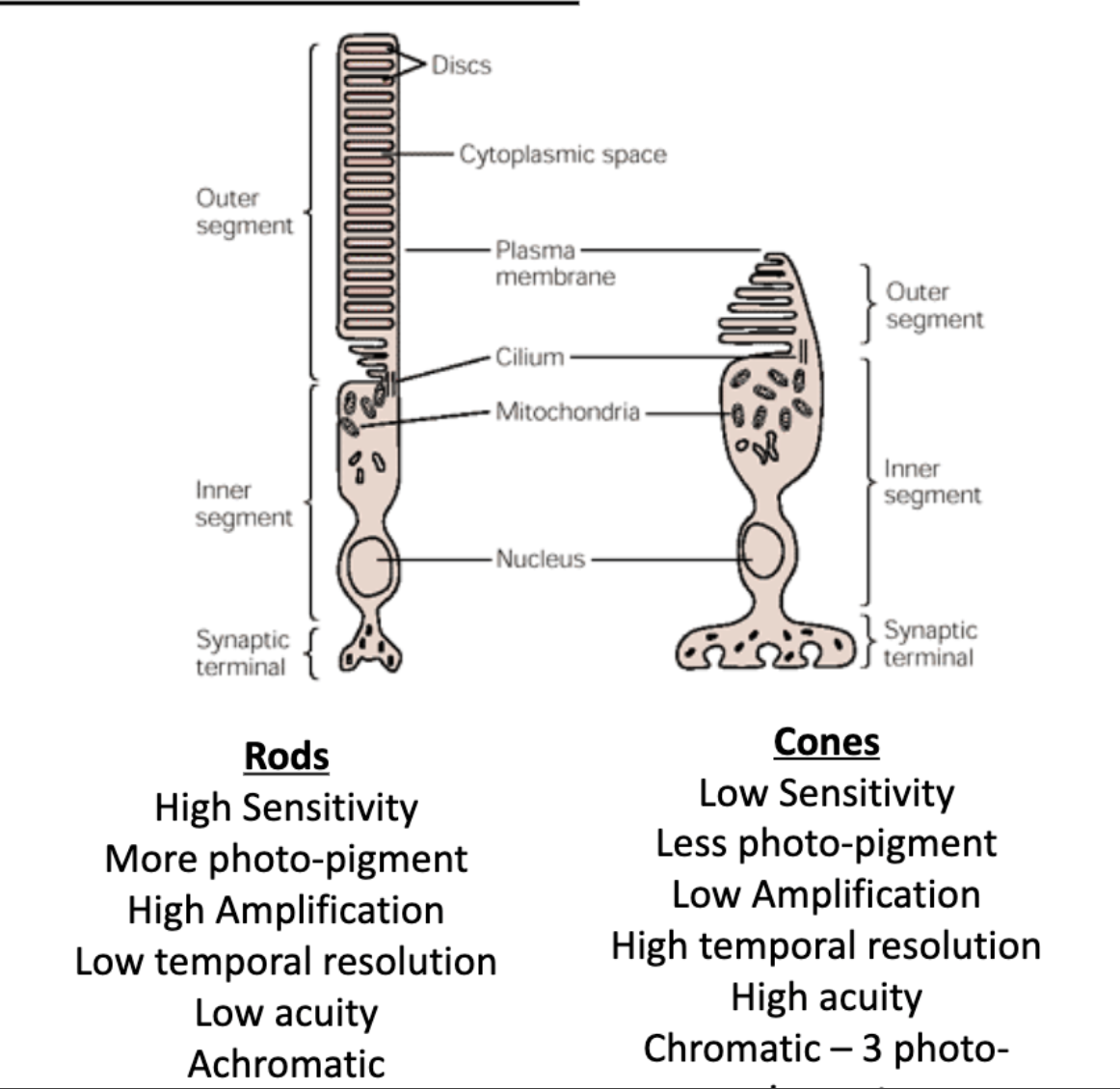
Rods/Cones concentrate in the fovea.
Rods/Cones are seen at a greater distance from the fovea.
Cones concentrate in the fovea, rod are seen at a greater distance from the fovea
Outer segments are fully replaced every __ days. Old membrane is shed and degraded by the …?
12
pigment epithelium
rods vs cones: sensitivity
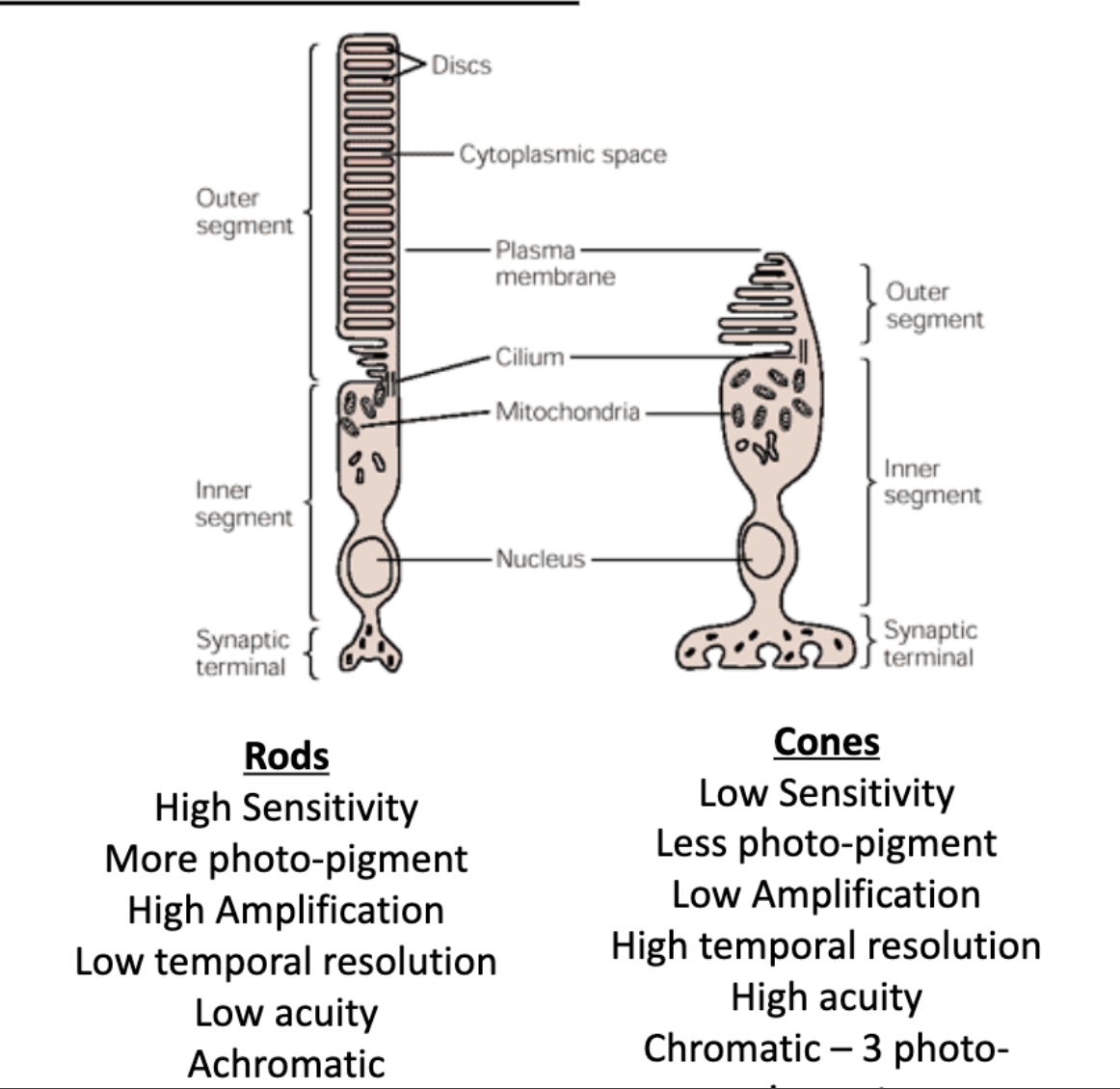
rods vs cones: amount of photo-pigment
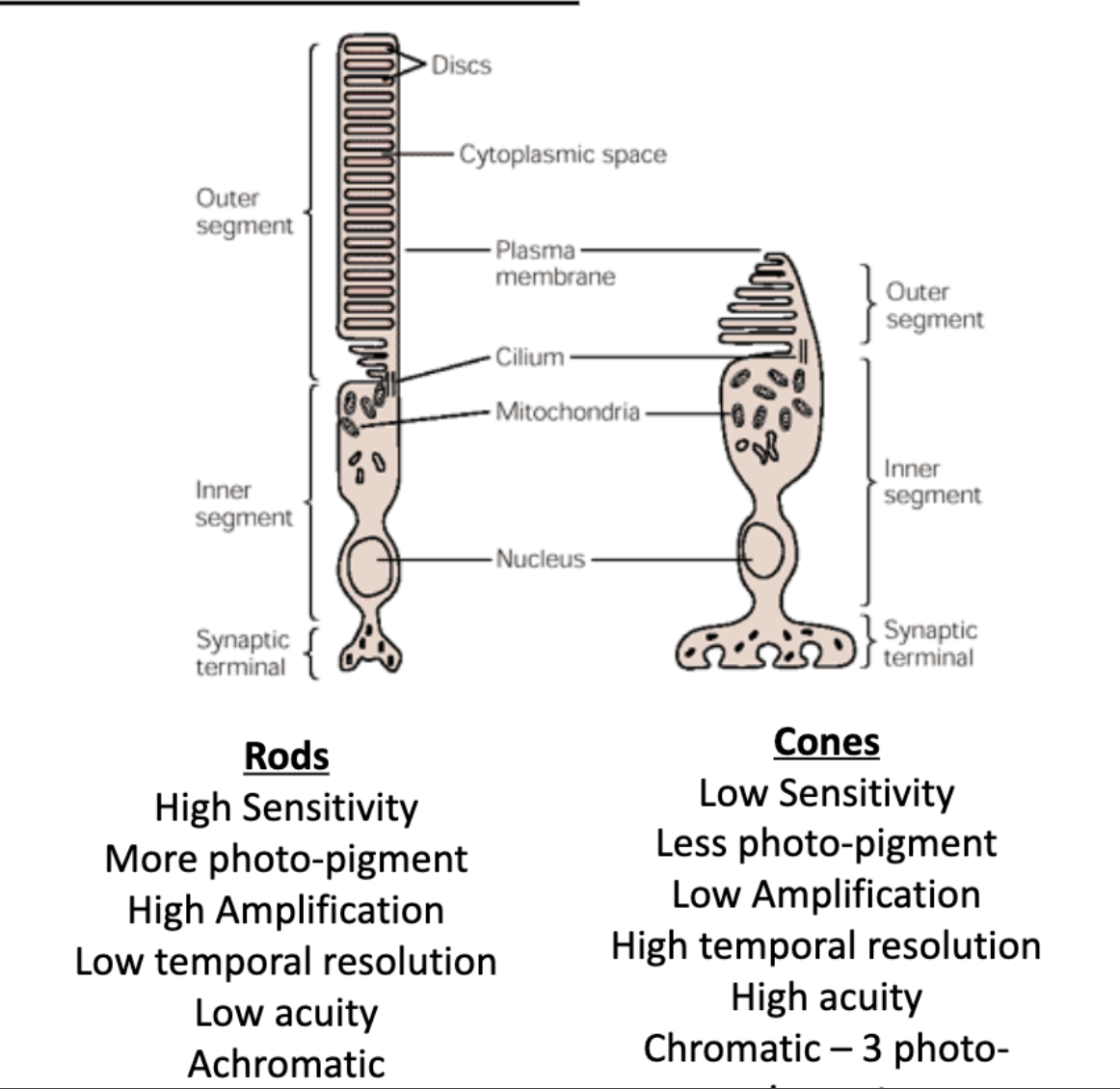
rods vs cones: amplification

rods vs cones: temporal resolution
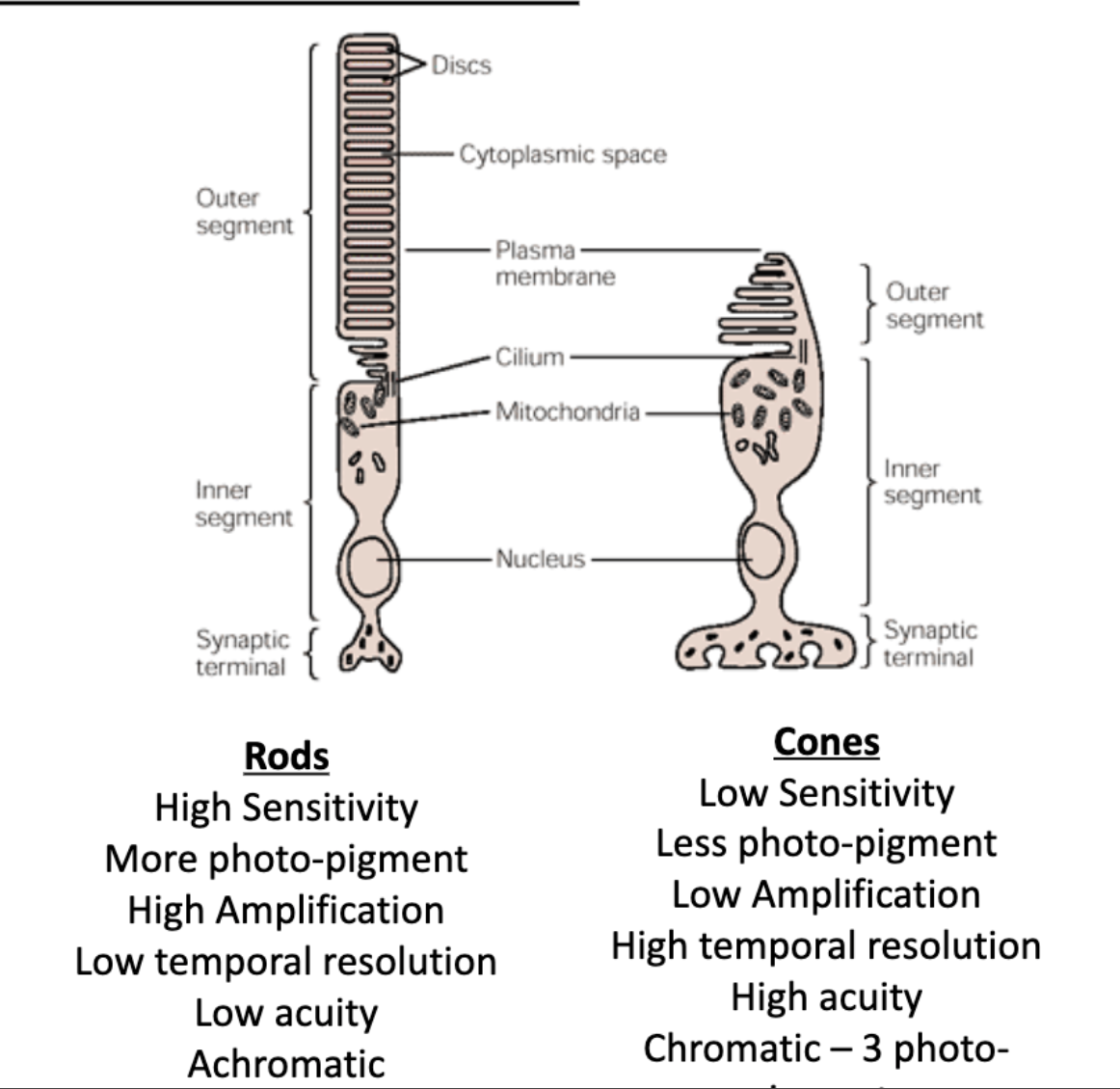
rods vs cones: acuity
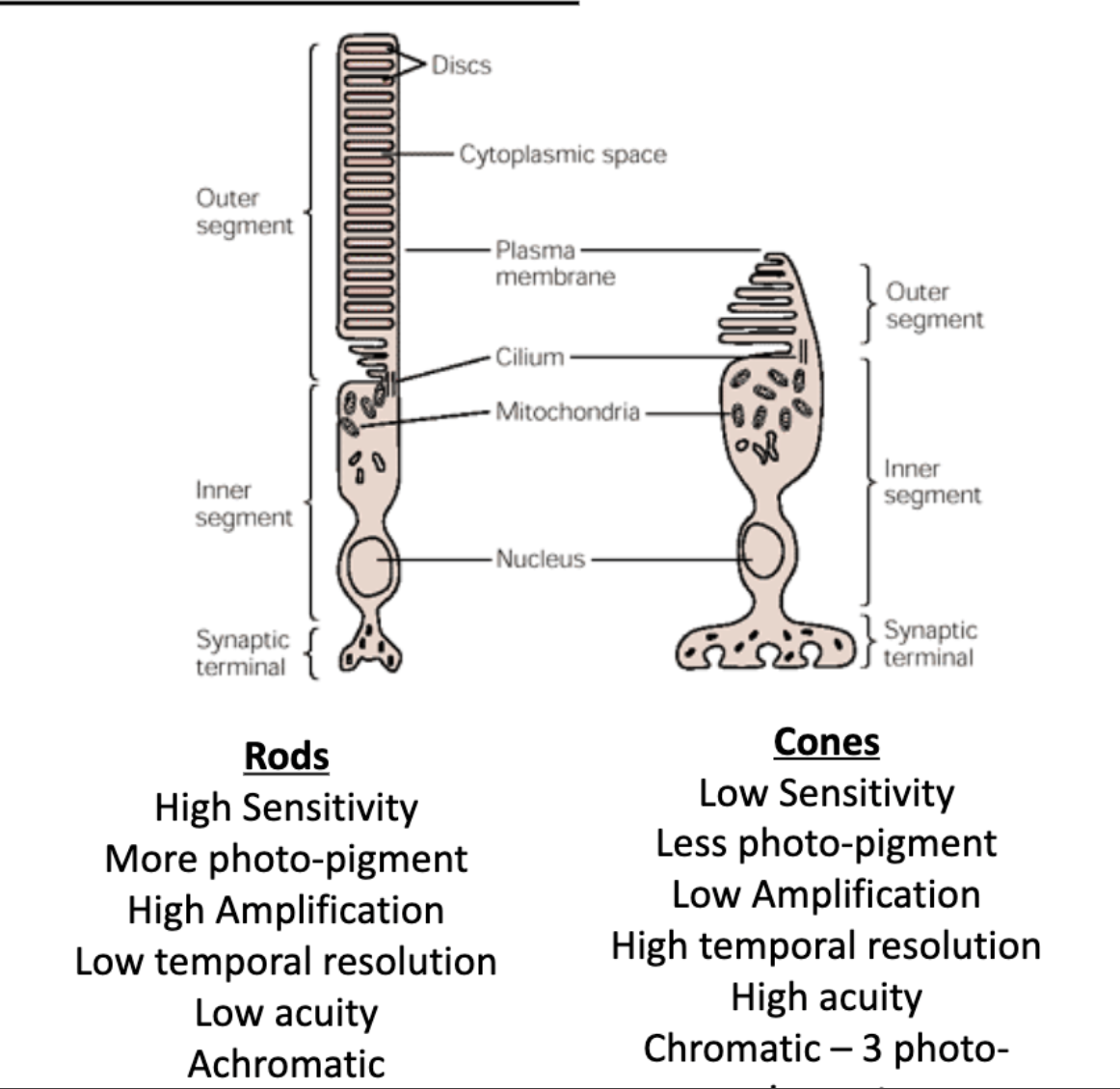
rods vs cones: chromativity
The optic nerves run to the optic chiasm where ≈ % cross to the contralateral side. The remaining ≈ % remain ipsilateral
60%
40%
Axons leave the retina via the optic disk and form the …?
optic nerve
The axons that cross to the contralateral side and come from the optic nerve come from the _______. The axons that stay ipsilateral come from the ________.
nasal retinal
temporal retina
describe the central visual pathway.
axons leave retina via optic disk to form optic nerve.
optic nerve runs to optic chiasm
60% cross to contralateral side (axons from nasal retinal)
40% remain ipsilateral (axons from temporal retinal)
visual info flows into lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus
retinal ganglion cells synapse onto cell bodies in RGN of thalamus
RGN neurons send projections to primary visual cortex
signals converted into our perception of visual world
The _______ is a relay station on the way to the visual cortex
thalamus
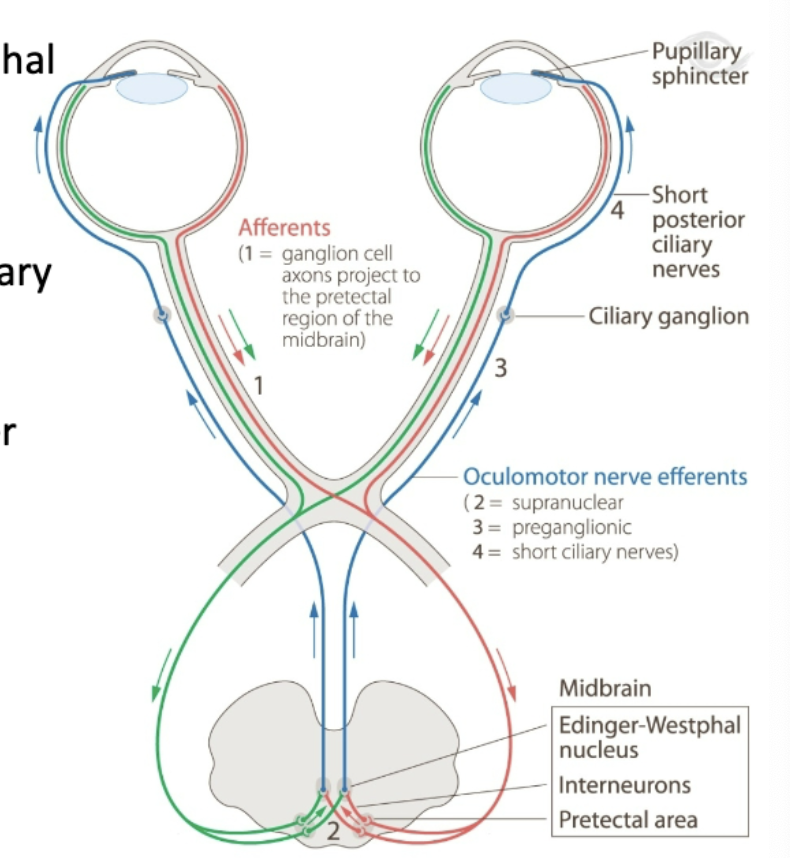
describe the pupillary light reflex pathway.
retinal ganglion cells synapse directly in midbrain onto interneurons in Edinger-Westphal nucleus
neurons project out of Edinger-Westphal nucleus and synpase on motor neurons in ciliary ganglion
circuit allows pupil to change diameter in response to light
describe the circadian rhythm pathway.
retinal ganglion cells synapse directly onto GABAergic cells in super-chiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of hypothalamus
SCN send projections throughout brain to pass along info about day/night and sleep/wake cycle
The _____ is a master clock that entrains the length and synchronization of biological clocks.
super-chiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Individual with optic nerve disease are 20X more likely to have…?
disruptions in their sleep cycle compared to normally sighted people
each side of the visual field is processed in the…?
lateral geniculate (The projections from each eye segregate into different layers of the LGN)
what is retinotopic representation?
Visual space is mapped out in the cortex
Larger areas are devoted to the fovea and macula
There are more photoreceptors and more visual acuity in these areas

simple cells in the visual cortex respond best to…? and derive information from a small sub-portion of the retina.
stationary bars or edges
what is steropsis?
sensation of depth that arises from viewing nearby objects with two eyes
steropsis is caused by…?
the disparity in the retinal position for the object relative to the fixation point
The fundamental organization of the visual cortex is the column. What are the types of columns?
Ocular dominance
preferred orientation
color
motion
Cells of all layers of the cortex along a line _________ to its surface will share characteristics
perpendicular