Tumors, Cancers, and Lesion Description
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Question-and-Answer flashcards reviewing lesion description, tumor terminology, and key facts about squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and osteosarcoma.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
When describing an oral or skin lesion, which five features should be documented?
Color, contents/inside material, size, texture/shape, and location.
In medical terminology, what does the suffix “-oma” generally signify?
That the lesion is a tumor (usually benign unless otherwise noted).
What is the general definition of a tumor?
A swelling or neoplasm; an abnormal growth of tissue.
What is the primary difference between a benign and a malignant tumor?
Benign tumors remain localized and do not spread; malignant tumors invade surrounding tissues and can metastasize to distant sites.
What is the name for a benign tumor composed of fat tissue?
Lipoma.
What is a benign tumor of the salivary glands called?
Adenoma.
What term describes a benign tumor arising from bone?
Osteoma.
What is a benign tumor of skeletal (striated) muscle called?
Rhabdomyoma.
What do we call a benign tumor of squamous epithelium that often presents as a wart-like growth?
Papilloma.
What is the term for a malignant tumor originating from epithelial tissue?
Carcinoma.
What name is given to a malignant tumor of connective tissue origin?
Sarcoma.
What is the malignant tumor of melanocytes called?
Melanoma.
Which cancer is the most common primary malignancy of the oral cavity?
Squamous cell carcinoma.
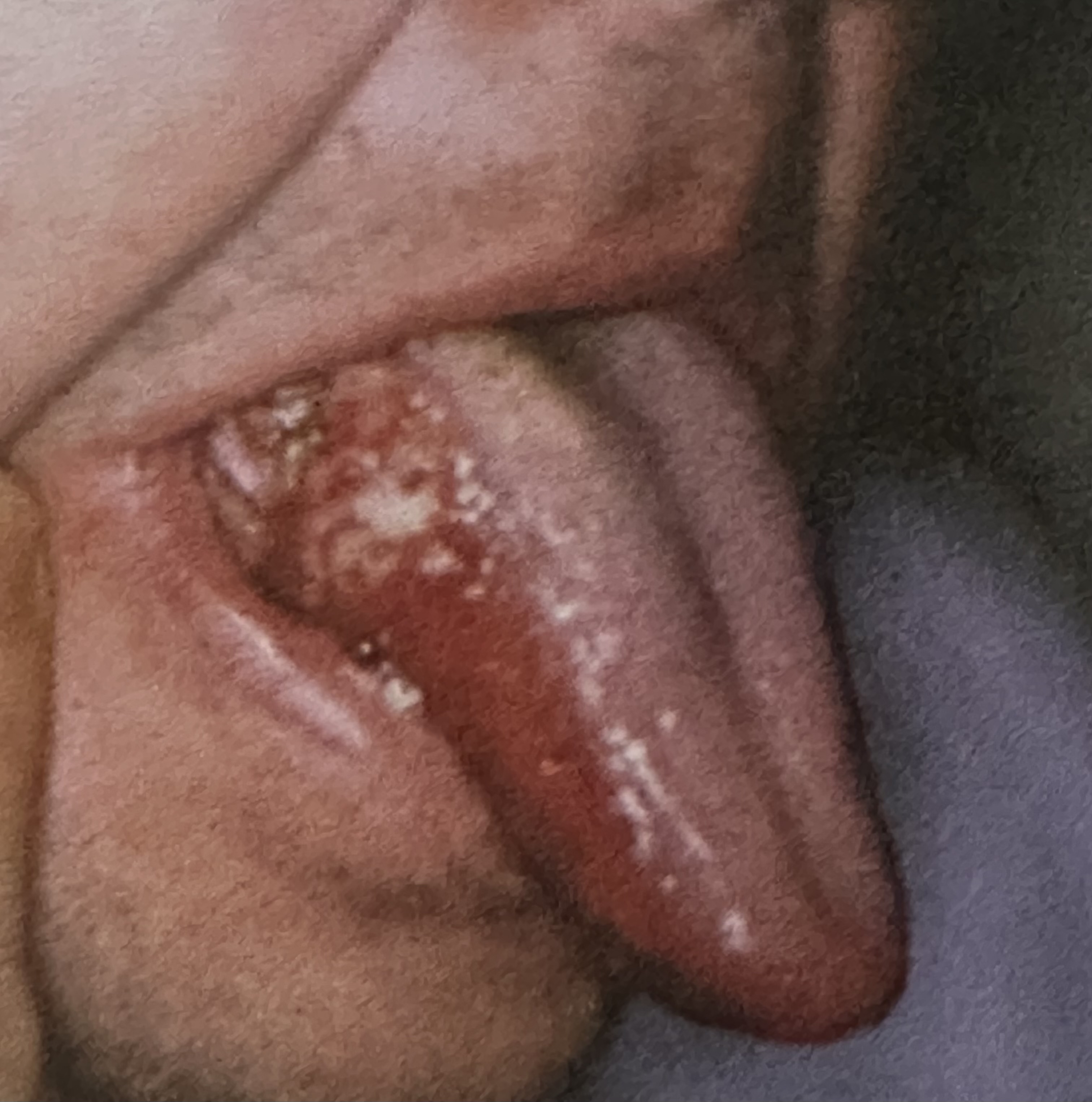
Early oral squamous cell carcinoma may appear clinically as which three lesion types?
Leukoplakia (white patch), erythroplakia (red patch), or a speckled red-and-white lesion.
Which two lifestyle habits together greatly increase the risk of developing oral squamous cell carcinoma?
Alcohol consumption combined with tobacco use.
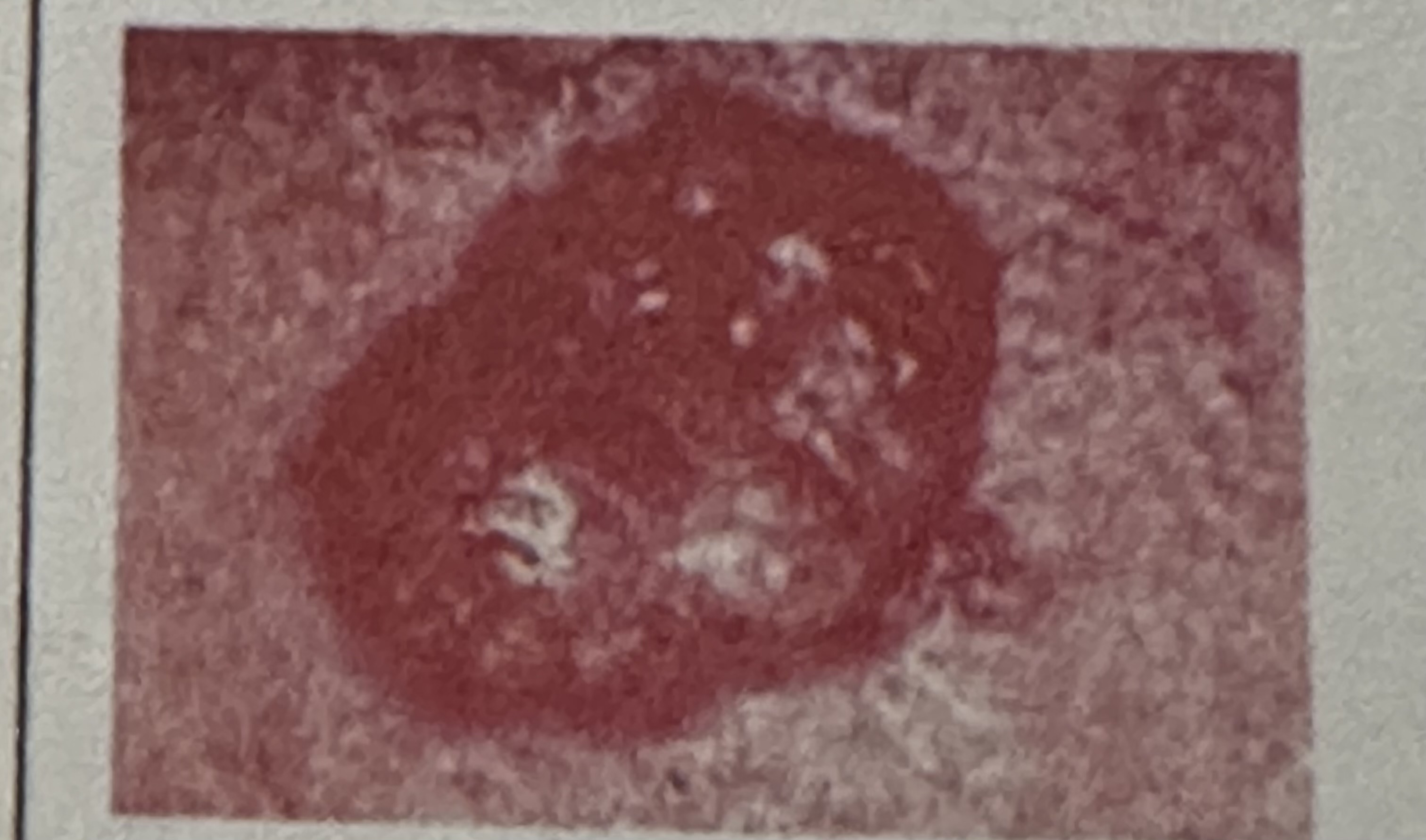
Basal cell carcinoma arises from which specific skin layer and is predominantly linked to what environmental factor?
It originates from the basal (deepest) layer of the epidermis and is strongly associated with excessive ultraviolet (UV) sun exposure.
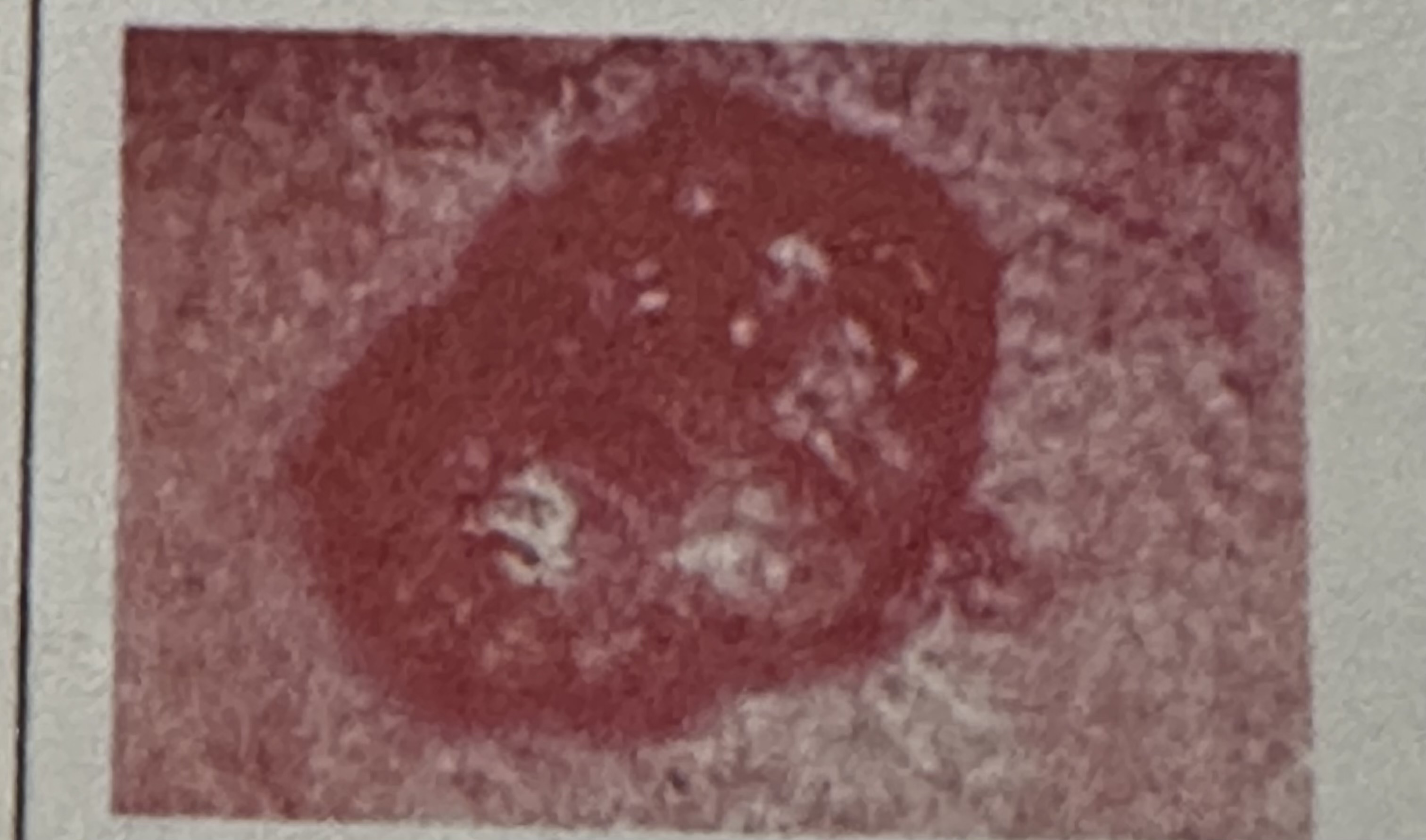
Clinically, how is basal cell carcinoma of the skin typically described?
As a non-healing ulcer with rolled borders.
Why is cutaneous melanoma considered more dangerous than most other skin cancers?
Because it can spread (metastasize) to other organs rapidly if not detected and treated early.
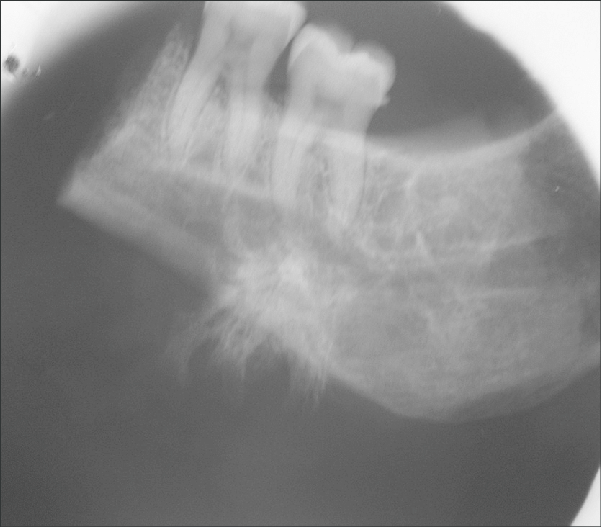
Which classic radiographic feature may be seen with osteosarcoma of the jaws or long bones?
A sunburst (spiculated) radiating bone pattern.
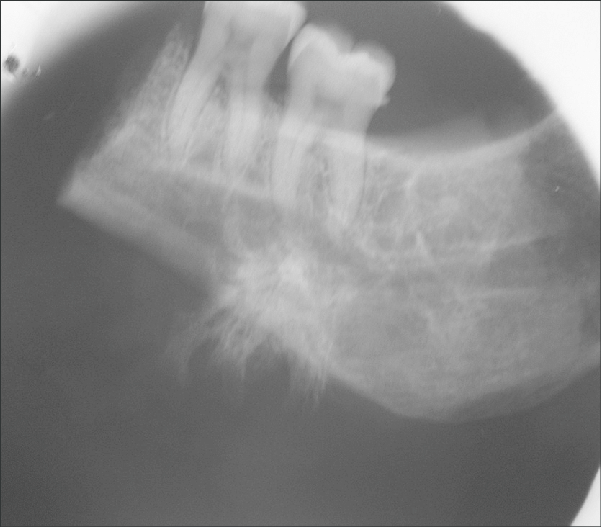
Osteosarcoma most commonly affects which two age groups?
Teenagers and the elderly.