HL DT - Topic 4 (part 1)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Physical Properties
characteristics of materials that can be identified through non-destructive testing, describes the state of materials
Mass
the amount of matter contained in a material
Weight
a measure of the force applied by a material due to gravity
Volume
the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed in a material
Density
the mass per unit volume of a material
Electrical Resistivity
a material's ability to conduct electricity
Thermal Conductivity
the rate at which heat is transferred through a material at a specific temperature
Hardness
a material's resistance to penetration or scratching
Mechanical Properties
how a material performs/reacts to applied force
Tensile Strength
a material's ability to withstand pulling forces
Compressive Strength
a material's ability to withstand squashing forces
Stiffness
an elastic body’s resistance to deflection
Toughness
the ability of a material to resist cracks
Ductility
the ability of a material to be drawn into a wire
Elasticity
the ability of a material to return to its original shape after being deformed
Plasticity
the ability of a material to change shape permanently under stress
Strain
the change in length caused by an applied force divided by the original length
Young's Modulus
a measure of stiffness for an elastic material, equal to stress divided by strain
Aesthetic Characteristics
aspects of a product relating to taste, texture, smell, and appearance
Smart Materials
materials that have properties that change when subjected to external stimuli
Piezoelectricity
a material that generates an electrical charge when deformed
Shape Memory Alloy
metals that can return to their original shape after being deformed (used in braces, stents in arteries, etc)
Photochromicity
a material that changes color in response to light (used in sunglasses/glasses)
Magneto Rheostatic
a fluid that undergoes a drastic change in viscosity when exposed to a magnetic field
Electro Rheostatic
a fluid that undergoes a drastic change in viscosity when exposed to an electric field
Aluminium Extraction
the process of extracting aluminium from bauxite ore through electrolysis (very costly and needs lots of energy)
Steel Extraction
the process of producing steel using a blast furnace, allows for recycling (oxygen furnace and electric arc furnace)
Grain Size
metals are crystalline structures with individual grains, grain size is determined by heat treatment
Alloy
a mixture that contains at least one metal
Work Hardening / Strain Hardening / Cold Working
the process of increasing a metal's hardness through plastic deformation
Tempering
increasing the toughness of a ferrous metal by heating it and allowing it to cool in air (increases ductility and decreases hardness/brittleness)
Super Alloys
alloys that exhibit good mechanical strength, resistance to thermal creep, surface stability, and resistance to corrosion
Creep
the gradual extension of a material under a constant force over time, dependent on temperature
Ferrous Metals
metals that contain iron (iron, stainless steel, mild steel, high speed steel)
Non-Ferrous Metals
metals that do not contain iron (brass, copper, tin, zinc, zluminium)
Hardwood (tree, properties, forest, eg)
wood from deciduous trees
good strength, hardness, and durability
found in tropical and temperate forests
beech, teak, oak
Softwood (tree, properties, forest, eg)
wood from coniferous trees
less dense and prone to water damage and color changes
found in temperate forests
pine, spruce, redwood
Air Seasoning
the process of drying fresh timber in the open or a large shed to reduce moisture content (less costly, but little control over drying process)
Kiln Seasoning
the process of drying fresh timber in a temperature and humidity controlled chamber system (expensive)
Man-Made Timber
made by binding strands or particles of fiber/veneers/boards together
Laminate Timber
timber made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together (grain rotated 90 degrees every layer)
Particle Board
made from wood chips and synthetic resin
Finishing Timbers
using additive preservatives to improve a timber’s natural resistance and improve durability
Glass
material made by rapidly cooling a mixture of sand, soda, and lime
Thermal Shock
cracking or shattering of glass due to rapid temperature changes
Tempered/Toughned Glass
glass that is heated to its almost melting point then chilled to make it impact resistance
Plastics
synthetic materials derived from natural resources, such as crude oil
Thermo Plastics
plastics that can be remolded when heated (eg. polypropylene, HDPE, HIPS, ABS, PET, PVC)
Thermosetting Plastics
plastics that cannot be remolded after their initial heat-forming (polyurethane, epoxy resin, melamine resin)
Bioplastics
plastics derived from renewable sources, such as vegetable fats/oils, corn starch, microbiota, etc
Fibers
elongated hair-like strands used in textiles
Weaving
the process of forming a sheet like material by interlacing long threads passing in one direction with others at right angle (done on a loom)
Knitting
the process of creating fabric by interlocking loops of yarn
Felting
the process of matting tarn together to create fabric
Composites
materials made from two or more different materials combined to enhance properties
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
A manufacturing process controlled by computers for precision.
Additive manufacturing
Techniques that add material to create a product, such as 3D printing.
Subtractive manufacturing
Techniques that remove material to create a product, such as cutting or drilling.
Stress
force on a material divided by the cross-sectional area of the material
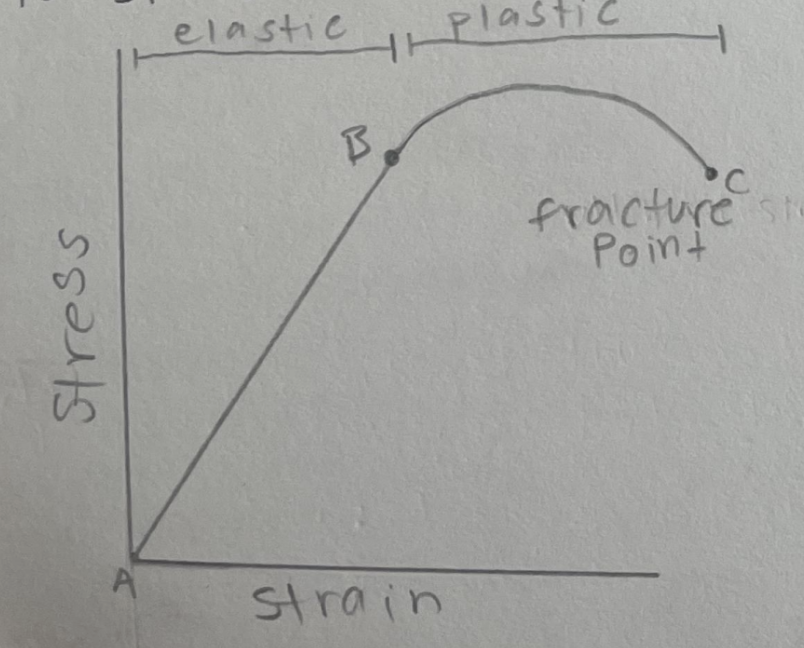
Points on a Stress/Strain Graph

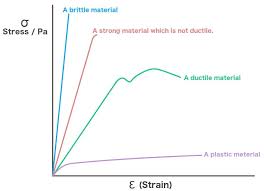
Materials on a Stress/Strain Graph
Small Grain Size
created by quick cooling, higher density/brittleness/hardness
Large Grain Size
created by slow cooling, higher toughness/ductility/flexibility
Timber
a renewable building material that is used directly from the tree after being seasoned
Air Seasoning Advantages
cheap
no equipment
small labour cost
uses little energy
environmentally friendly
Air Seasoning Disdvantages
takes longer
large space needed
Kiln Seasoning Advantages
kills insects
little stacking space
controllable
dries quickly
defects can be controlled
Kiln Seasoning Disadvantages
uses lots of energy
expensive
produces weaker timber
requires a skilled operator
Uses of Recycled Wood
used in panel boars, animal beddings, equestrian landscaping, etc
Characteristics of Glass
amorphous (solid but not crystalline), transparent, chemically inert, non-toxic, brittle, hard, electrical insulator, cheap, biocompatible
Soda Glass
soda lime composition that is cheap but very brittle and has poor thermal shock resistance
Pyrex Glass
glass with improved thermal shock properties and is non potus (reduces cross contamination when cooking)
Laminate Glass
two thin sheets of glass with a sheer of plastic glued in between (plastic retains fragments when it shatters, making it safer)
Recycling Glass
glass products can be broken up and melted back down, not degradation in the quality in this process
Monomer
a relatively small molecule
polymer
monomers joined together (all plastics are polymers)
Natural Plastics
naturally occurring materials that can be shaped and moulded by heat (eg. cellulose amber)
Semi-Synthetic Plastics
made from natural resources but have been mixed with other materials (eg. cellulose acetate)
Synthetic Plastics
made from breaking down/cracking carbon based materials
Natural Fiber
from a plant or animal (silk, cotton, wool)
Synthetic Fibers
created by a chemical process (nylon, polyester, lycra)