protists
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Features of protists
Have a true nucleus, can be unicellular or multicellular, heterotroph or autotroph
Example of a unicellular protist
amoeba
Example of a heterotrophic protist
amoeba
Example of a multicellular protist
algae
Example of a autotrophic protist
green algae
Where does amoeba live?
Fresh water e.g. pond
What do you need to see amoeba?
Microscope (microscopic)
Amoeba structure
Cytoplasm surrounded by a cell membrane, they have no fixed shape, have pseudopodia (false feet), contractile vacuole
Draw the structure of an amoeba
...
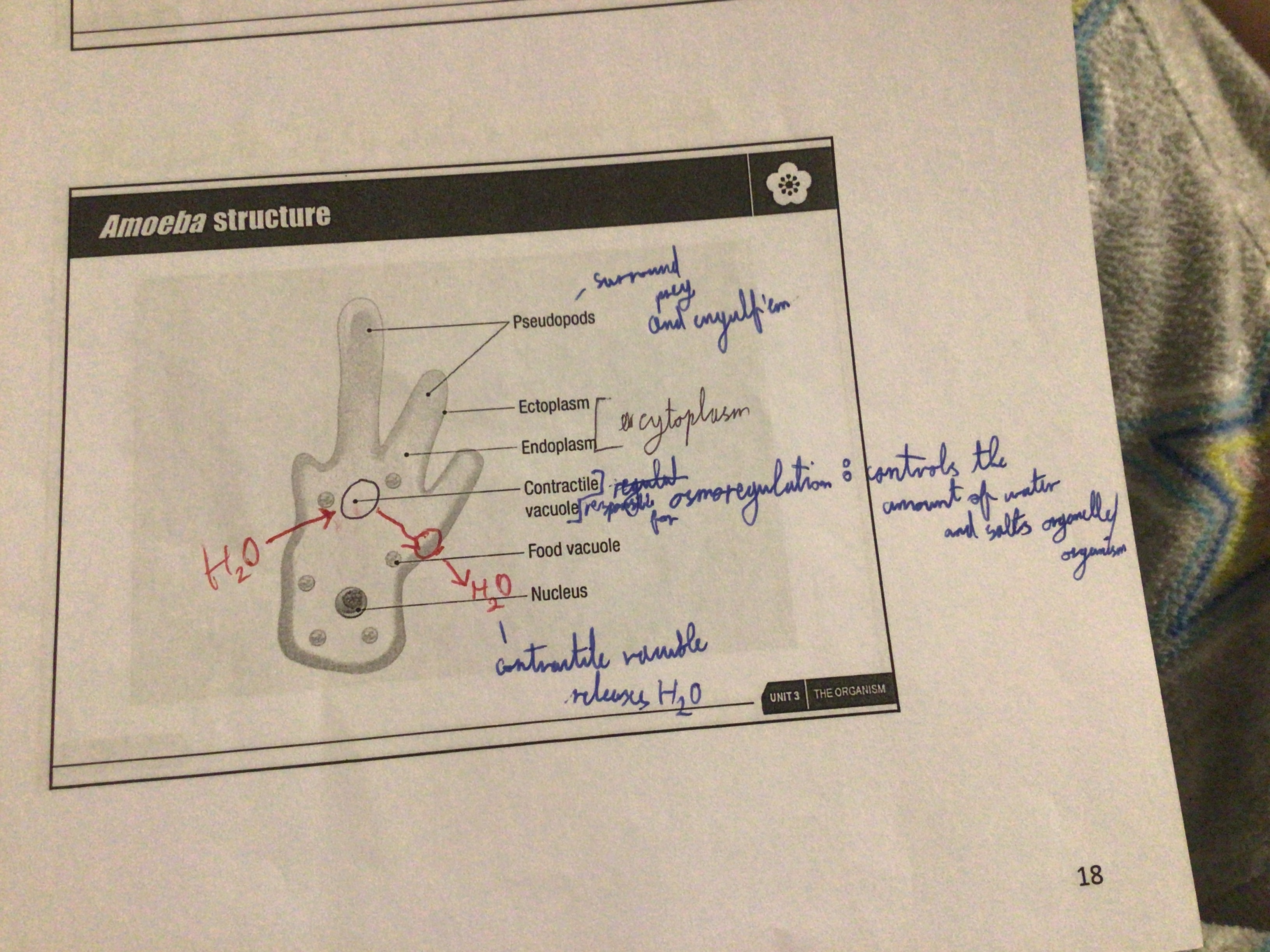
Nucleus (function)
controls the activity of the cell
Food vacuole (function)
digests ingested food particles. Secretes enzymes digest prey
Pseudopodia (function)
"false feet". Extend in whatever amoeba needs to move
Contractile Vacuole (function)
Osmoregulation
Cell Membrane (function)
allows diffusion of gases/water
Contractile Vacuole
Water enters amoeba due to osmosis. Vacuole collects water that enters the amoeba. Moves to edge of the cell where it bursts and releases the water collected out of the cell. A new one is formed and it repeats. This requires energy