Tissues and the Integumentary System
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Four Main Types Of Animal Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Connective Tissue
Epithelial Tissue - Functions
Protection
Covers external and internal body surfaces
Physical barrier
Protects underlying tissues from pathogen invasion, toxin exposure, thermal and mechanical trauma
Absorption/Secretion
It allows absorption of nutrients, water, molecules from digested food (intestine) and blood (capillaries), secretion of enzymes, hormones and mucus (glands eg, liver, pancreas, thyroid)
Epithelial Cells- Functions
Filteration/Excretion
Of waste products from blood (kidneys)
Filtration of inhaled air (lungs)
Excretion of sweat (skin)
Regulation
Body temperature
Hydration etc
Apical-basal of epithelial cells
Apical- top
Basal - bottom
Apical-basal polarity of epithelial cells
Apical Membrane -
- Faces the inside of a cavity or the outside of the body
- Usually exposed to fluid or air
- Specialised for absorption,secretion and sensation
Basal Membrane-
- Faces the underlying cells
- Lies on top of the basement membrane
Apical- basal polarity of epithelial cells
Lateral Membrane-
- In contact with surrounding cells through adhesion molecules (eg. Tight junctions)
- These membranes hold the epithelium together and block paracellular diffusion
- Epithelium offer a mechanical and chemical barrier against the toxic molecules and pathogens
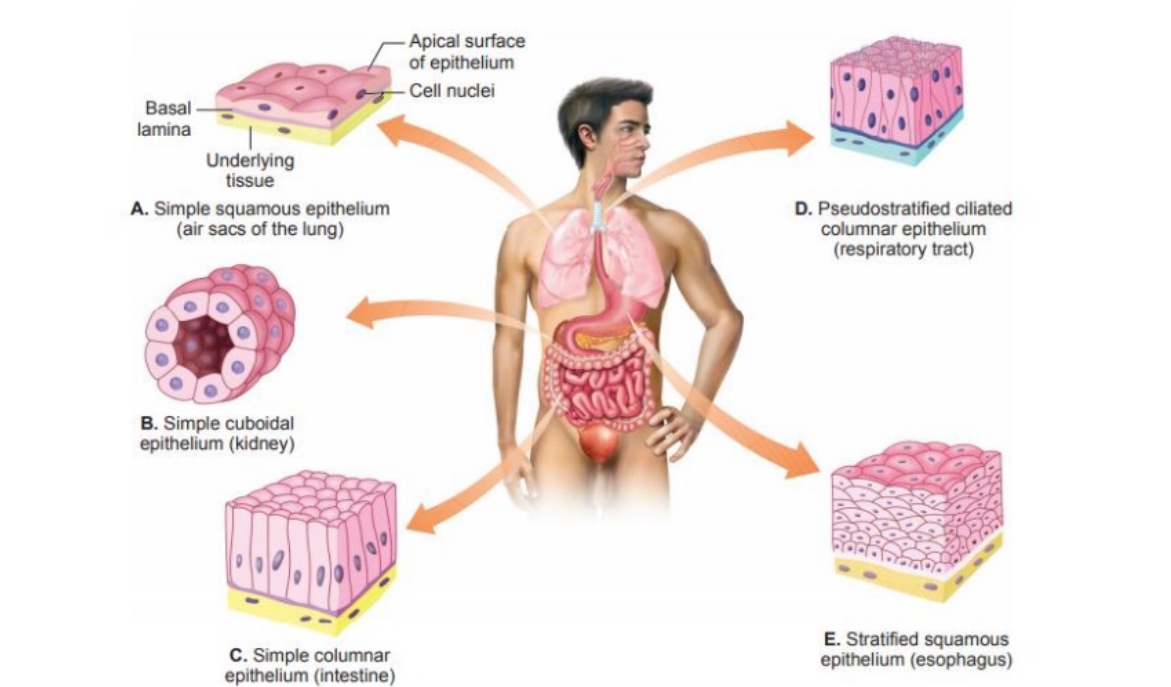
Types of epithelial tissue
Squamous Epithelium
Cuboidal Epithelium
Columnar Epithelium
Simple Epithelium
Stratified Epithelium
Squamous Epithelium
Flat and sheet like in appearance
Cuboidal Epithelium
Equal width, height and depth
Columnar Epithelium
Taller and wide
Simple Epithelium
Single layer
All cells are bound to the basement membrane
Main functions: Absorption, secretion and Filteration
Stratified Epithelium
Multiple layers of cells stacked
Only cells in basal layer are bound to the basement membrane
Main function: Protection
Types of Epithelial Tissue
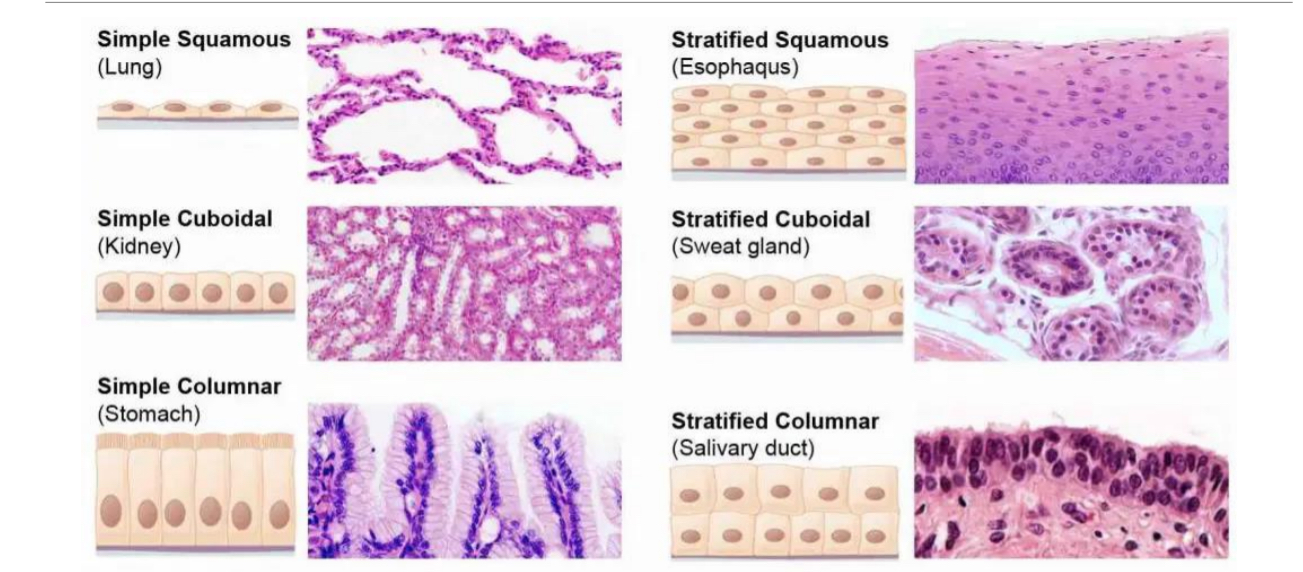
Types of Epithelial Tissue 2
Function of muscle tissue
Production of body movements:
- Contains contractile proteins responsible for generating force and enabling body movements and locomotion
Stabilisation of the body position:
- Ensures posture and stability by constantly acting against the force of gravity
Storage and transport of substances within the body:
- Allows transport of blood, lymph and food.
- Stores carbohydrates in the form of glycogen
Heat generation: - 70-80% of energy generated during MC released as heat
Muscle cell- Myocyte
Contains 2 contractile proteins: Actin and Myosin
Skeletal Muscle- Striated or Striped muscle
-Myocytes are elongated, cylindrical in shape and contains more than one nucleus - arranged into bundles
-30-40% of total body mass
-Connected to the bones through tendons
-Voluntary contraction
Cardiac Muscle
Found only in walls of the heart
Not under voluntary control
Striated but smaller than skeletal myosytes, branched and only has 1 nucleus (Uninucleated)
Connected by intercalated discs that allow their synchronous contraction
Nervous Tissue - Functions