CARBOHYDRATES
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
carbohydrates are
sugars with building blocks as monosaccharides
function of carbohydrates
energy source (too much stored will be glycogen → fat), components of cell wall (glycolipids), components of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), and lipid modification
monosaccharide is the
simplest form of sugar
sugar can be subdivided into 2 categories
aldehydes (aldose) and ketones (ketose)
empirical formula for aldose and ketose
(CH2O)n
n=3 is the smallest possible sugar
when n = 3 for aldose →
dihydroxyacetone
when n=3 for ketose →
glyceraldehyde
dihydroxy… for aldose draw
okay
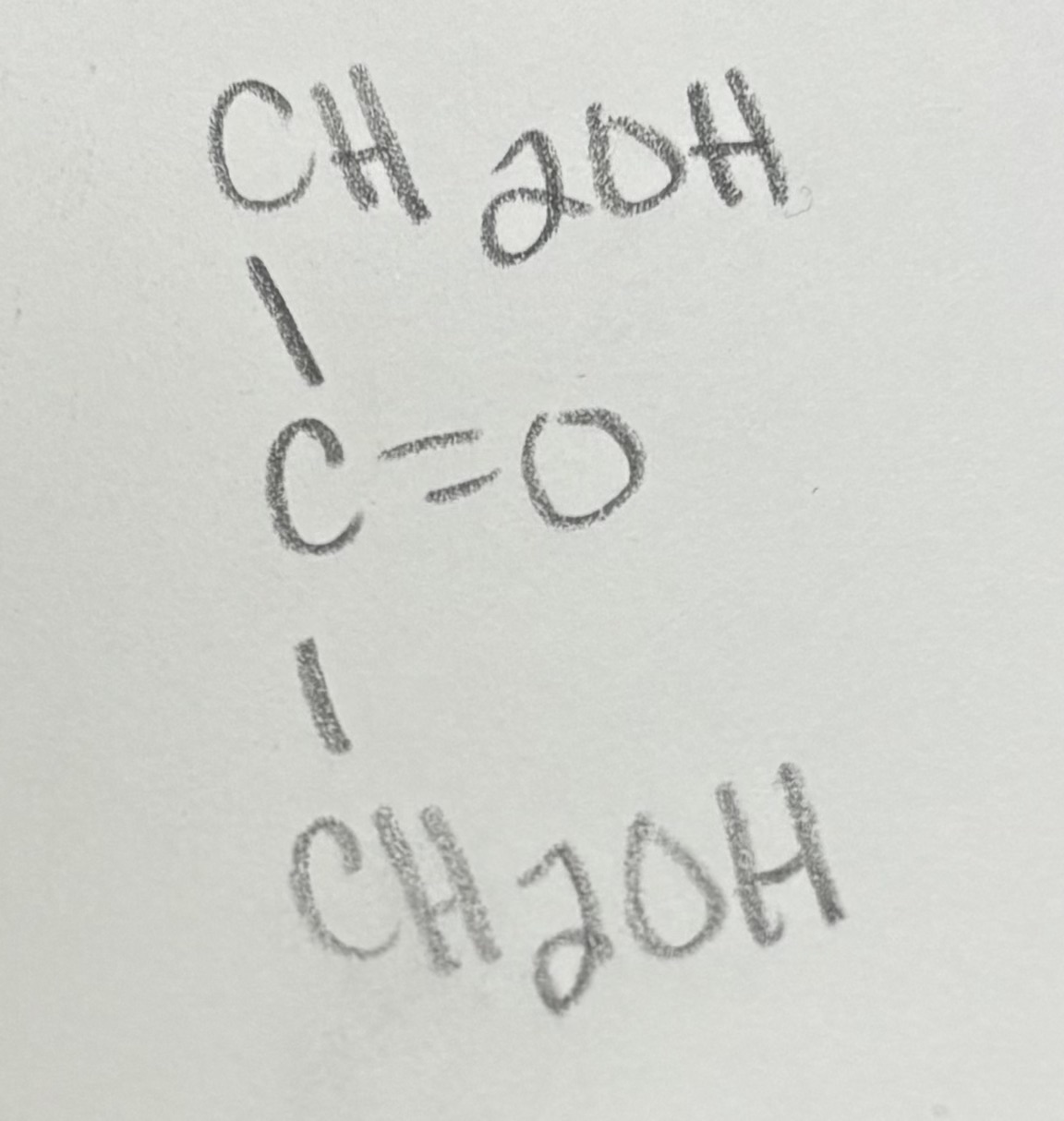
glycer… for ketose has 2
isomers L and D which are enantiomers (mirror images)
draw D-erythorose
okay
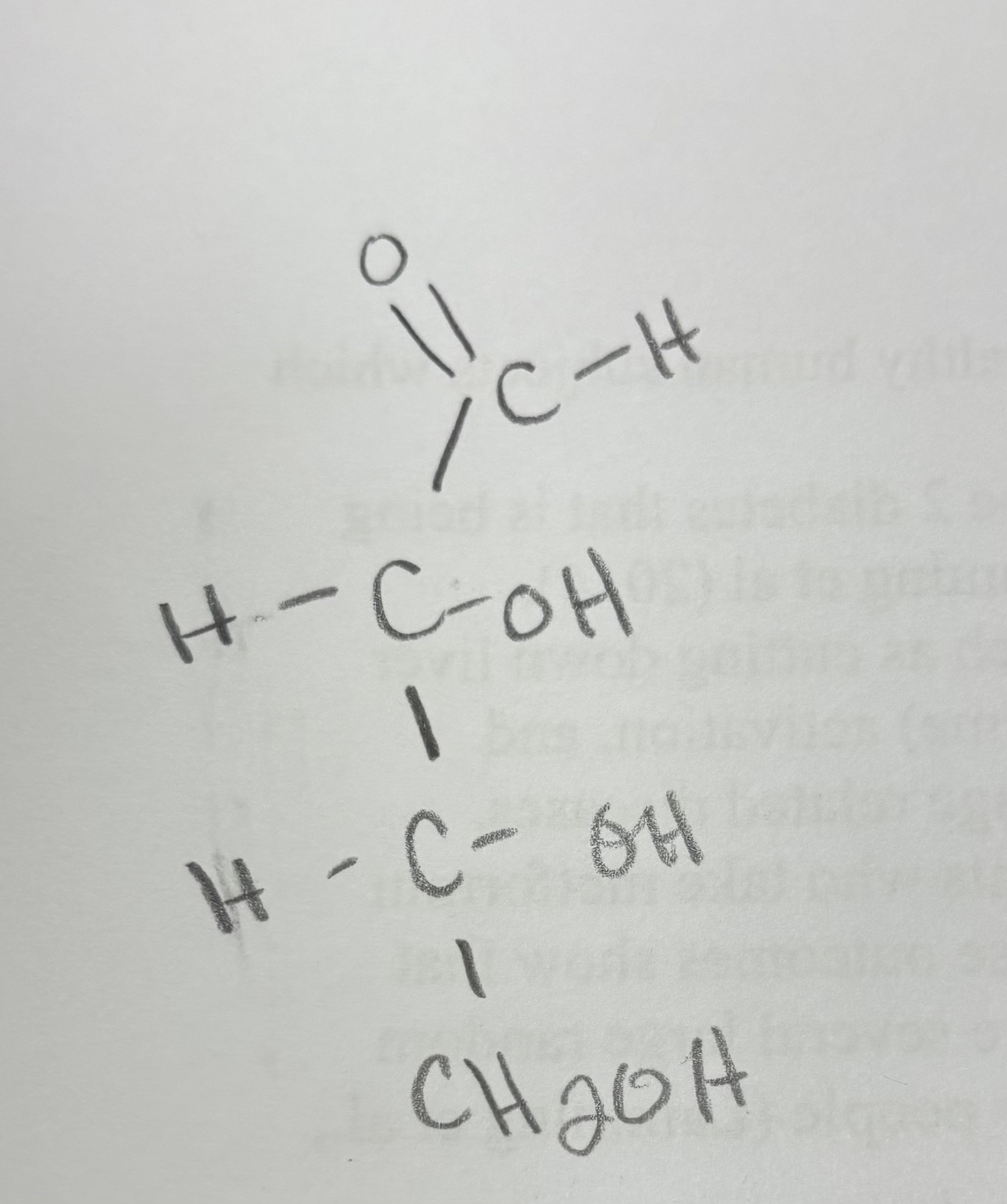
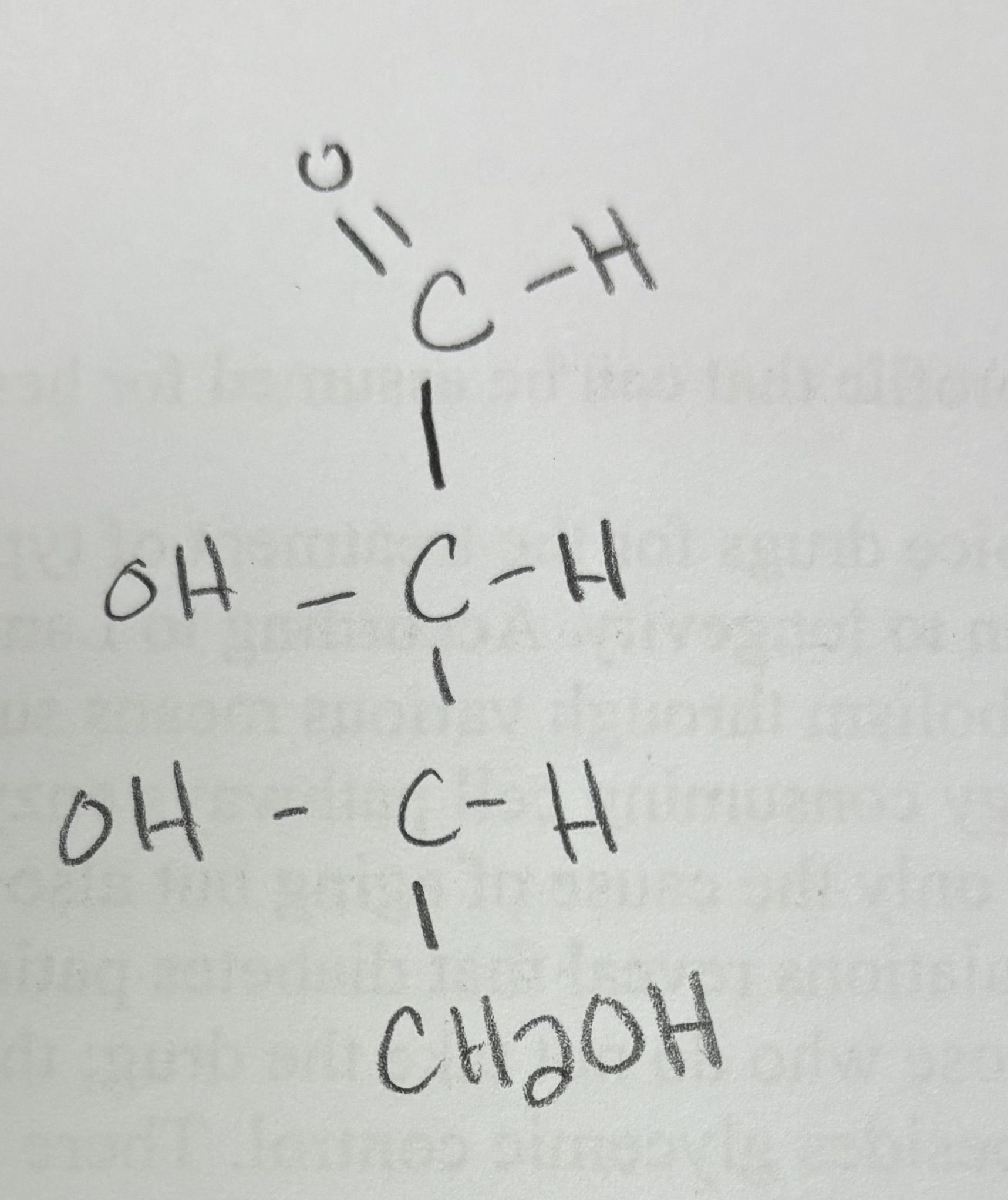
draw L-erythrose
okay
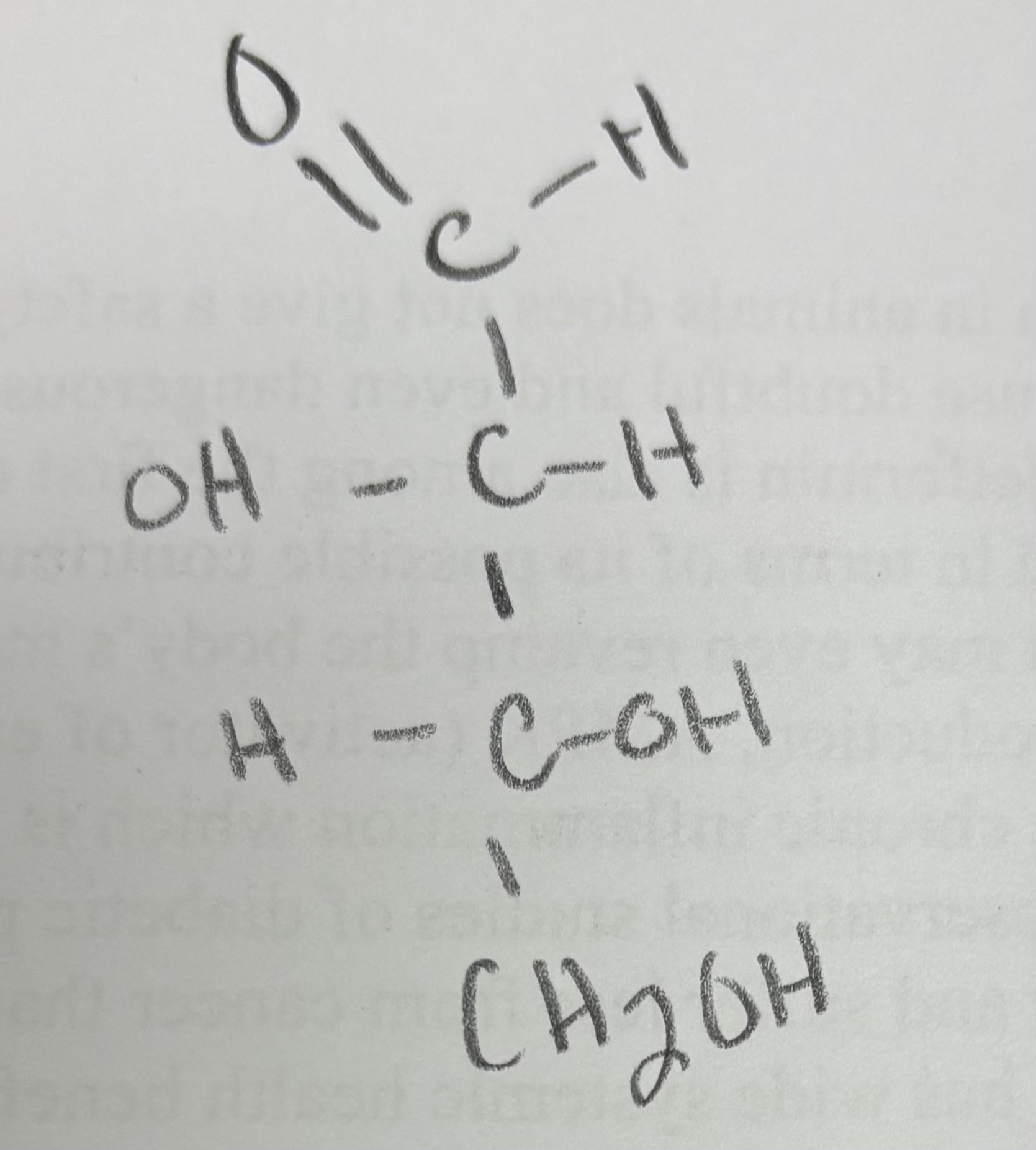
draw D-threose
okay
the hydroxyl group on the chiral carbon further away from the functional group determines
D or L
epimers are a
subgroup of diasteriomers which are sugars that are different in stereochemistry only at a single chiral carbon
epimers are important because
an open chain form is less stable → aldehyde groups open to changes and in order to stabilize it undergoes cyclization to give you the cyclic ring form
the cyclization is between a
nucleophile (the alcohol) and the carbonyl carbon
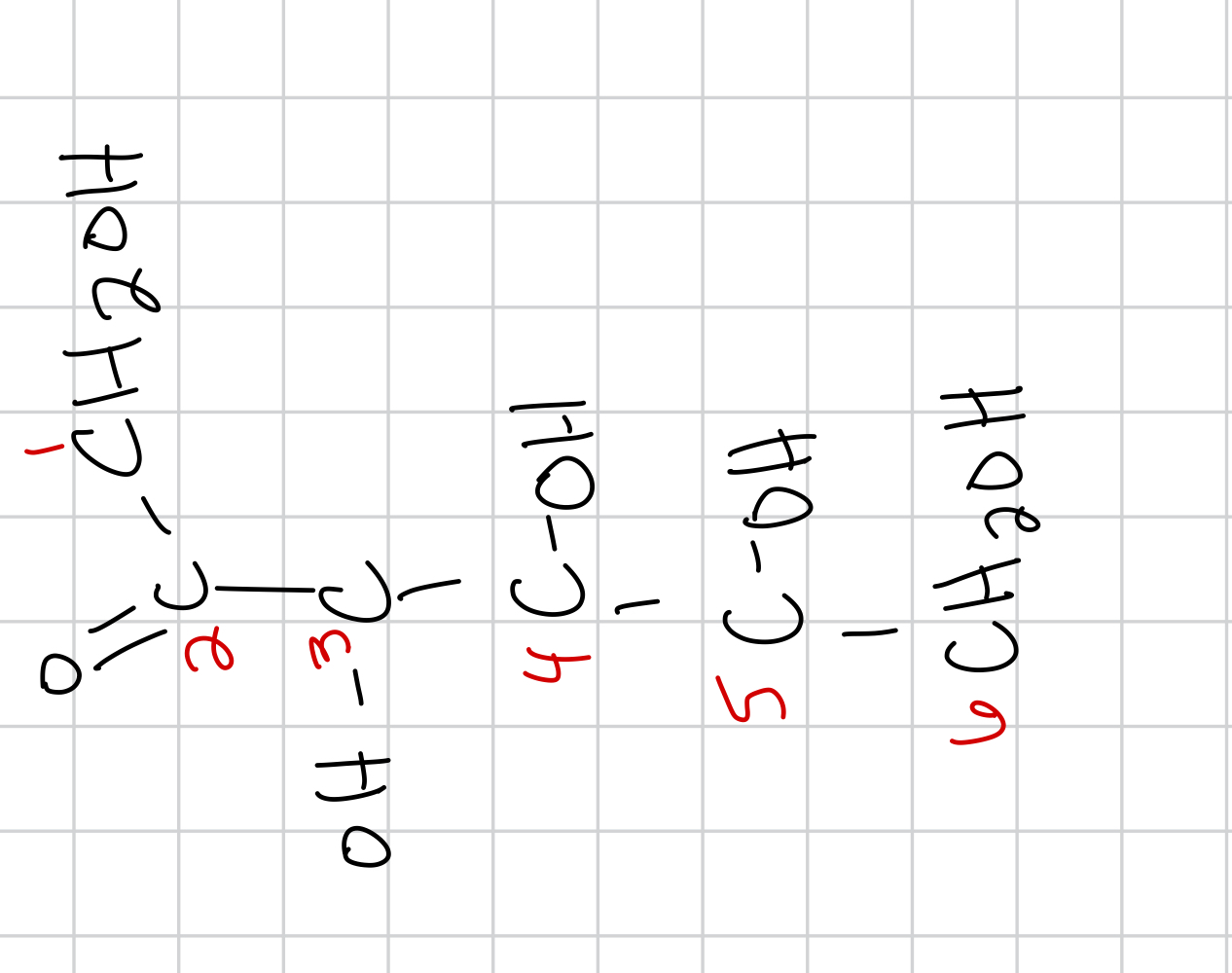
draw D glucose chain
okay
draw D mannose
okay
aldehyde + alcohol makes a
hemiacetol
ketone + alcohol makes a
hemiketal
explain the cyclization of D glucose
the oxygen on C5 attacks the carbonyl carbon and makes it chiral (the carbon is now called anomeric carbon)
draw when the cyclization occurs in D-glucose
okay
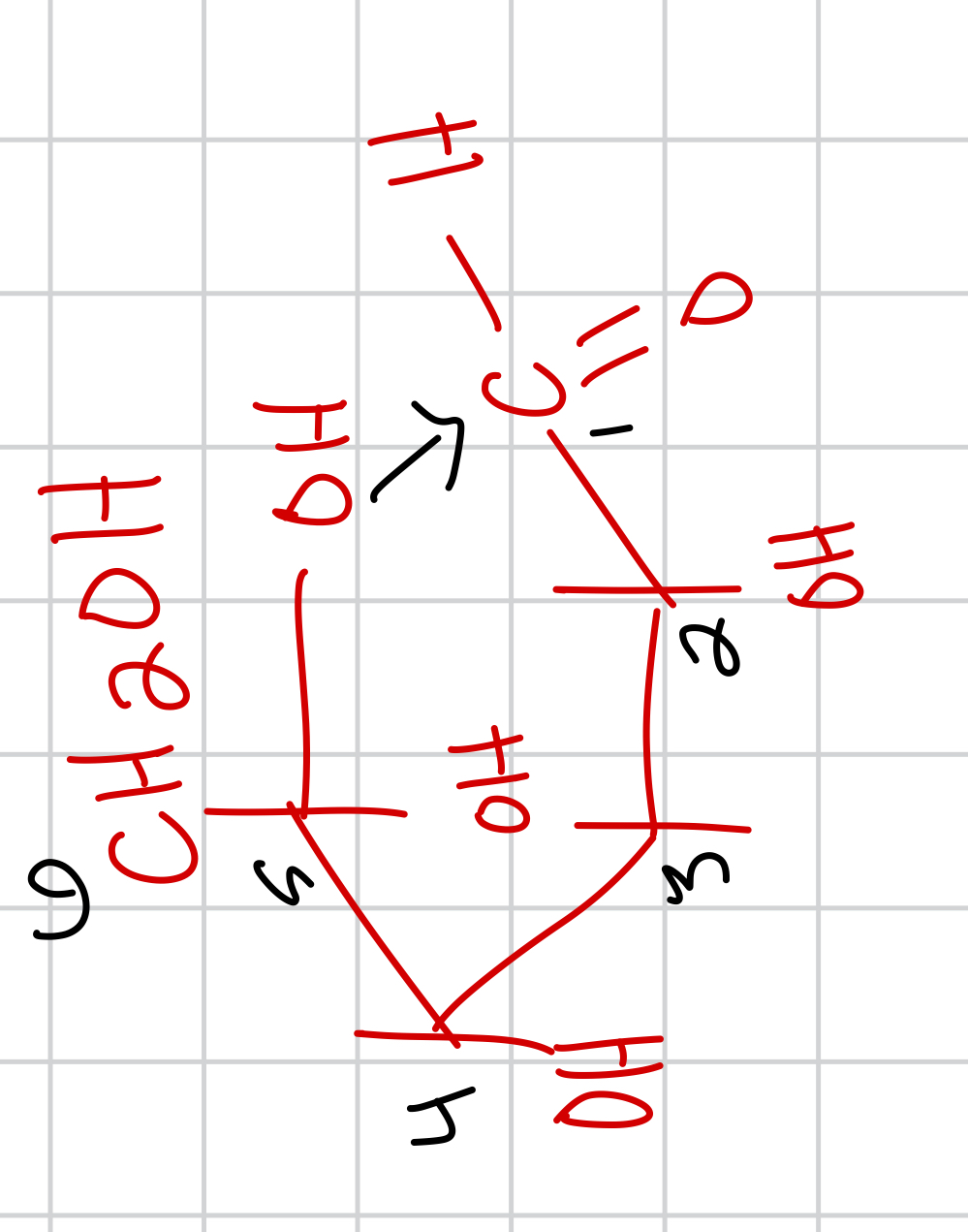
draw what happens when you redox the cyclized D-glucose as alpha and name it and tell its prominence
not as prominent it exists in 1/3 called alpha-D-glucopyranose
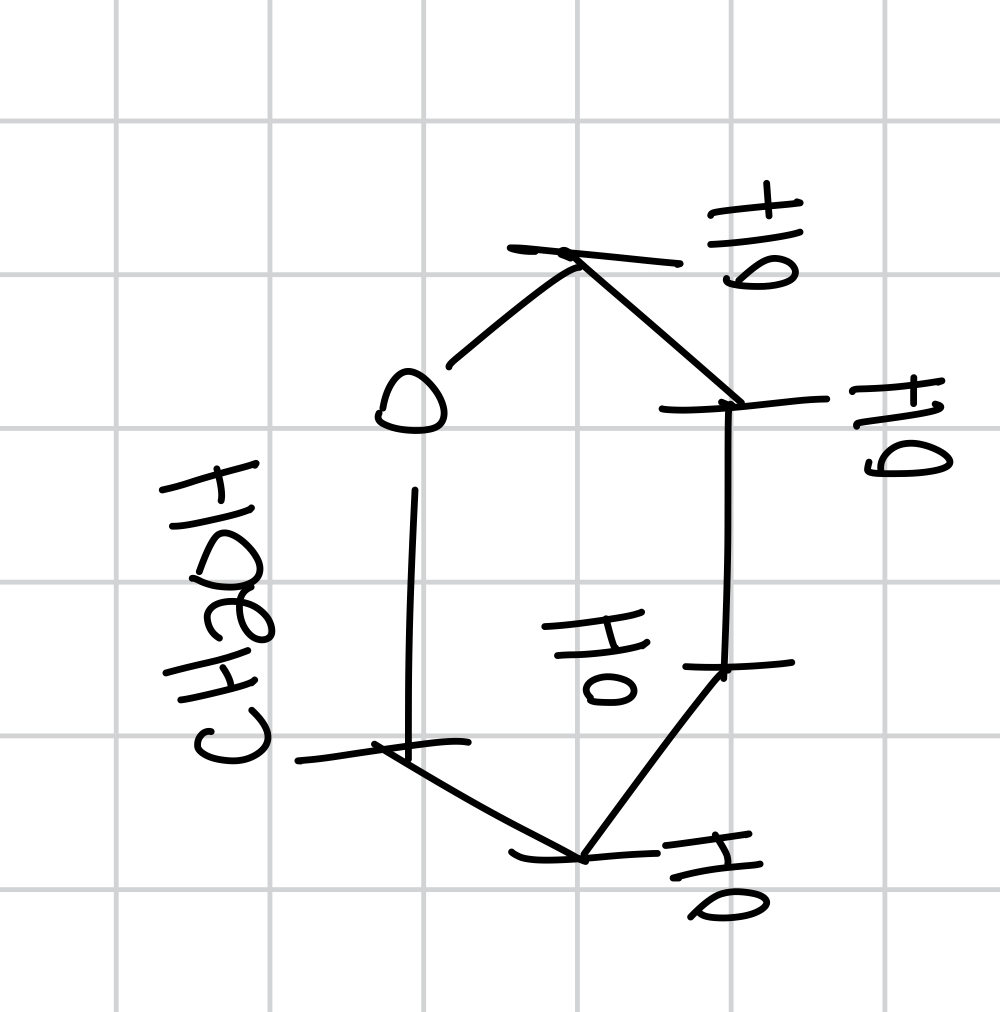
draw what happens when you redox the cyclized D-glucose as beta and name it and tell its prominence
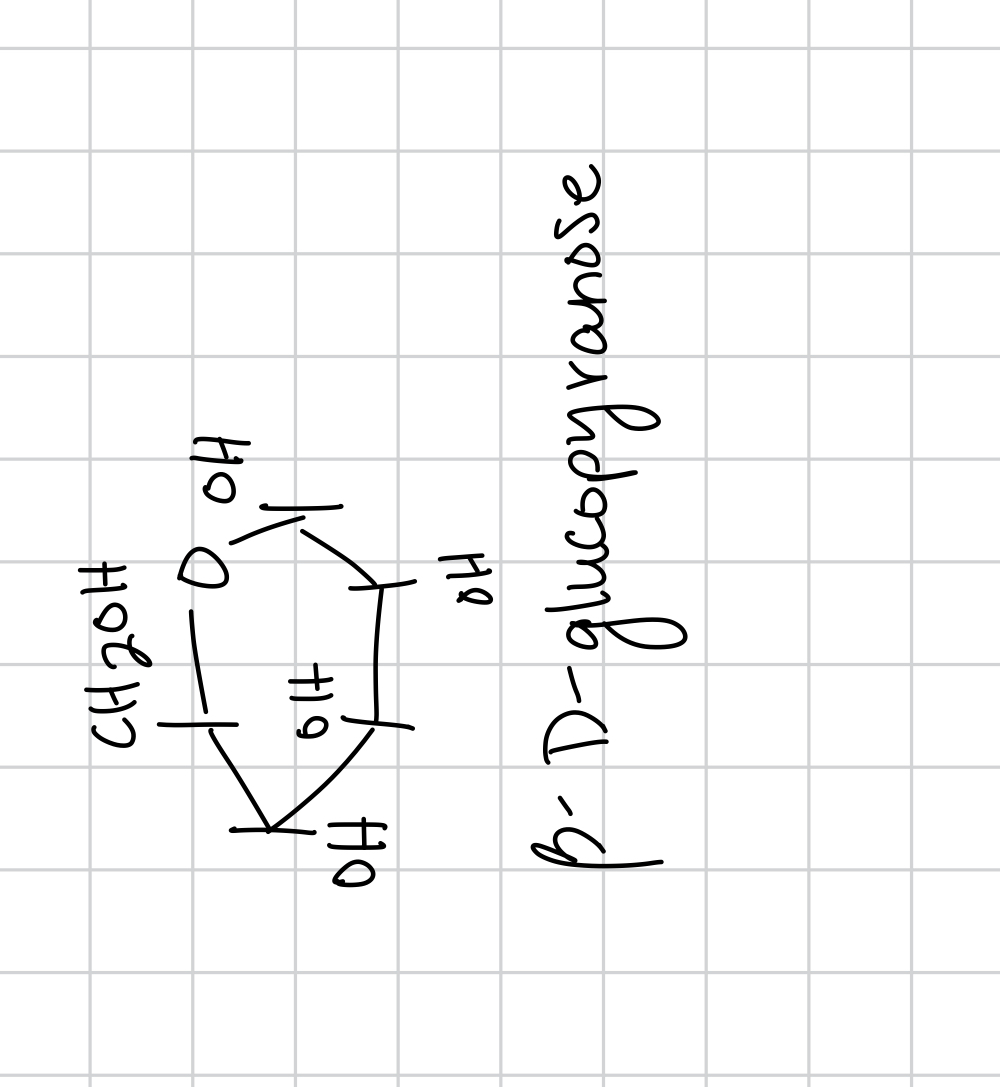
most prominent (2/3) called B-D-glucopyranose
the functional group for glucose is and name
aldohexose functional group is aldehyde
D-fructose functional group and name
ketohexose functional group is ketone
draw D-fructose
okay
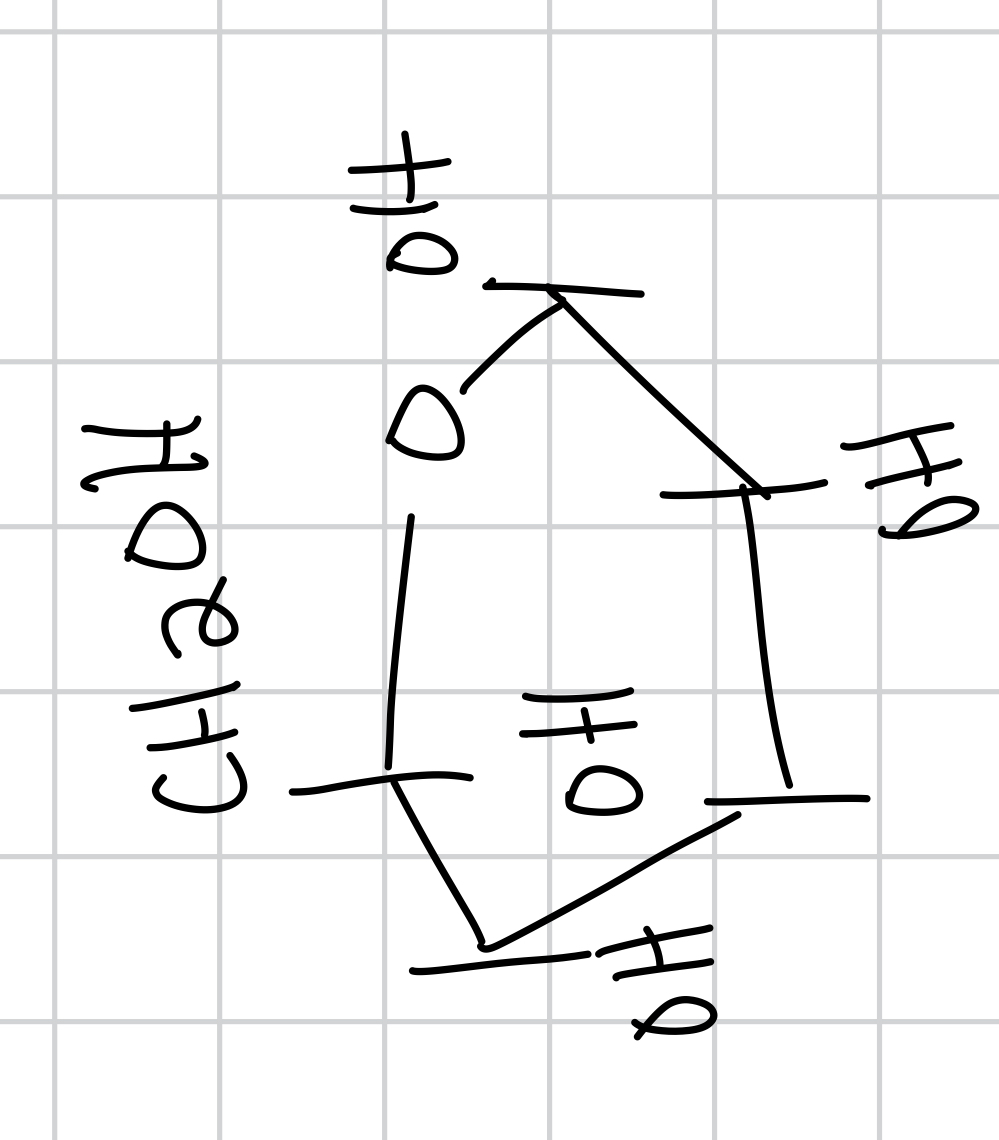
draw the cyclization of D-fructose
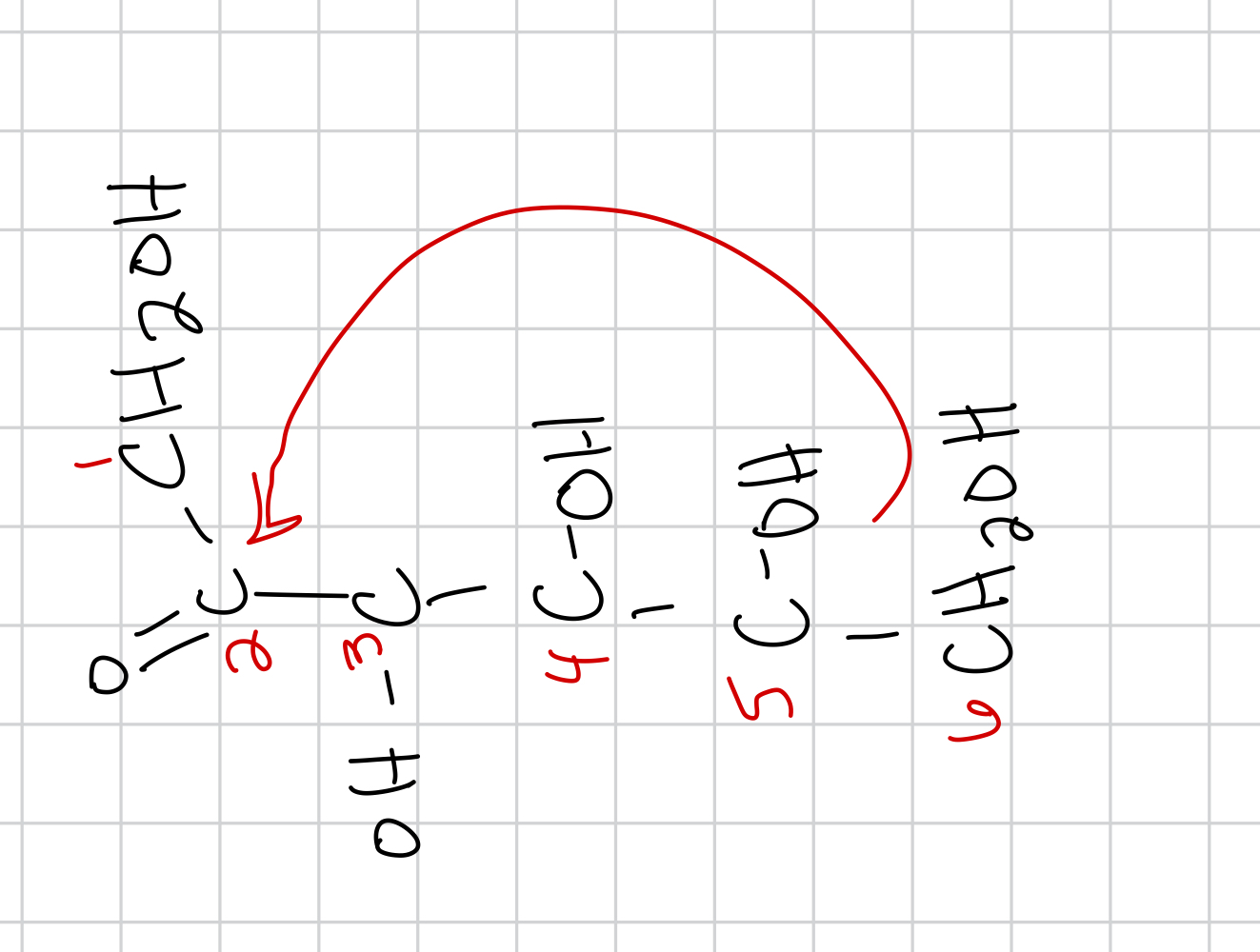
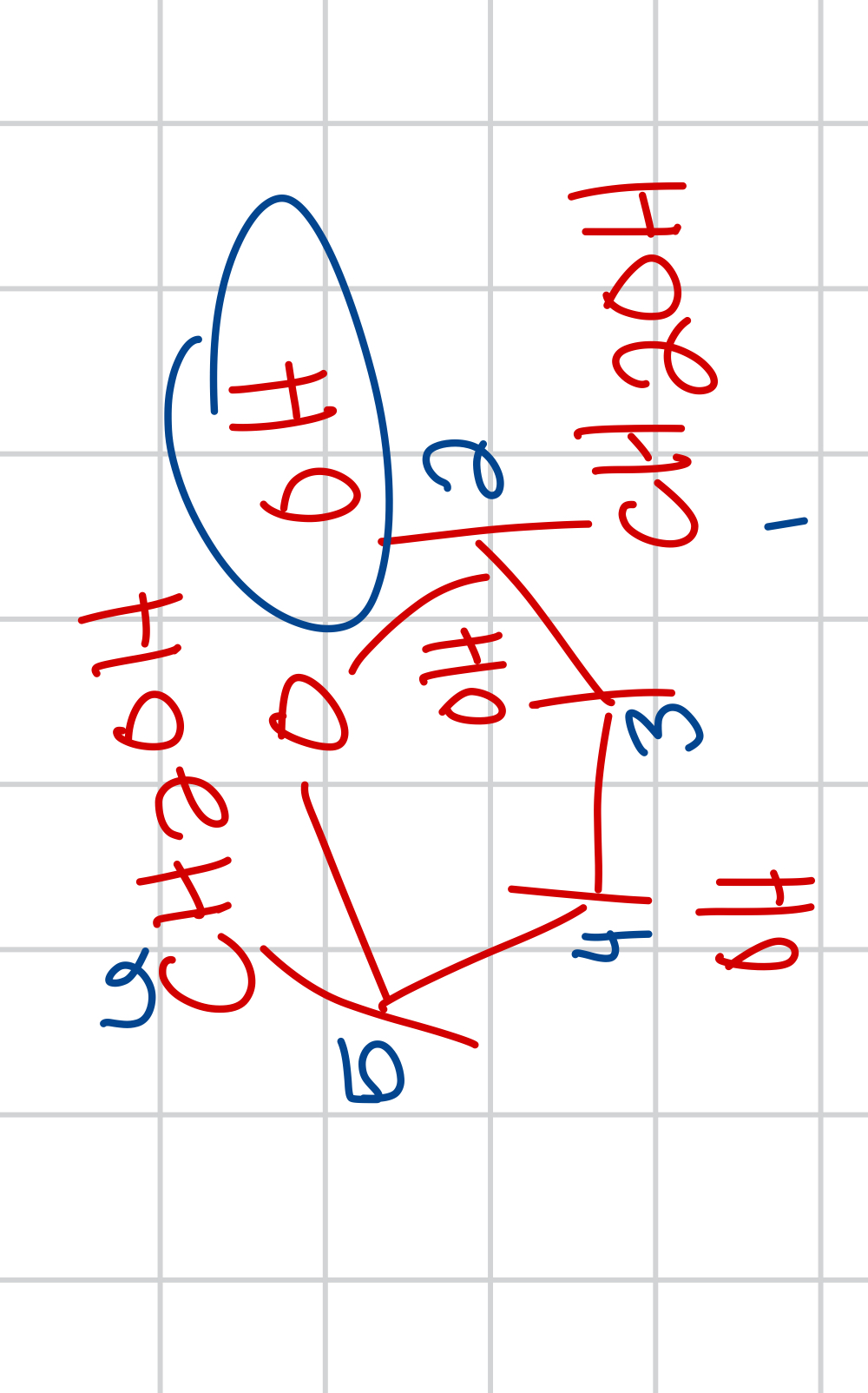
draw the beta form of D-fructose and give the name and prominence
B-D-fructofuranose (2/3) predominant
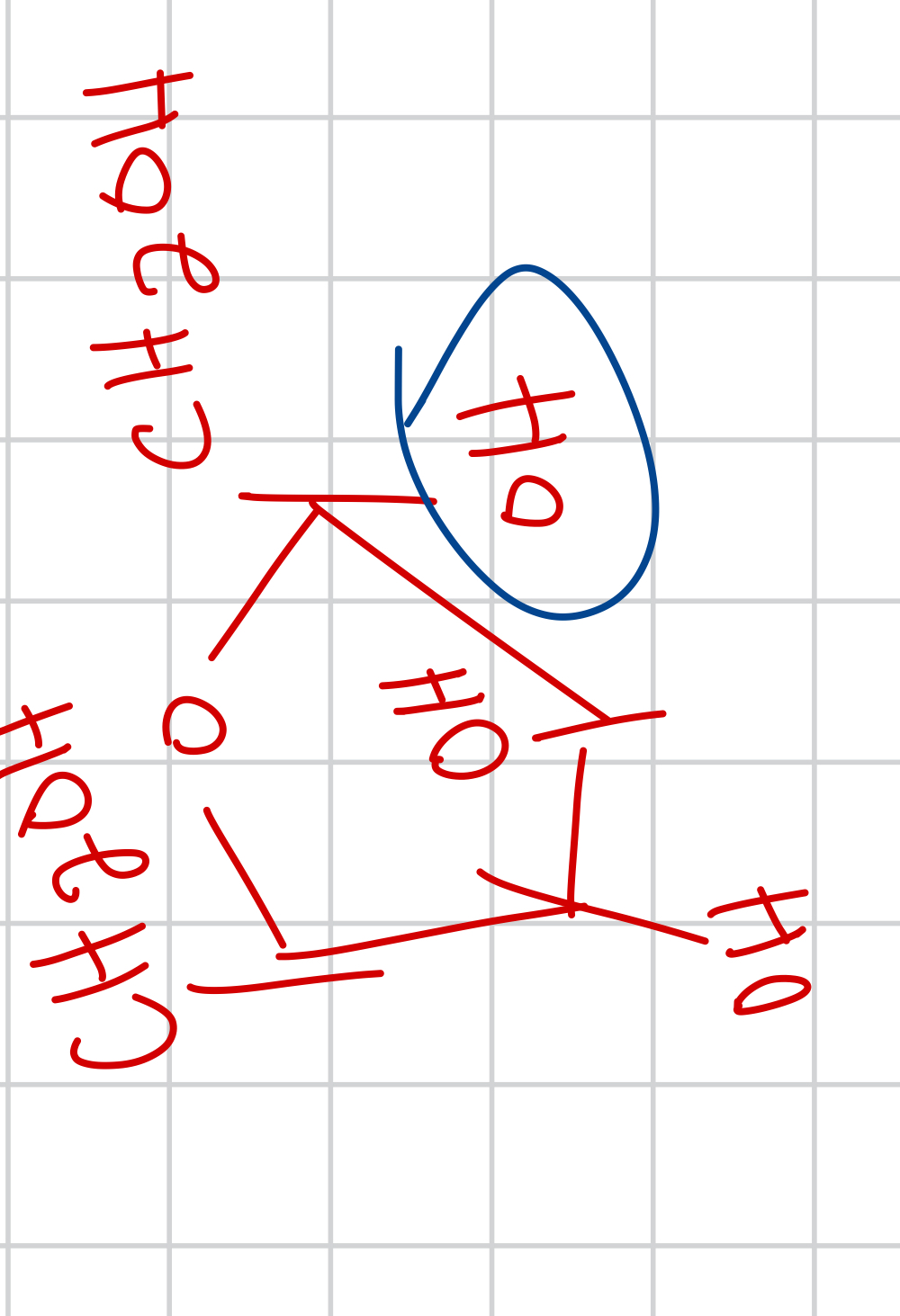
draw the alpha form of D-fructose and give the name and prominence
A-D-fructofuranose
explain the folding purpose
folds to protect the functional group because open chain functional group is more reactive and the cyclized form is more stable
modifications of sugars
only breaks down if ATP is needed so we modify
the modifications of sugars allows cells to
change properties and functionalities of sugar
the changes to the properties and functionalities of sugar are
phosphorylation and glycosidation
when you phosphorylate the sugar you are
making the sugar more negative/polar (1st step) and make it harder to leave (2nd step) and this triggers glycolysis and keeps glucose in
draw the phosphorylation of glucose
then you can add another Pi

the sugar chains are ___ agents and you can add in an ____ agent that turns ___
reducing, oxidizing, the aldehyde or the ketone into a carboxylic acid
the sugar itself is a reducing agent and is called a
reducing sugar
glycosidation is transforming
glucose to glycosides
draw B-D-glucopyranose
glycosidation is when the
acid will protonate the OH group and it turns into a carbocation intermediate where ROH is the nucleophile
draw the glycosidation
okay
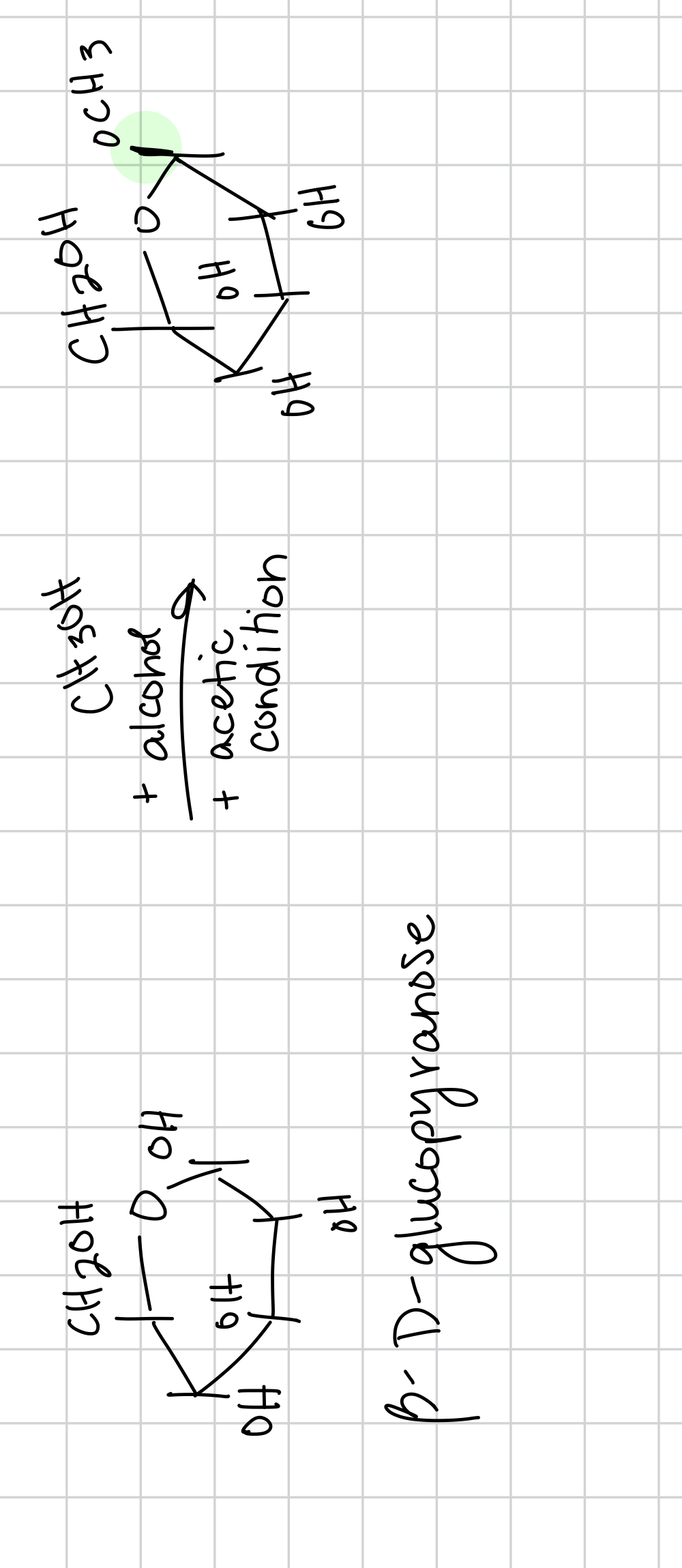
the bond between the OCH3 in the carbocation intermediate in glycosidation is called
O-glycosidic linkage and it is between C1 of glucose and O of alcohol
phosphodiester bonds mean you have a
fatty acid
disaccharides come from
building blocks of monosaccharides
the disaccharides are
lactose, fructose, and maltose
alpha and beta mean where the hydroxyl group is in
disaccharides
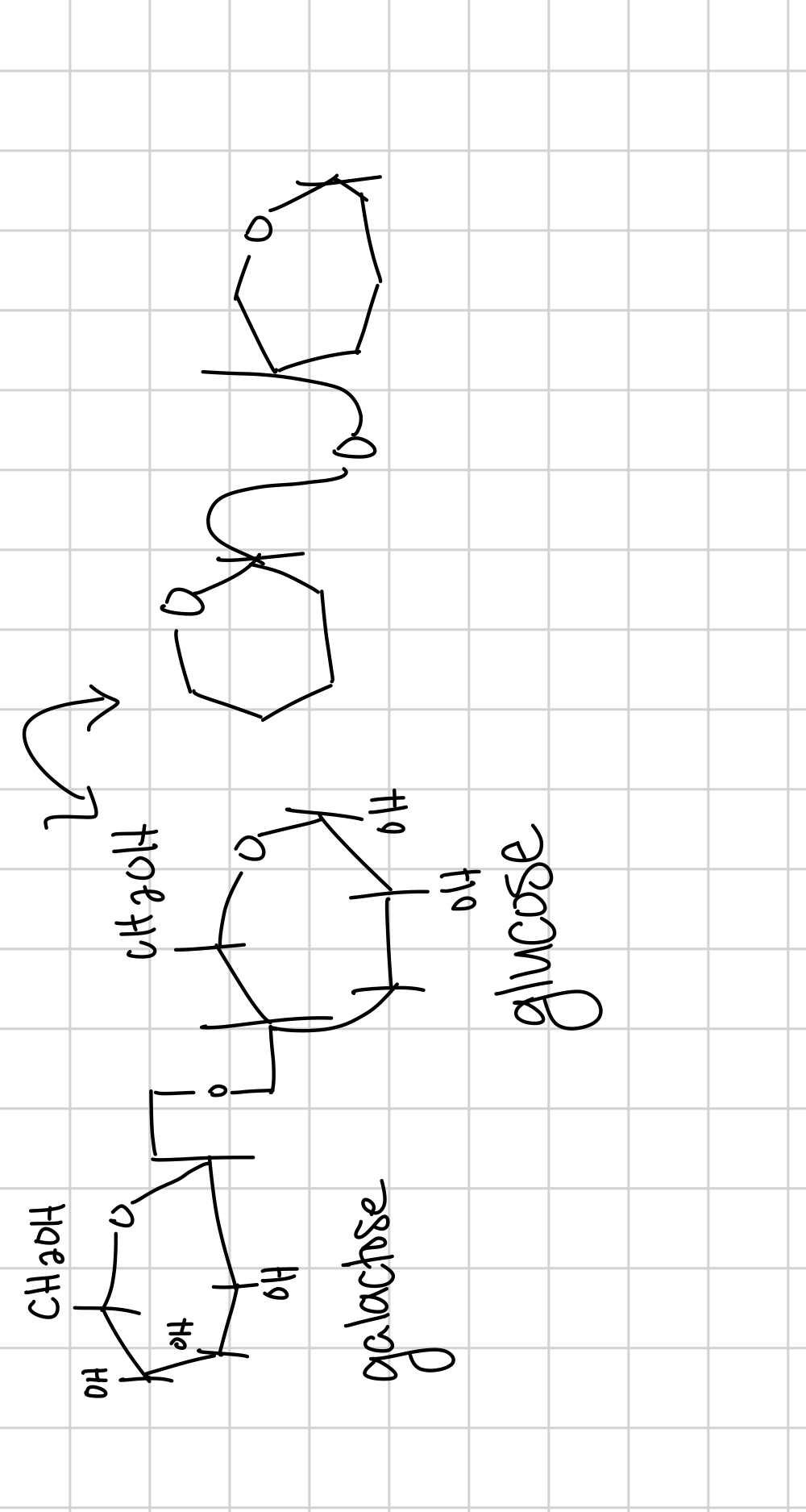
lactose is the
milk sugar
lactose is composed of
d-galactose and d-glucose
lactose bond is
glycosidic bond specifically b-1,4-glycosidic
the b-1,4-glycosidic bond the first number is between
C1 of the first monomer
the b-1,4-glycosidic bond the second number is between
C4 of the 2nd monomer
draw lactose
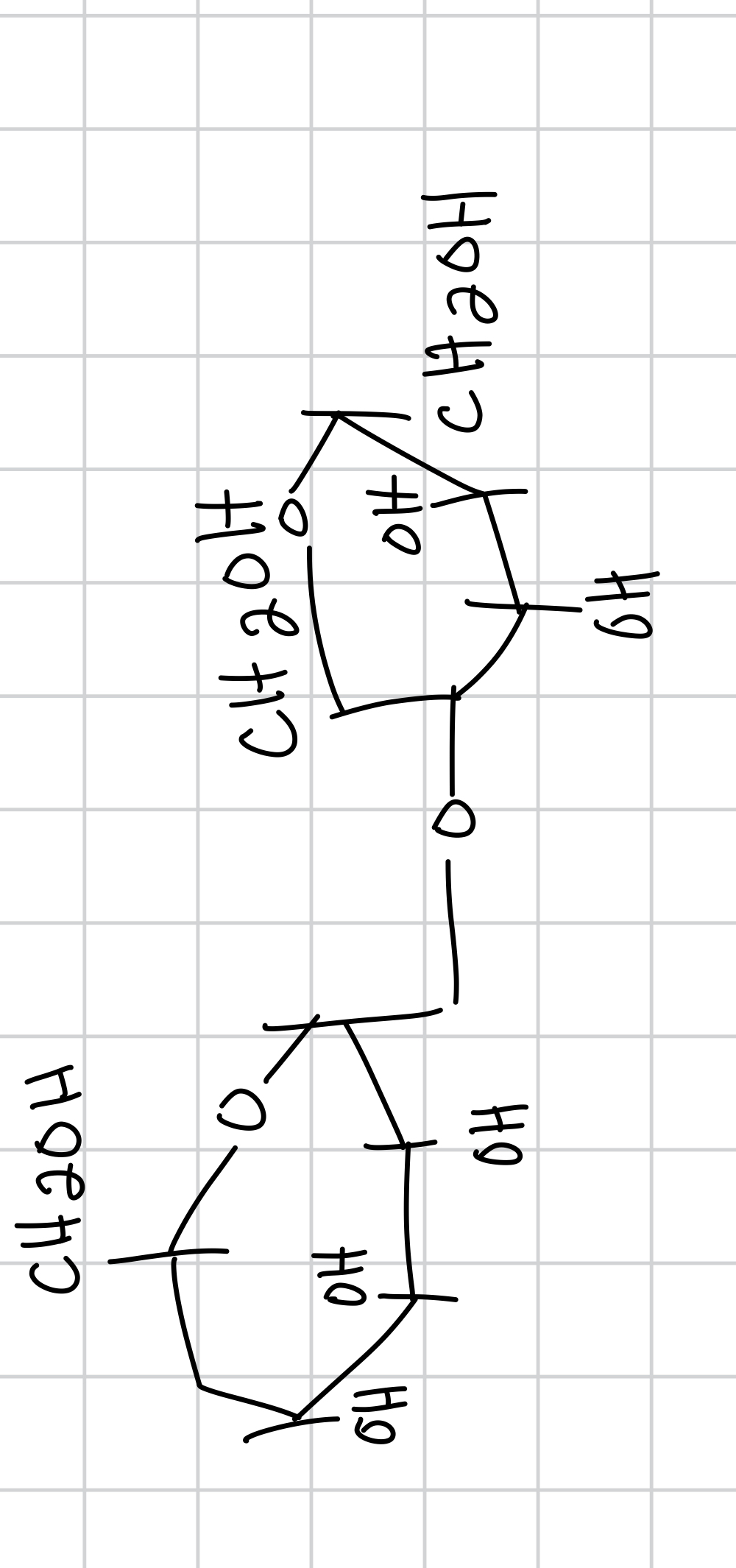
sucrose is special because
it is a none reducing sugar and will not undergo redox
sucrose is between
alpha - D-glucose and Beta-D fructose
what is the bond of sucrose
alpha - 1,2- glycosidic
draw sucrose
okay
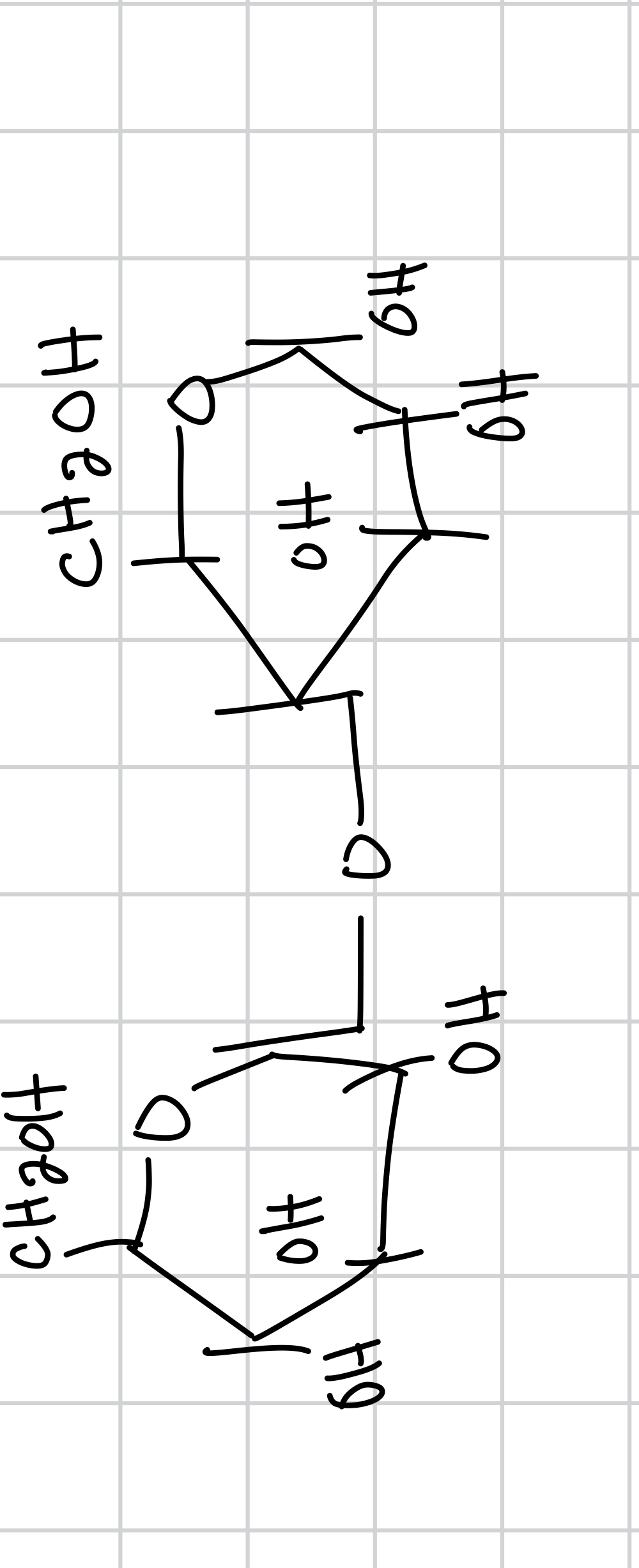
reducing sugars can be
oxidized
maltose is between
2 glucose molecules
the bond for maltose is
alpha 1,4 glycosidic
maltose is the backbone for
polysaccharides
draw maltose
okay
the 3 polysaccharides are
glycogen, starch, and cellulose
polysaccharides are broken into
2 categories homopolymer and heteropolymer
glycogen breakdown
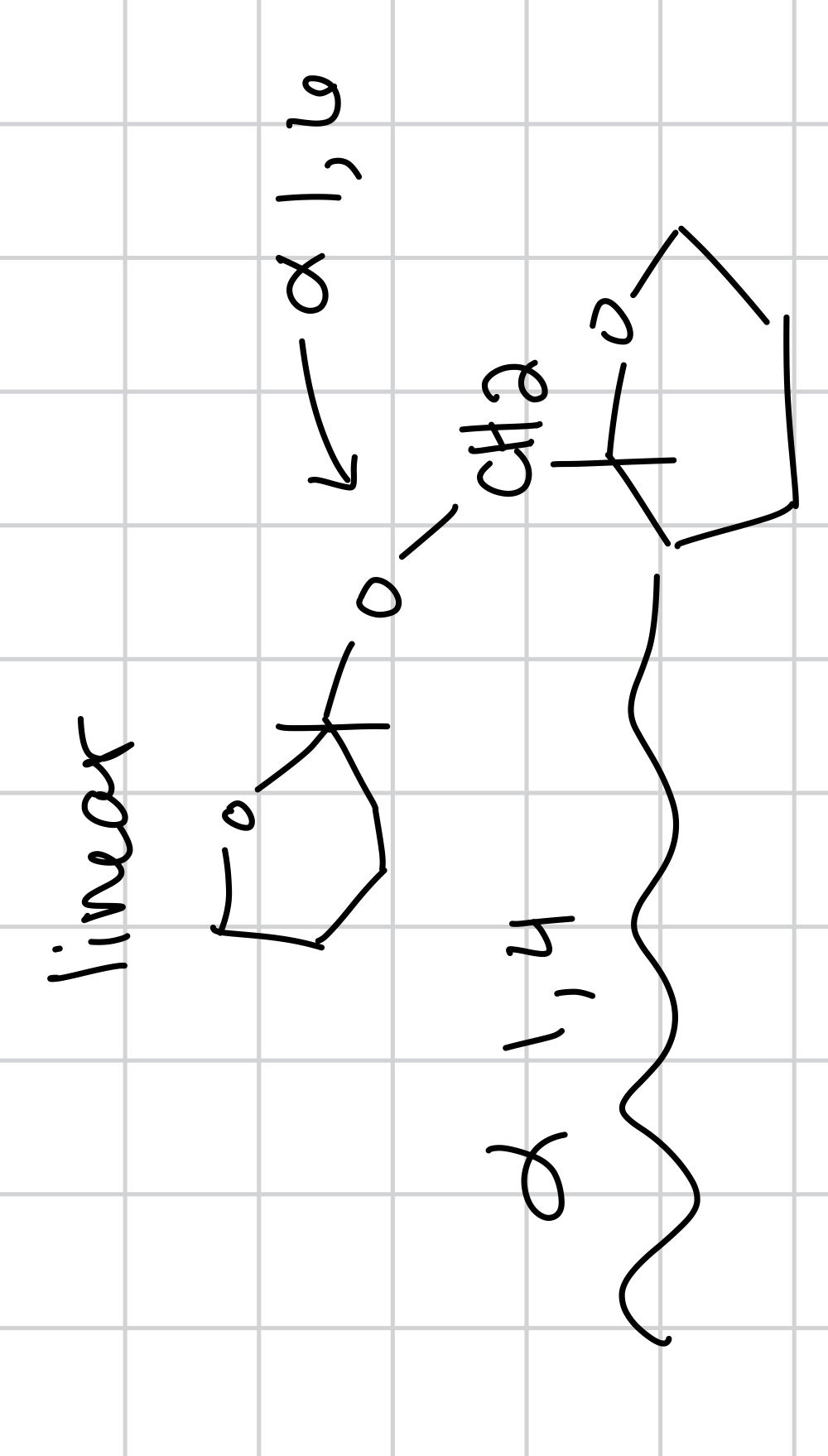
energy storage in animals and humans, most common, monomer is glucose, branches (every 10 residues) it is a continuation of maltose, it goes glucose → maltose → glycogen and the linkage is alpha -1,4- glycosidic (for linear chain) and alpha 1,6 glycosidic (when it branches)
glycogen is more
helical because the amount of branching
draw the basic bonding structure for glycogen
okay
starch is the energy storage for
plants
starch can be broken down into two types:
amylose and amylopectin
amylose is the
unbranched alpha 1,4, linkage
amylopectin is the
branched alpha 1,4 and alpha 1,6 linkage
the backbone for starch is
glucose
amylopectin is not as
branched as glycogen it is every 30 or so resides are branched
cellulose is in
plants
cellulose linkage is
beta-1,4-glycosidic linkage
cellulose backbone is
glucose
cellulose is used for
structure and strength
cellulose dietary fiber is when you
consume food not everything goes at the same rate and speeds up the rate
cellulose is used as a structure because the
beta 1,4 stacks easier than alpha 1,4
draw blood type O order
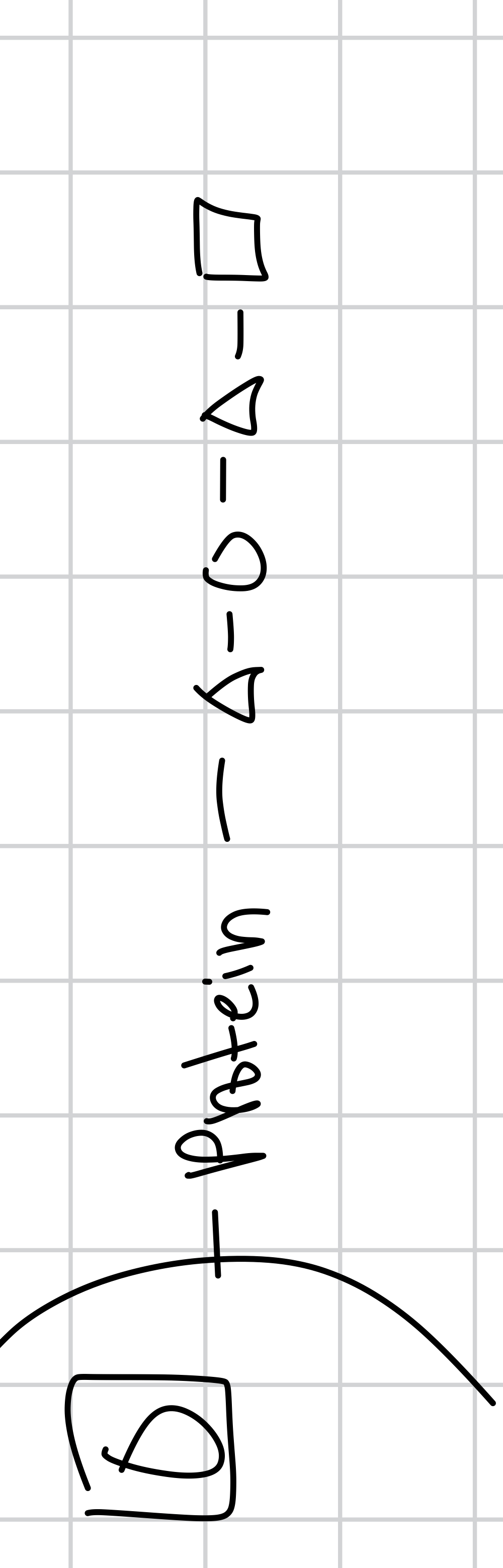
draw blood type A order

draw blood type B order

triangle in blood type order means
galactose
circle in blood type order means
N-acetyl-glycosamine
square in blood type order means
fructose
pentagon in blood type order means
N-acetyl-galactosamine