Part 2: Aviation 2100 final
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
Hypoxia
a state of Oxygen deficiency in the body, there are 4 types
4 types of hypoxia
hypoxic,
hypemic,
histotoxic,
stagnant
HyPOxic
due to decrease in Pressure at altitude; the body is not able to get enough Oxygen
HypEMiC
blood is not able to carry oxygen because of smoking, anEmia, Carbon Monoxide poisoning
HistoTOXIC
the body is not able to use the oxygen efficiently because of ALCOHOL
(Stag)nant
the body is not able to circulate blood effectively because of a Heart Attack (staggering) or g-forces
Hazardous Attitudes
Anti-authority
Impulsivity
Invulnerability
Macho
Resignation
Anti-Authority
"Don't tell me what to do"
Solution: Follow the rules they are usually right
Impulsivity
"Do something quickly"
Solution: not so fast! think first.
Invulnerability
"It won't happen to me"
Solution: It could happen to me
Macho
"I can do it!"
Solution: Taking chances is foolish
Resignation
"What's the use?"
Solution: I am not helpless. I can make a difference.
Special Disorientation
A lack of orientation regarding the position, attitude, or movement of the aircraft in space
How does Special disorientation happen?
VFR pilot flies into IMC
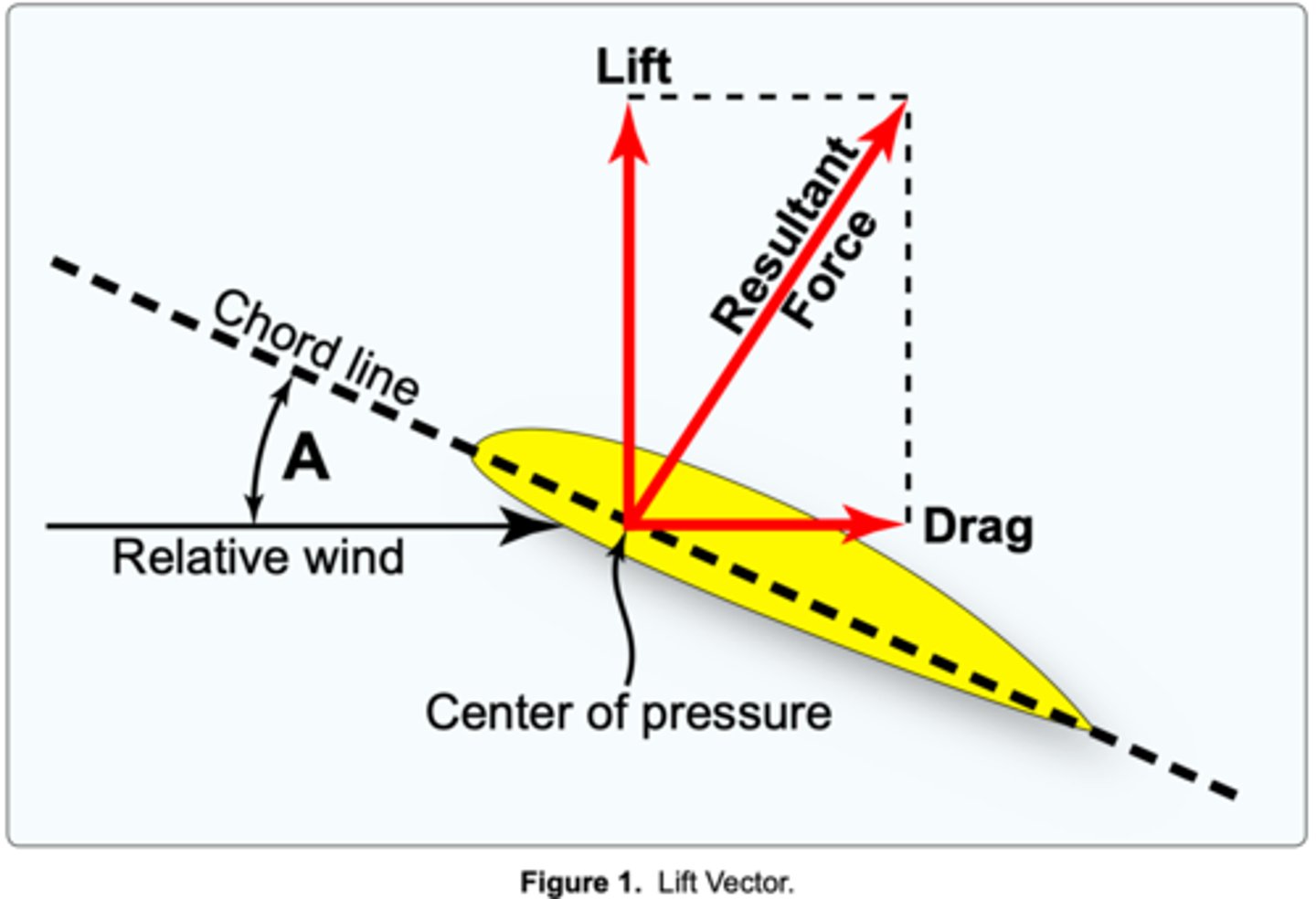
What is the Chord Line?
An imaginary straight line from the leading edge to the training edge of an airfoil
What is Relative Wind?
the direction of the wind in relation to the airfoil
What is Angle of Attack?
Angle between relative wind and the chord line
What are the 4 forces acting on an airplane in flight?
lift, weight, thrust, and drag
When are the 4 forces in equilibrium?
During unaccelerated straight and level flight
Density Altitude
The altitude the aircraft feels like it is at. So, a high density altitude would make the aircraft behave the same as if it were flying high in the mountains. Performance would suffer. Climbs rate would slow, and power would decrease.
What controls Roll?
Ailerons (longitudinal axis - lateral stability)
What controls Pitch?
elevator (lateral axis - longitudinal stability)
What controls Yaw?
rudder (Vertical axis - directional stability)
Why use Flaps on Approach and Landing?
to enable the pilot to make steeper approaches to a landing without increasing the airspeed
What is wake turbulence?
wingtip vortices created by large aircraft tend to sink below the aircraft generating turbulence
What is magnetic deviation?
error caused by magnetic fields within the aircraft distorting the lines of magnetic force
what is magnetic variation?
the angular difference between magnetic and geographic North
when is a compass most accurate?
only in straight-and-level unaccelerated flight
What instruments are connected to the pitot tube?
Airspeed indicator
what instruments are connected to the static port?
all 3 instruments: Vertical speed indicator (vsi), Altimeter, and airspeed indicator (asi)
what instruments become inoperative if pitot tube becomes clogged?
airspeed indicator
what instruments don't work if the static port is clogged?
all 3 instruments
On the airspeed indicator: what is the White arc?
flap operating range
On the airspeed indicator: what is the Green arc?
normal operating range
On the airspeed indicator: what is the Red Radial line?
never exceed speed
Indicated Altitude
read on instrument
True Altitude
the vertical distance of the aircraft above mean sea level (MSL)
Absolute Altitude
the vertical distance above the surface or above ground level (AGL)
Pressure Altitude
height above standard datum plane (29.92" Hg)
Why do aircraft separate the ignition and electrical systems?
The Electrical system powers the avionics and radios by using the battery and alternator to provide power.
The Ignition system powers the ignition (spark plugs) utilizing two independent magnetos providing reliability
If you had an electrical failure (battery and alternator) during flight would the engine stop working
the avionics equipment in the aircraft might fail but the engine would keep running because it is powered directly by the dual magnetos
Why do we have to keep adjusting the fuel/air mixture as we climb?
decreases air density so we need to decrease the fuel
what causes carburetor ice?
fuel vaporization and decreasing air pressure in the venturi. as pressure decreases so does temperature
how would we know we have carburetor ice?
a loss in RPM (engine revelations per minute) then a gradual increase as the ice melts.
what is the risk of operating an engine with excessively high oil temperature?
may use more oil, lose power, or may result in permanent engine damage.
Who is responsible for checking the engine oil level and during preflight to determine the aircraft is safe for flight?
the PIC
Detonation
the unburned fuel/air charge explodes due to pressure instead of burning normally with spark ignition. Grade of fuel used in an aircraft engine is lower than specified for the engine
Pre-ignition
The uncontrolled firing of the fuel/air charge in advance of normal spark ignition is known as a 'hot spot'
Required Documents with the pilot
pilot certificate of appropriate grade, medical certificate of appropriate grade, government issued photo ID
Medical certificate length
is valid through the last day of the month regardless of the day the physical exam was given
1st Class Medical
over 40, expires after 6 calendar months
under 40, expires after 12 calendar months
Needed if exercising privileges of an airline transport pilot certificate
2nd Class medical
needed if exercising the privileges of a commercial pilot certificate
privileges valid for 12 calendar months
3rd Class medical
needed for student, recreational, private, or flight instructor certificate
under 40: valid for 60 calendar mothers (5 years)
40 and older: valid for 24 calendar months
Safety Belts
Crew: during takeoff, landing, and while enroute, each required crew member shall keep their seatbelt fastened while at their station. During takeoff and landing, this includes wearing a shoulder harness (if installed) unless it interferes with required duties
91.15 dropping objects
PIC may not allow any object to be dropped from an aircraft in flight that creates a hazard to people or property. This does not prohibit the dropping of an object if reasonable precautions are taken to avoid injury or damage to persons or property on the surface
Right of way Rules: Overtaking
the aircraft being overtaken has the right of way. the overtaking aircraft shall alter course to the right when passing
right when passing: Landing
aircraft on final approach have right of way over other aircraft in flight or on the surface (cannot use this rule to force an aircraft off the runway surface)
aircraft approaching an airport to land: lower aircraft has the right of way (but it shall not take advantage of this rule to cut in front of or to overtake another)
VFR cruising altitude
between 3,000 AGL and 18,000 MSL you must fly these specific altitudes while in VFR cruising flight (based on the aircraft's magnetic course)
Magnetic Track above 3000 AGL (VFR crushing altitudes)
VFR odd 1000s+500 from 0degrees to 179
VFR even 1000s+500 from 180degrees to 359
Why listen to land and hold short?
it can greatly increase efficiency of traffic flow at airports
why decline a land and hold short?
safety, PIC has final authority
Land and Hold Short Operations (LAHSO)
ATC tool to increase airport capacity; pilot must accept; no student solo pilots may participate.
How does the wind tetrahedron work?
the tiny point points the way you should land and take off because the tip faces the wind
When taxing in winds remember:
Turn into a headwind and dive away from a tailwind
Thumbs up it's up
Dive away=elevator down
If you have a headwind taxing what do you do?
Wind coming from the right= up aileron on right side and neutral elevator
Wind coming from the left= up aileron on left side and neutral elevator
If you have a tailwind while taxing what do you do?
Wind from left back= down aileron on left wind and down elevator
Wind from right back= down aileron on right wing and down elevator
After what kind of incident do you need to inform NTSB immediately?
Flight control system malfunction, inability for crew member to preform their duties due to injury or illness, failure of any internal turbine engine component that results in debris escaping somewhere other than in the exhaust path, inflight fire, Mid-air collision, damage to property (other than aircraft) exceeding $25,000
Visual Approach Slope Indicator (VASI)
A visual aid of lights arranged to provide descent guidance information during the approach to the runway. A pilot on the correct glideslope will see red lights over white lights.
VASI red over white
on glide path (you're all right)
VASI white over white
Too high (you'll be flying all night)
VASI red over red
Too low (you're dead)
Characteristics of Unstable air:
Cumulus clouds, showery precipitation, good visibility, strong surface winds, rough air
Characteristics of Stable Air
Stratiform clouds and fog
Continuous precipitation
Smooth air
Fair to poor visibility in haze and smoke
Stable air resists upward or downward movement
How are cloud families classified?
according to their height range
what are the four cloud families?
Low (strato), middle (alto), high (cirro), & extensive vertical development (thunderstorms)
Stratus clouds
flat clouds associated with stability
Nimbus clouds
rain clouds
Cumulus clouds
heaped clouds associated with instability
Recipe for Cumulonimbus (thunderstorm)
Moisture for sufficient water vapor
Instability for unstable lapse rate
Lifting mechanism to get it started
life cycle of a thunderstorm:
cumulus stage: all updrafts,
mature stage: precipitation beginning to fall, dissipating stage: characterized predominantly by downdrafts
Conditions necessary for the formation of cumulonimbus clouds are?
Lifting action and unstable, moist air
Which weather usually signals the beginning of the mature stage of a thunderstorm?
precipitation beginning to fall
During the life cycle of a thunderstorm, which stage is characterized predominately by downdrafts?
dissipating stage
Are winds given based on true or magnetic north?
true north
What does MSL mean?
Mean Sea Level
What does AGL mean?
Above Ground Level
Weight and Balance formula
Weight x Arm = Moment
Moment /Arm = Weight
between the wing chord line and the relative wind.
The term "angle of attack" is defined as the angle
Stalled
In what flight condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin?
developing lift.
Wingtip vortices are created only when an aircraft is
less than the length of the wingspan above the surface.
Floating caused by the phenomenon of ground effect will be most realized during an approach to land when at
attack.
(Refer to Figure 1.) The acute angle A is the angle of
During unaccelerated flight.
When are the four forces that act on an airplane in equilibrium?
The downwash on the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced and elevator effectiveness is reduced.
What causes an airplane (except a T-tail) to pitch nose down when power is reduced and controls are not adjusted?
aerodynamic balance and controllability.
Changes in the center of pressure of a wing affect the aircraft's
heavy, clean, and slow.
The greatest vortex strength occurs when the generating aircraft is
light quartering tailwind.
The wind condition that requires maximum caution when avoiding wake turbulence on landing is a
The horizontal component of lift.
What force makes an aircraft turn?
less stable at all speeds.
Loading an airplane to the most aft CG will cause the airplane to be
chord line of the wing and the relative wind.
The term angle of attack is defined as the angle between the