Glaciers 1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are some key reasons to study glaciers
sea level rise
the economy
ecology
hazards/slope stability
irrigation
civil engineering
cultural significance
What are the climate factors influencing glaciers?
solar radiation
latitude
altitude
precipitation
How does altitude influence glaciers?
as altitude increases, precipitation increases and temperature decreases
cold air holds less moisture, so releases it
low temperature means precipitation as snow more likely
What is the solar radiation effect and how does it relate to glaciers?
the way in which solar radiation circulates effects the earth’s surface temperature
polar locations are ideal for ice build-up due to large land + consistent high snowfall
Describe a glaciers mass?
a natural open system
made of accumulated crystalline water
snow becomes ice when snowpack/glacier density increases
firn - old snow, atleast a year old
Dry vs Wet snow?
Dry - requires more snow to form ice
Wet - easier to form ice as water trickles down into the ice pack and freezes
presence of meltwater = increased rate of ice formation and metamorphism
What is Glacier mass balance/mass budget?
o Quantative expression of the volumetric change that ice mass expiernces
o Describes the inputs and outputs of snow, firn and ice at various spatial and temporal scales
o Can help us understand the objective ‘health’ of a glacier and the impact of climate change
What is glacier mass ablation?
when ice bodies lose mass as a response to temperature, pressure and humidity changes
What are the factors affecting ablation?
altitude - decreases with increased altitude
wind - impacts turbulent heat flux
cleanness of snow - albedo is higher in clean winter snow and lower in dirty summer snow(0.9 vs 0.3)
calving - when large chunks break off ice bodies (ice sheets/shelves)
sublimation - occurs are lower temperatures with strong winds, intense sunlight and very low air pressure
surface melting
internal and basal melting - mass lost by water flow
What is the Equilibrium Line Altitude(ELA)?
the boundary between ice and snow at the surface at the end of melt season
The altitude at which there is no net annual gain or loss of ice body mass is key for monitoring mass balance
What is the Glacial net balance
Reflects the difference between accumulation(gain) and ablation(loss) usually for a whole glacier over one year
Net balance usually calculated over a balance year, end of summer to end of summer
Can be calculated over measurement year defined by fixed calander dates
Measures in units of equivalent volumes of water per unit area
Net balance = the difference between the winter balance and summer balance
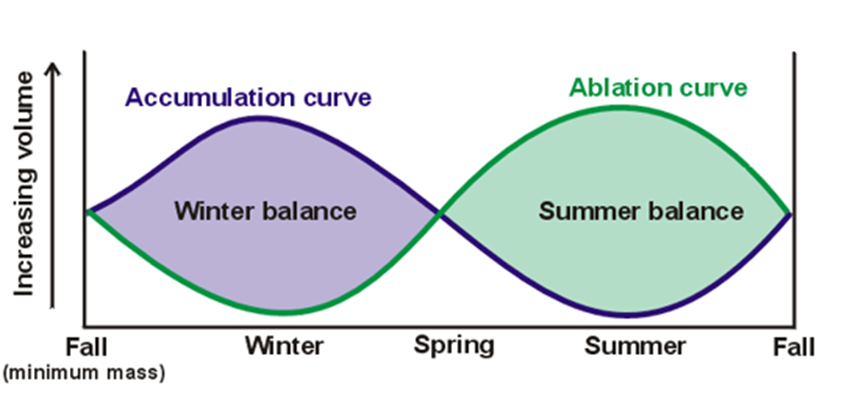
What can mass balance tell us?
Information about glacier advance or retreat
Glacier flowàhigh accumulation = high flow rate, low accumulation = low flow rate
Flow allows mass to be transferred from accumulation area to the ablation area
What do global patterns in the net balance value show?
a global pattern of increasing negative net balance(glacier retreat)
Continental vs maritime type glaciers
continental-type glacieràlow accumulation, low ablation = low balance gradient(e.g major ice sheets, high Arctic glaciers)
maritime-type glacieràhigh accumulation, high ablation = high balance gradient(e.g southern alps, new zealand, European alps)