Relearning Human Anatomy
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
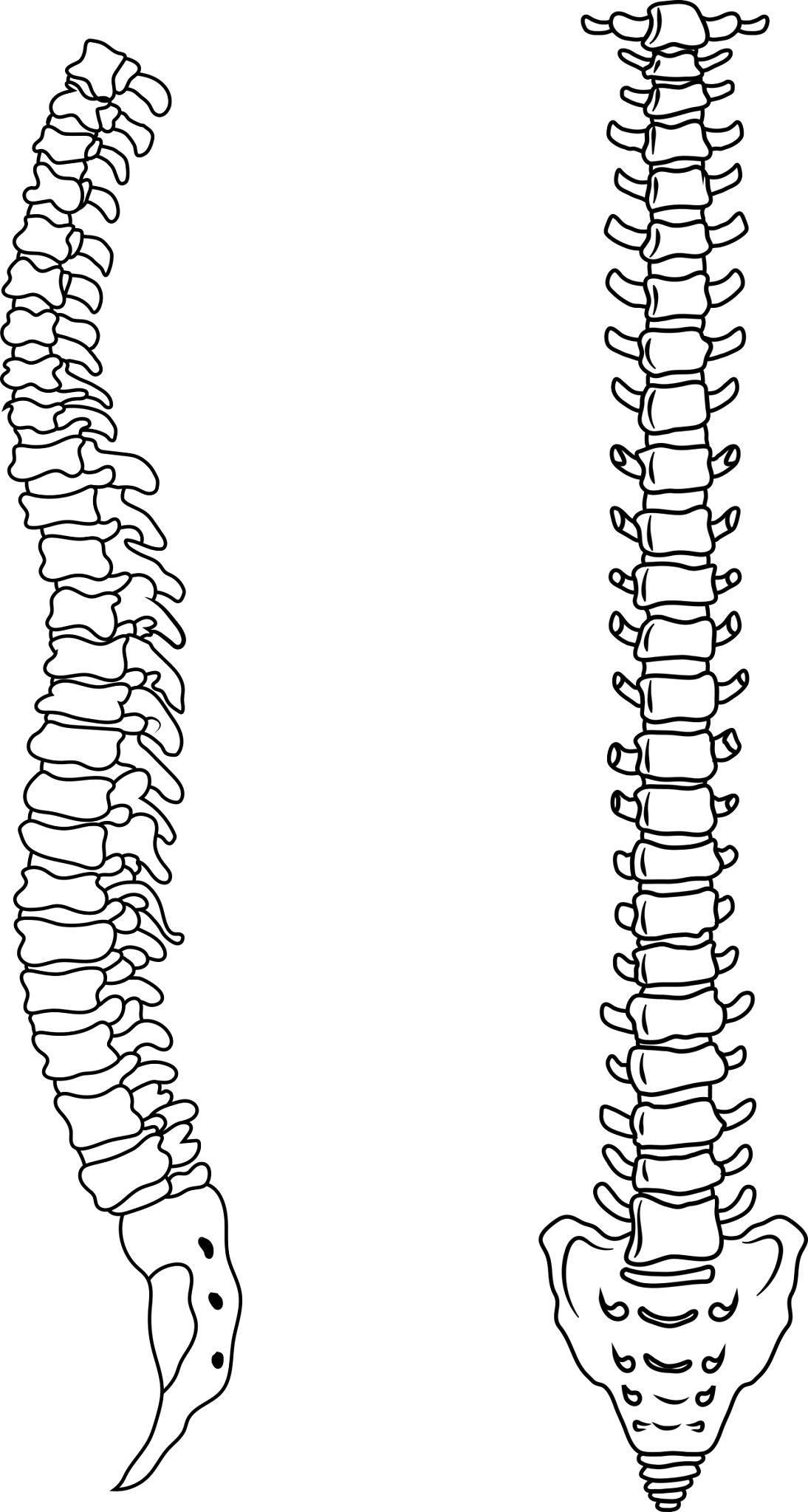
How many sections make up the Vertebral Column
5 sections
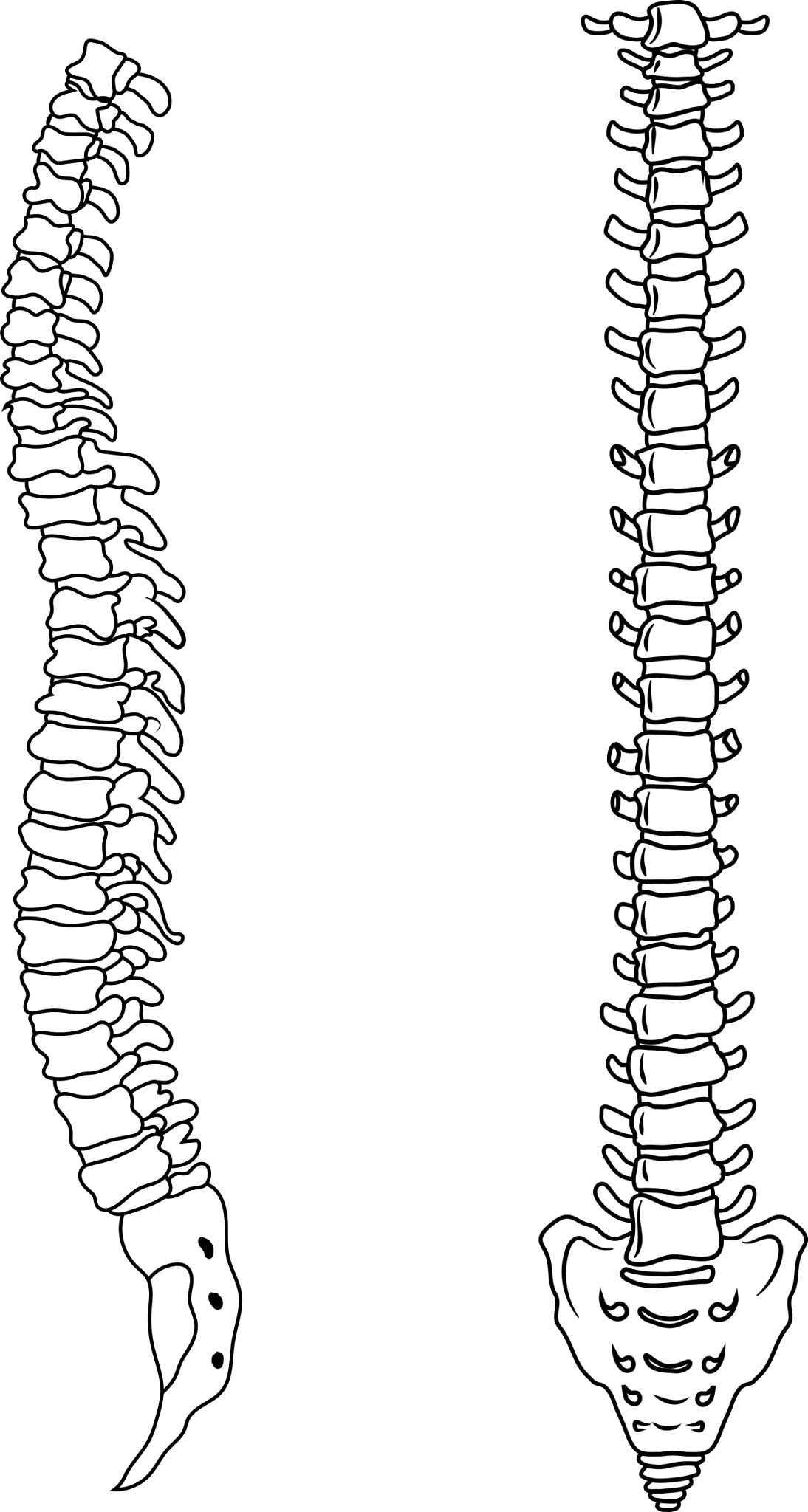
What are the sections that make up the Vertebral Column
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccyx
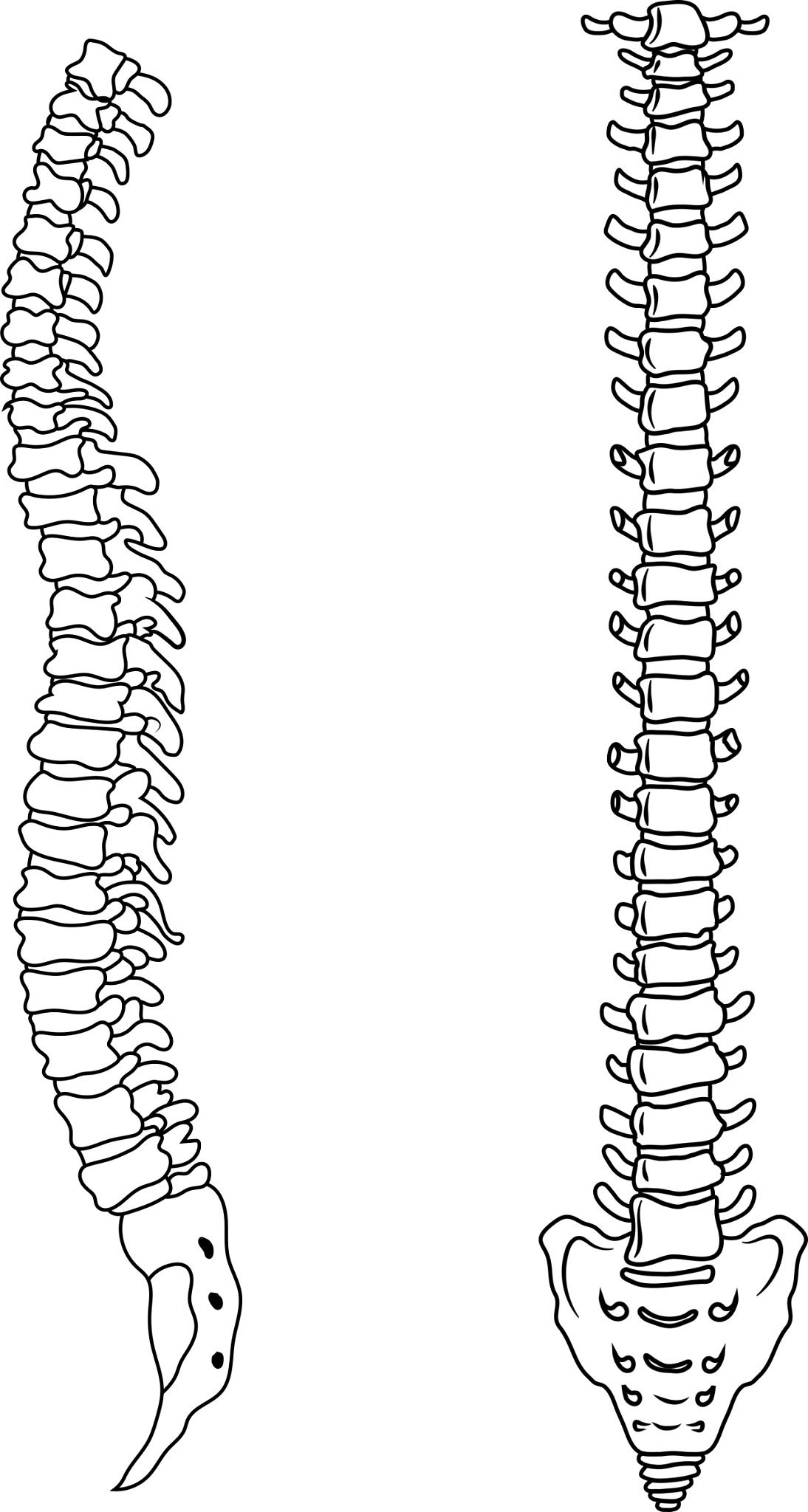
Primary Functions of Vertebral Column
The 33 vertebrae function together to aid movement and posture as well as providing support and protection of the Spinal Cord.
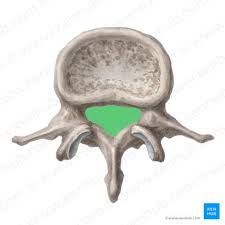
Vertebral Foramen
The hole created by the load-bearing vertebral body & vertebral arch. When aligned they create a channel to protect and enclose the spinal cord.
Vertebral Arch
Has multiple features which act as articulation for other bones or attachment sites for ligaments & muscles.
spinous processes
transverse processes
pedicles
lamina
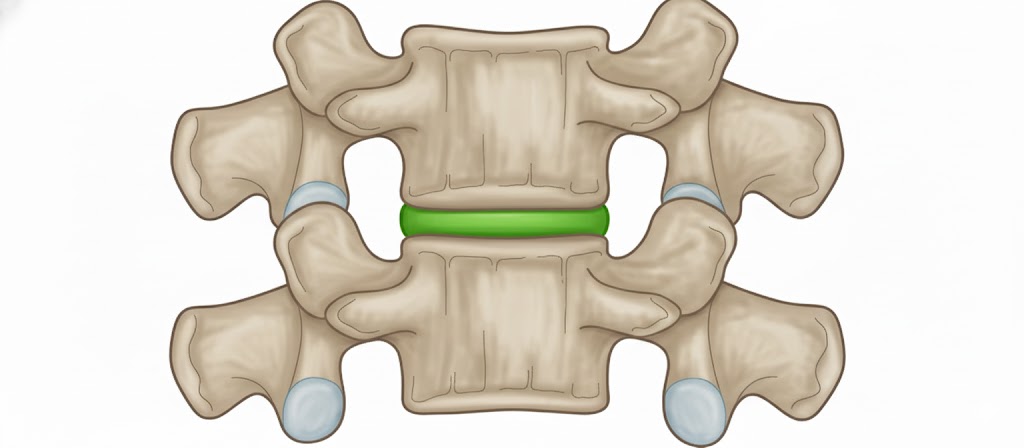
Intervertebral disc
Allow for shock absorption and movement
Ligaments that articulate with the Bones of the Back
ligamentum flavum
interspinous ligament
supraspinous ligament
intertransverse ligaments
anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments
Muscles of the Back
Can be arranged into 3 categories based on location:
Superficial
Intermediate
Intrinsic
Superficial back muscles
found just under the skin
Allows movement of the shoulder
latissimus dorsi, trapezius, levator scapulae and the rhomboids
Intermediate back muscles
Work to elevate and depress the rib cage
Serratus posterior superior
serratus posterior inferior
Intrinsic back muscles
Help movements of the vertebral column & control posture
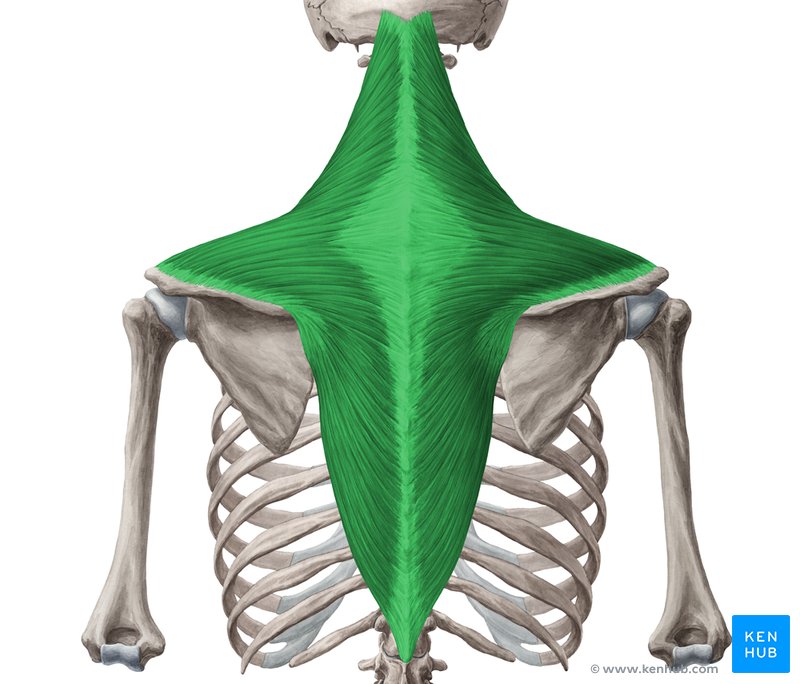
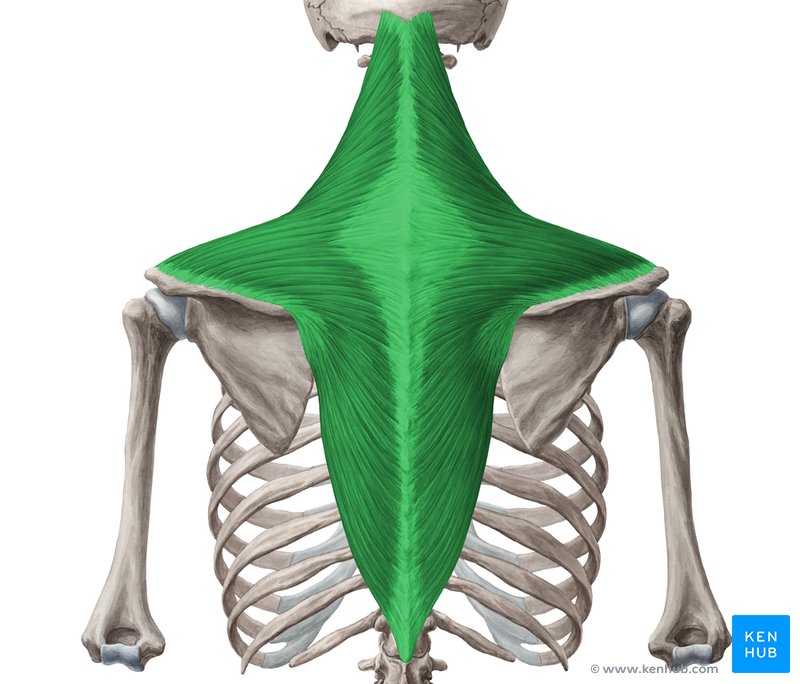
Trapezius Origin:
Bottom of the skull
ligamentum nuchae
spinous processes of C7-T12
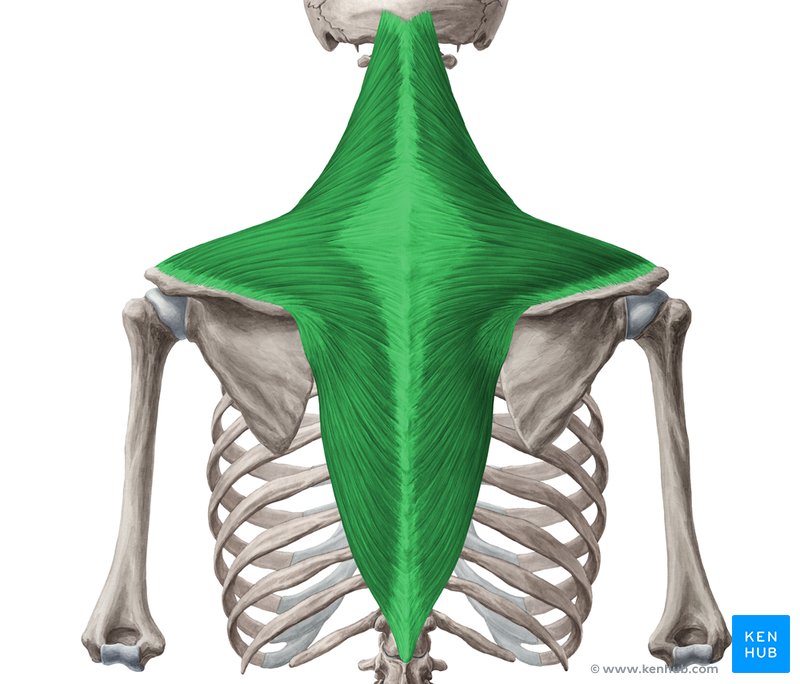
Trapezius Insertion
Clavicle
Acromion
Scapula spine
Trapezius Innervation
Motor innervation from accessory nerve
Receives propriorecptor fibres from C3+C4 spinal nerves
Trapezius Action
The upper fibres of the trap elevates the scapula + rotates scapula during abduction of the arm
The middle fibres retract the scapula
The lower fibres pull the scapula inferiorly
Trapezius
A broad flat triangular muscle. Most superficial of all back muscles
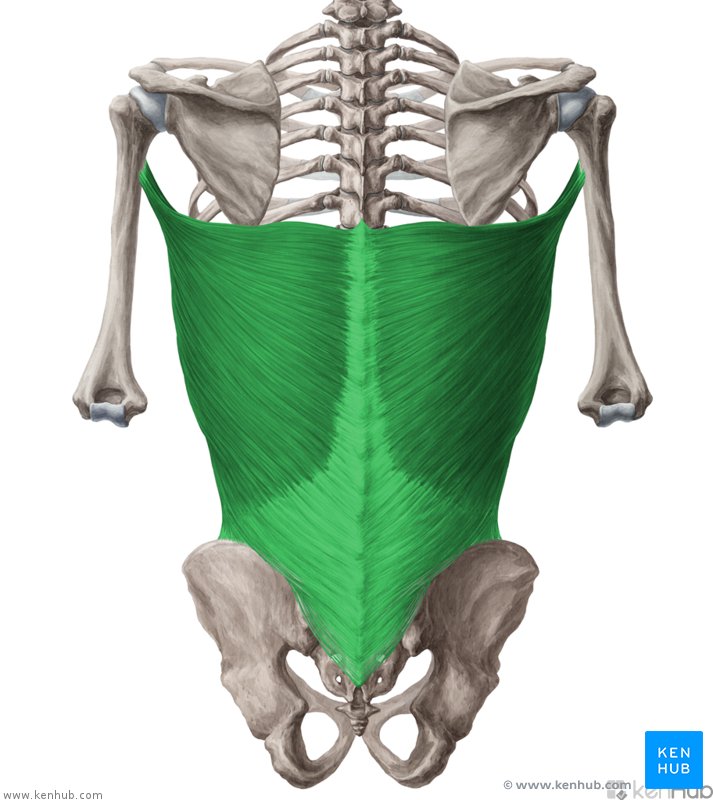
Latissimus Dorsi
This muscle originates from the lower part of the back, where it covers a wide area
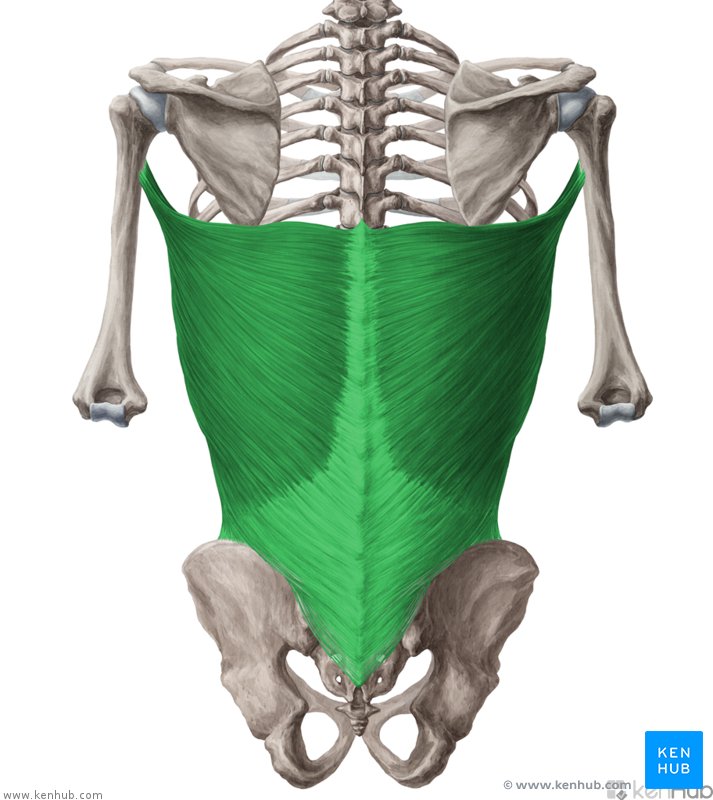
Latissimus Dorsi Origin
Spinous processes of T6-T12
Thoracolumbar fascia
Iliac crest
inferior 3 ribs
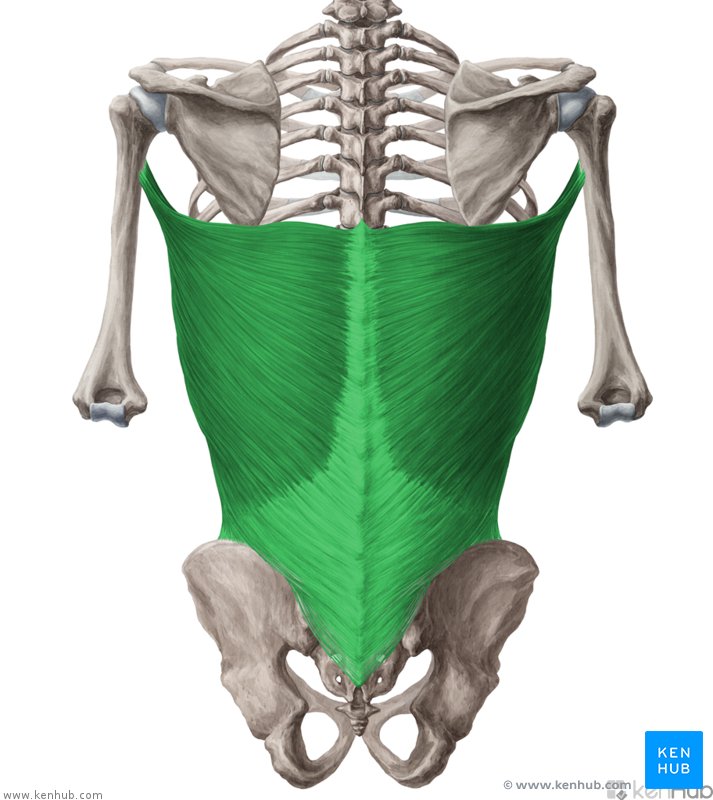
Latissimus Dorsi Insertion
The fibres converge into a tendon that attaches to intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
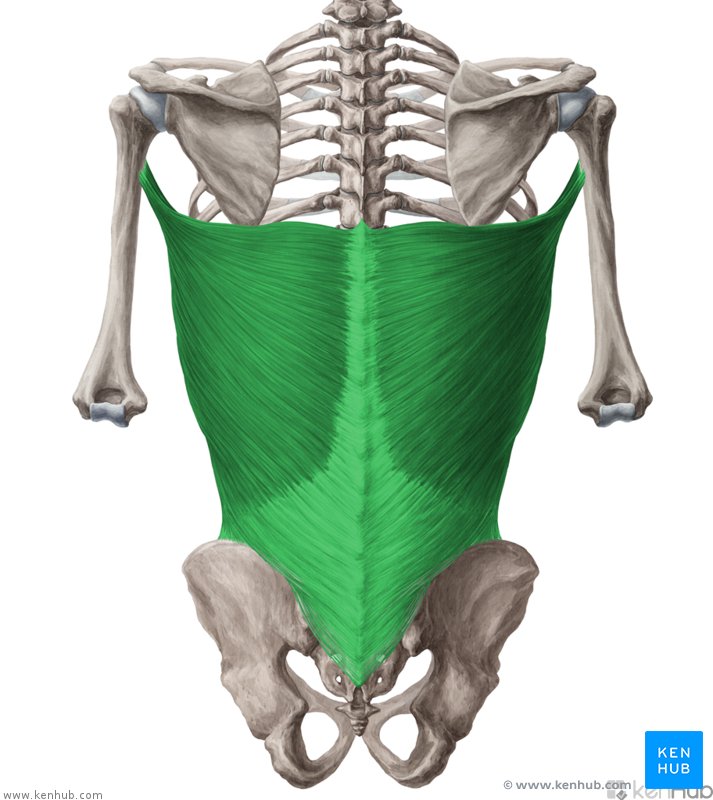
Latissimus Dorsi Innervation
Thoracodorsal Nerve
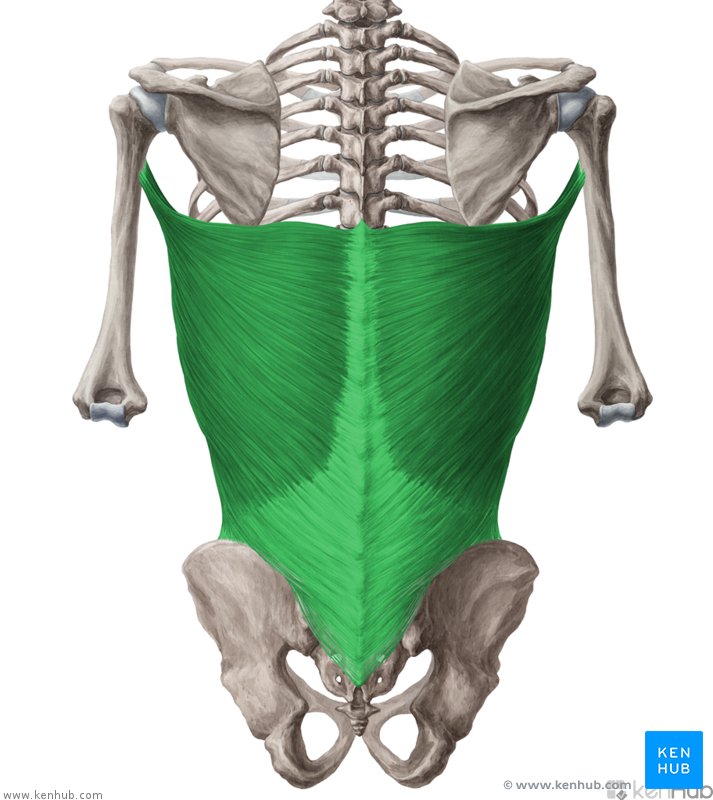
Latissimus Dorsi Action
Extends upper limb
Adducts upper limb
medially rotates the upper limb
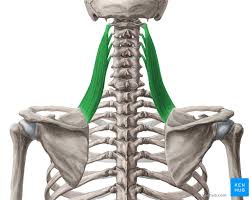
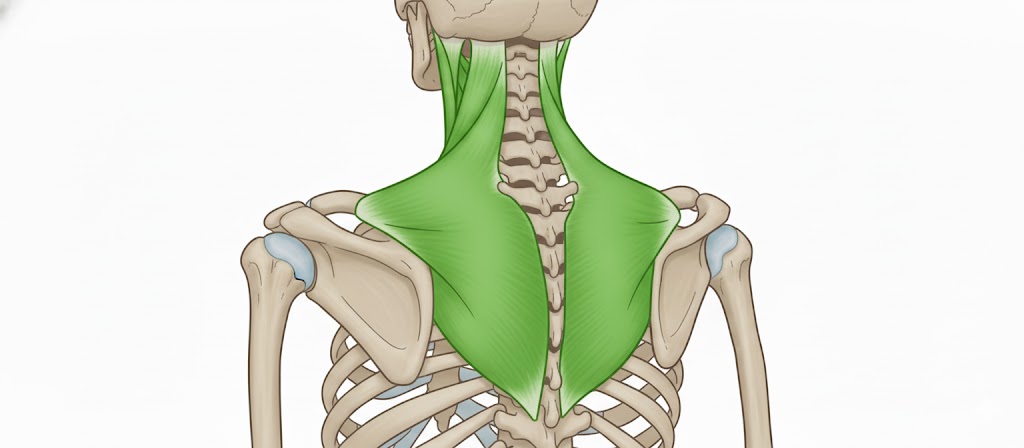
Levator Scapulae
A small strap-like muscle. It begins at the neck and descends to attach to the scapula
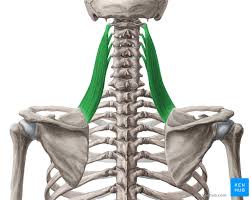
Levator Scapulae Origin
Transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae
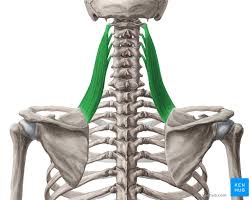
Levator Scapulae Insertion
Medial border of the scapula
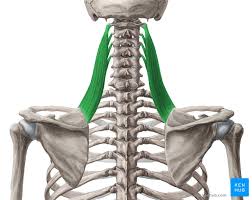
Levator Scapulae Innervation
Dorsal scapular nerve
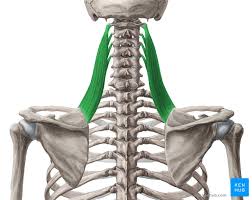
Levator Scapulae Action
Elevates the scapula
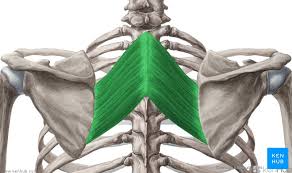
Rhomboid Major Origin
Spinous processes of T2-T5 vertebrae
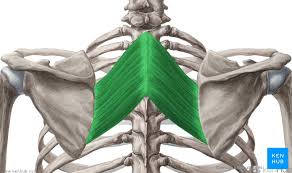
Rhomboid Minor Origin
Spinous processes of C7-T1 vertebrae
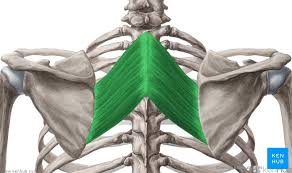
Rhomboid Major Insertion
Medial border of scapula (between scapula spine + inferior angle)
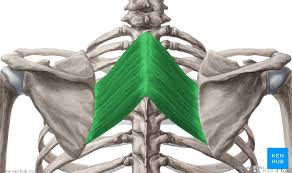
Rhomboid Minor Insertion
Medial border of the scapula, at the level of the spine of the scapula
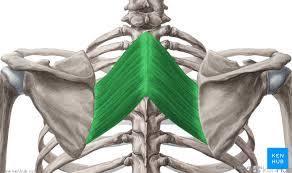
Rhomboid Major + Minor Innervation
Dorsal scapular nerve
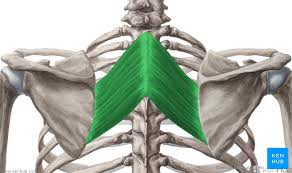
Rhomboid Major + Minor Action
Retract the scapula
Rotate the scapula
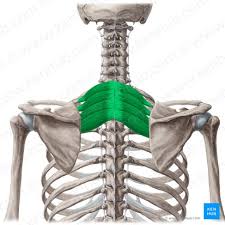
Serratus Posterior Superior
This muscle is a thin, rectangular shaped muscle. It lies deep to the rhomboid muscles on the upper back
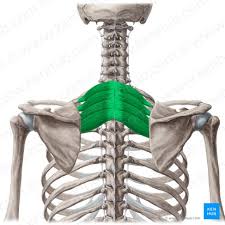
Serratus Posterior Superior Origin
Lower portion of ligamentum nuchae
Cervical + thoracic spines C7-T3
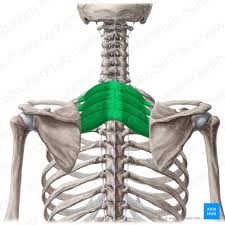
Serratus Posterior Superior Insertion
Ribs 2-5
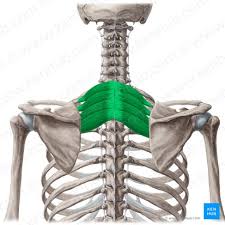
Serratus Posterior Superior Action
Elevates ribs 2-5
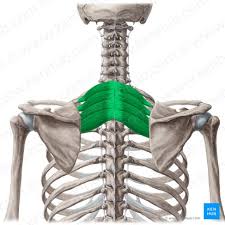
Serratus Posterior Superior Innervation
Intercostal nerves
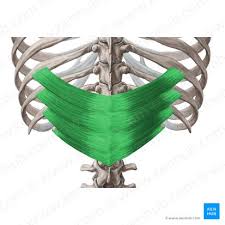
Serratus Posterior Inferior Origin
Thoracic + Lumbar spines (T11-L3)
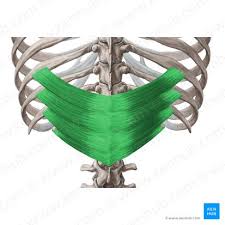
Serratus Posterior Inferior Insertion
Ribs 9-12
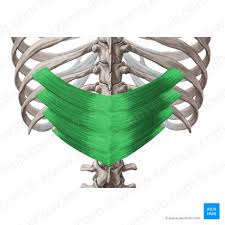
Serratus Posterior Inferior Action
Depress ribs 9-12
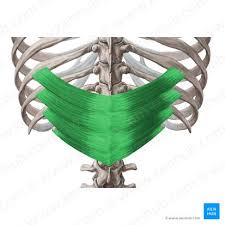
Serratus Posterior Inferior Innervation
Intercostal nerves
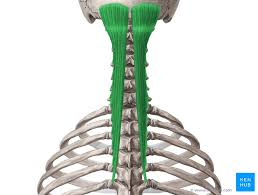
Semispinalis Capitis Origin
Transverse processes of C4-T10
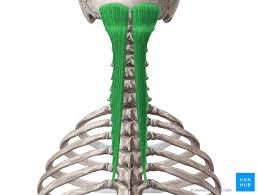
Semispinalis Capitis Insertion
Spinous processes of C2-T4
Occipital bone of the skull
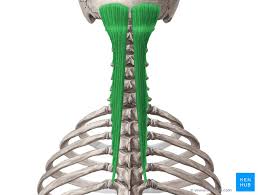
Semispinalis Capitis Innervation
Posterior rami of the spinal nerves
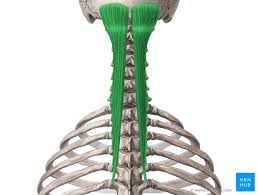
Semispinalis Capitis Actions
Extend the hed
Contralaterally rotates the head
Contralaterally rotates the vertebral column
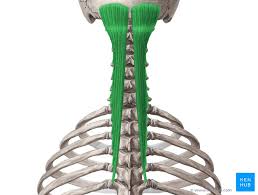
Semispinalis Capitis
The most superficial of the deep intrinsic muscles. It can be divided by its superior attachments into thoracic, cervicis, and capitis
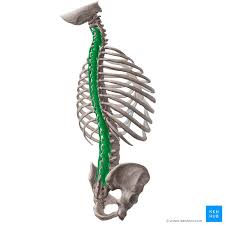
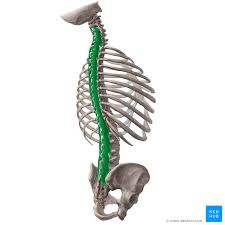
Multifidus
Located underneath the semispinalis muscle. It is most developed in the lumbar area
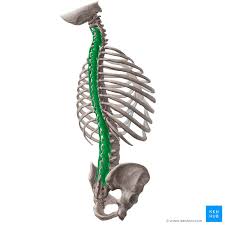
Multifidus Origin
Sacrum
Posterior iliac spine
erector spinae
mamillary processes of lumbar vertebrae
transverse processes of T1-T3
Articular processes of C4-C7
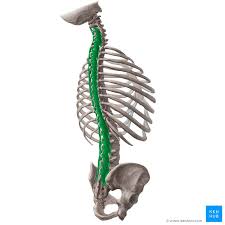
Multifidus Inse
Vertebral spinous processes
Multifidus Innervation
Posterior rami of the spinal nerves
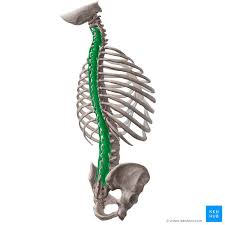
Multifidus Action
Stabilizes the vertebral column
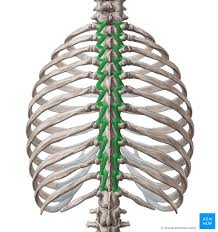
Rotatores
The deepest muscles of the transversospinales group. They are the most prominent in the thoracic region.
Rotatores Origin
Vertebral transverse processes
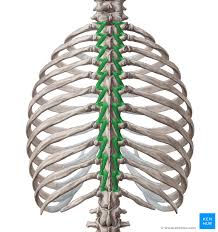
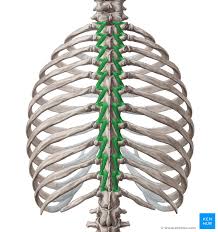
Rotatores Insertion
Lamina + spinous processes of the vertebrae above
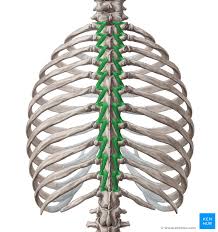
Rotatores Action
Extension of vertebral column
rotation of vertebral column
stabilizes the vertebrae
Proprioceptive function
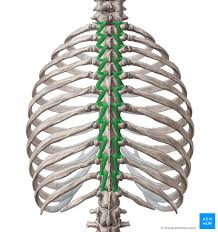
Rotatores Innervation
Posterior rami of the spinal nerves
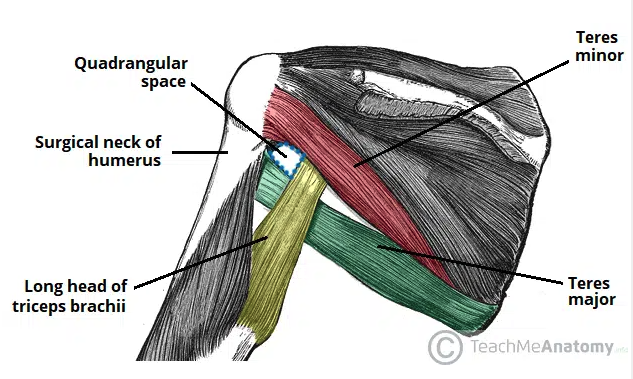
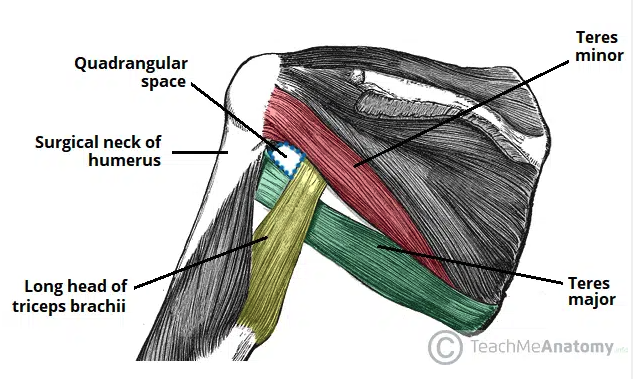
Quadrangular Space
The anatomical space located in the posterior axilla region
Provides a conduit for structures to pass between the axilla and posterior compartment of the arm (axillary nerve)
Borders:
Superior: inferior margin of teres minor
Lateral: surgical neck of the humerus
Medial: long head of triceps brachii
Inferior: superior aspect of teres major
Quadrangular Space Syndrome
Refers to compression of the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery as they pass through the space
Thought to be caused by hypertrophy of the muscular borders of the space, or by the formation of fibrotic bands between muscles
Clinically displays as pain and paraesthesia in the distribution of the axillary nerve as well as pain upon shoulder abduction and external rotation
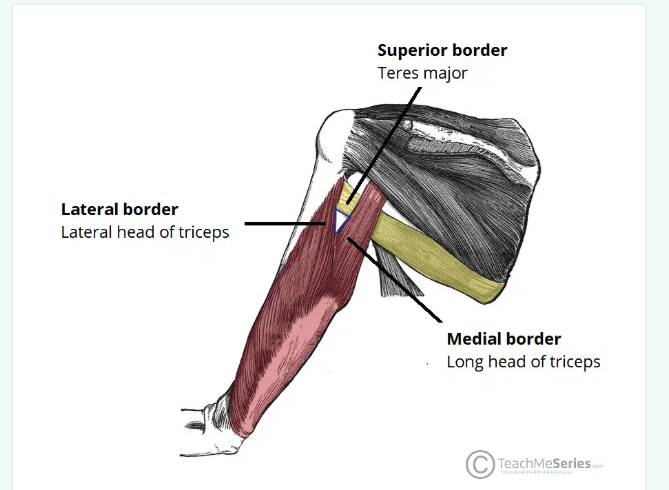
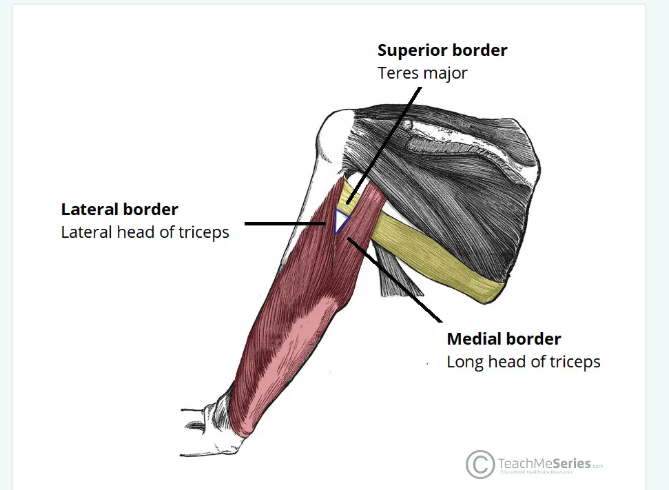
Triangular interval
An anatomical space located immediately below the axilla region
allows structures to pass between anterior and posterior compartments of the upper arm (radial nerve)
Boarders
Inferior: teres major
Lateral: shaft of humerus/lateral head of triceps brachii
Medial: lateral border of long head of the triceps brachii
Triangular interval syndrome
Refers to compression of the radial nerve as it passes through the triangular interval
Thought it can occur due to hypertrophy of triceps brachii or teres minor
Clinically presents as neuropathic pain or paraesthesia in sensory distribution radial nerve, or weakness in extension of elbow, wrist, or digits
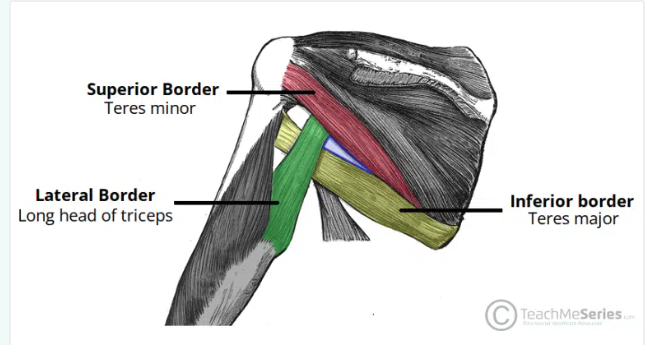
Triangular Space
Refers to the anatomical space located in the axilla
Allows structures to pass between the axilla and posterior scapular region (Circumflex scapular artery)
Boarders:
Lateral: medial margin of the long head of the triceps brachii
Inferior: superior margin of the teres major
Superior: inferior border of the teres minor (or subscapularis)$
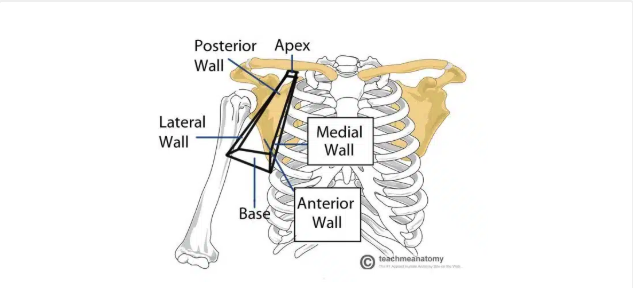
Axilla
The area that lies underneath the glenohumeral joint at the junction of the upper limb and thorax
Is a passageway by which neruovascular and muscular structures can enter and leave the upper limb
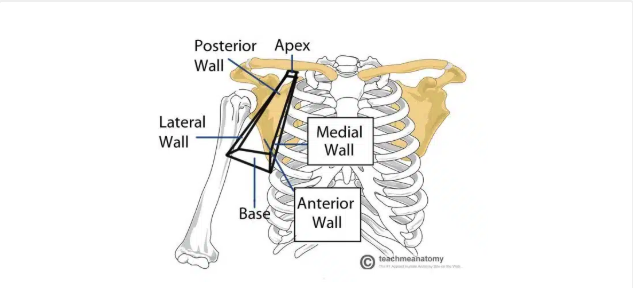
Axilla region borders
Apex: axillary inlet (formed by lateral border of first rib, superior border of scapula, posterior border of clavicle)
Lateral wall: formed by inter-tubercular groove of the humerus
Anterior wall: contains the pectoralis major and the underlying pectoralis minor and subclavius muscles
Medial wall: consists of the serratus anterior and the thoracic wall
Posterior wall: formed by the subscapularis, teres major, and latissimus dorsi
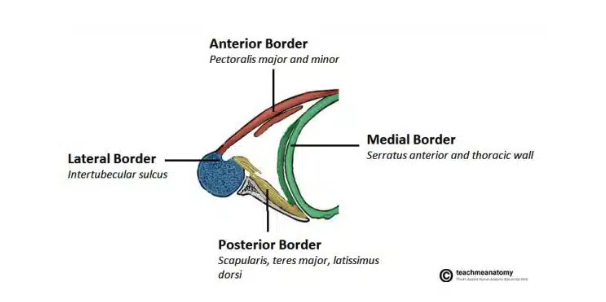
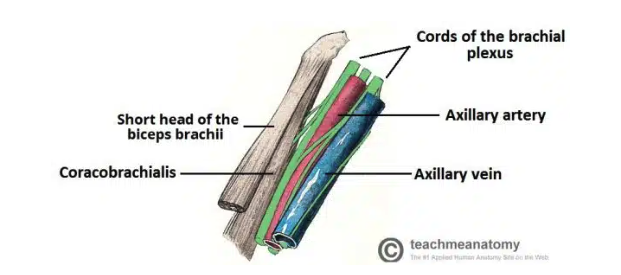
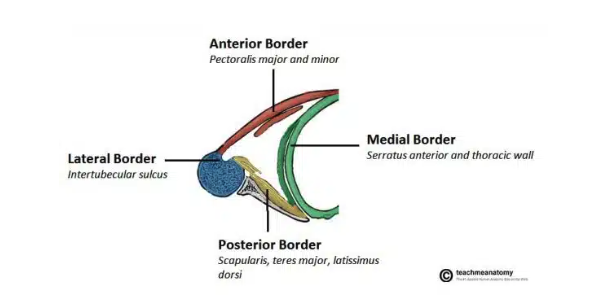
Axillary region contents
Axillary artery: the main artery supplying the upper limb
Axillary vein: main vein draining from upper limb
Brachial plexus: collection of spinal nerves that form peripheral nerves of upper limb
Axillary lymph nodes: filters lymphatic fluid drained from upper limb
Biceps brachii + coracobrachialis: these muscle tendons move through the axilla
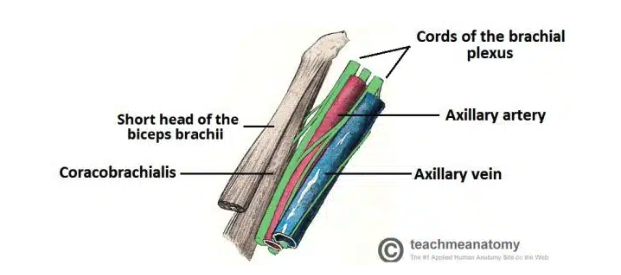
Passageways Exiting the Axilla
Inferiorly and laterally into the upper limb
Through the quadrangular space (branch of axillary artery)
Clavipectoral triangle (cephalic vein, medial + lateral pectoral nerves)$
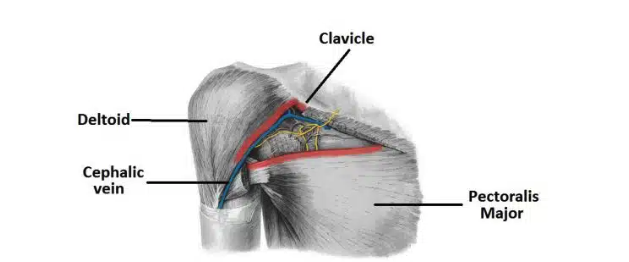
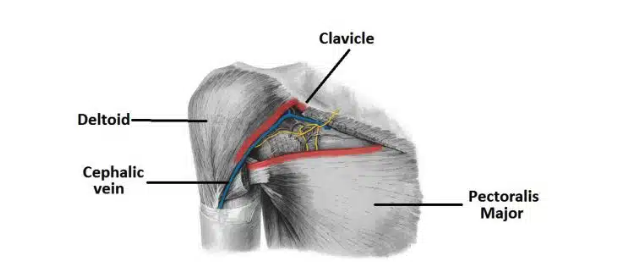
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
compression of the vessels and nerves in the apex of the axilla region
Common causes:
Trauma
Repetitive movements
Extra cervical rib
Present as pain in affected limb, tingling, muscle weakness, and discoloration
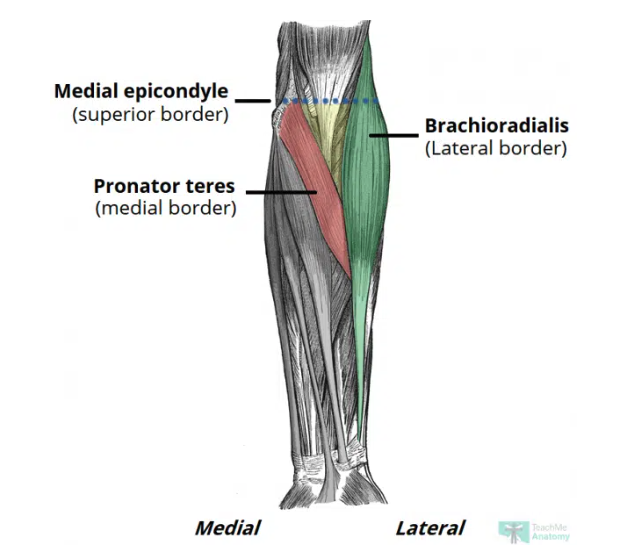
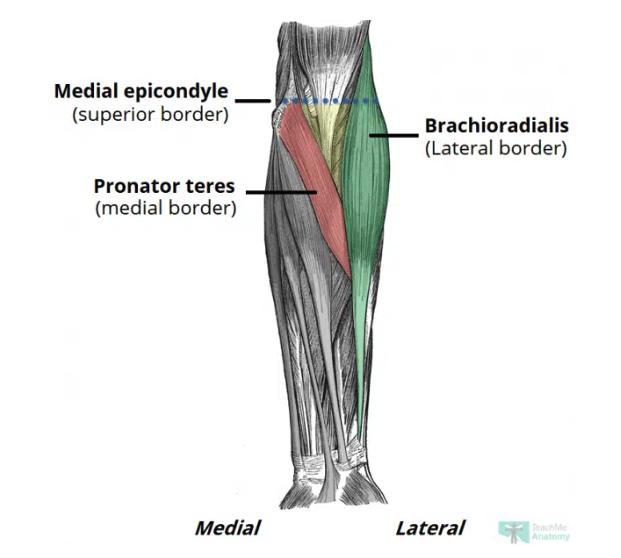
Cubital fossa
A triangular-shaped depression over the anterior aspect of the elbow joint
Area of transition between arm and forearm
Borders
Lateral: medial border of brachioradialis
Medial: lateral border of pronator teres
Superior: horizontal line drawn between epicondyles of humerus
Roof: bicipital aponeurosis, fascia, subcutaneuous fat, and skin
Floor: brachialis & supinator
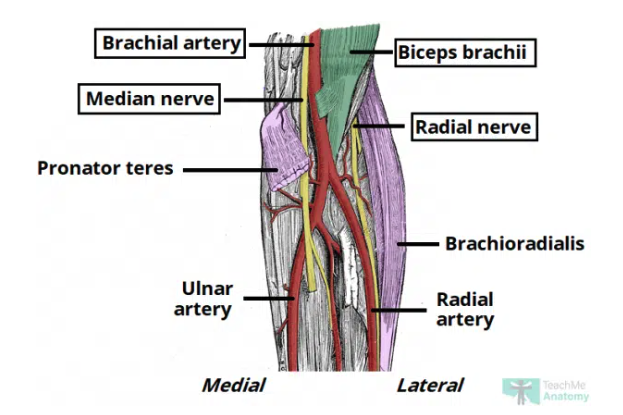
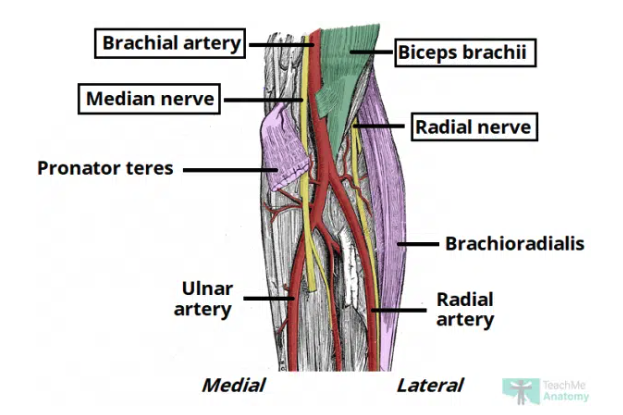
Cubital fossa contents
Radial nerve: travels along lateral border of cubital fossa (motor and sensory of posterior forearm & hand)
Biceps tendon
Brachial artery: bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at apex
Median nerve: passes through fossa passing between two heads of pronator teres (motor and sensory function anterior forearm & hand)
Supracondylar Fracture
Fracture to the distal humerus
Typically transverse or oblique most commonly caused by falling on an outstretched arm
Can cause damage to the brachial artery or anterior interosseous nerve
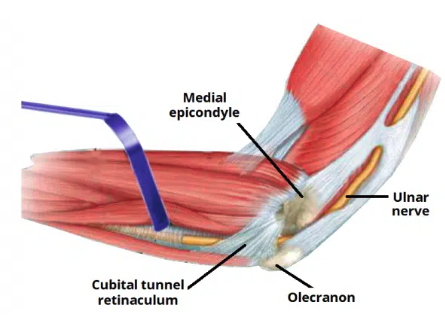
Ulnar tunnel
The fibro-osseous space located on the posteromedial aspect of the elbow
Transmits the ulnar nerve from the arm into the forearm
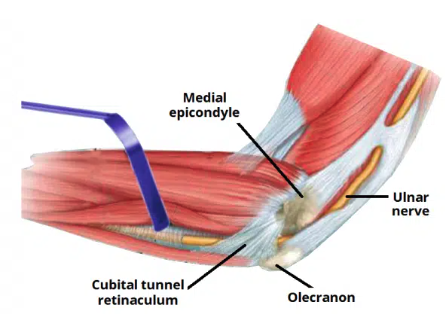
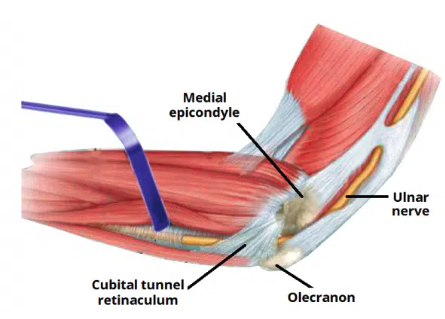
Ulnar tunnel borders
Medial: medial epicondyle of the humerus
Lateral: olecranon of the ulna
Floor: elbow joint capsule and medial collateral ligament of the elbow
Roof: ligament spanning between the medial epicondyle and olecran
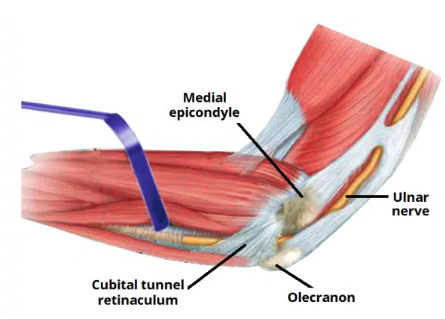
Cubital tunnel syndrome
refers to compression of the ulnar nerve within the ulnar tunnel
One of the most common peripheral neuropathy of the upper limb
Patient experience altered sensation, loss of motor function (including weakness and wasting of intrinsic hand muscles), pain during elbow flexion.
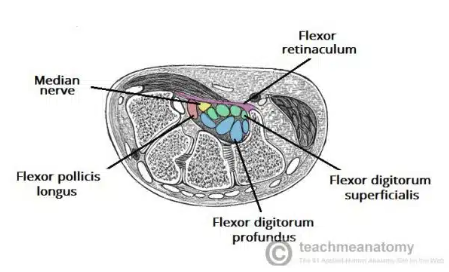
Carpal Tunnel
A narrow passageway found on anterior portion of the wrist
Is the entrance to the palm for several tendons and the median nerve
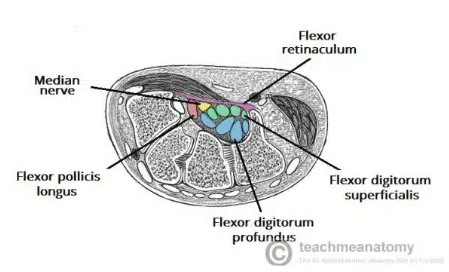
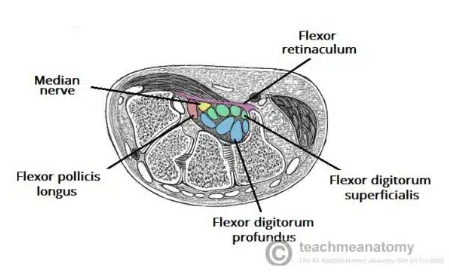
Carpal Tunnel borders
Deep carpal arch
superficial flexor retinaculum
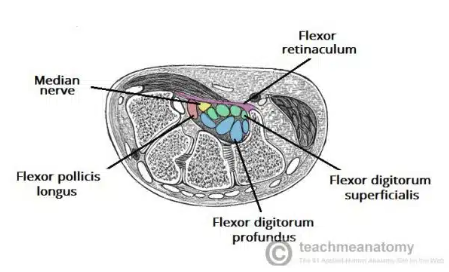
Carpal Arch
concave on palmar side (forms base & sides of carpal tunnel)
Scaphoid and trapezium tubercles (form lateral border)
hook of the hamate and pisiform (form medial border)
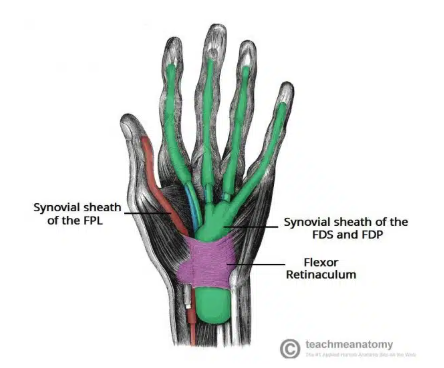
Flexor retinaculum
Thick connective tissue which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel
Turns the carpal arch into the carpal tunnel by bridging space between medial and lateral parts of the arch
spans between hook of the hamate and pisiform
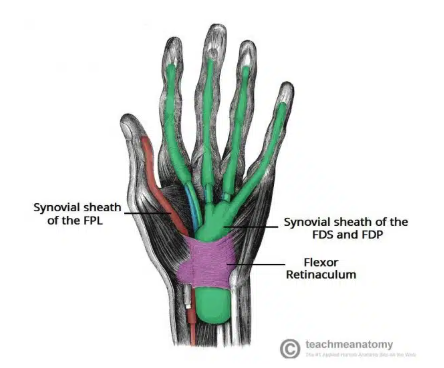
Carpal tunnel contents
flexor pollicis longus tendon
four flexor digitorum profundus tendons
four flexor digitorum superficialis tendons