Final Study Set (Labs 7-11)
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
mnemonic for cranial nerve type
some say money matters but my bother says big brains matter more
sensory cranial nerves
I, II, VIII (olfactory, optic, vestibulocochlear)
motor cranial nerves
III, IV, VI, XI, XII (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, accessory, hypoglossal)
mixed (both sensory AND motor) cranial nerves
V, VII, IX, X (trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus)
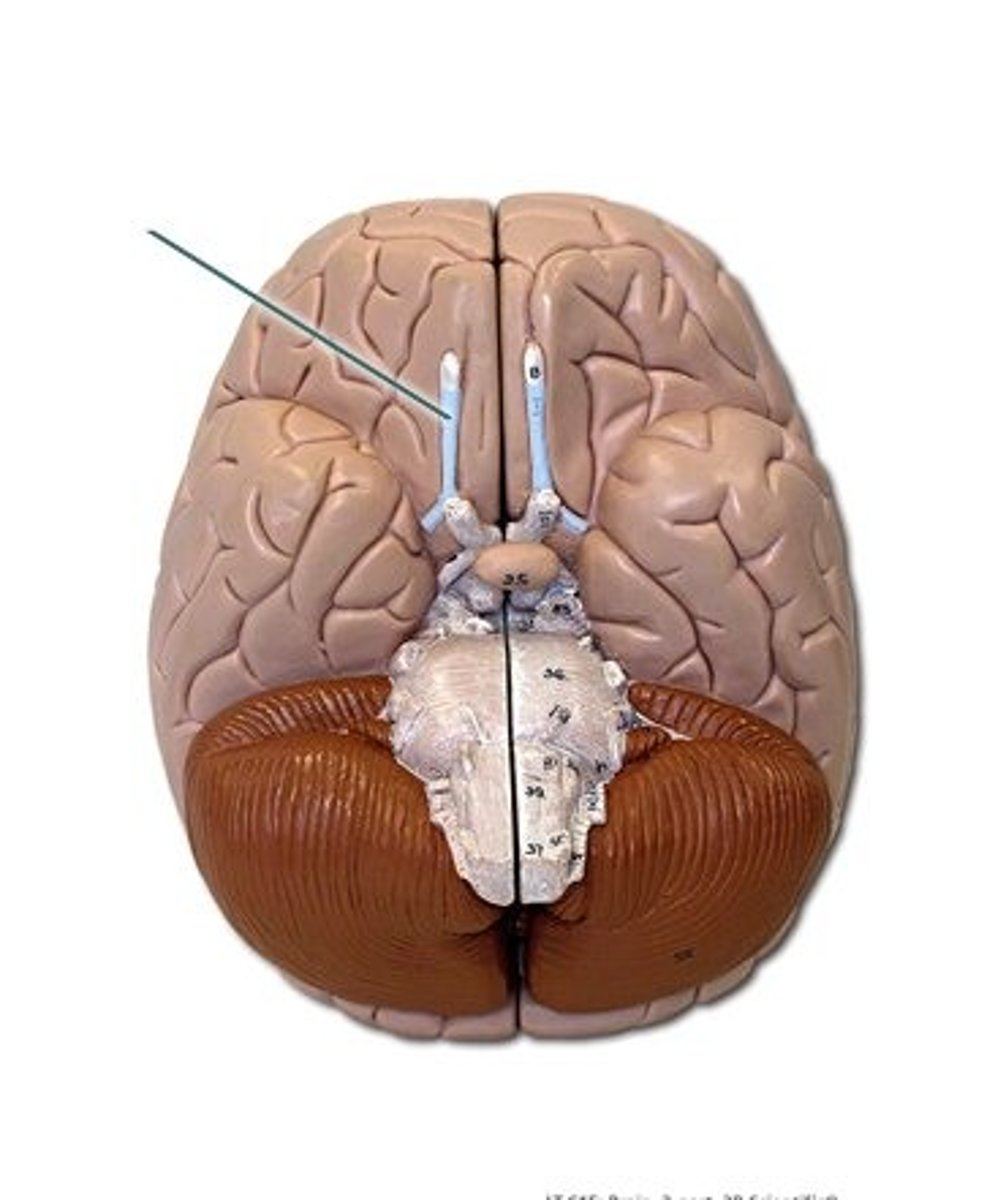
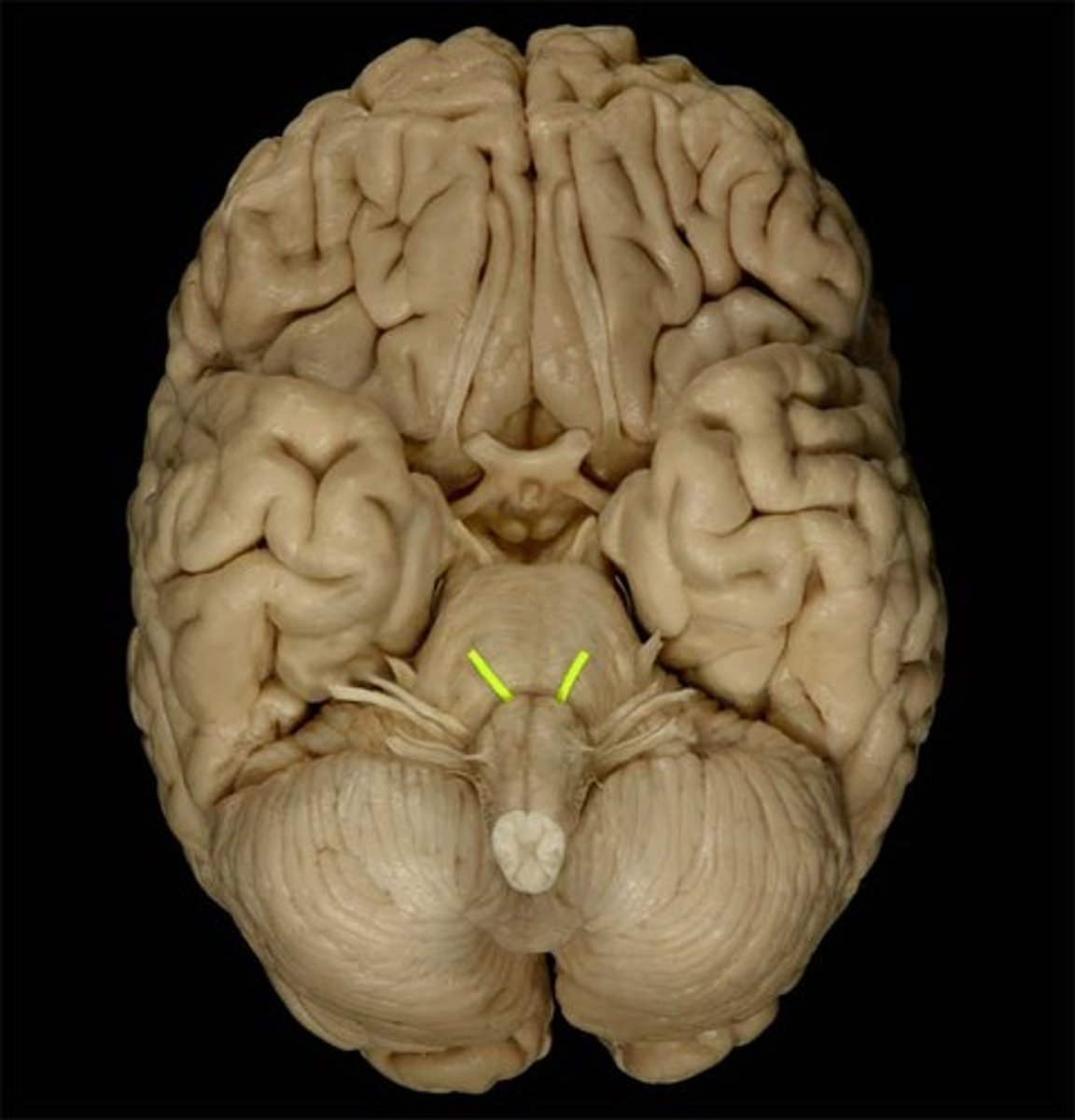
olfactory nerve (CN I)
Sensory cranial nerve related to smell
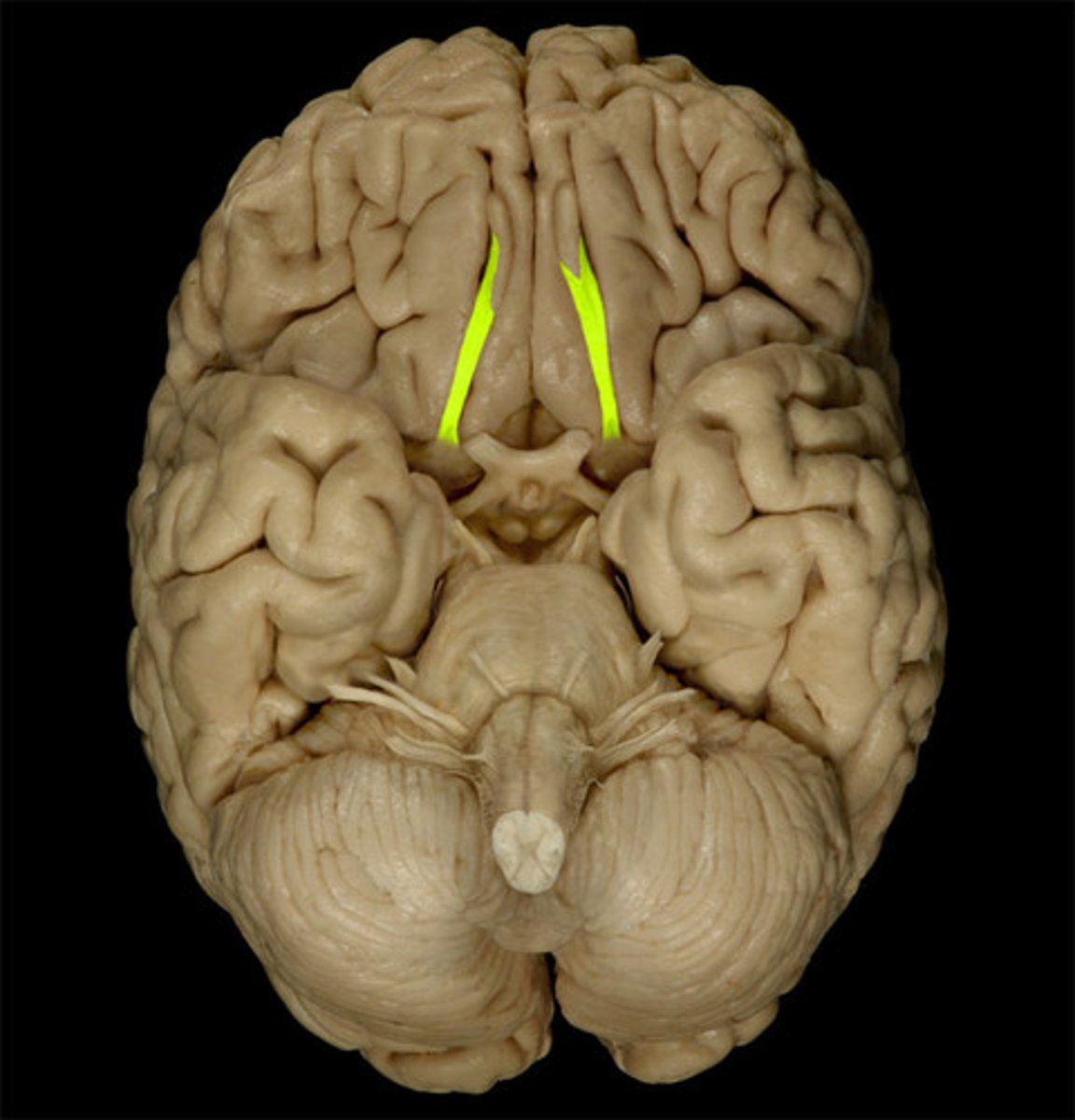
olfactory tract
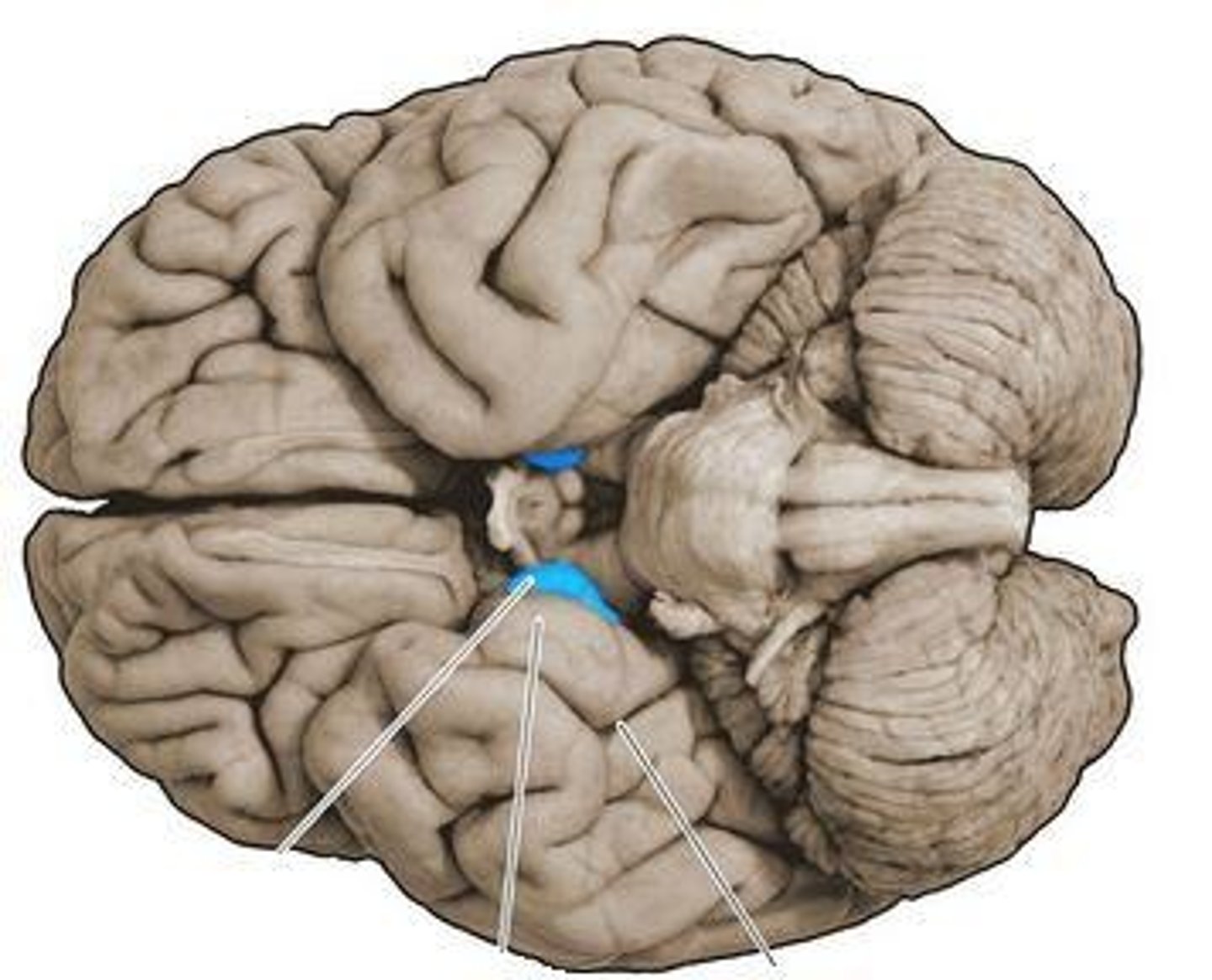
primary olfactory cortex (uncus)
•Located within temporal lobe
•Receives, processes, stores odor information
olfactory bulb
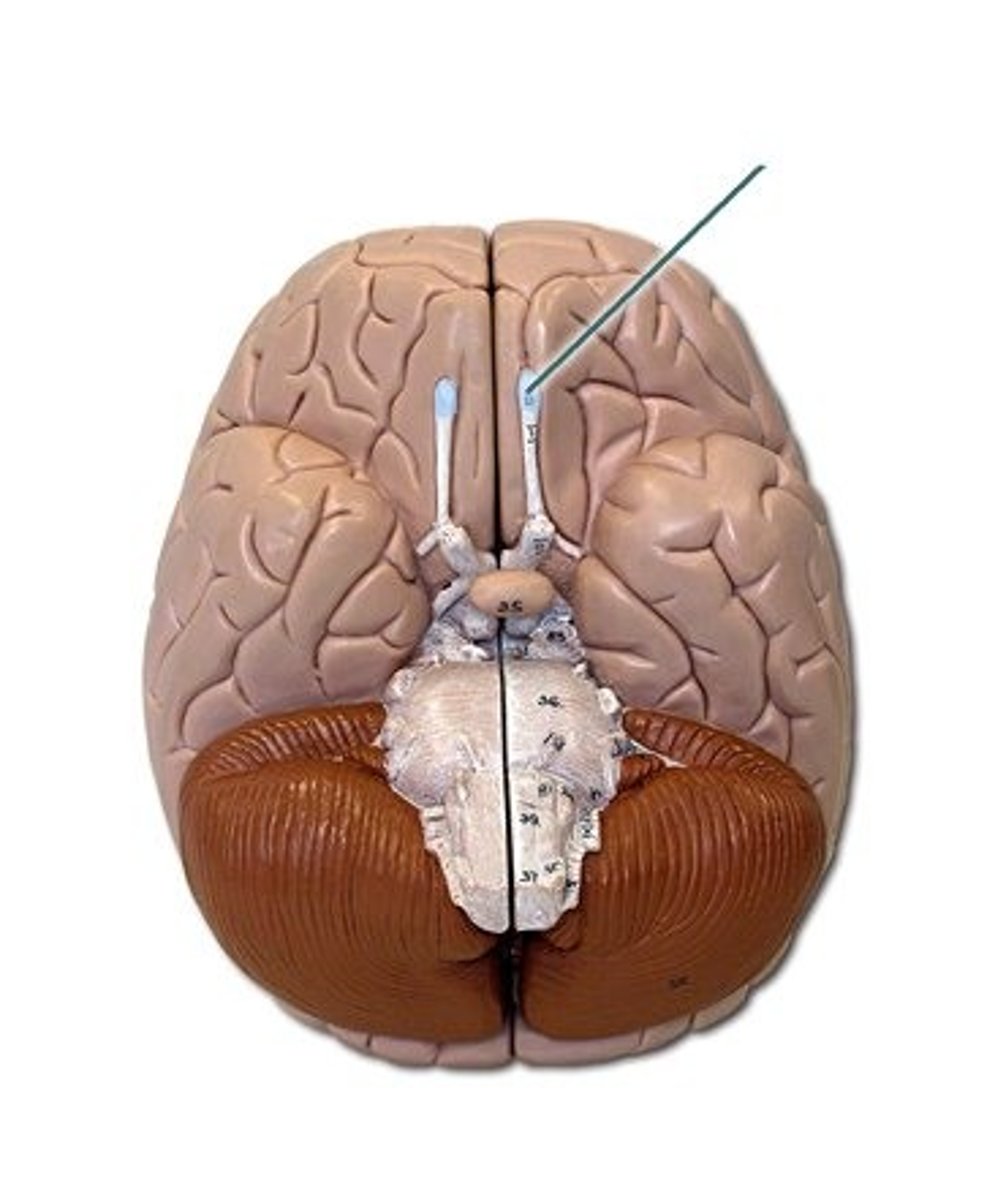
optic nerve (CN II)
Sensory cranial nerve related to vision
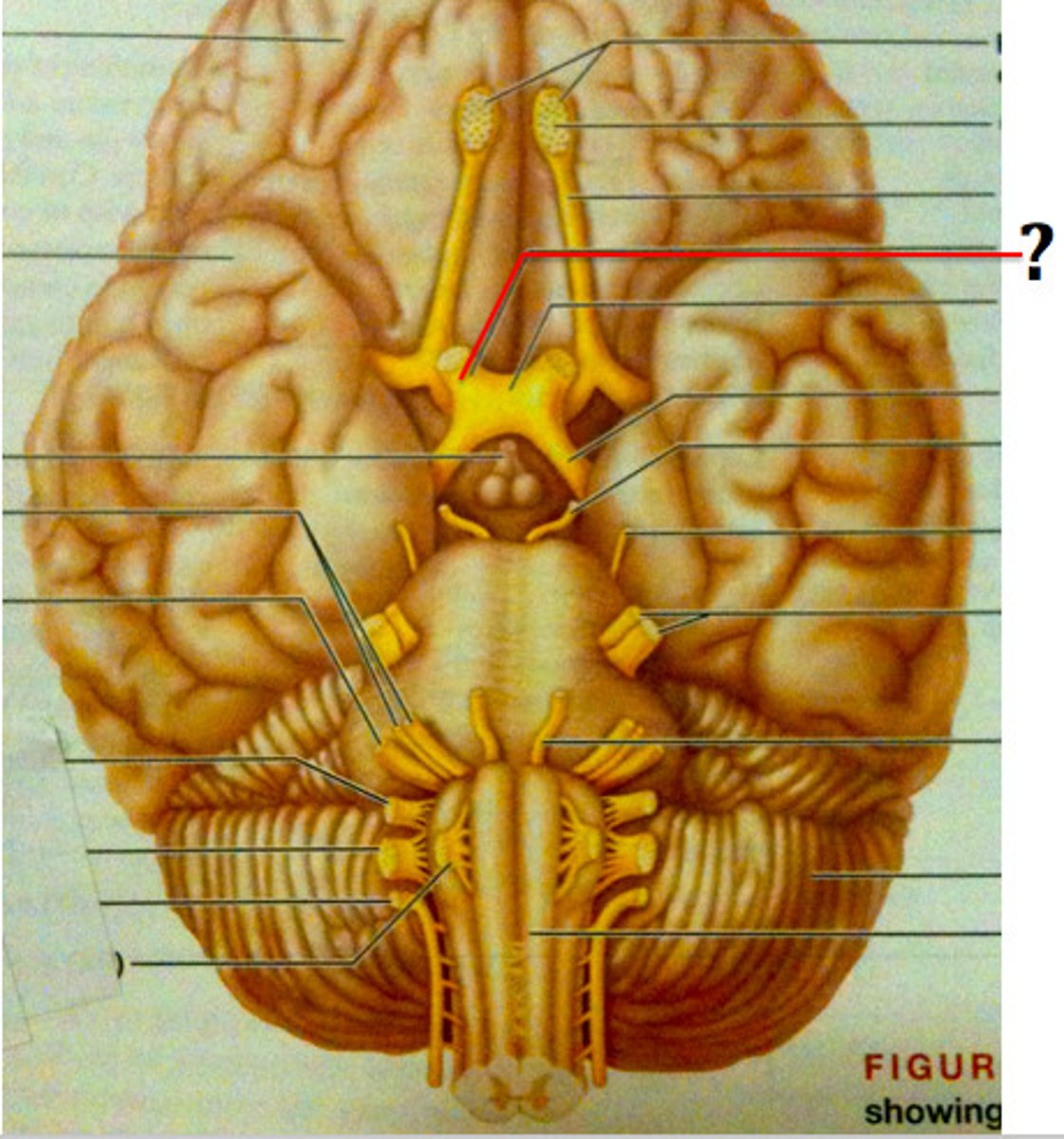
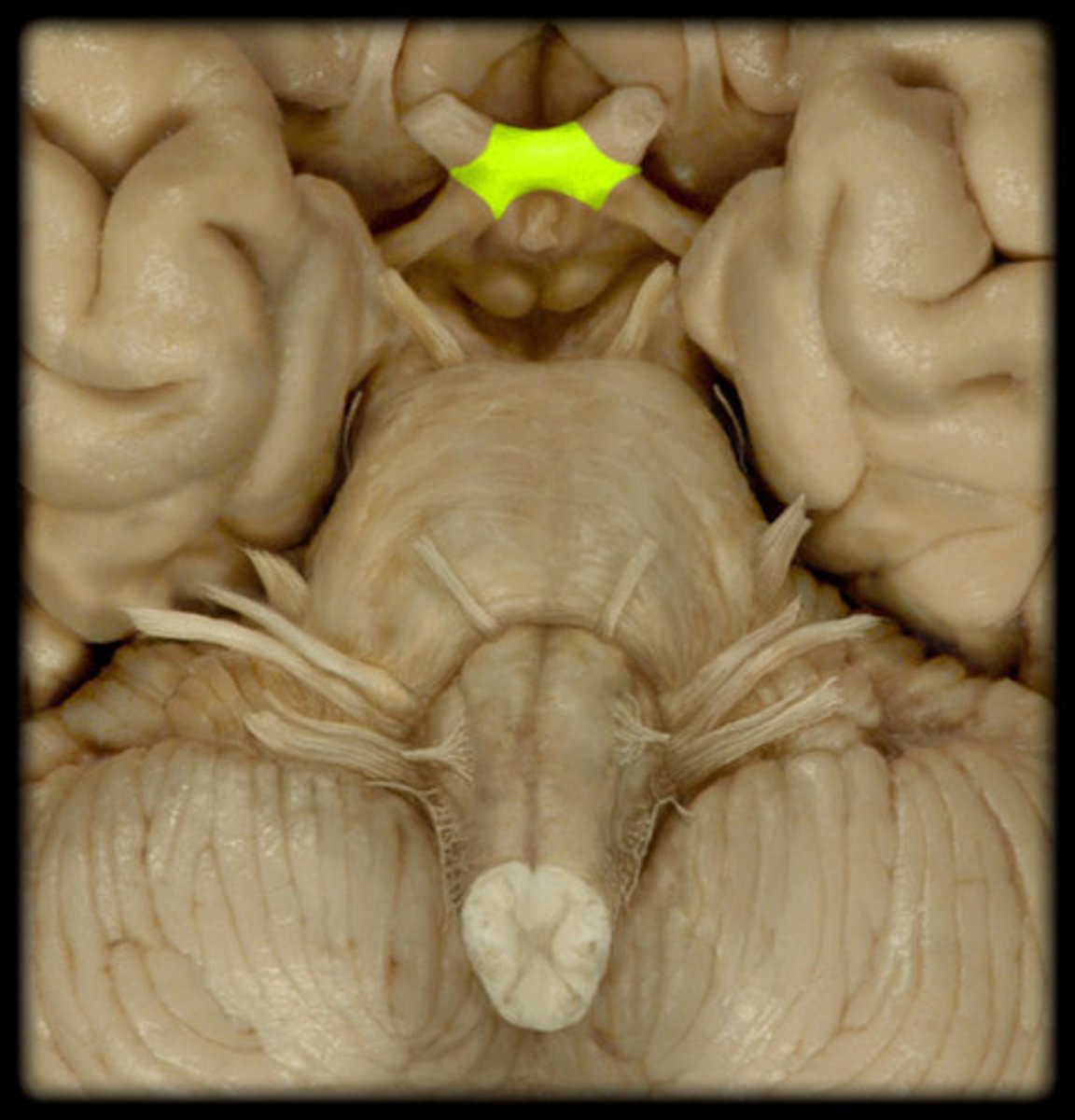
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
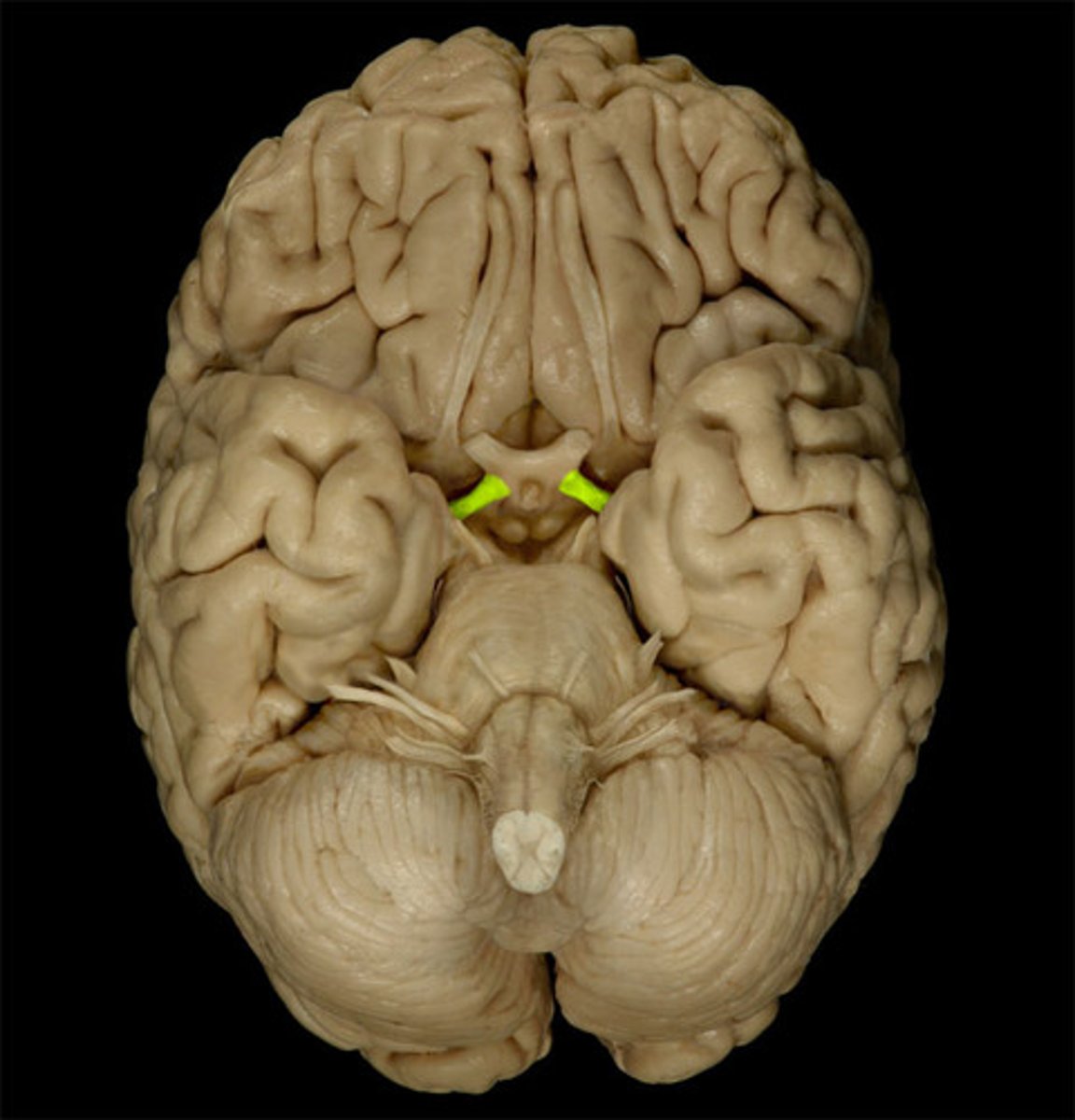
optic tracts
the continuation of the optic nerve fibers beyond the optic chiasma
primary visual cortex
•Located within occipital lobe; receives, processes, stores visual information

oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Motor cranial nerve that innervates extraocular and intraocular muscles involved in eye movement (up, down, medial), eyelid elevation, and pupil constriction; involved in direct light reflex, consensual light reflex, and accommodation reflex
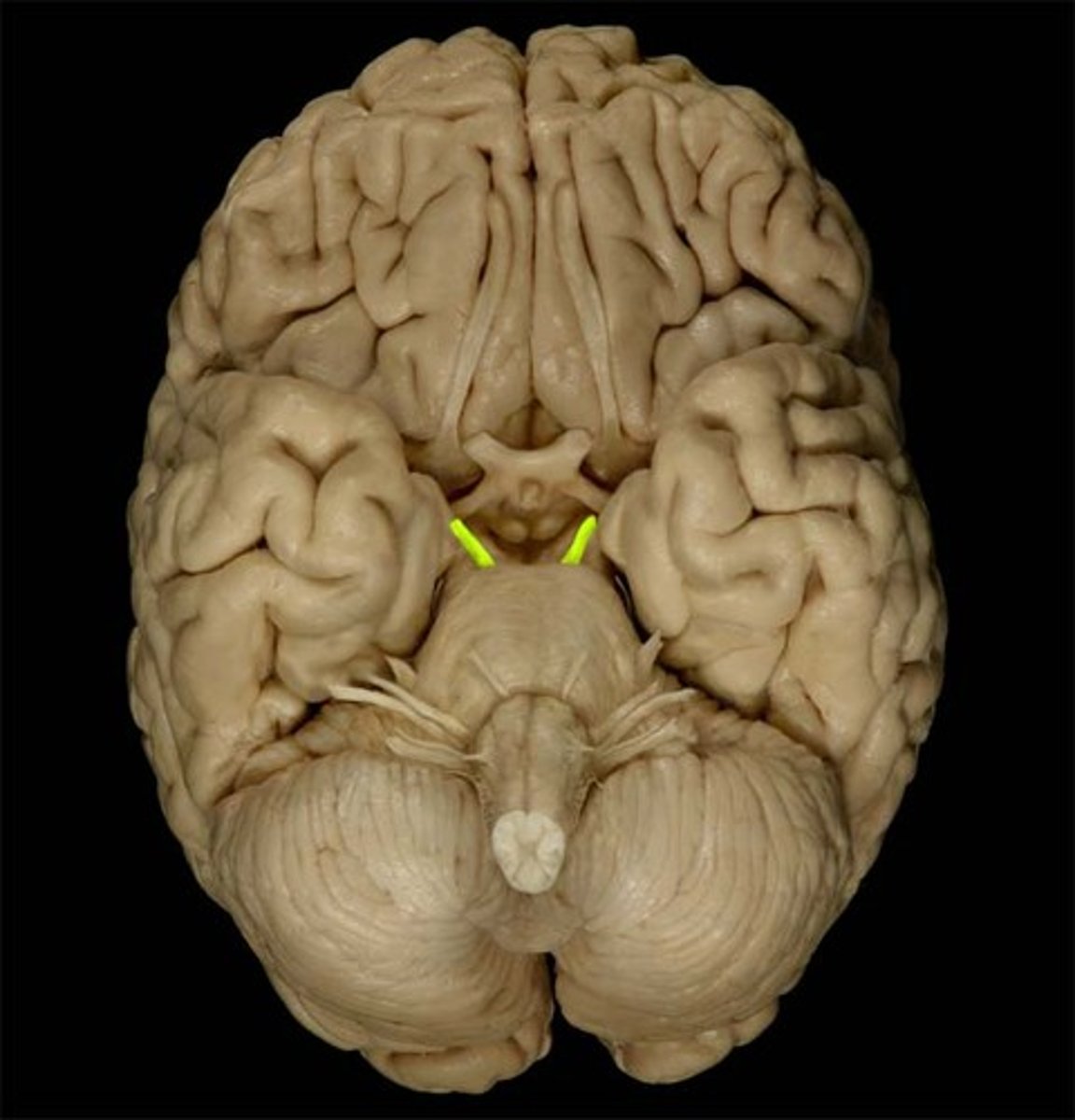
trochlear nerve (CN IV)
Motor cranial nerve that controls movement of the eye inferiorly and laterally; innervates superior oblique muscle
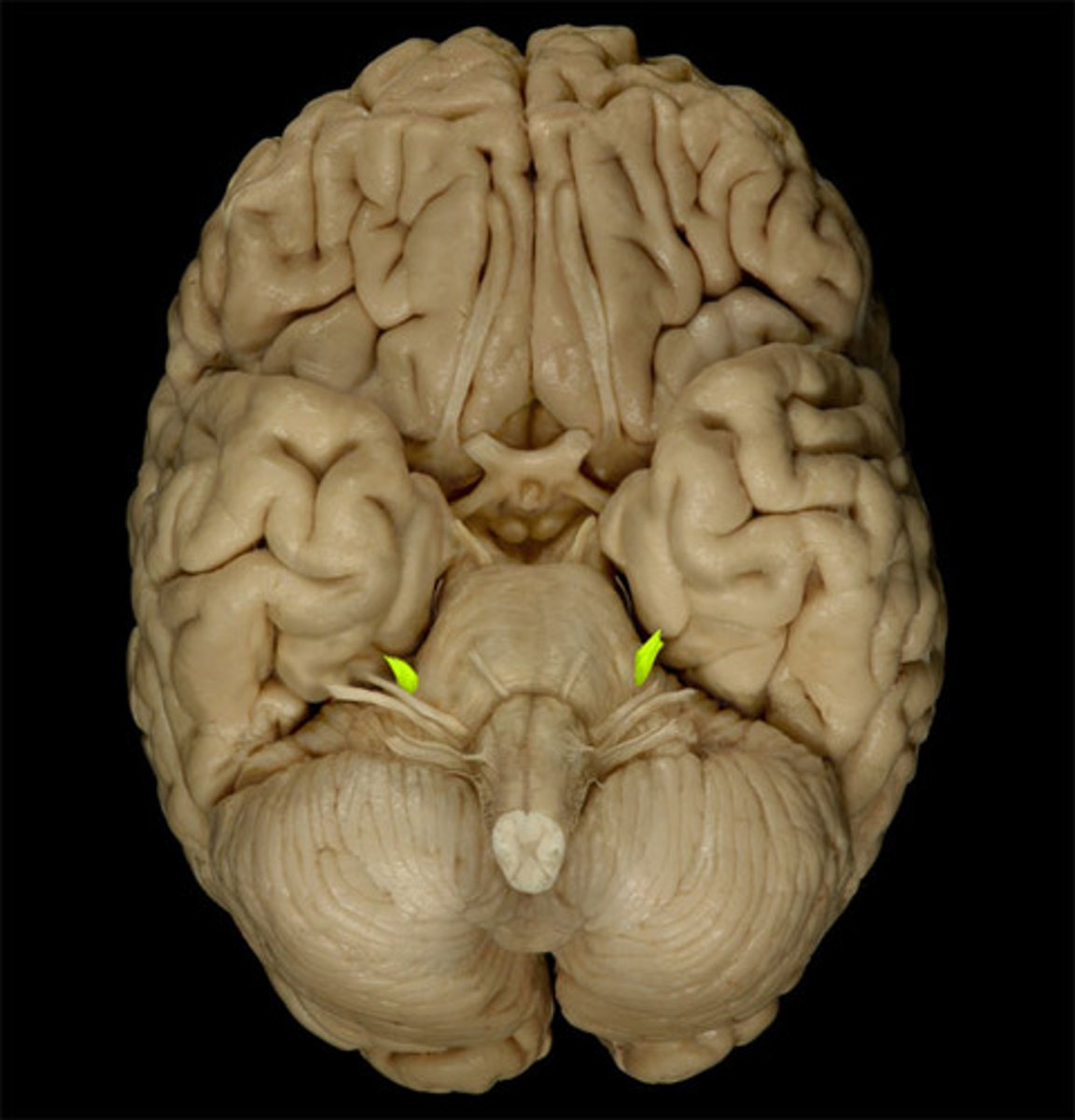
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Mixed cranial nerve that receives sensory nerve signals from face, oral cavity, nasal cavity, meninges, and anterior scalp and innervates muscles of mastication
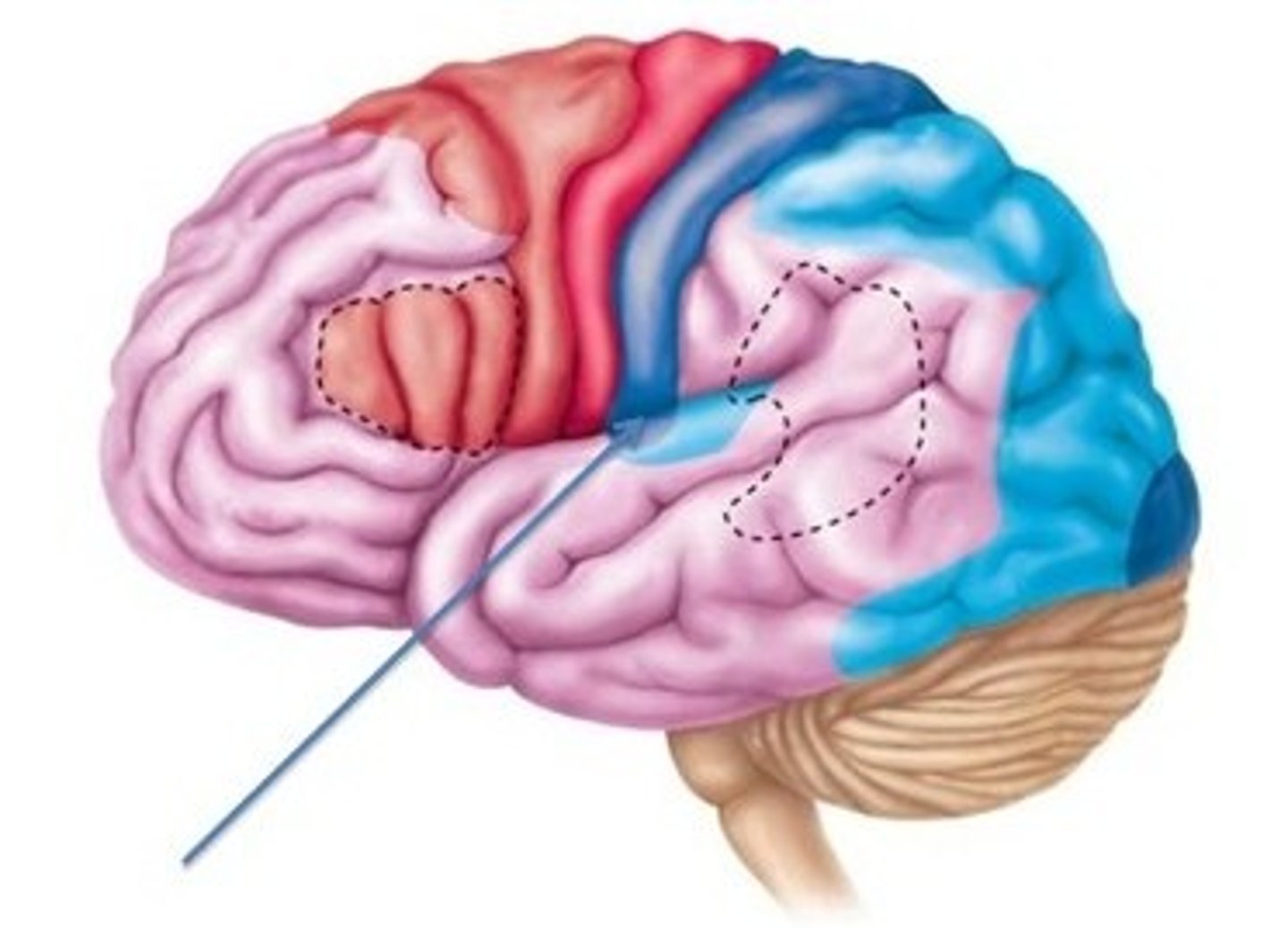
primary somatosensory cortex
•Located in postcentral gyrus of parietal lobes
•Receives somatic sensory information from
•Proprioceptors, touch, pressure, pain, temperature receptors
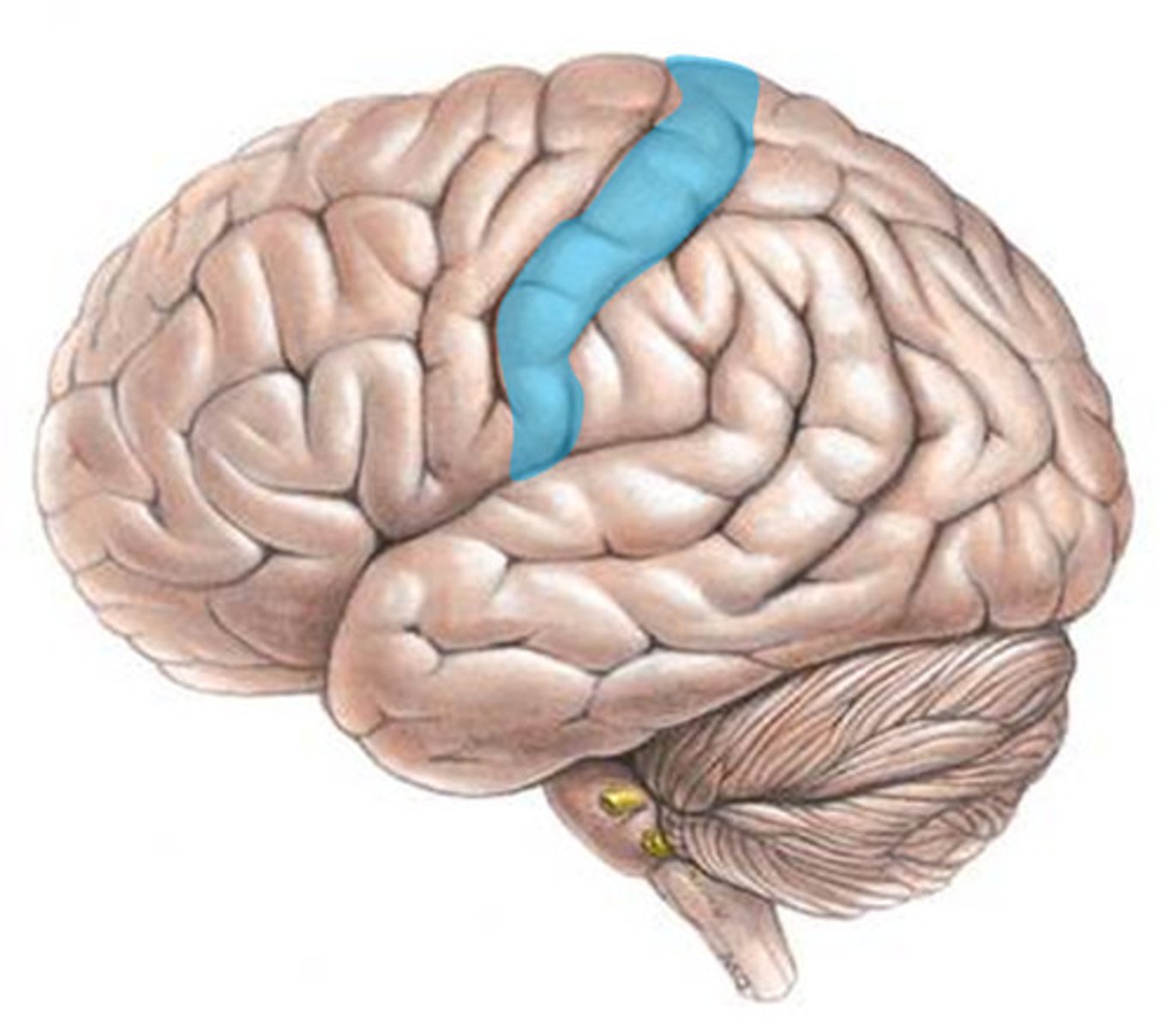
postcentral gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that receives somatosensory information from the entire body
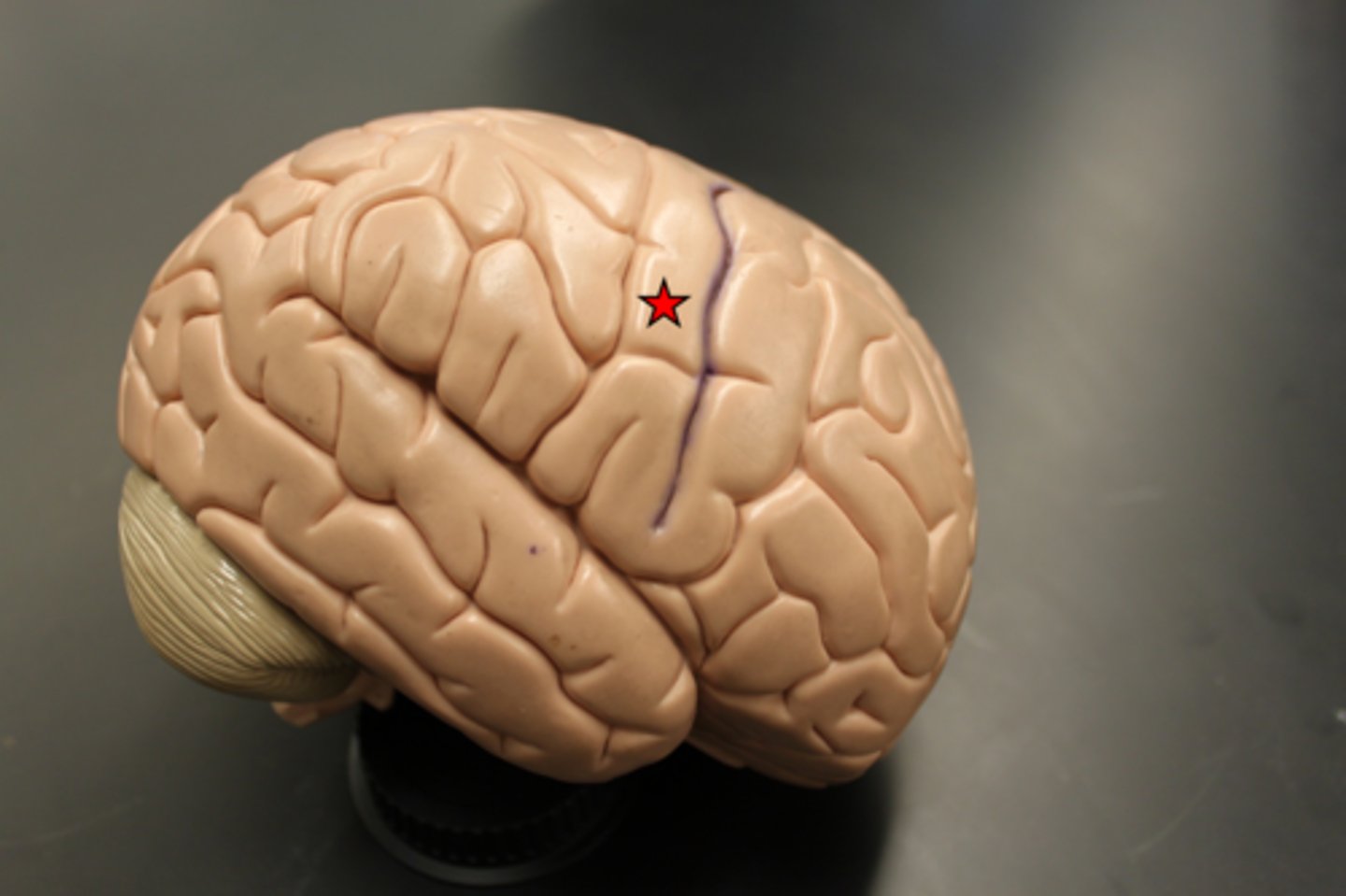
abducens nerve (CN VI)
Motor cranial nerve that controls abduction (lateral movement) of the eye; innervates lateral rectus muscle
facial nerve (CN VII)
Mixed cranial nerve that receives sensory information from the anterior 2/3s of the tongue and innervates the muscles of facial expression; and increases secretions from the lacrimal, submandibular salivary, and sublingual salivary glands
primary gustatory cortex
•Located within insula
•Receives, processes, stores taste information
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Sensory cranial nerve with two branches that transmits equilibrium and auditory (hearing) sensations from inner ear to brain
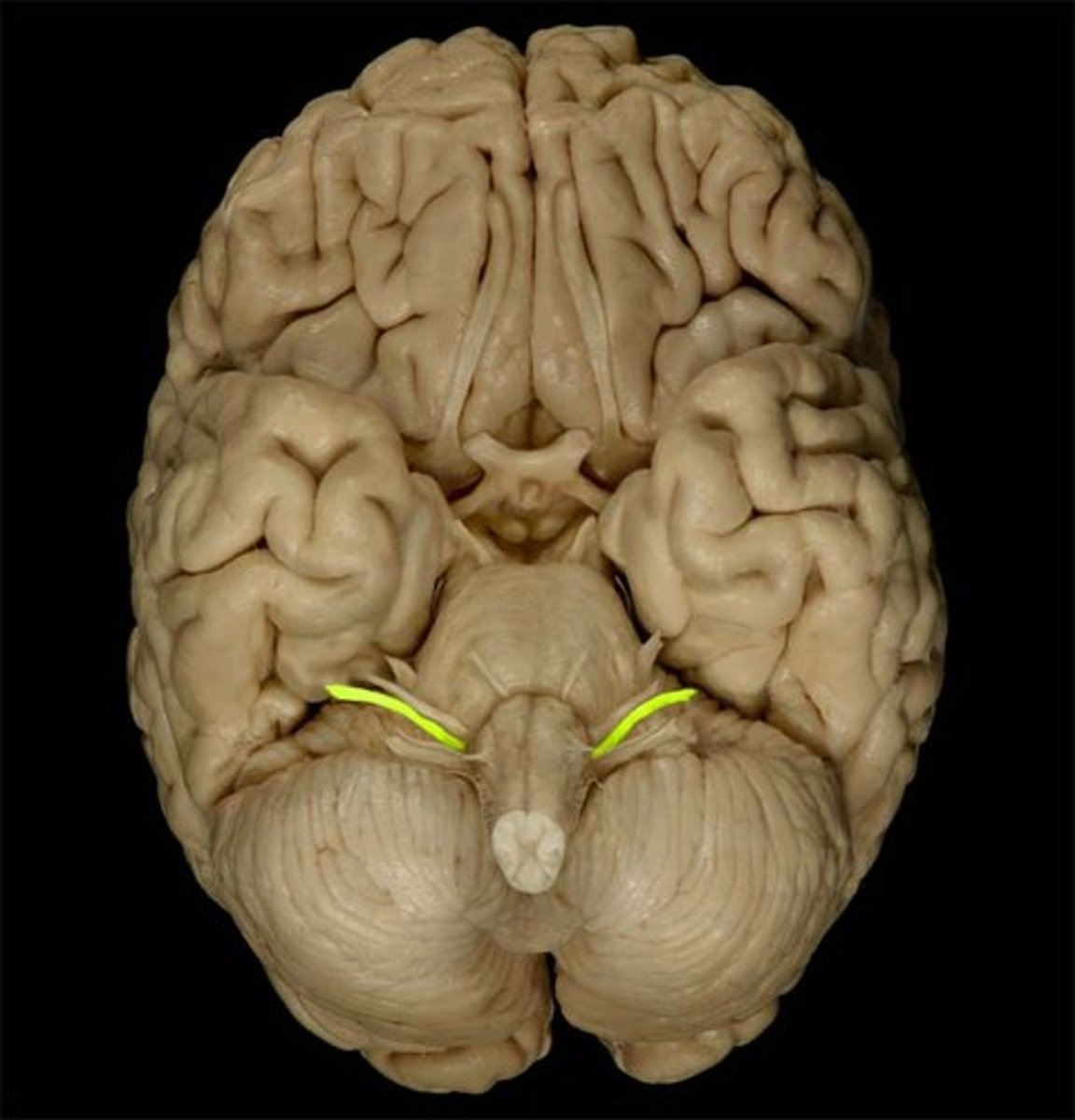
primary auditory cortex
•Located within temporal lobe; receives, processes, stores auditory information
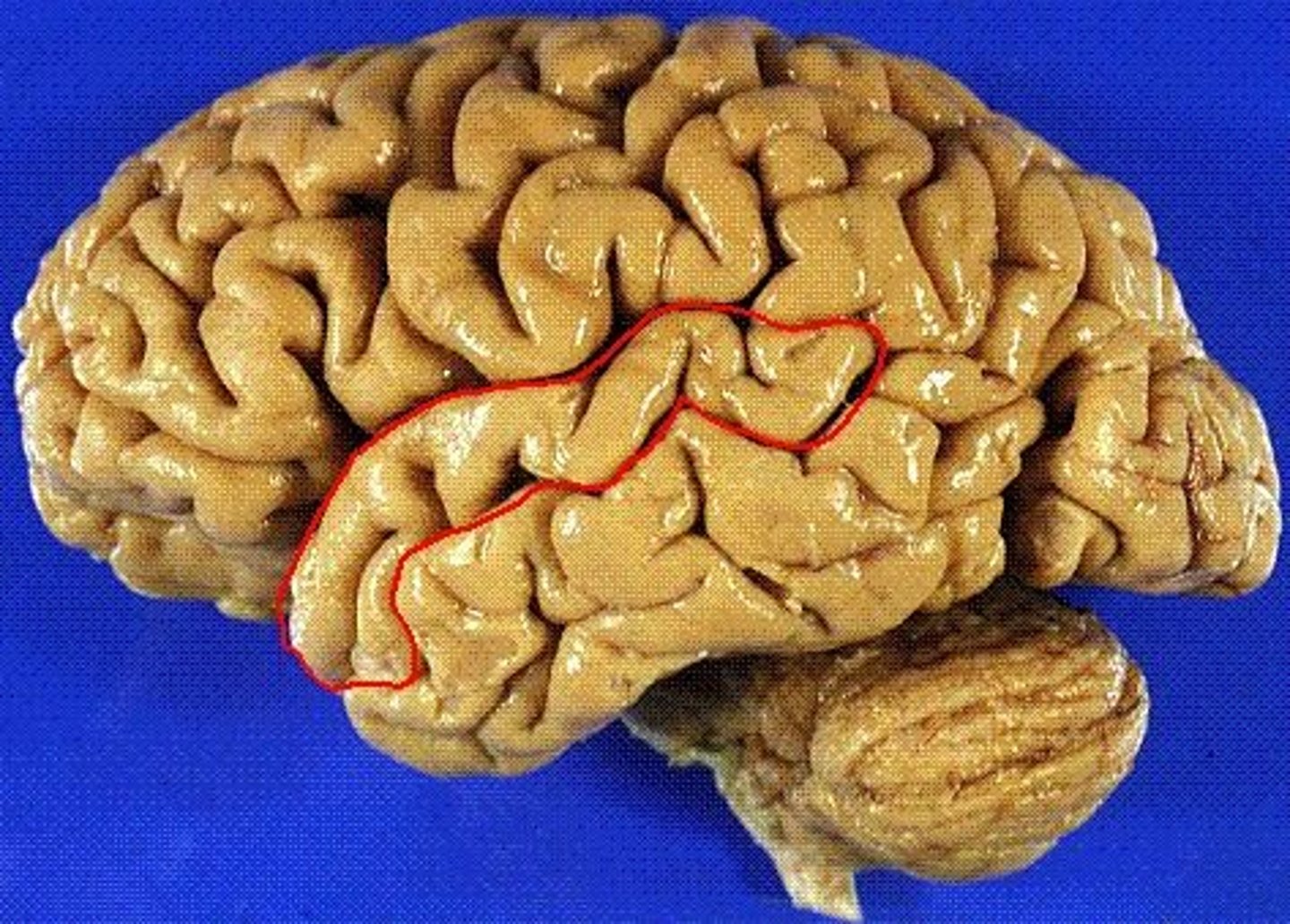
superior temporal gyrus
the large gyrus of the temporal lobe adjacent to the lateral fissure; the location of auditory cortex
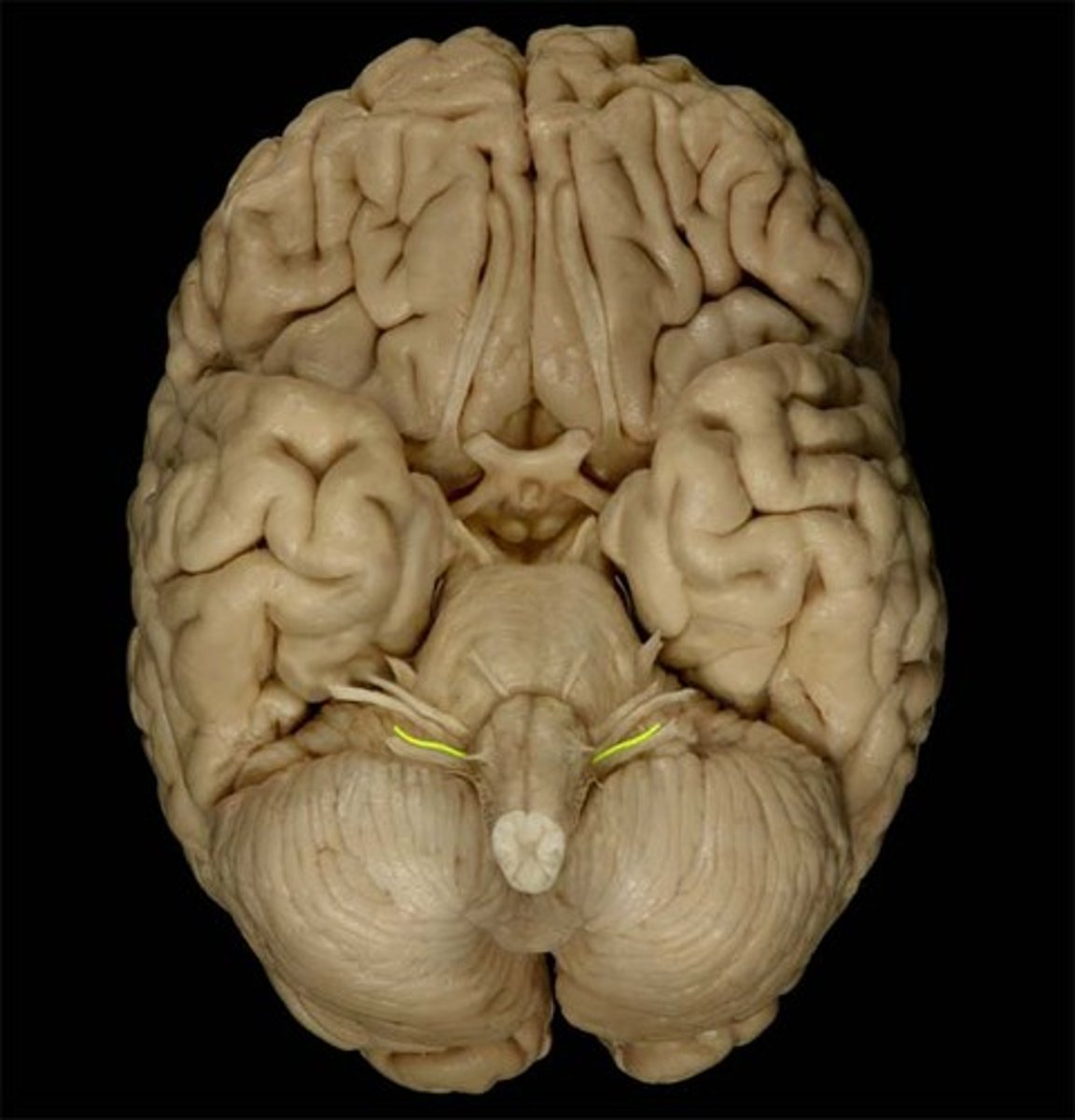
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Mixed cranial nerve that transmits taste and touch sensations from posterior one-third of the tongue and innervates a pharynx muscle involved in swallowing; and increases secretions of the parotid salivary glands
vagus nerve (CN X)
Mixed cranial nerve that innervates structures in the head and neck and in the thoracic and abdominal cavities; major role in the control of cardiac, pulmonary, digestive, and urinary function ;also involved in swallowing, and speech
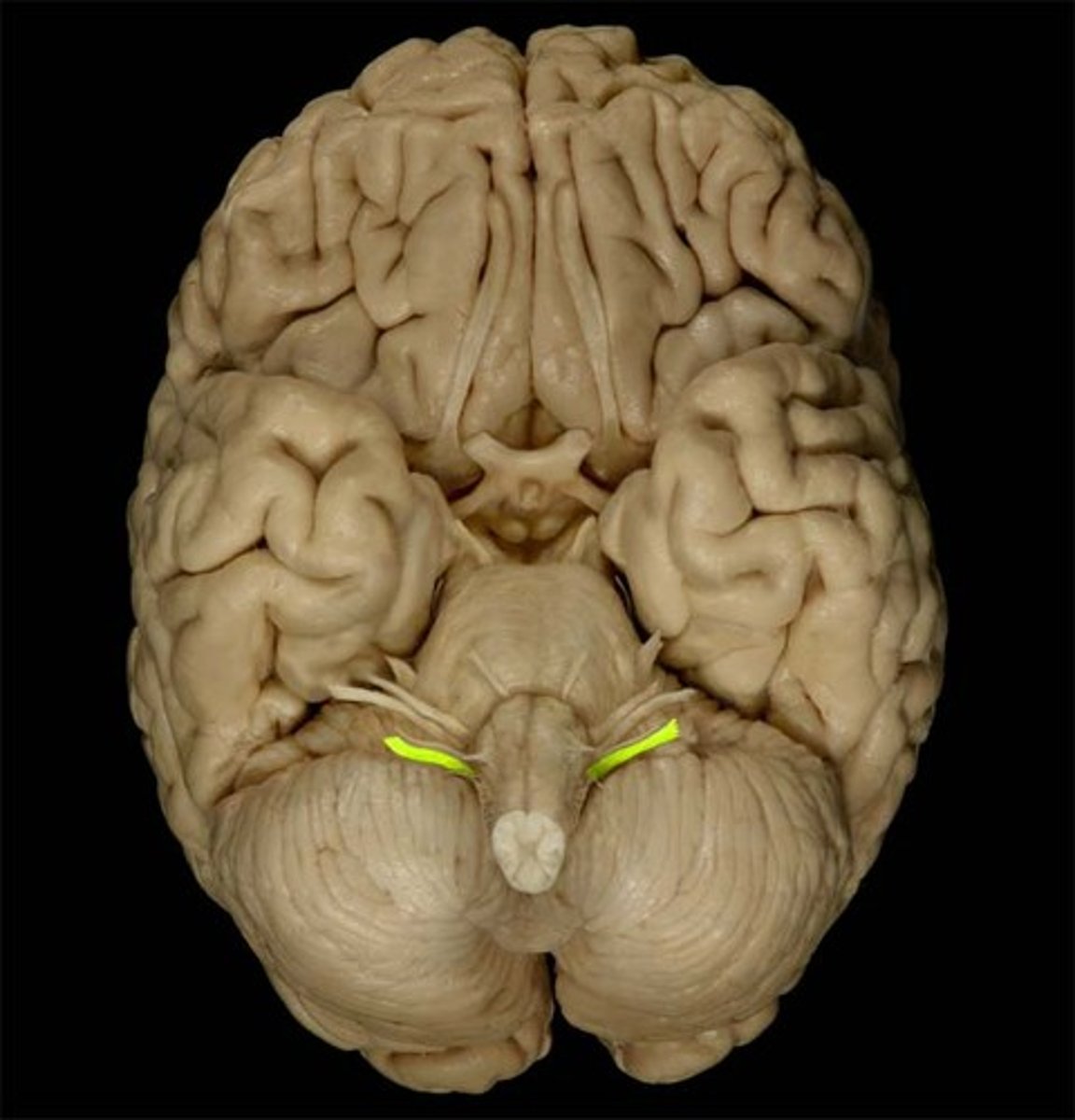
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
Motor cranial nerve involved in swallowing and head, neck, & shoulder movement; innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
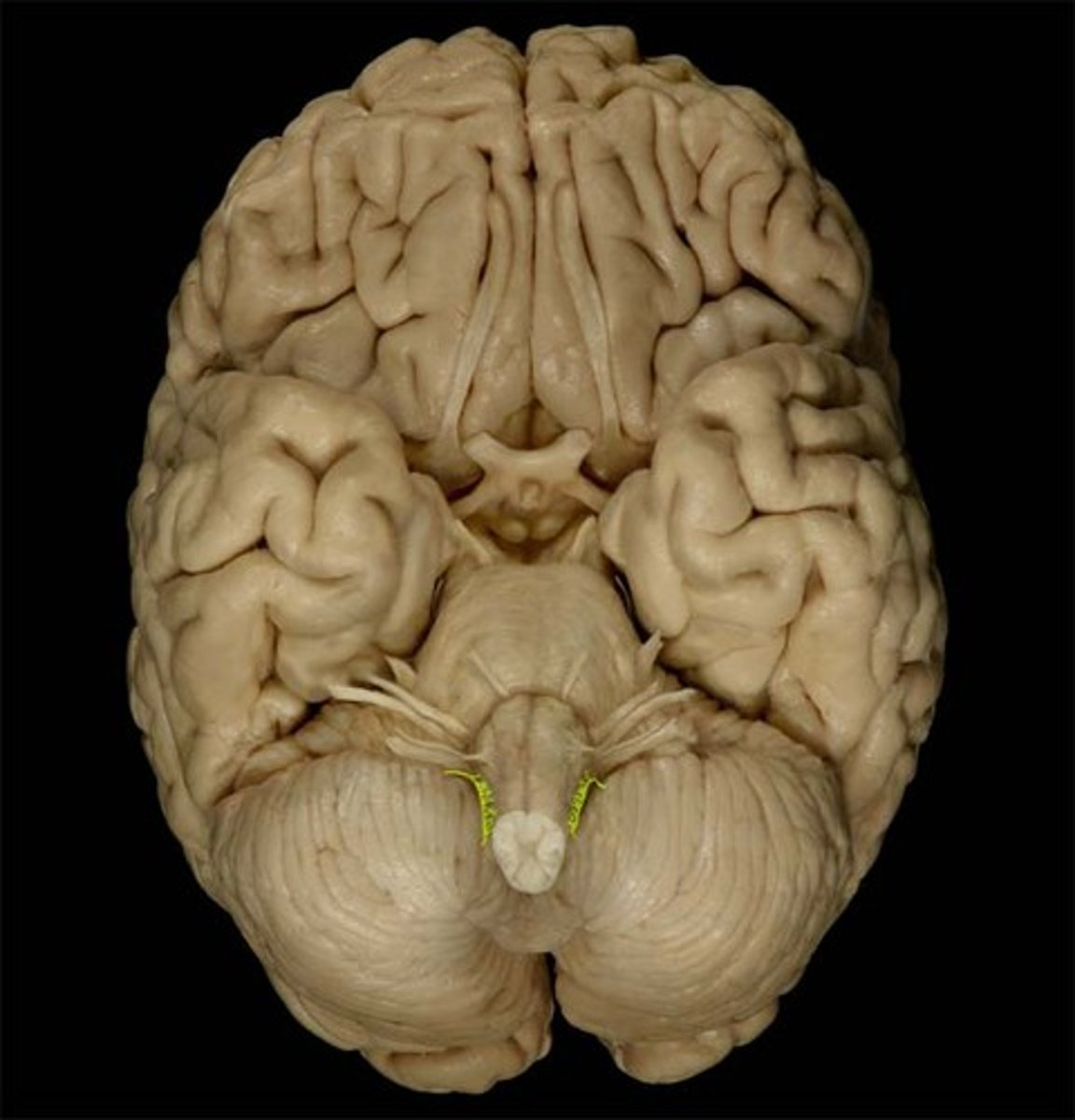
hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII)
Motor nerve involved in tongue movement
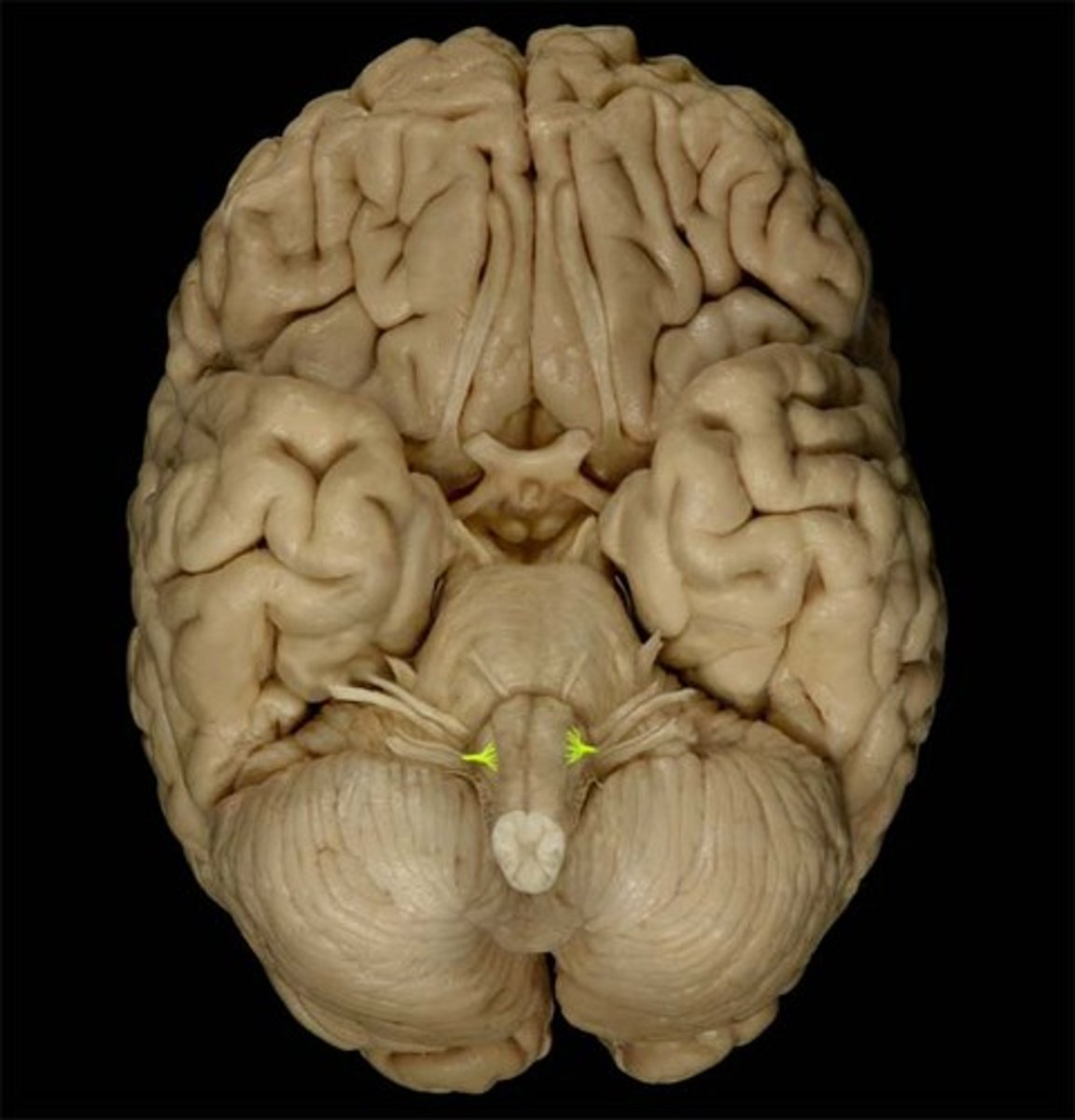
gyrus (pl. gyri)
Large folds of tissue covering the surface of the cerebrum
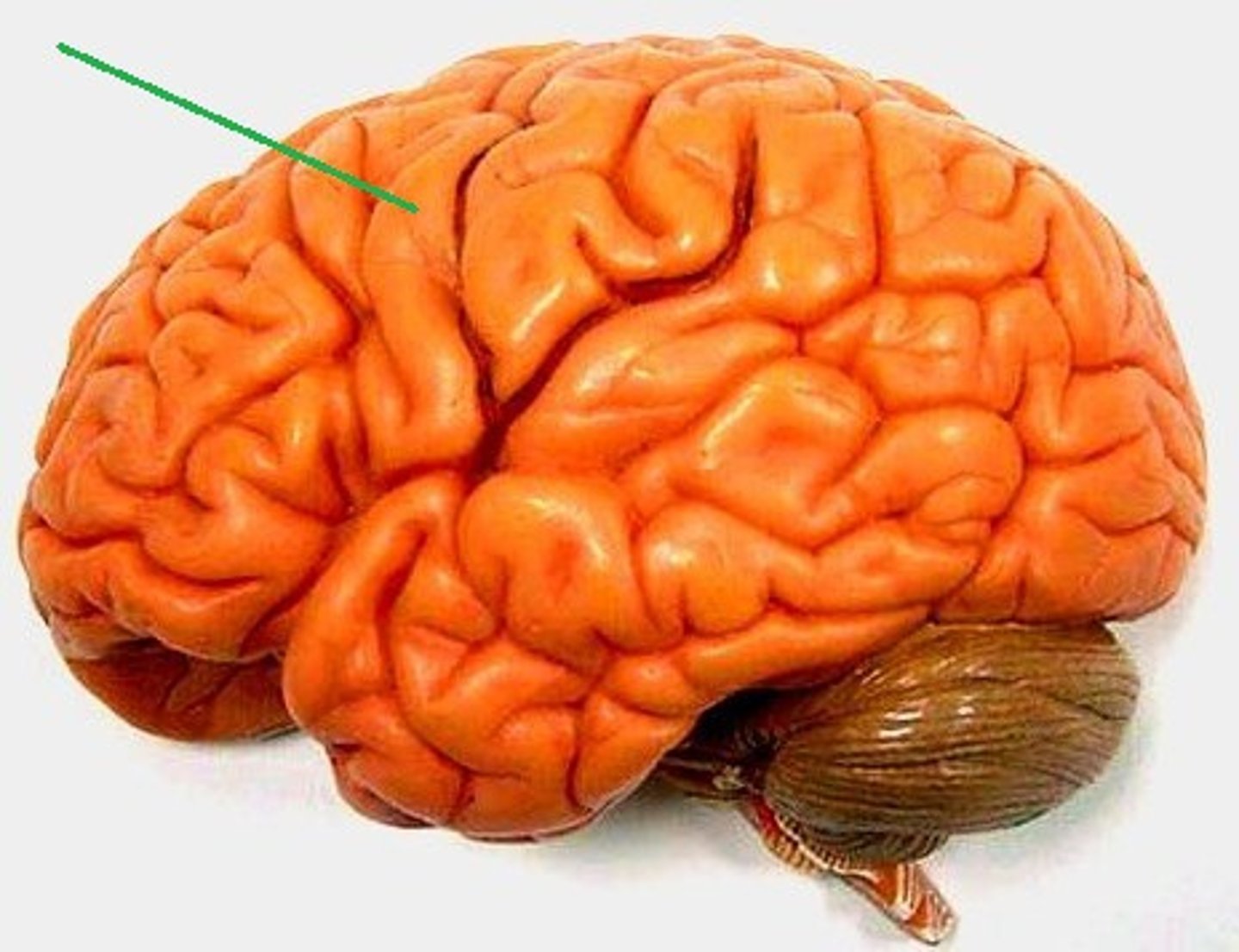
sulcus (pl. sulci)
shallow grooves separating the gyri
cerebrum
•Origin of the brain responsible for all complex intellectual functions
•Two large hemispheres on superior aspect of brain
•Center of
--Intelligence and reasoning
--Thought, memory, and judgment
--Voluntary control of skeletal muscle
--Conscious perception of senses
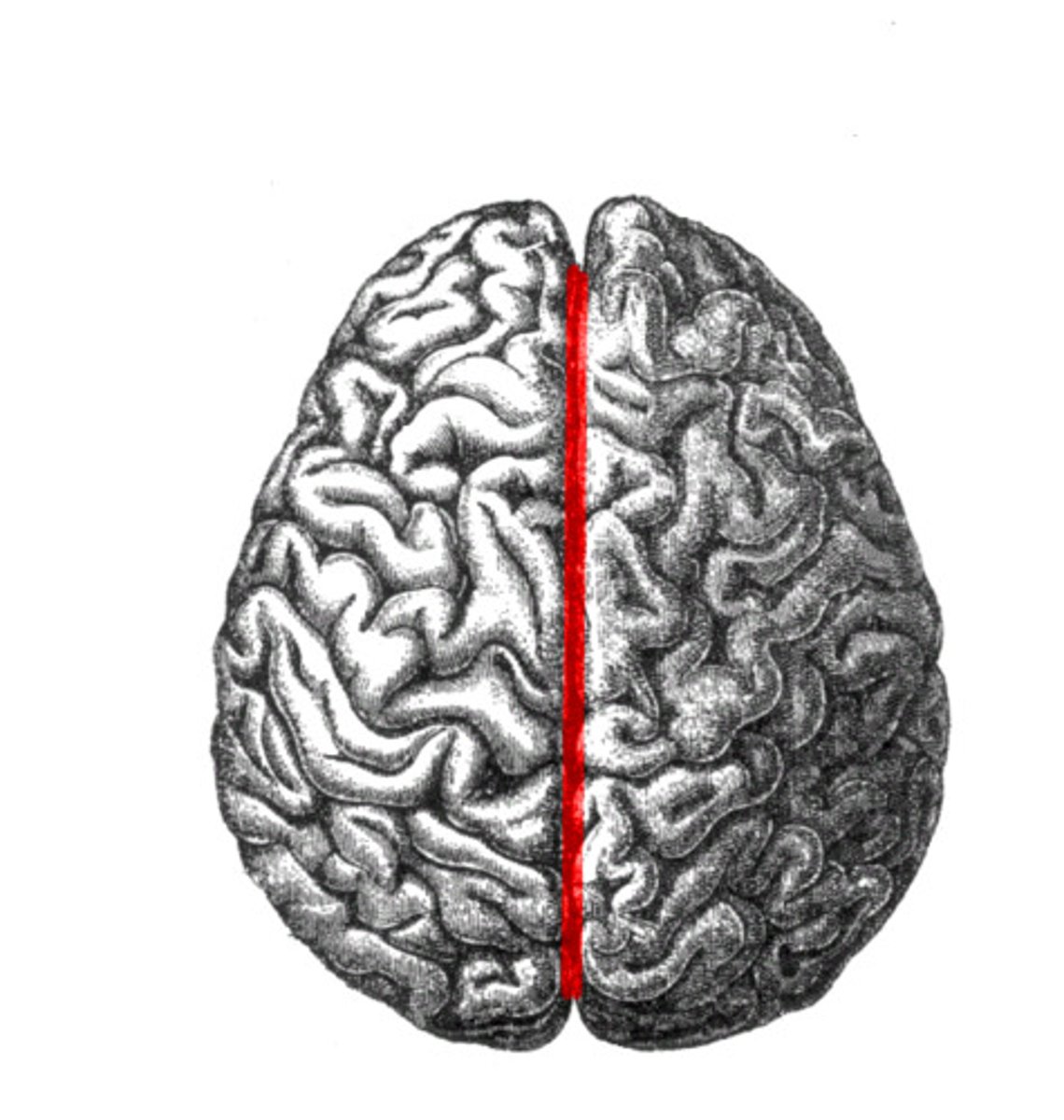
longitudinal fissure
deep cleft that separates cerebral hemispheres
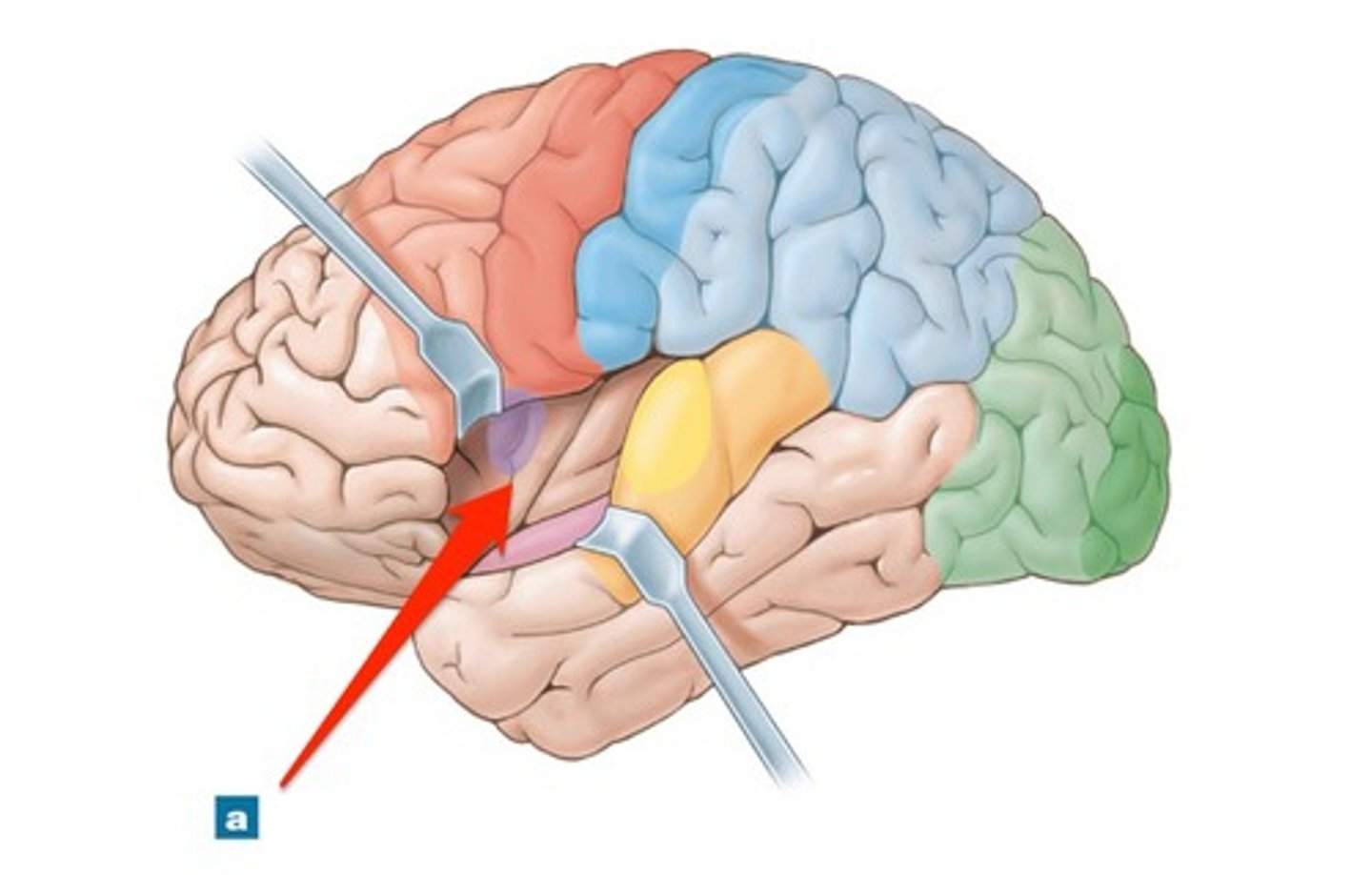
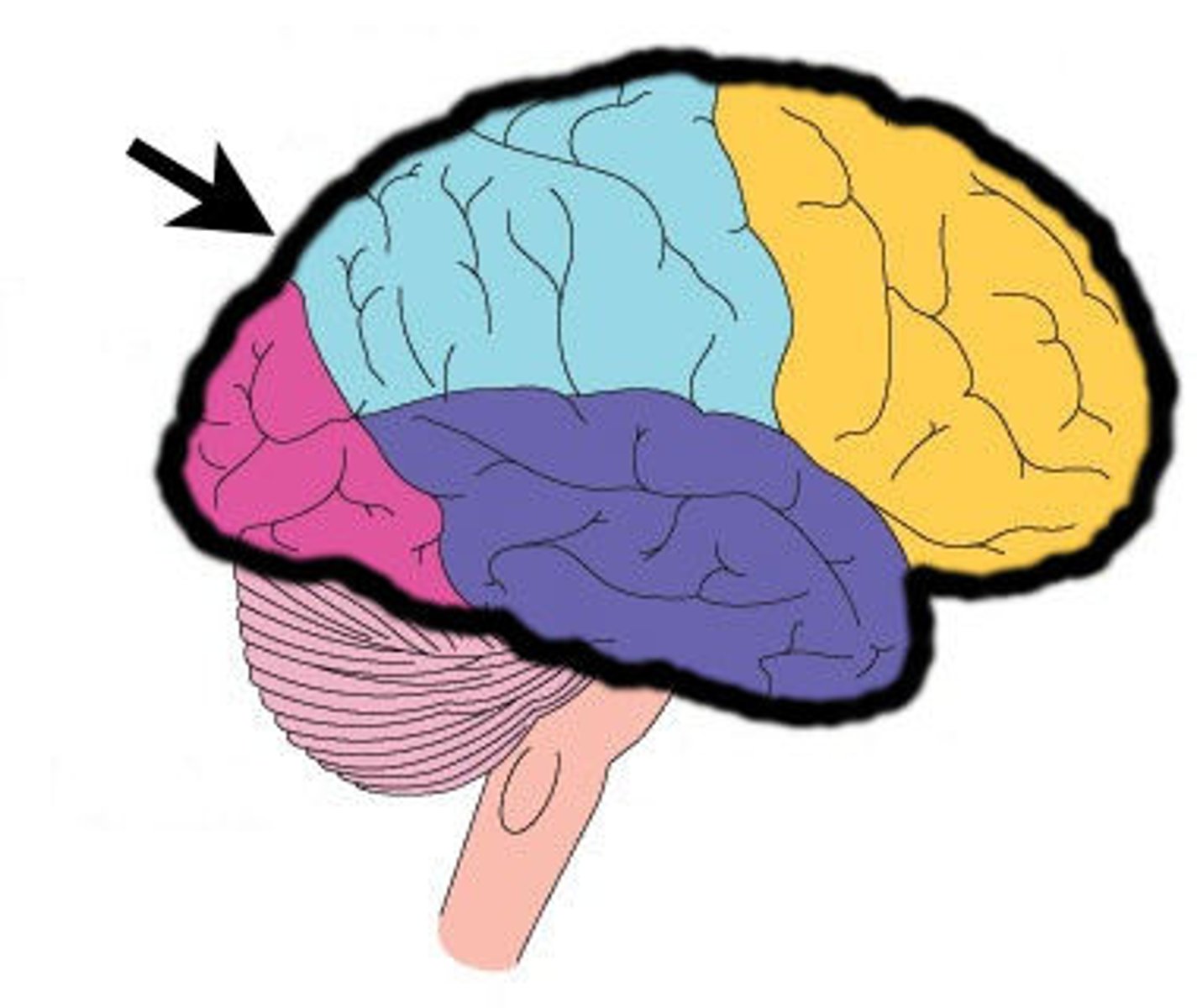
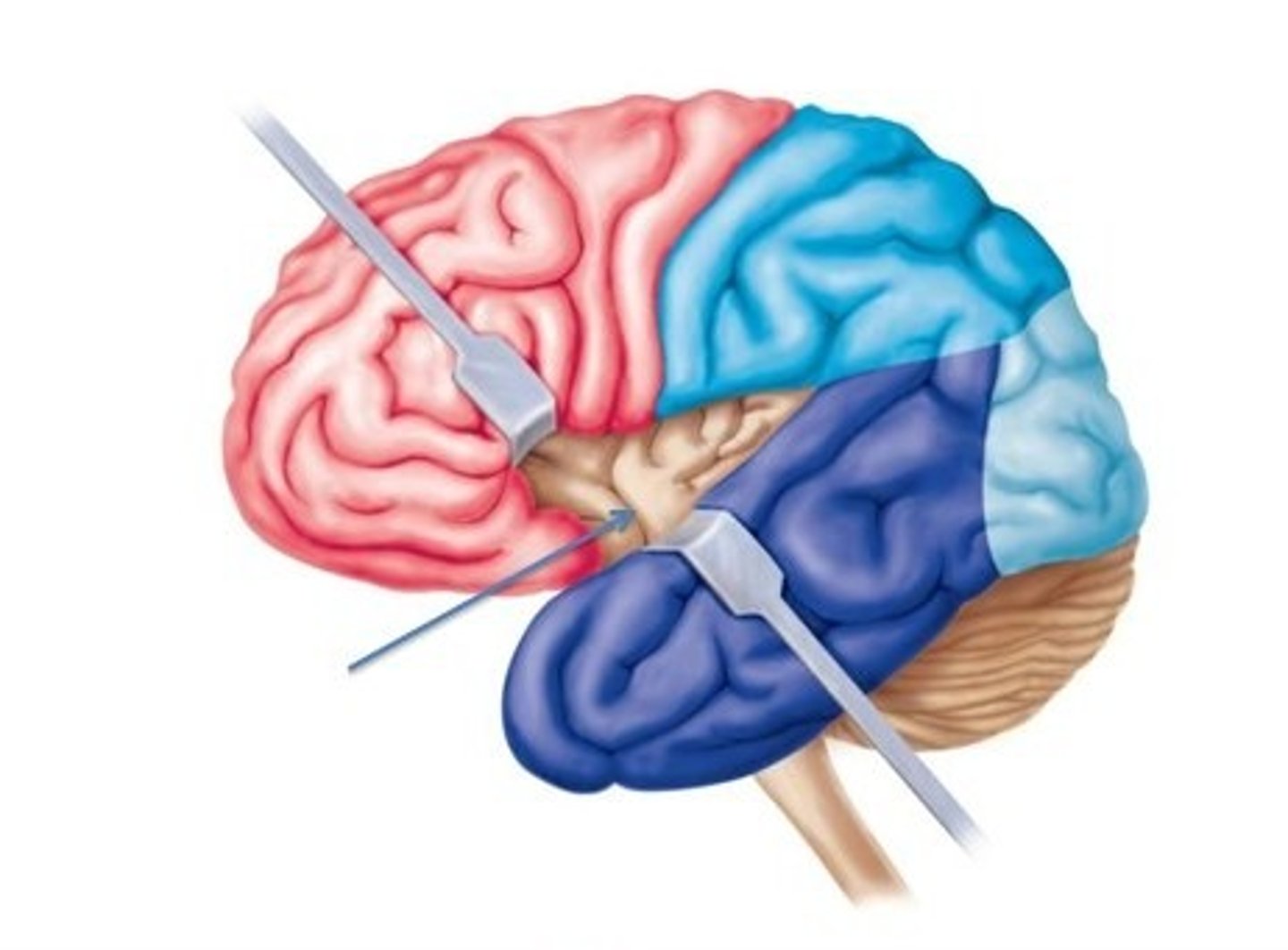
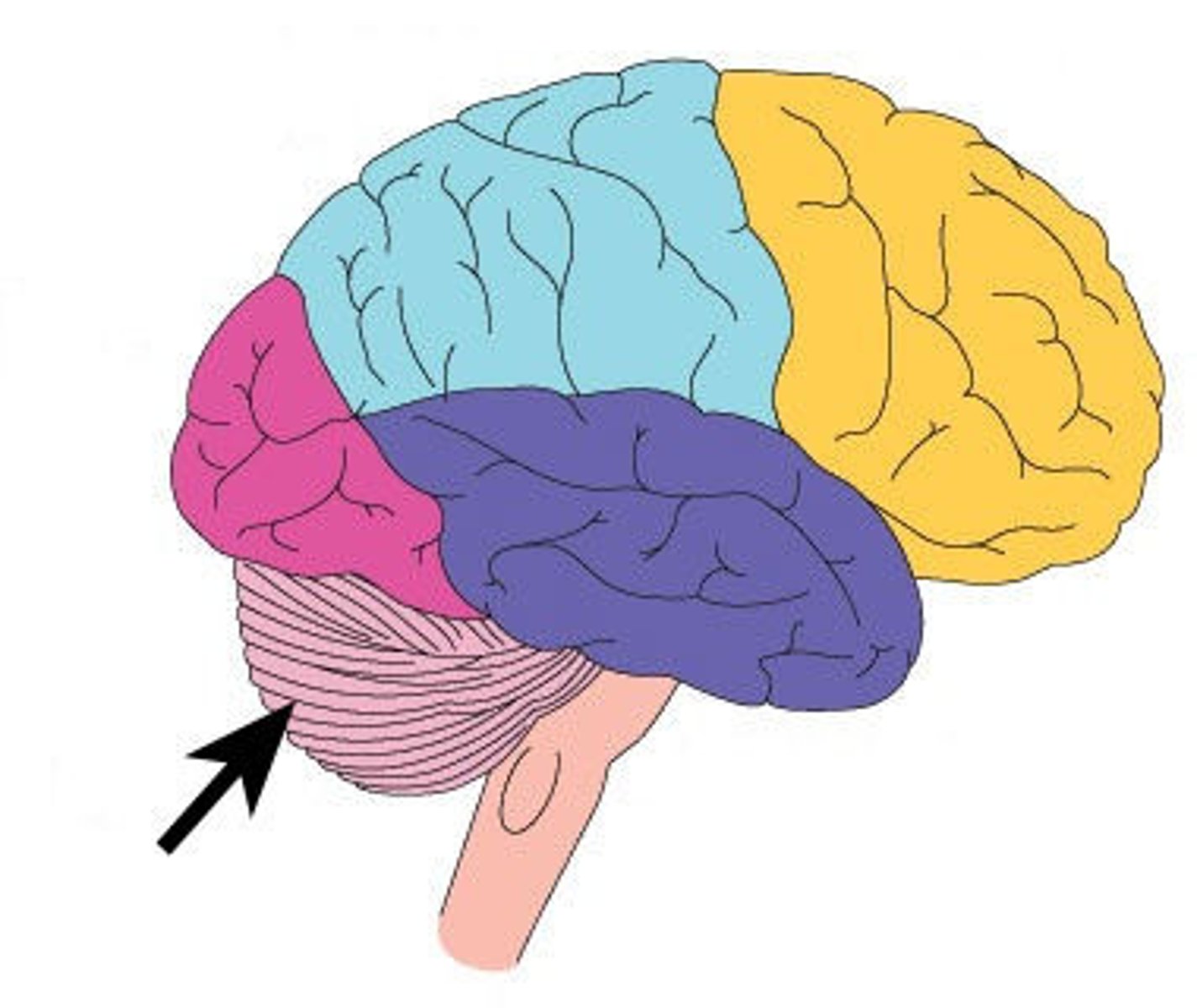
lobes of the cerebrum
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula
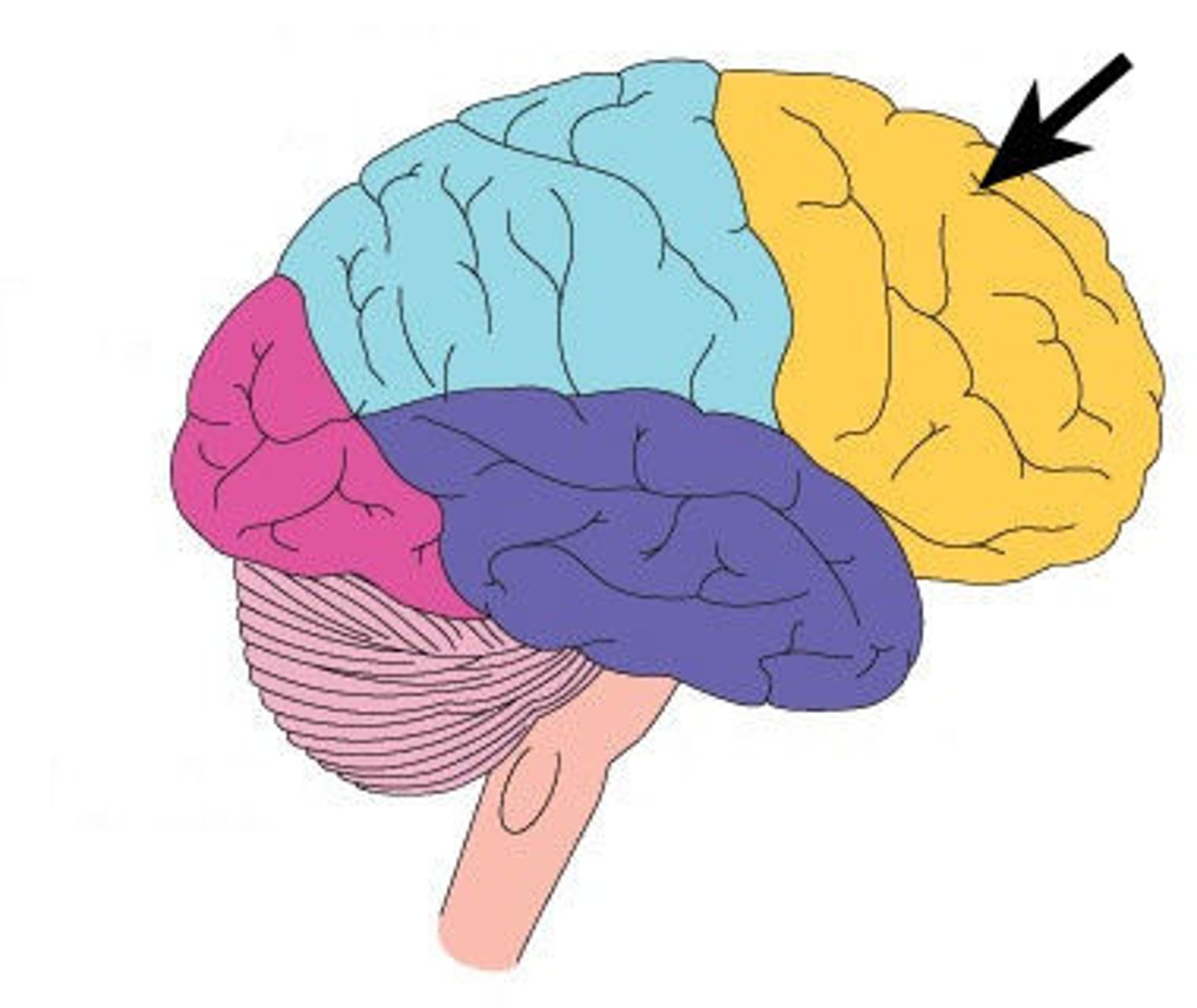
frontal lobe
Regions of the cerebrum involved in:
•Voluntary motor functions
•Motor control, concentration, verbal communication, decision making, planning, personality
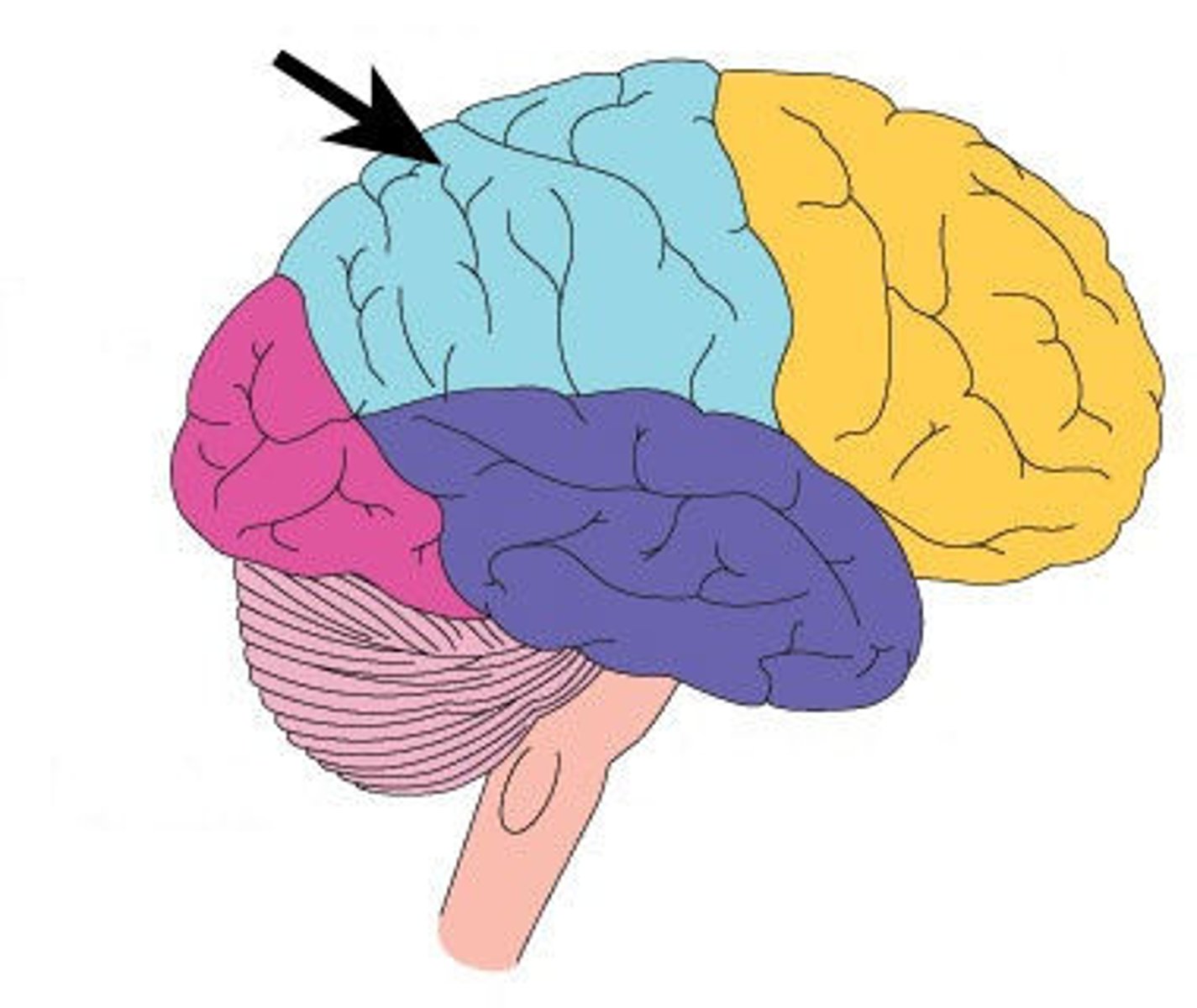
parietal lobe
Region of the cerebrum that:
•receives and integrates general sensory information (shape, texture), taste and some visual processing
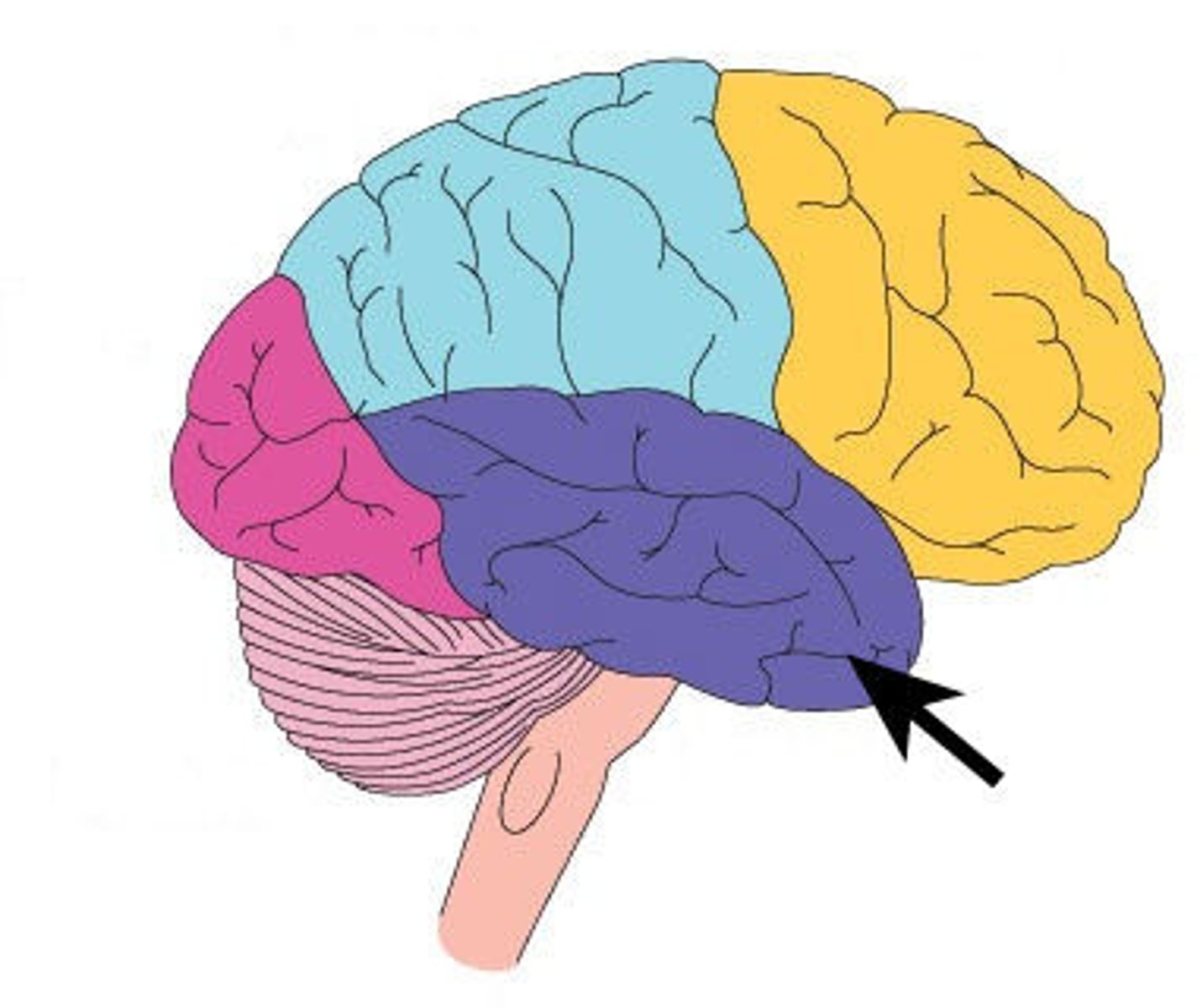
occipital lobe
•primary visual center of brain (vision and visual memories)
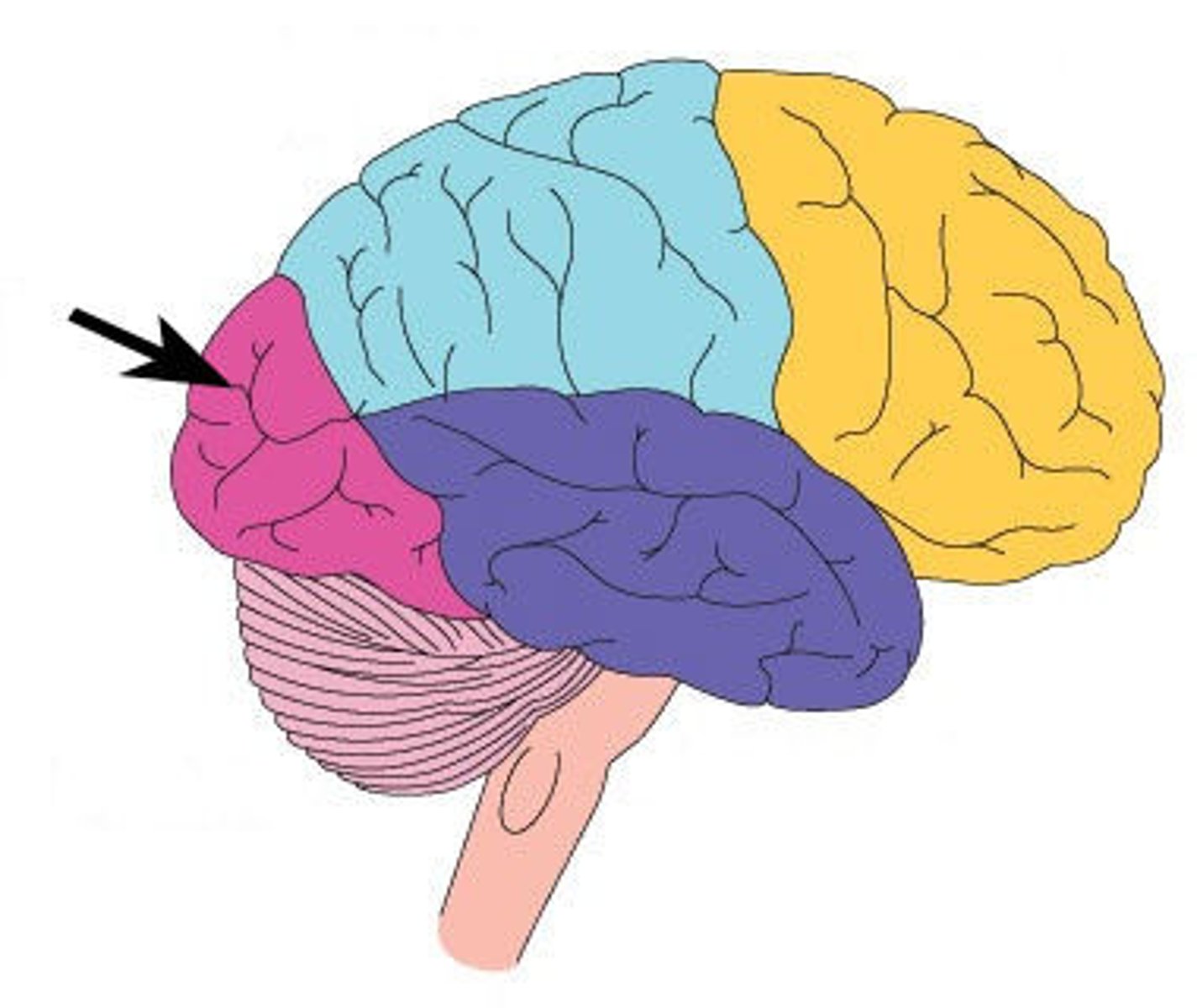
temporal lobe
Regions of the cerebrum that:
•contains areas for hearing, smell, learning, memory, and some aspects of vision and emotion
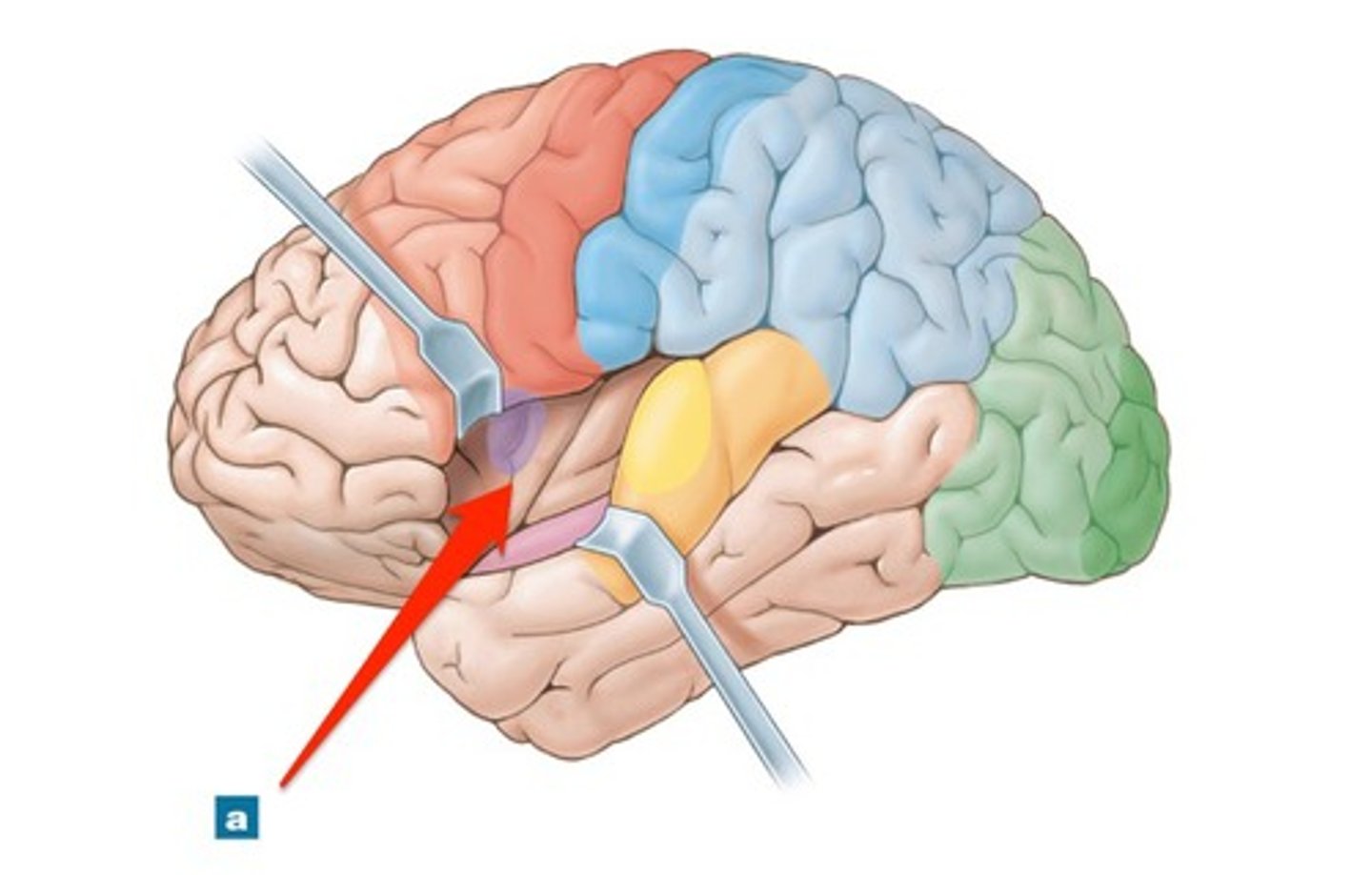
insula
cerebral lobe located deep within lateral sulcus
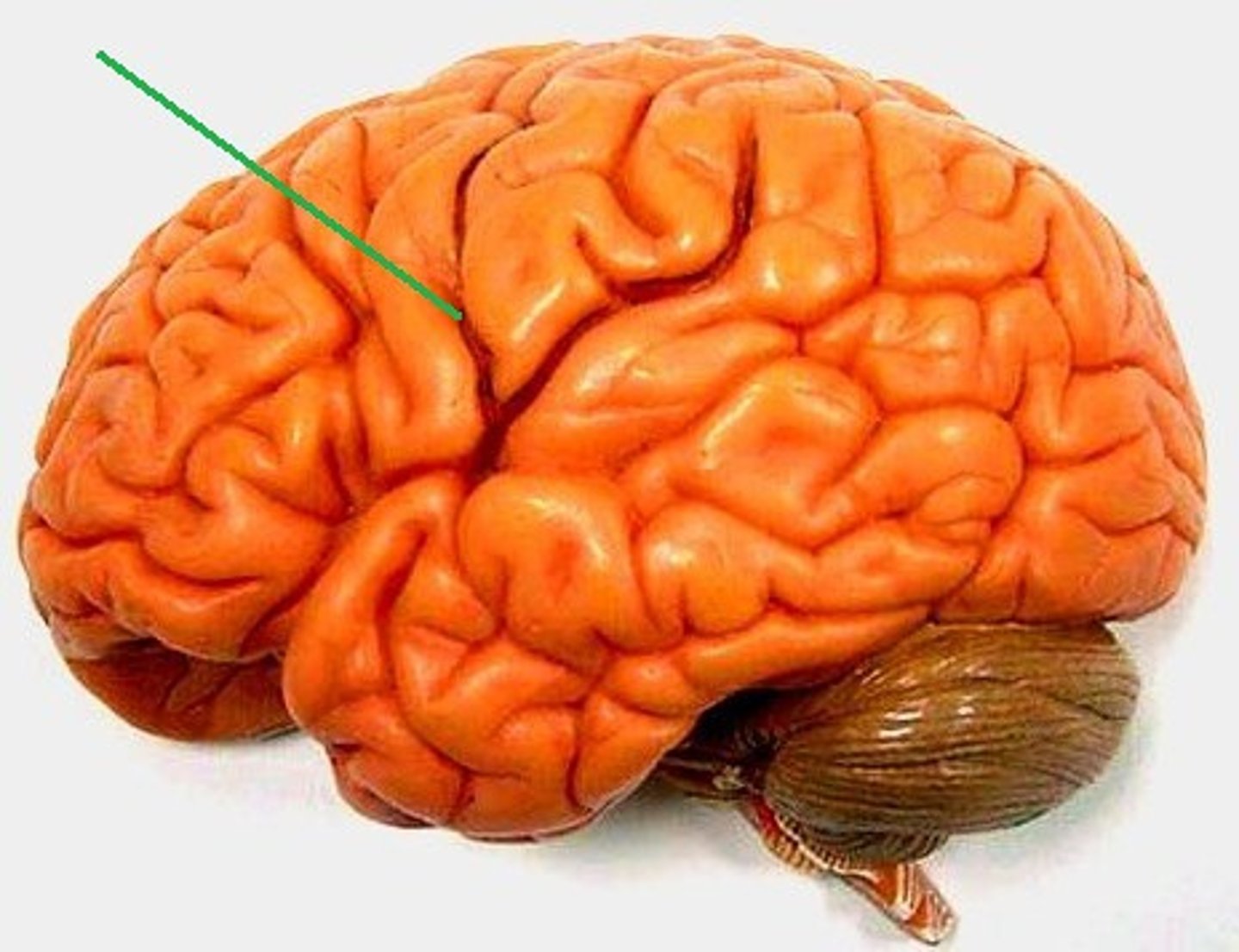
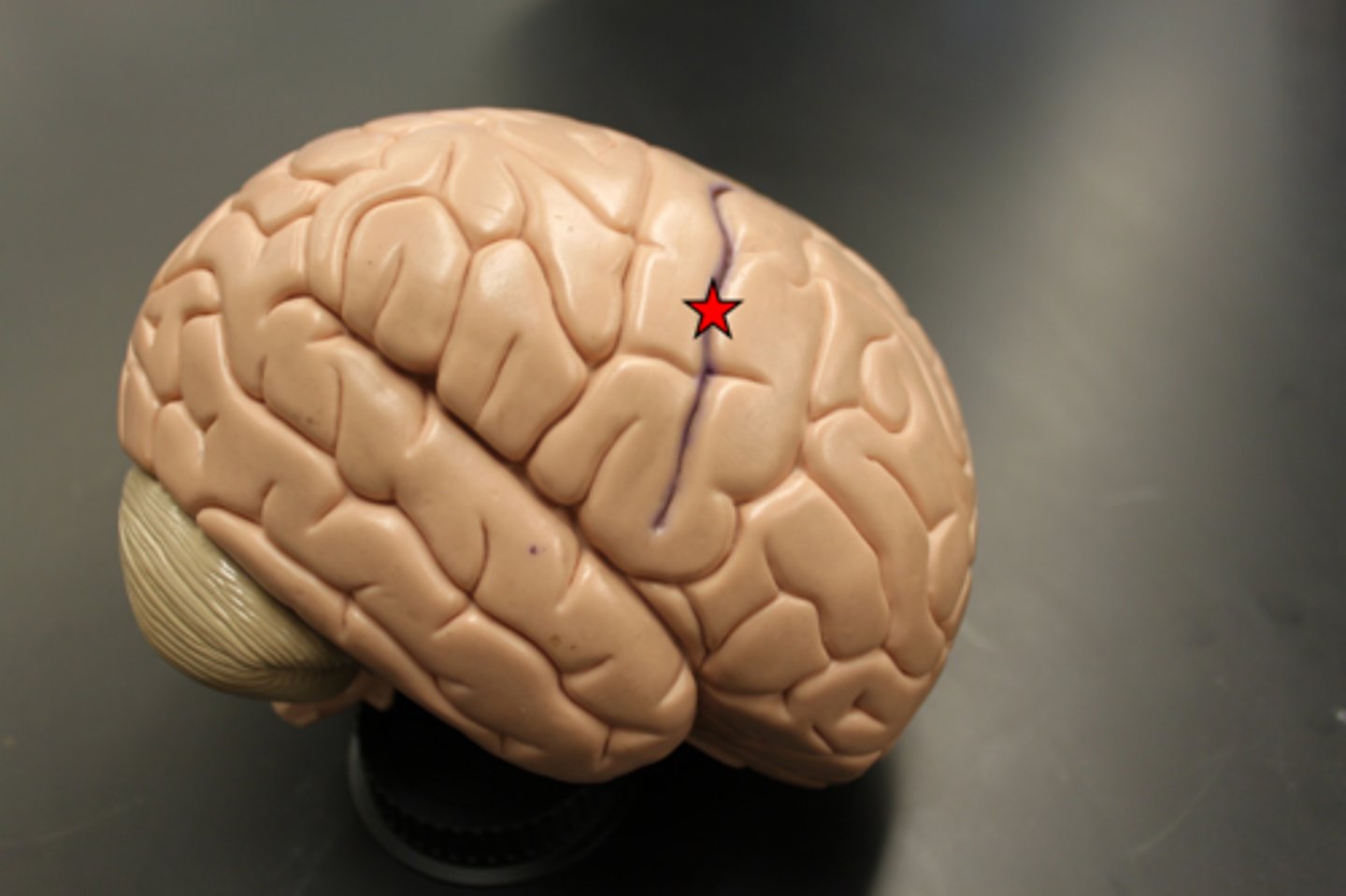
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
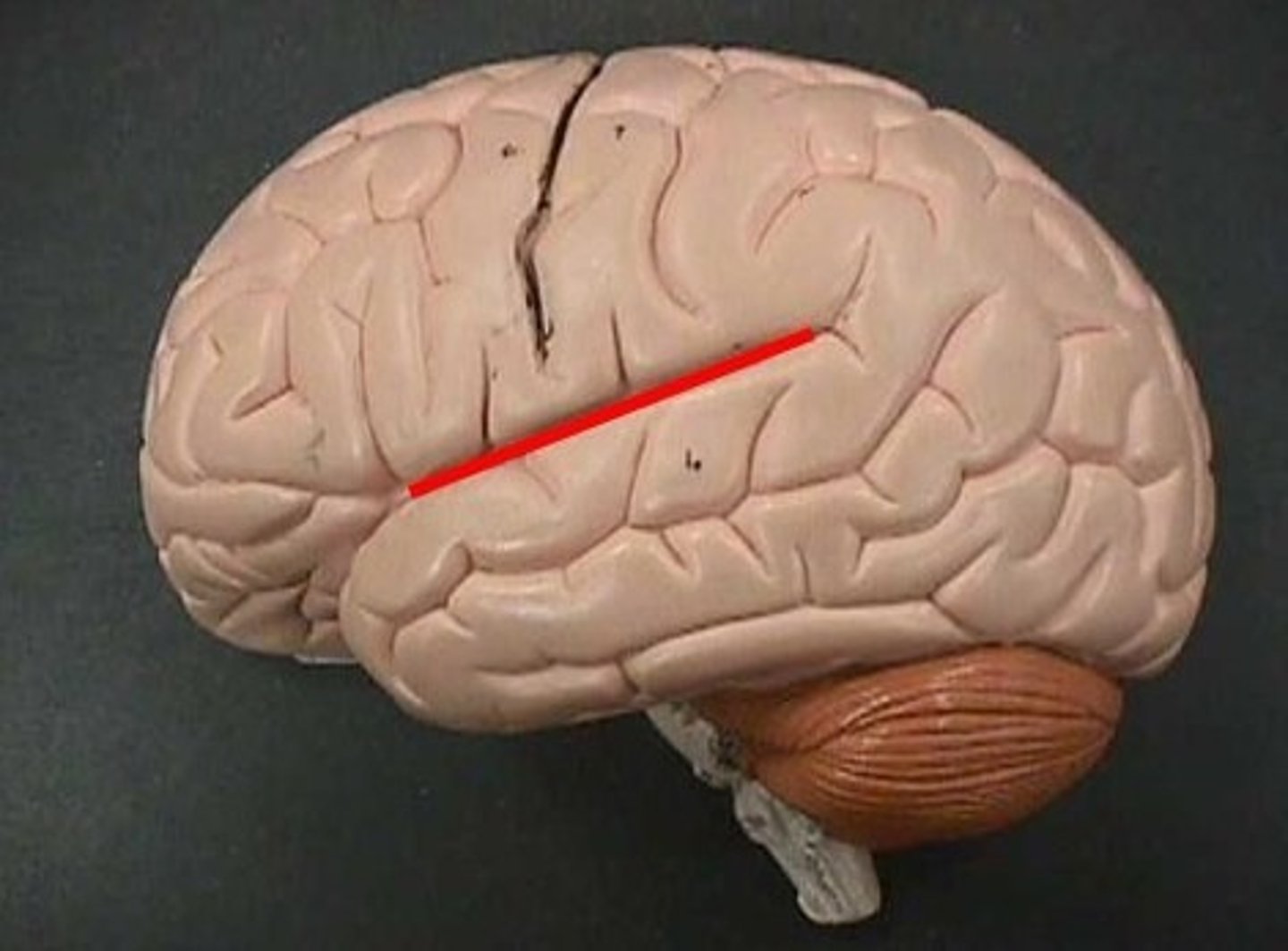
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
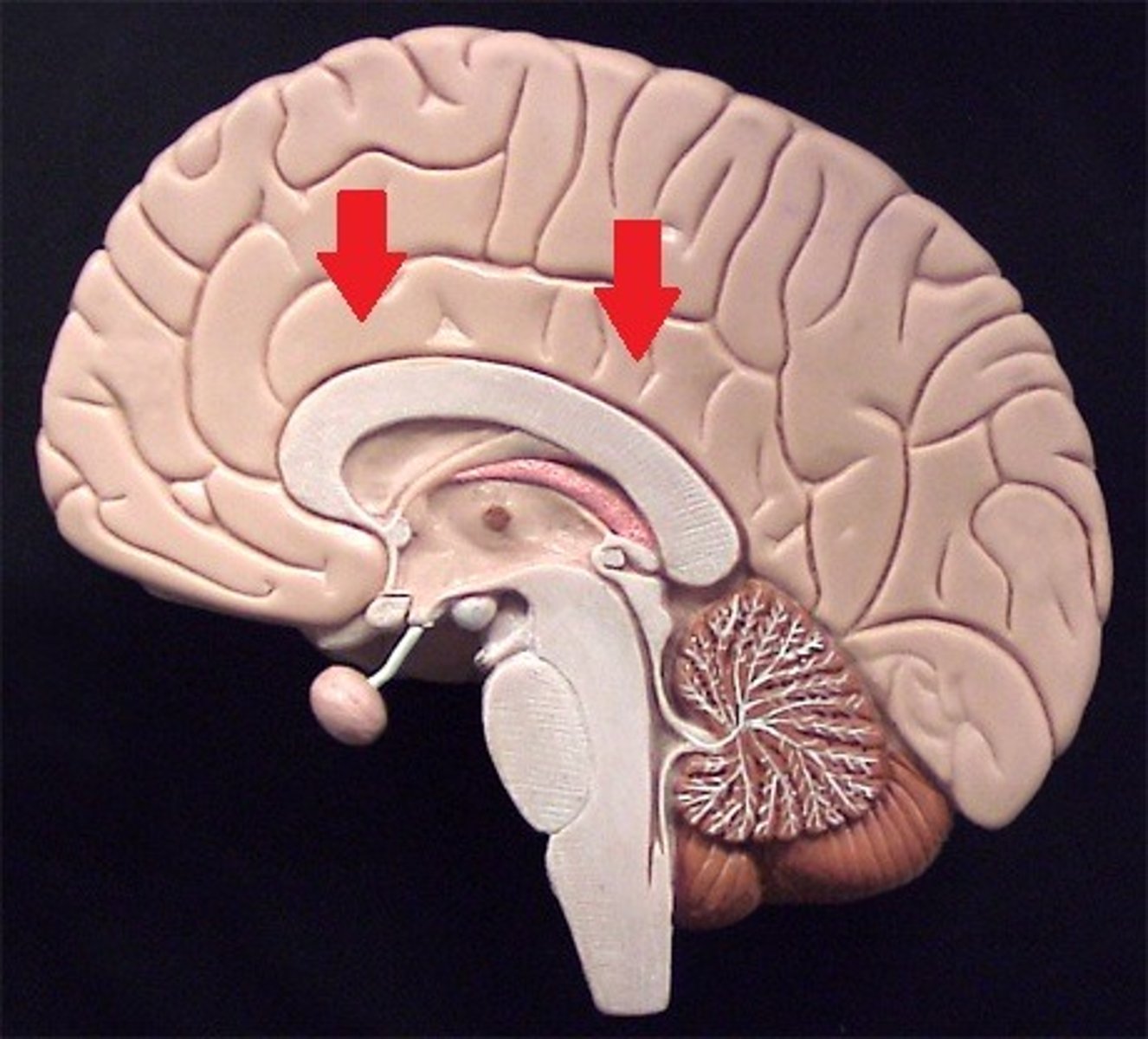
cingulate gyrus
plays role in expressing emotions via gestures and resolves mental conflict
corpus callosum
A thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.
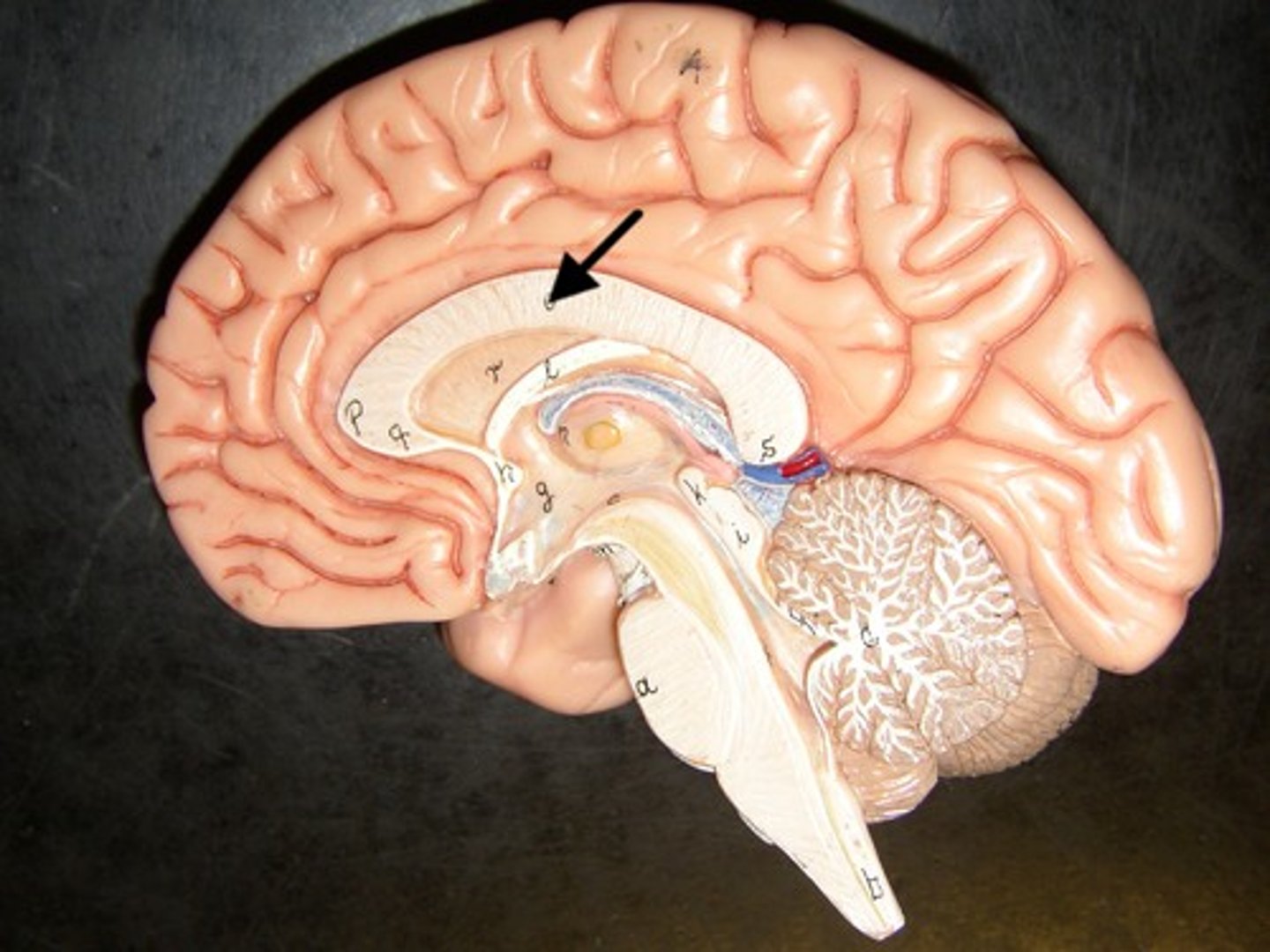
Diencephalon
central part of the brain made up of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
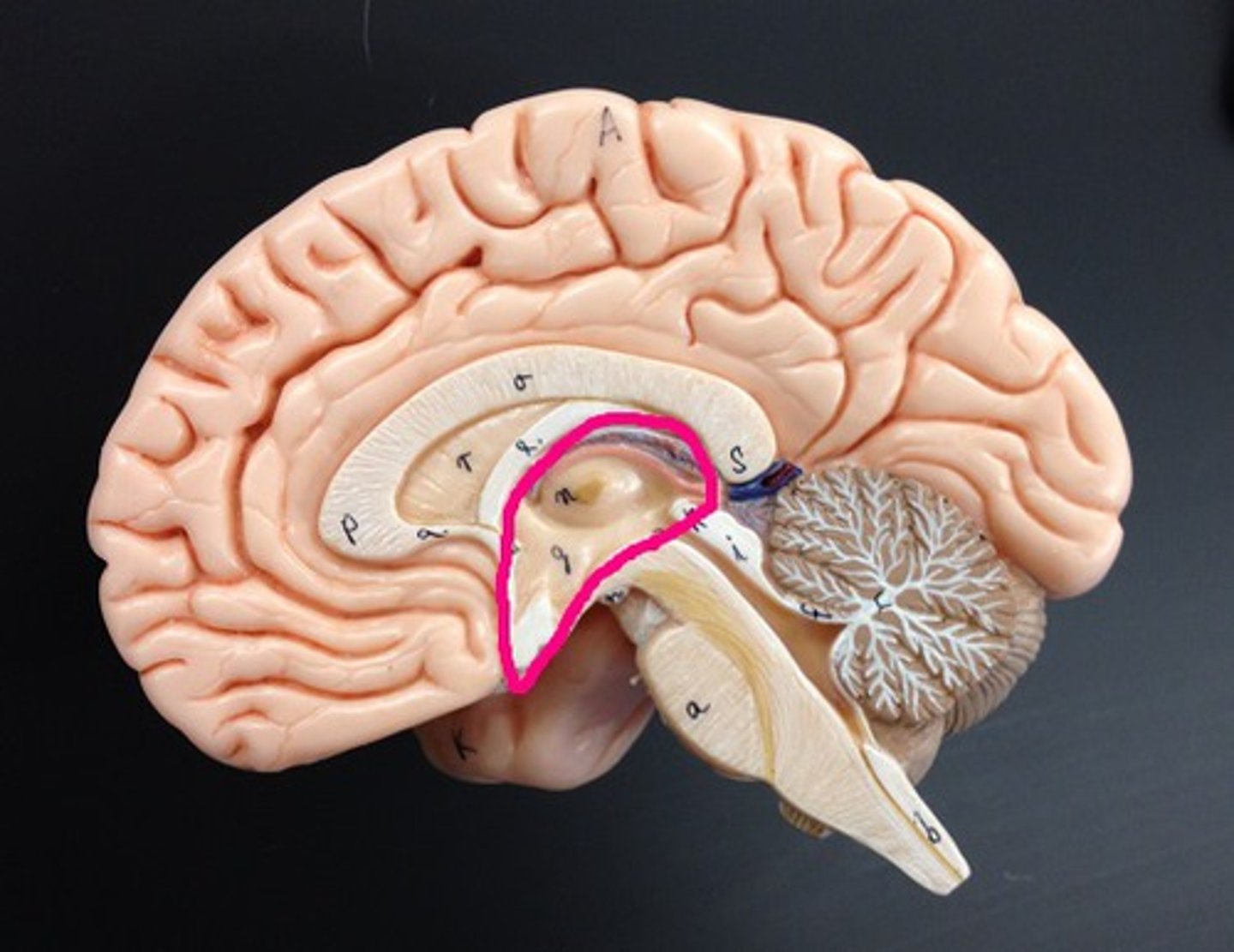
thalamus
•Oval masses of gray matter on lateral sides of third ventricle
•“Relay center” - Receives signals from all conscious senses except olfaction and relays some signals to appropriate part of cortex and filters out other signals distracting from subject of attention (for example, background noise in crowded room)
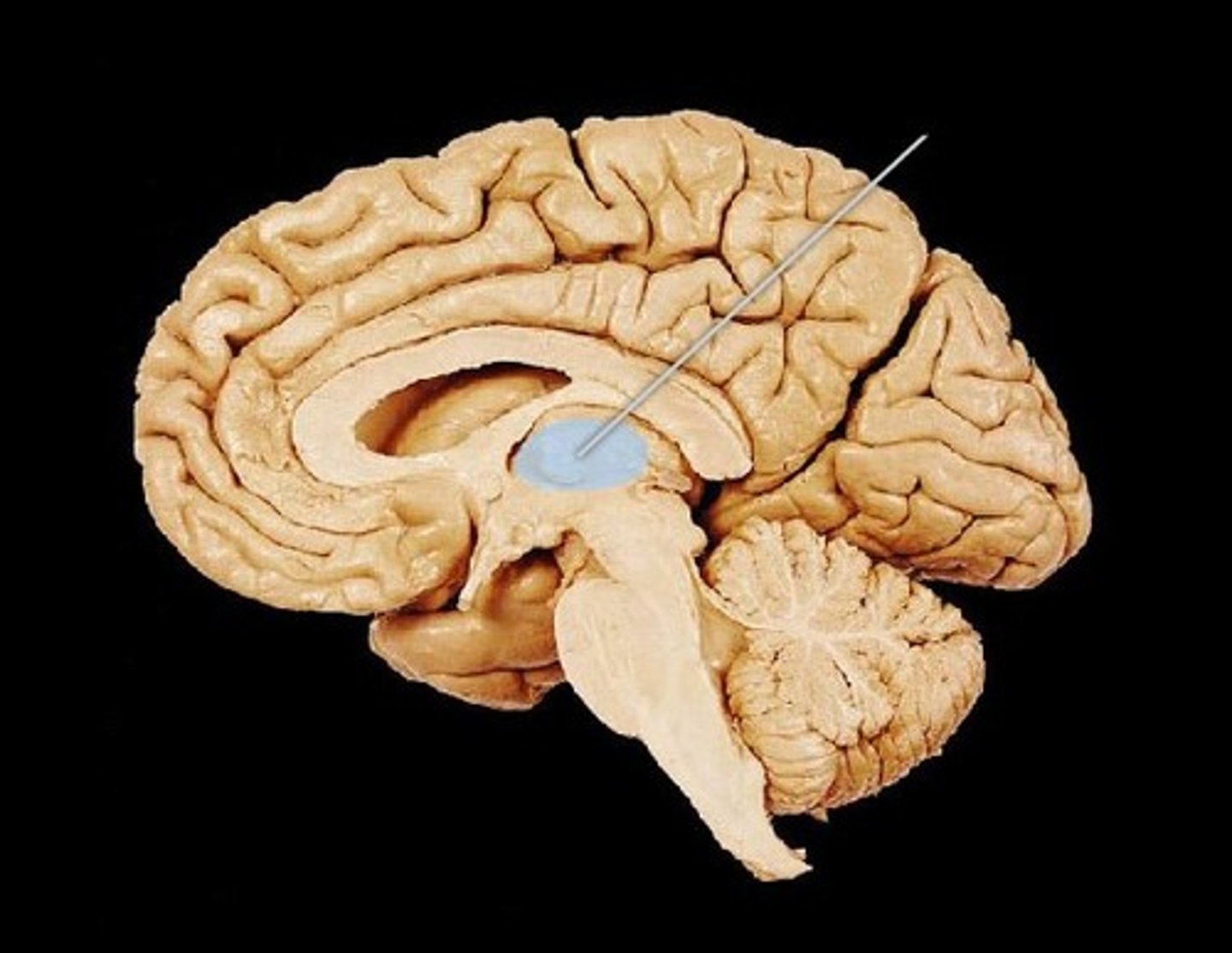
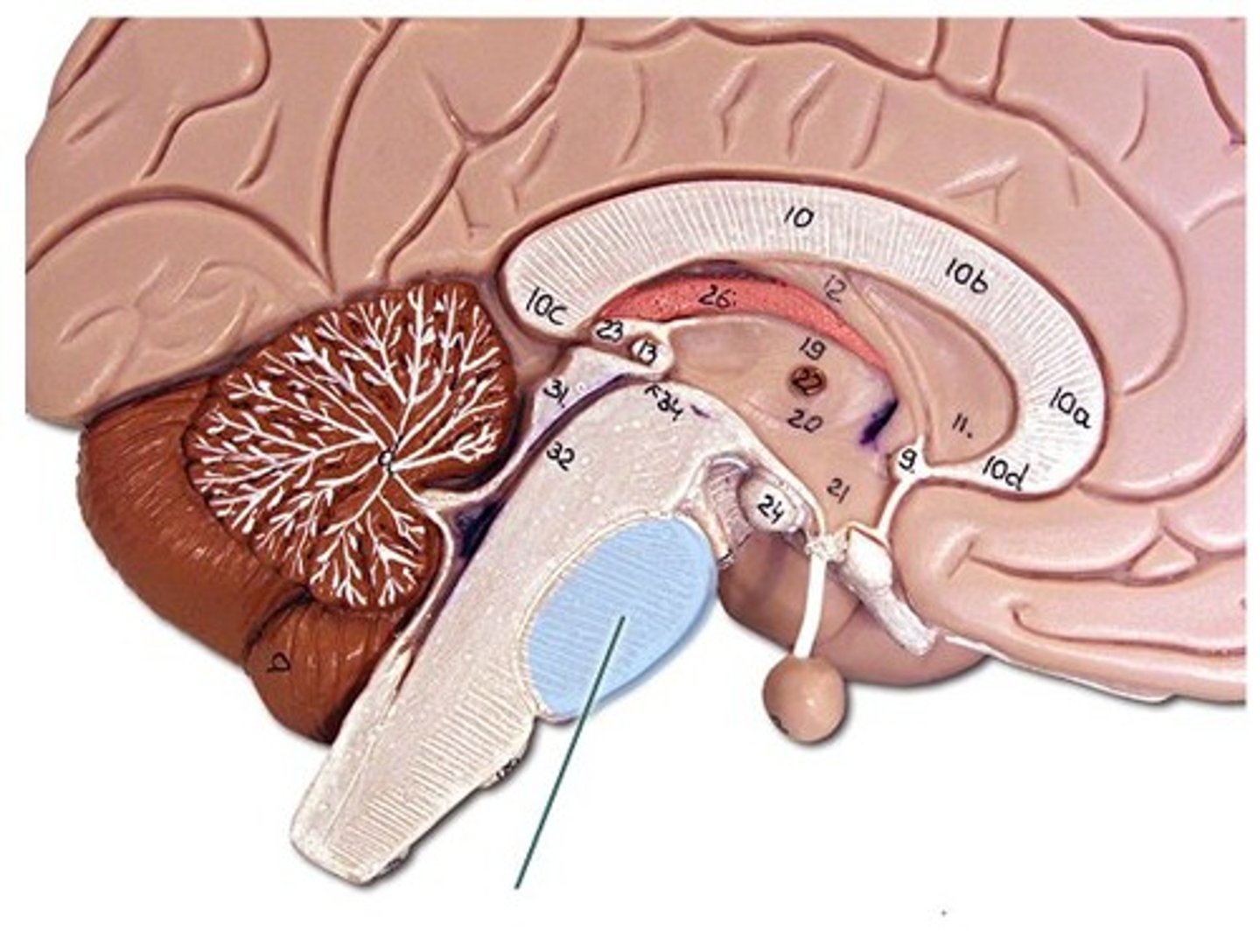
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
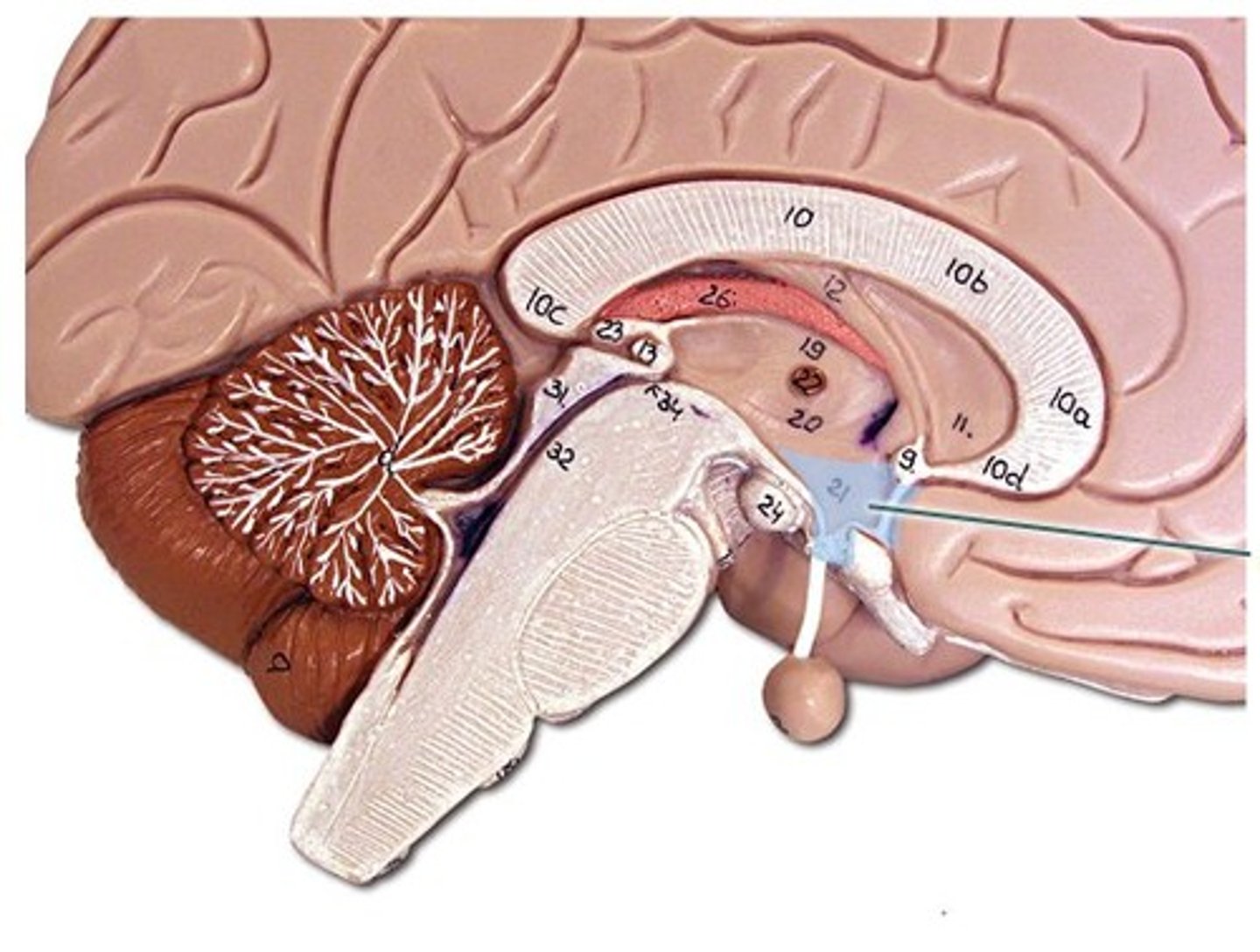
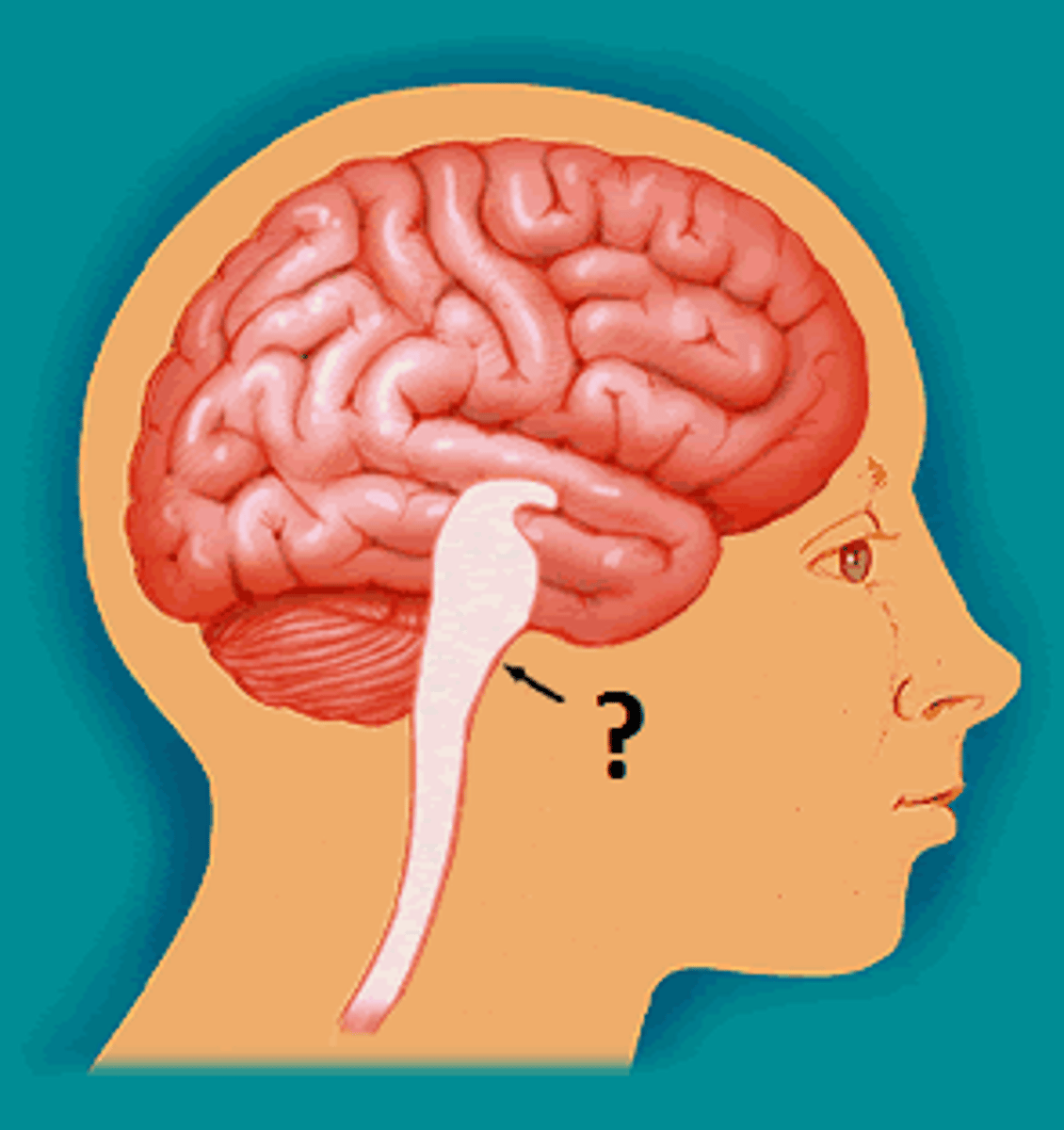
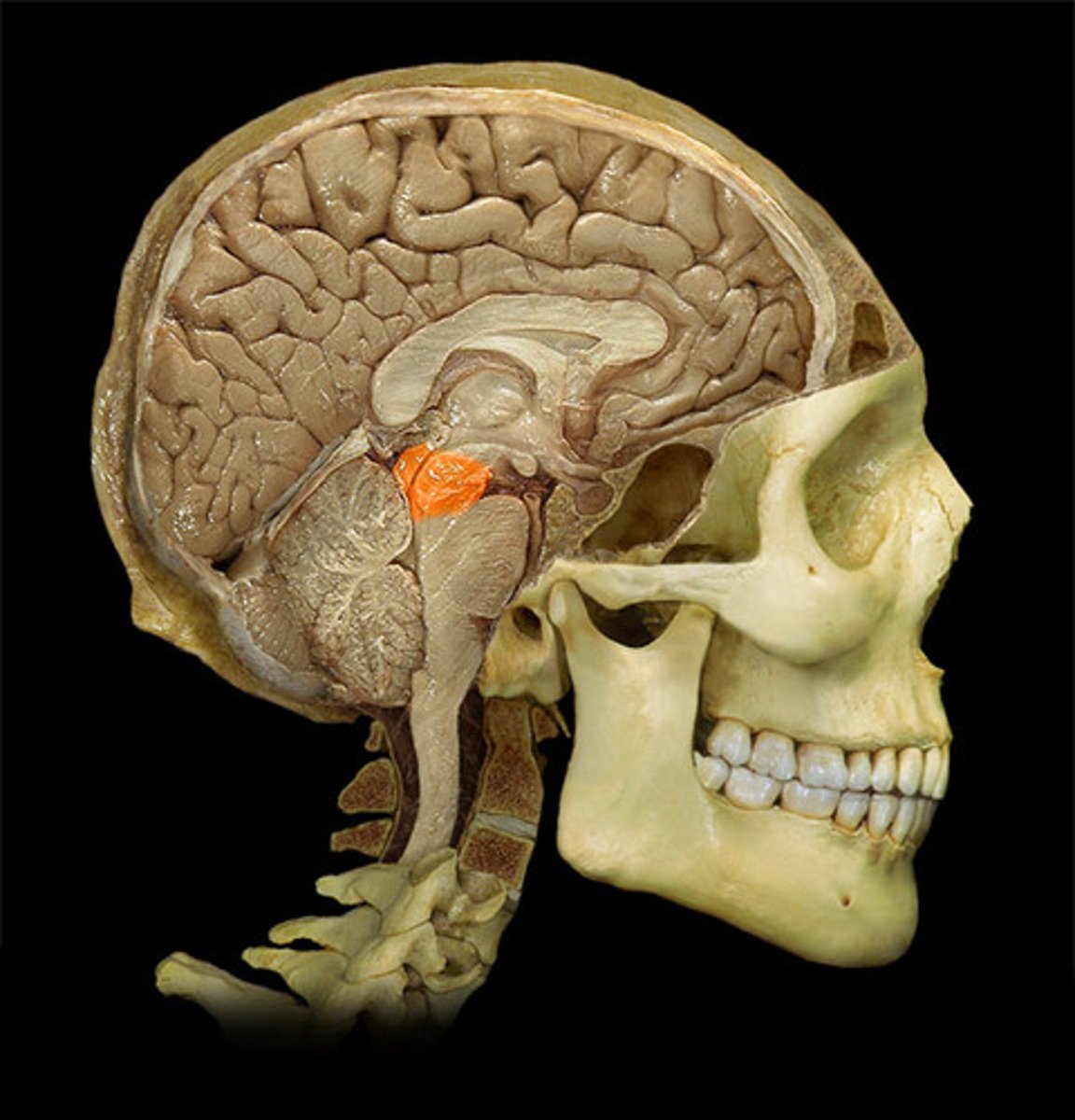
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
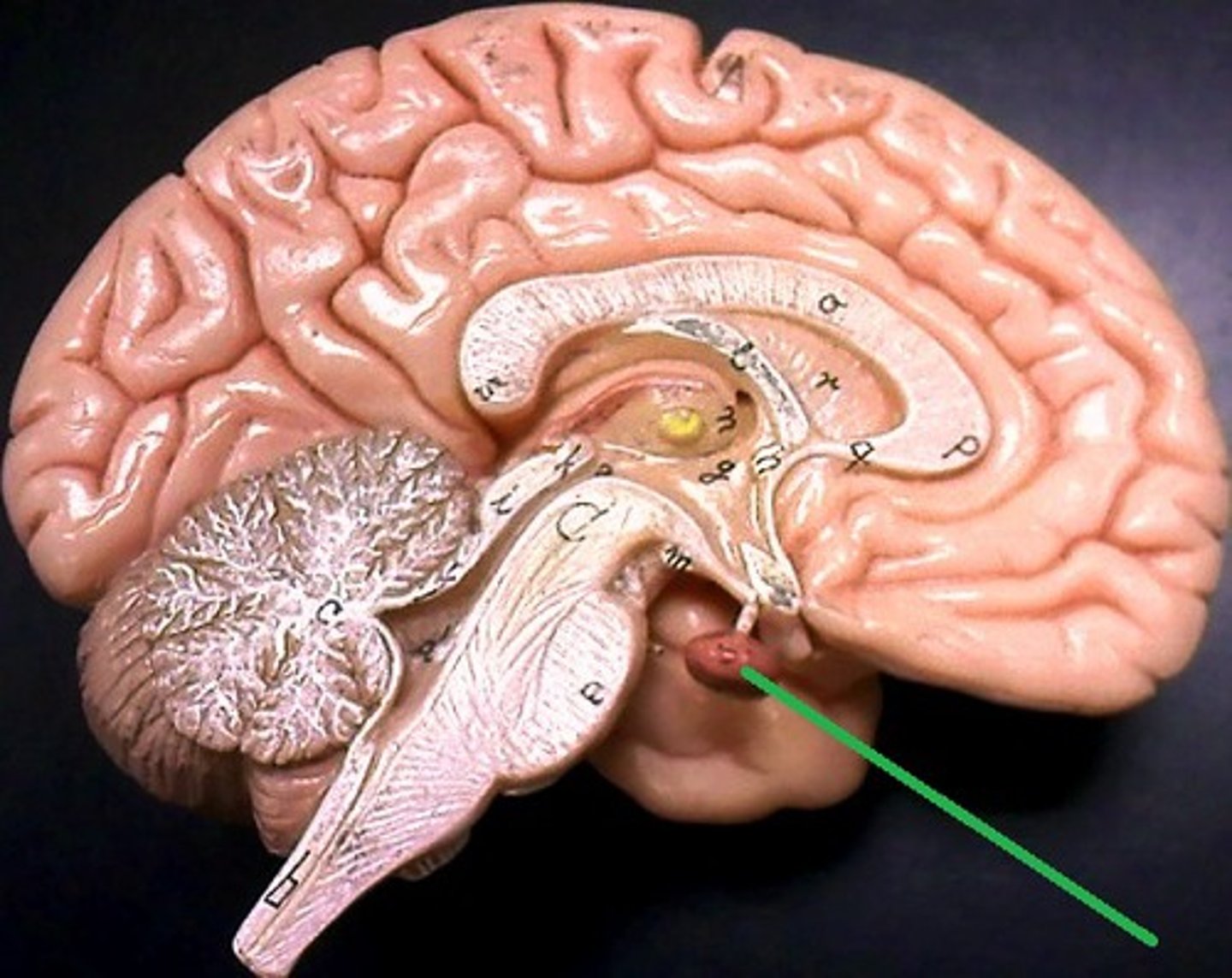
brainstem
•Connects cerebrum, diencephalon, and cerebellum to spinal cord
•Contains ascending and descending tracts connecting brain and spinal cord
•Contains autonomic nuclei, nuclei of cranial nerves, and reflex centers; required for regulating body functions necessary for life (including breathing and blood pressure)
•Consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
midbrain (mesencephalon)
a small part of the brainstem above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward
pons
a brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
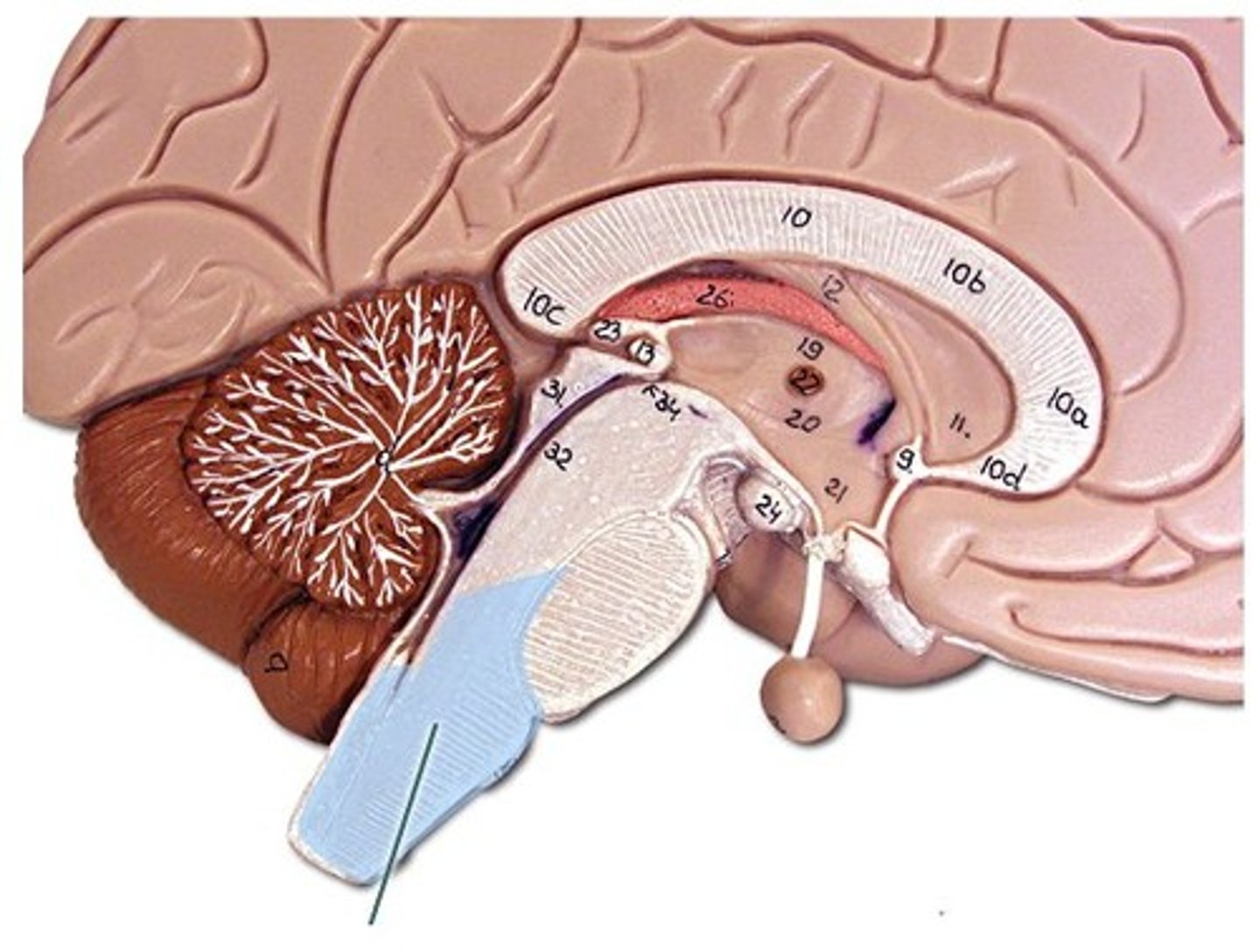
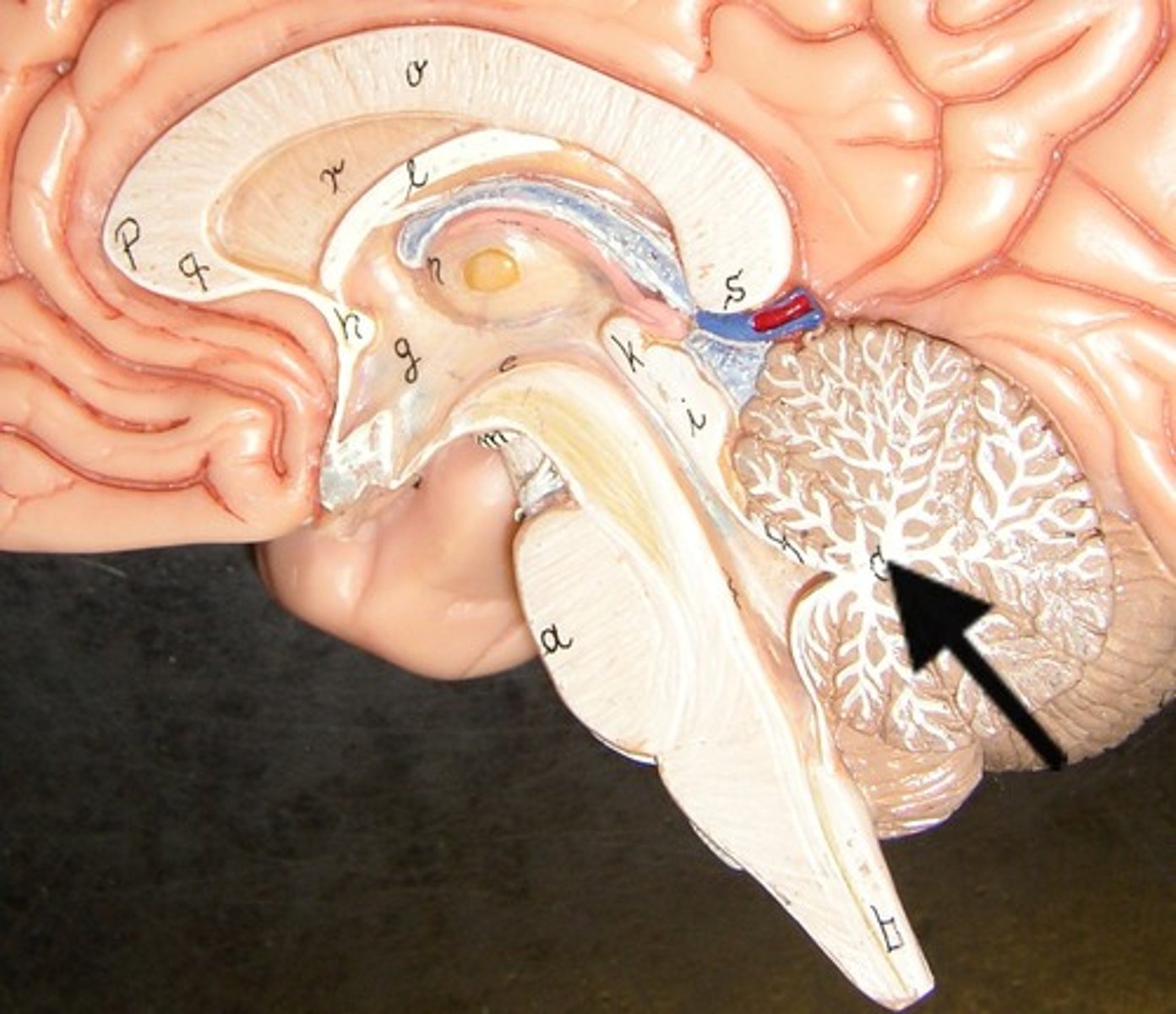
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brain; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
arbor vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
meninges
•Three connective tissue layers
•Separate and support soft tissue of brain
•Enclose and protect blood vessels supplying the brain
•Help contain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
•From deep to superficial (PAD to protect the brain)
--Pia mater
--Arachnoid mater
--Dura mater
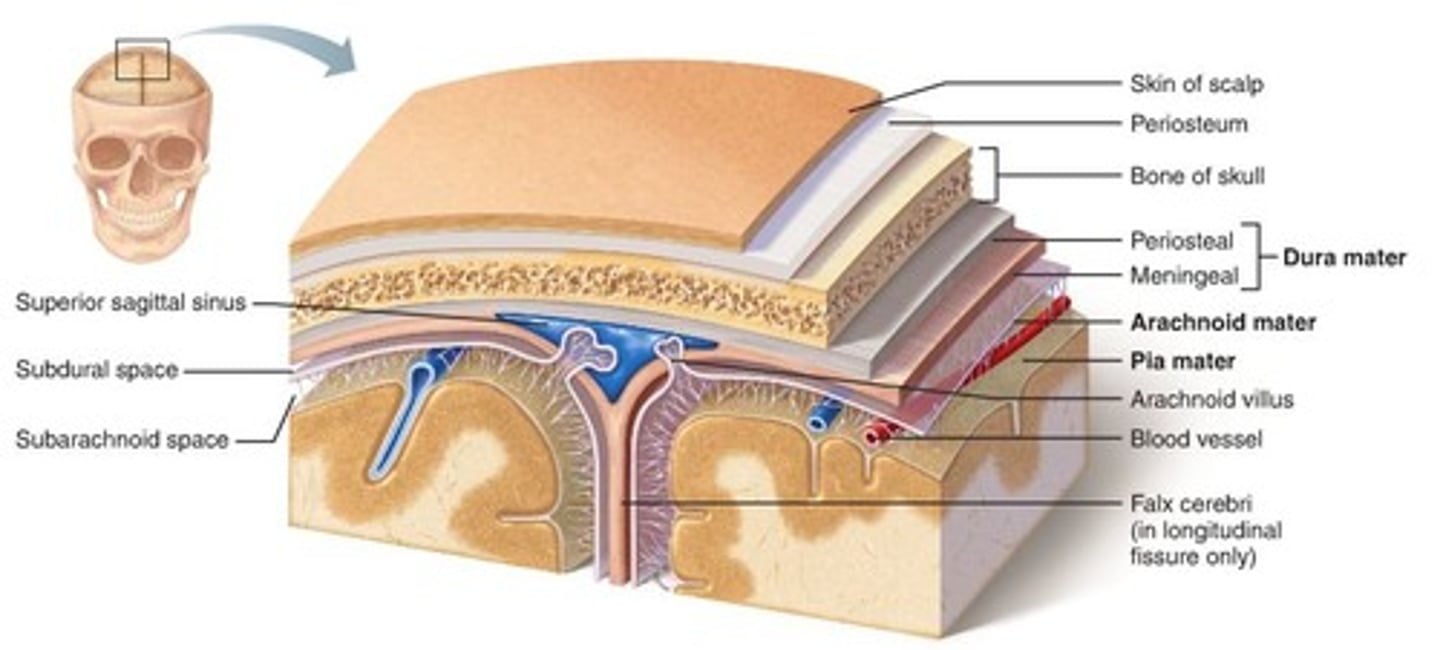
dura mater (brain)
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
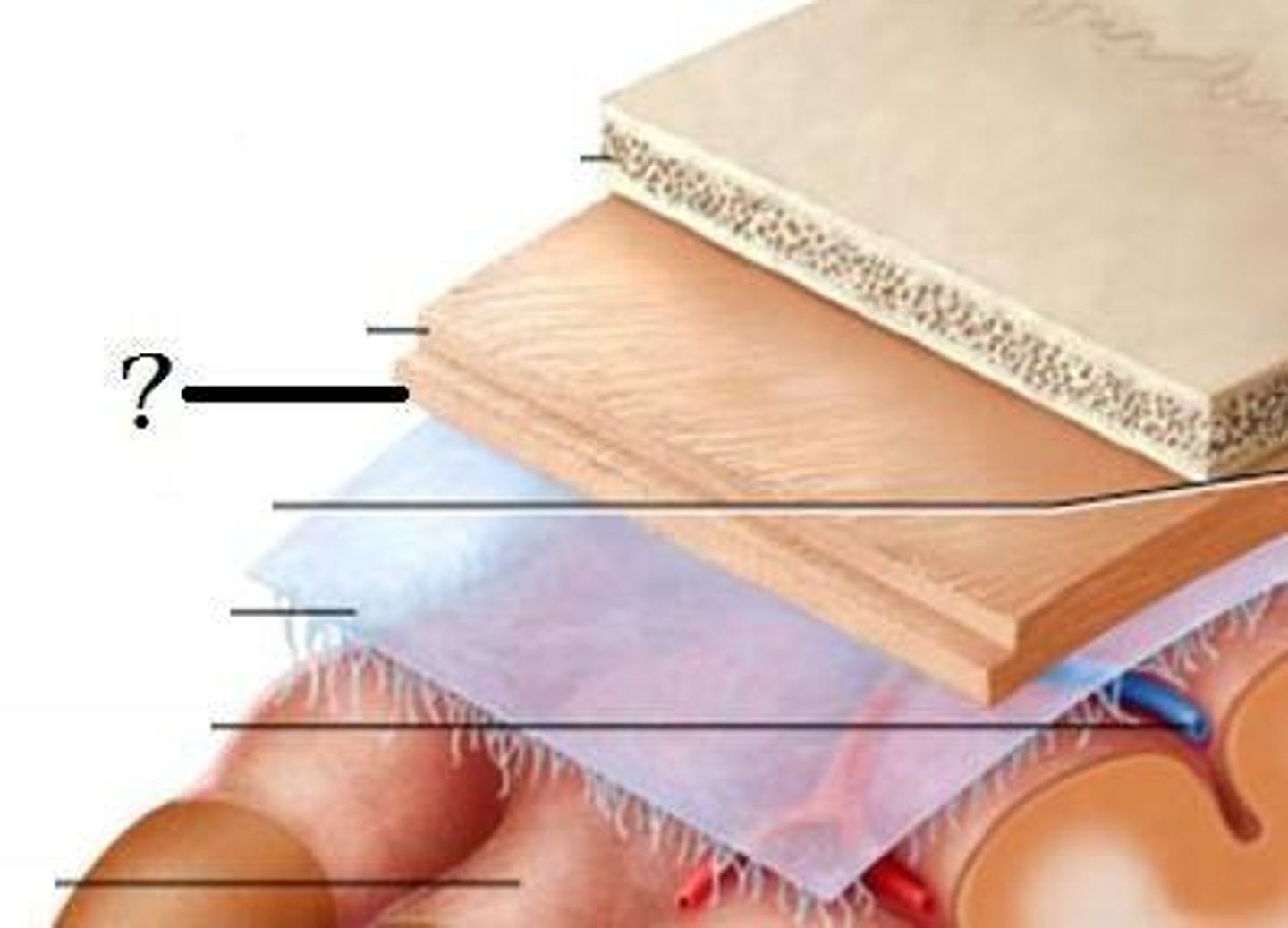
arachnoid mater (brain)
middle web-like layer of the meninges
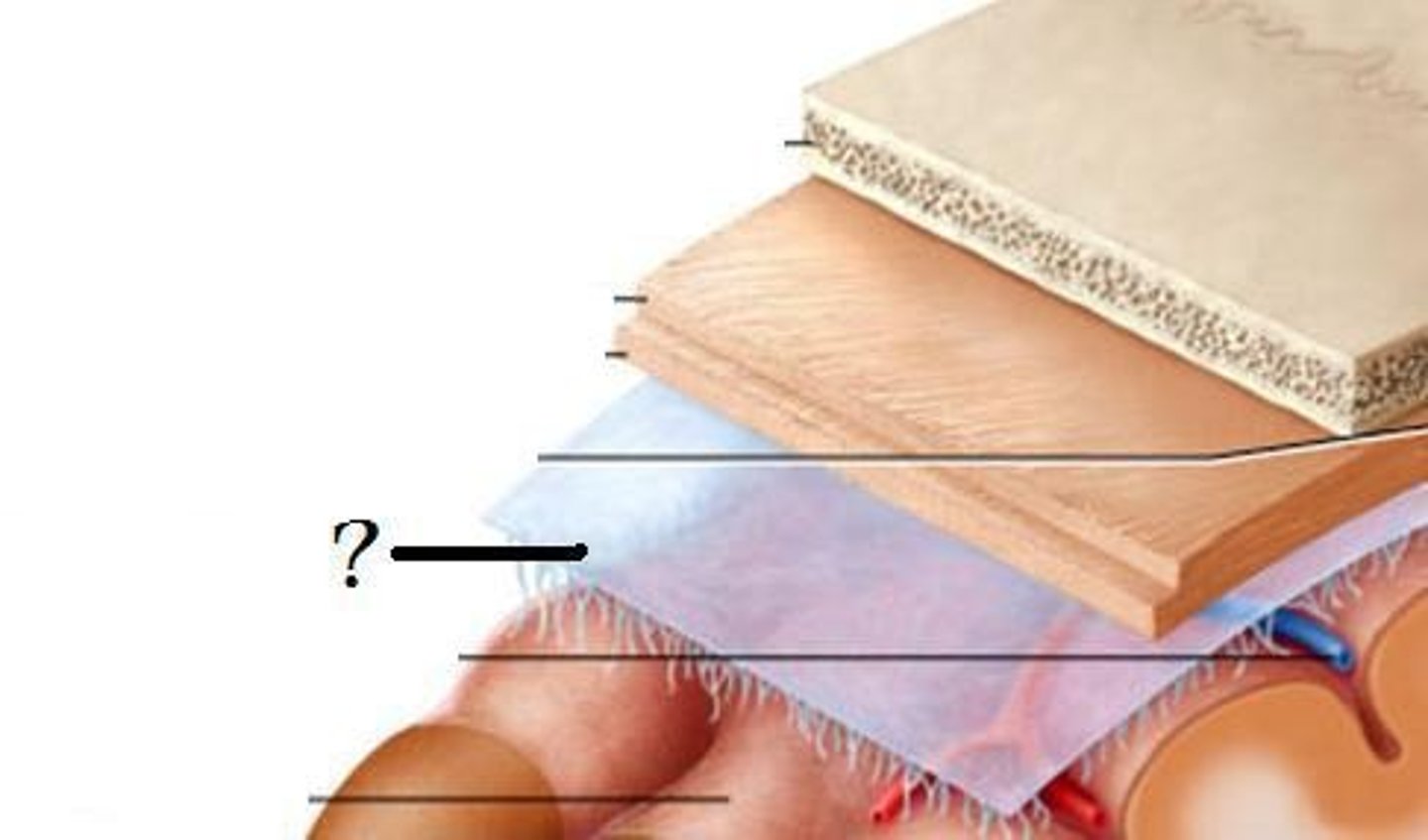
pia mater (brain)
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
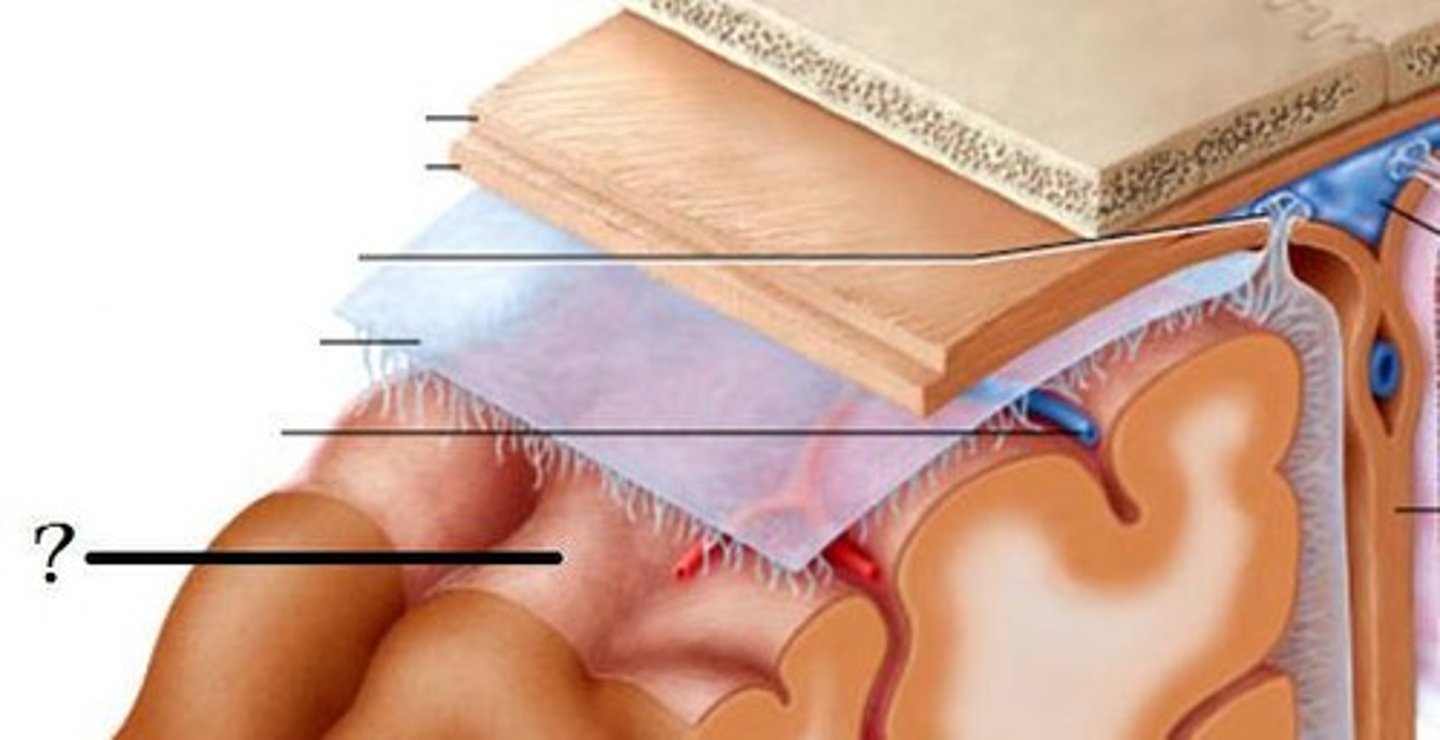
gray matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and unmyelinated axons.
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of myelinated axon
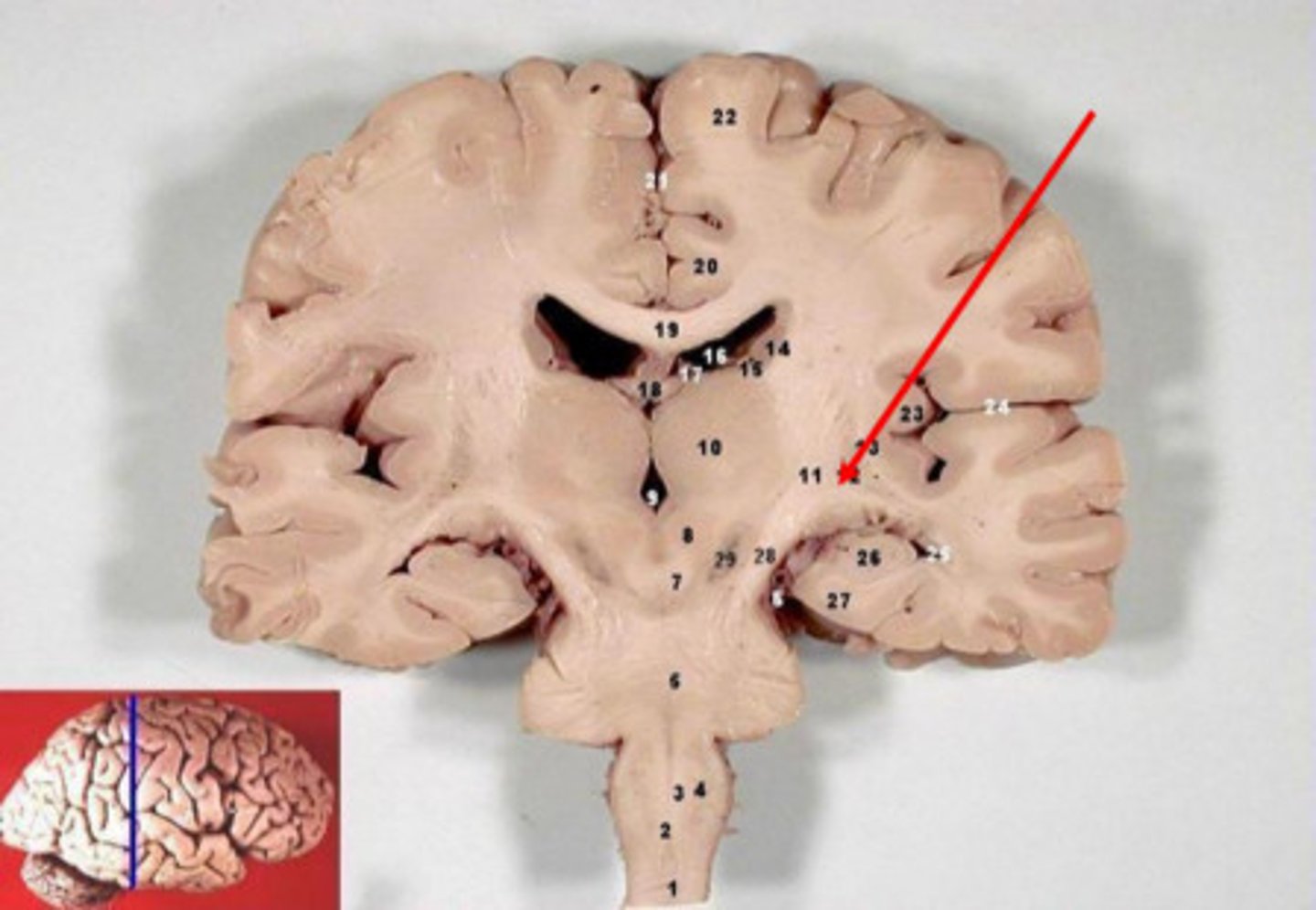
eye muscle(s) innervated by CN III (oculomotor)
superior rectus muscle
inferior rectus muscle
medial rectus muscle
inferior oblique muscle
eye muscle(s) innervated by CN VI (abducens)
lateral rectus muscle
eye muscle(s) innervated by CN IV (trochlear)
superior oblique muscle
direct light reflex
shining a light into one eye causes pupil of that eye to contract
consensual light reflex
shining a light into one eye causes the pupil of the other eye to contract
sensory receptor
specialized cell that transmits signals to sensory neurons
modality gated channel
opens in response to a stimulus other than a neurotransmitter or a voltage change at the plasma membrane
sensory modalities
Different forms of sensation (e.g., touch, pain, pressure, heat, cold, vision, taste, hearing, and smell)
receptive field
the region of the sensory surface that, when stimulated, causes a change in the firing rate of that neuron; •Smaller fields allow more precise stimulus localization
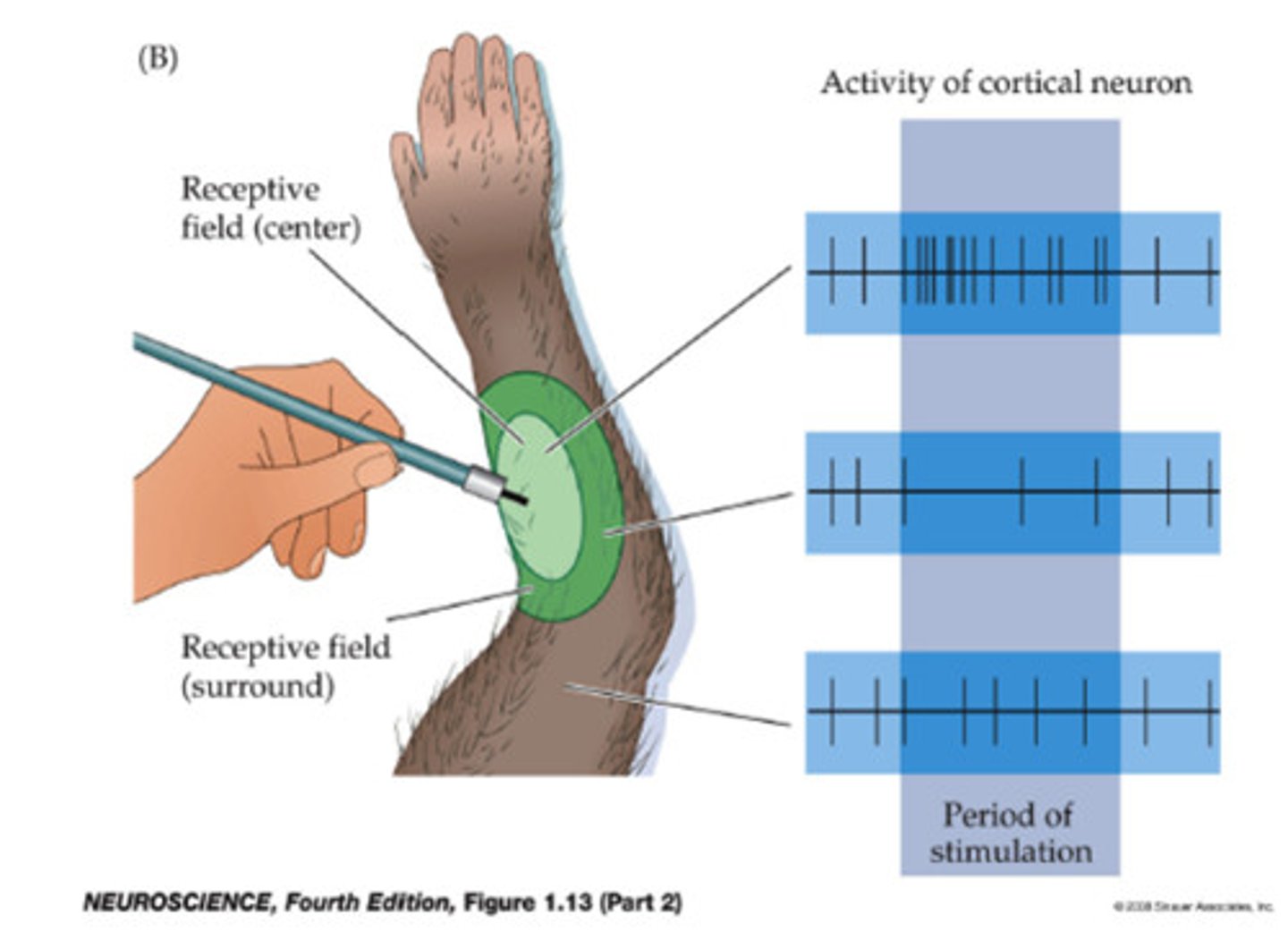
sensation
stimulus we are consciously aware of
adaptation
•decreased awareness continuous stimulus due to decrease in frequency of action potentials despite stimulus
•ex. no longer smelling a certain smell in an area
tonic receptor
a receptor in which the frequency of action potentials declines slowly or not at all as stimulation is maintained; limited adaptation - respond continuously ex. proprioceptors and nociceptors (pain receptors)
phasic receptor
a receptor in which the frequency of action potentials drops rapidly as stimulation is maintained; adapts rapidly - will only respond to new stimuli; ex. mechanoreceptors
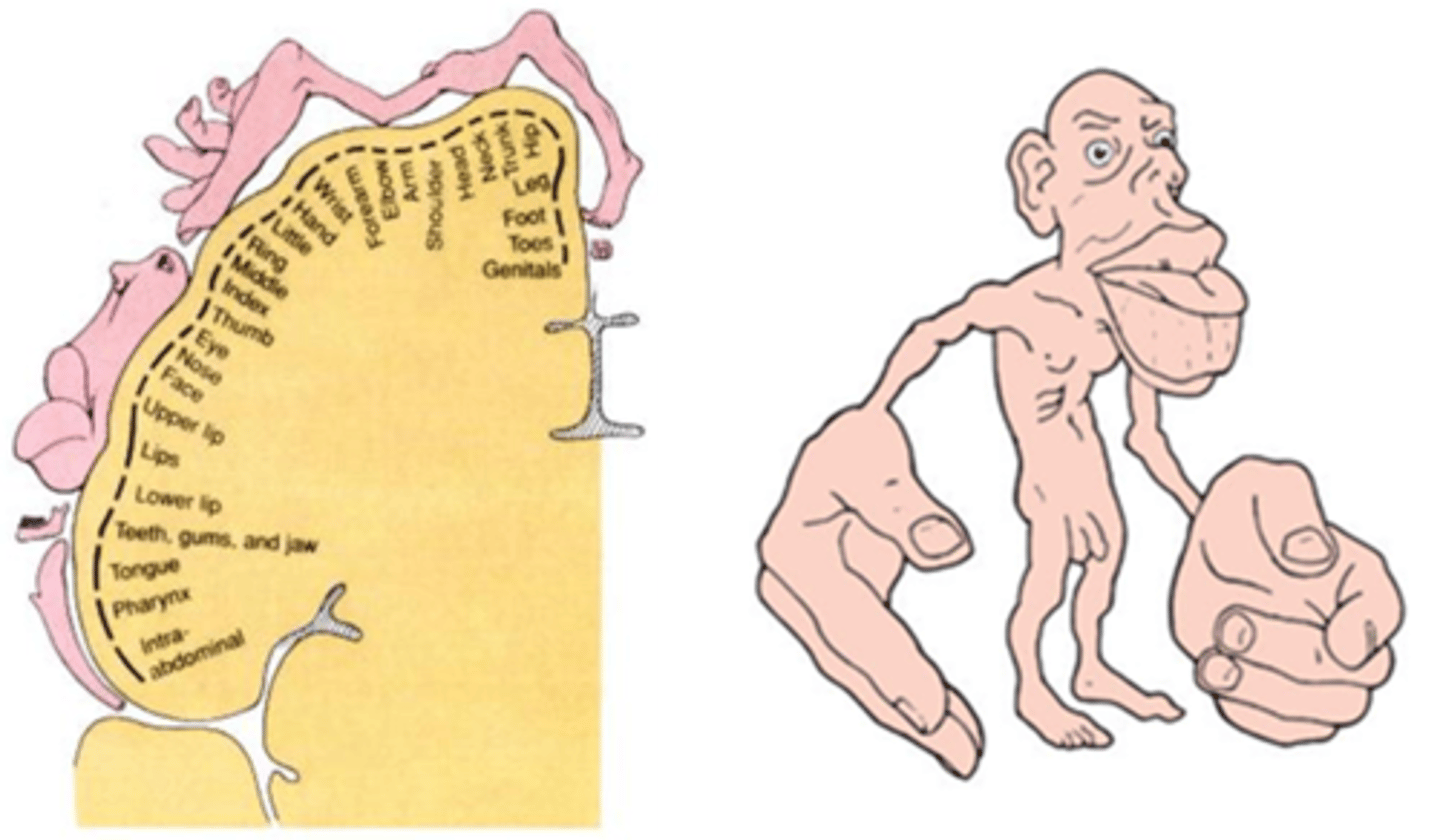
sensory homunculus
Demonstrates that the area of the cortex dedicated to the sensations of various body parts is proportional to how sensitive that part of the body is
reflex
rapid, preprogrammed, involuntary responses of muscles or glands to a stimulus
•A stimulus is required to initiate
•Response is rapid; involves a chain of only a few neurons
•The response is preprogrammed; always the same
•The response is involuntary; no intent or awareness before it happens
•A survival mechanism - we respond to a potentially detrimental stimulus immediately and awareness comes later
reflex arc
sensory receptor → sensory neuron → (interneuron), motor neuron → effector
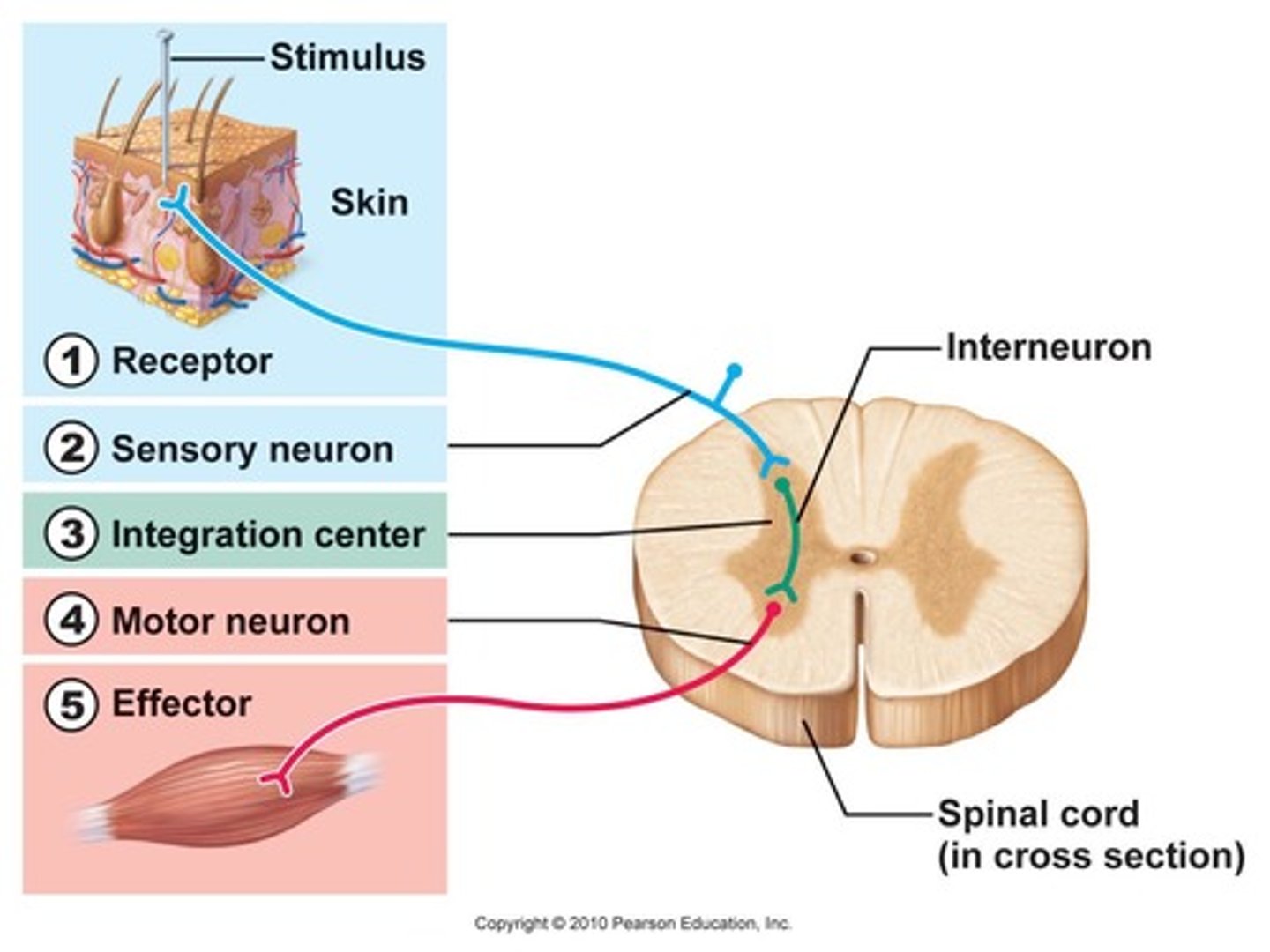
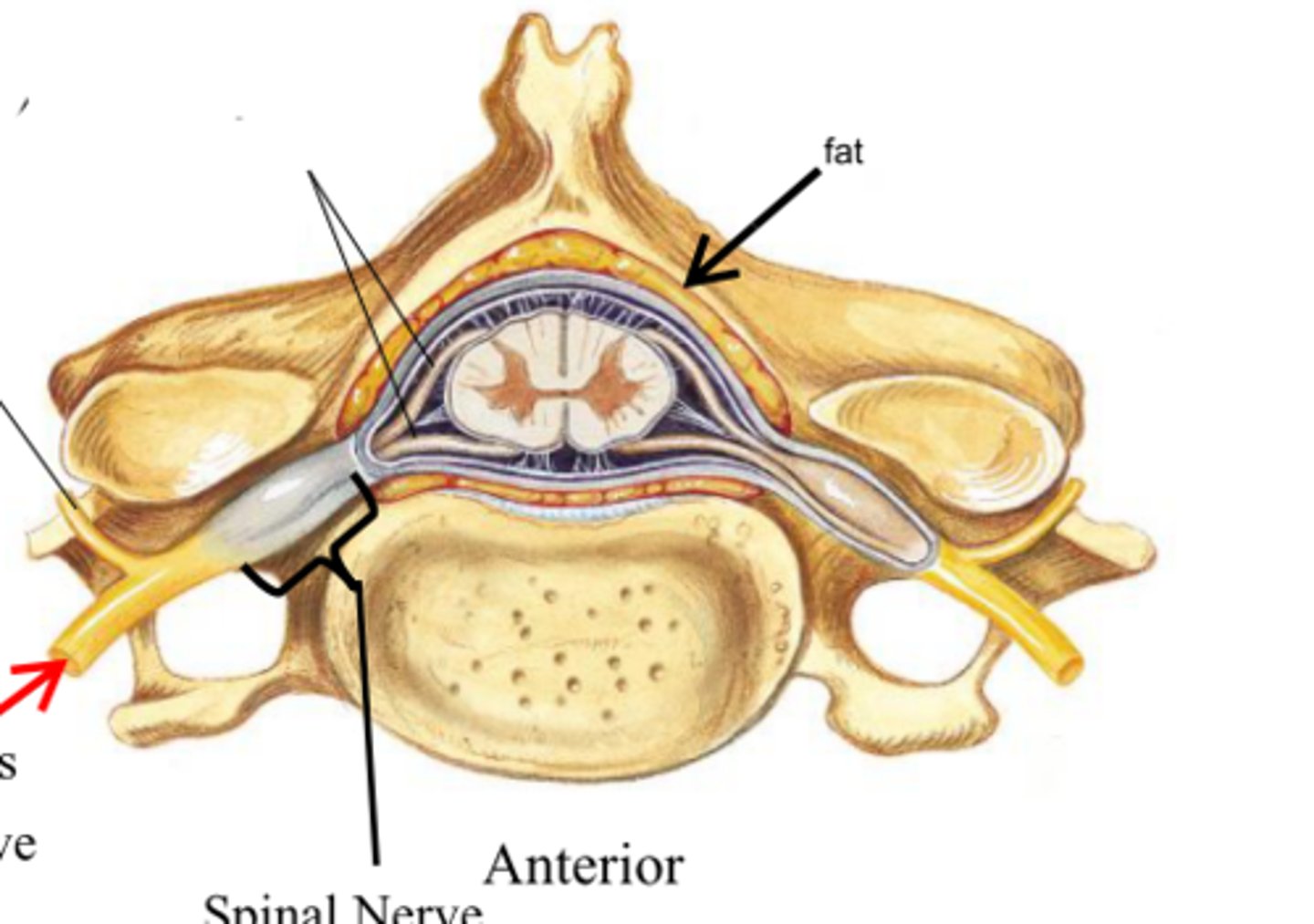
spinal cord
a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain; housed within the vertebral canal
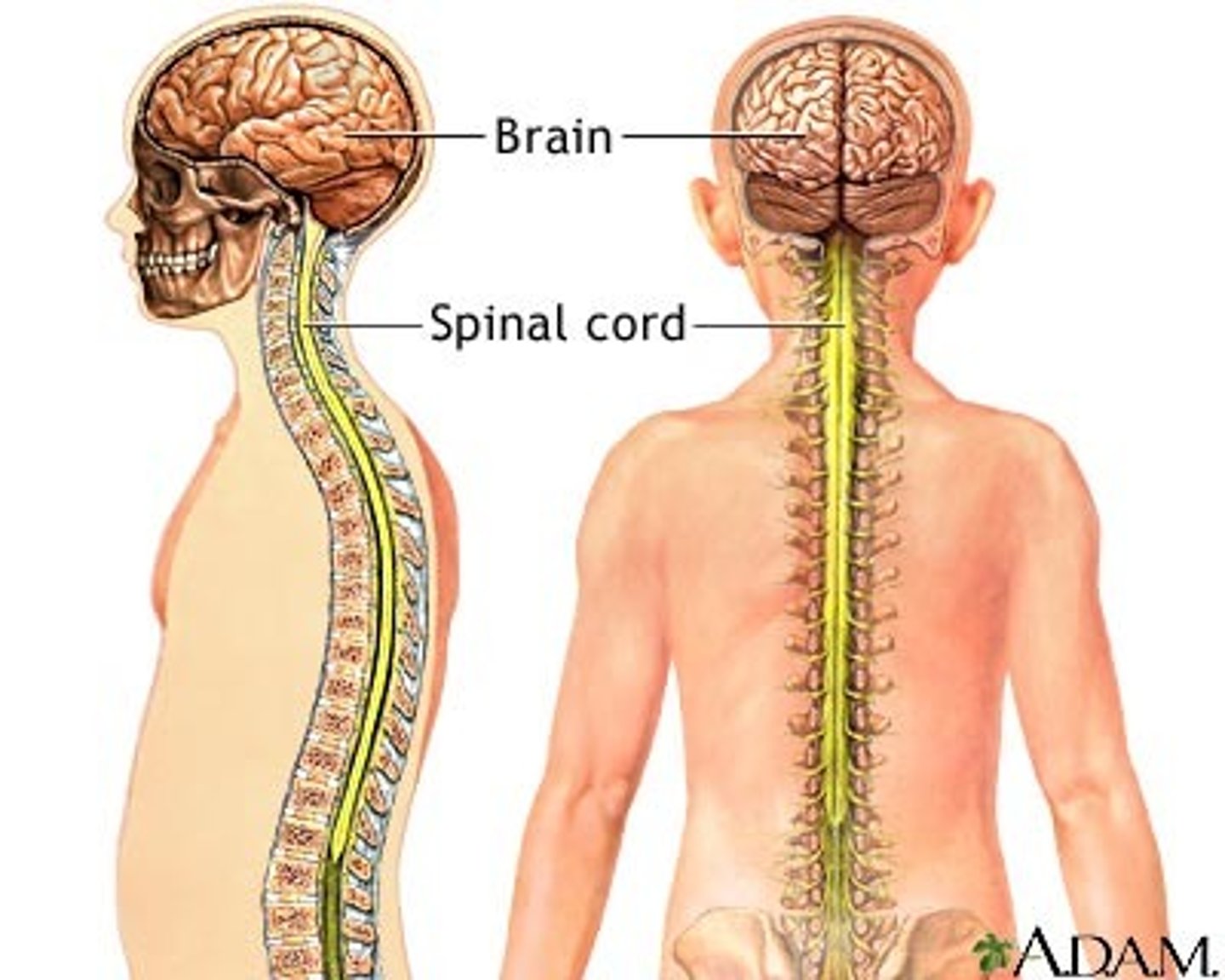
nerve
bundle of axons in PNS
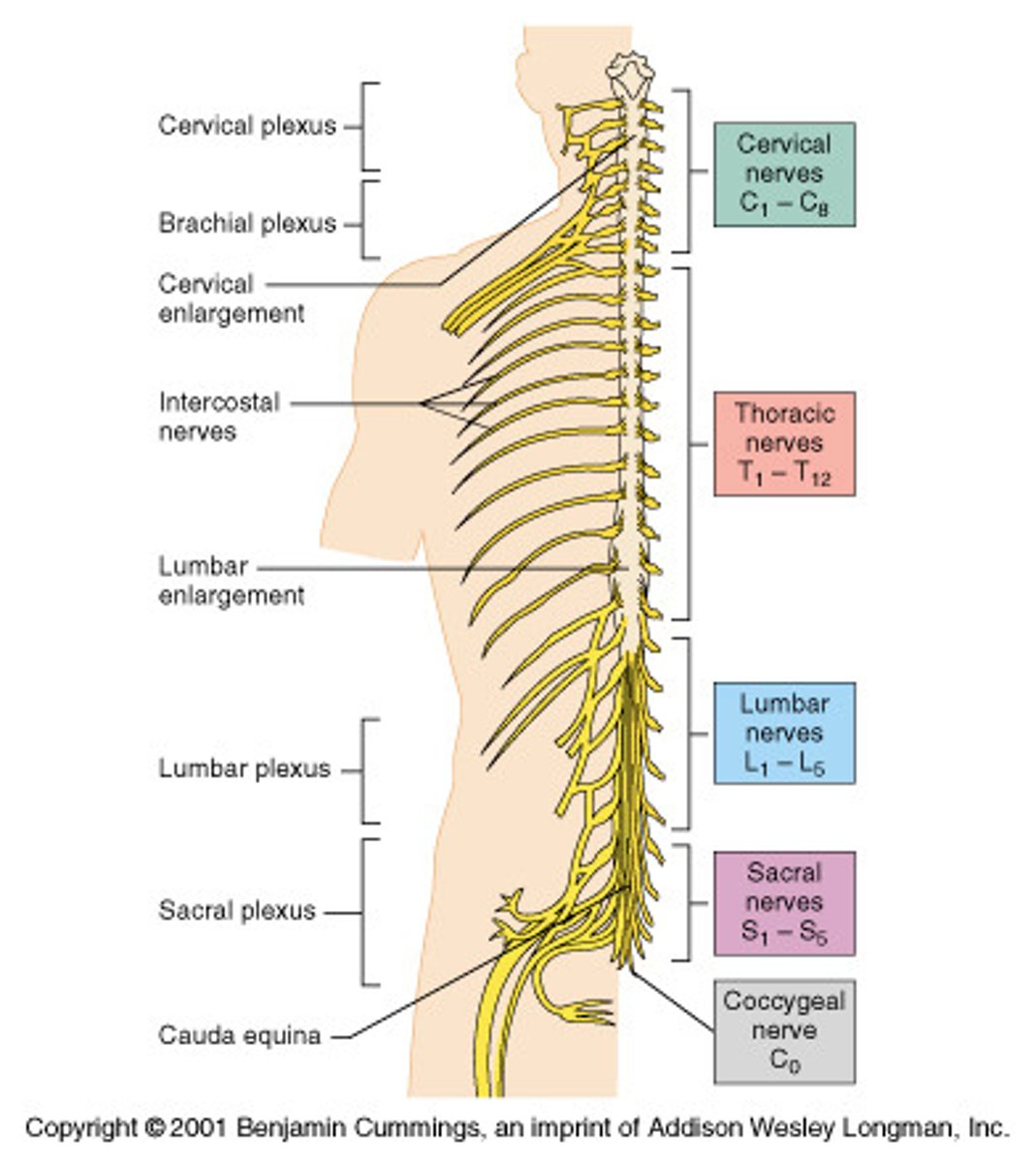
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord; letter abbreviation for region of spine they originate from; forms where the anterior and posterior roots join; mixed nerves (contain sensory and motor fibers)
posterior (dorsal) rootlets
merge to form a root
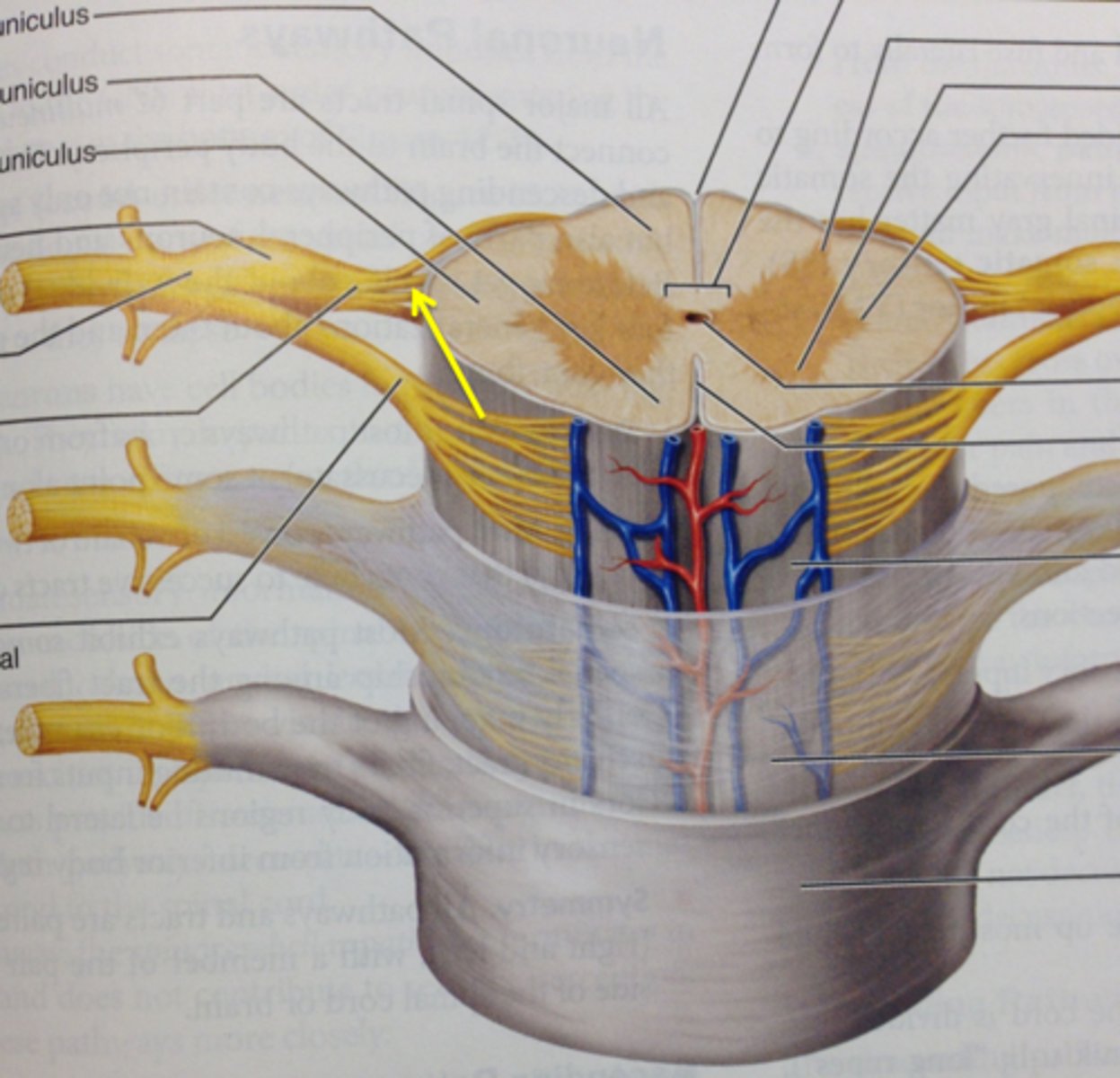
posterior (dorsal) root
contains sensory axons
posterior (dorsal) root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
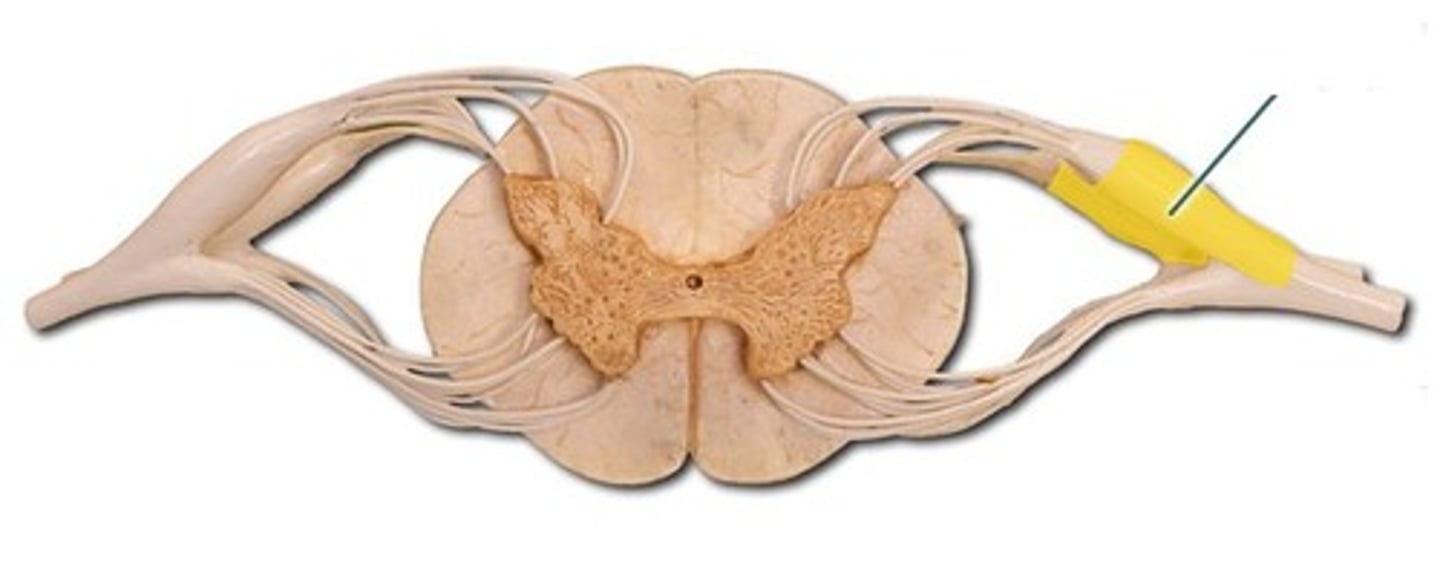
true spinal nerve
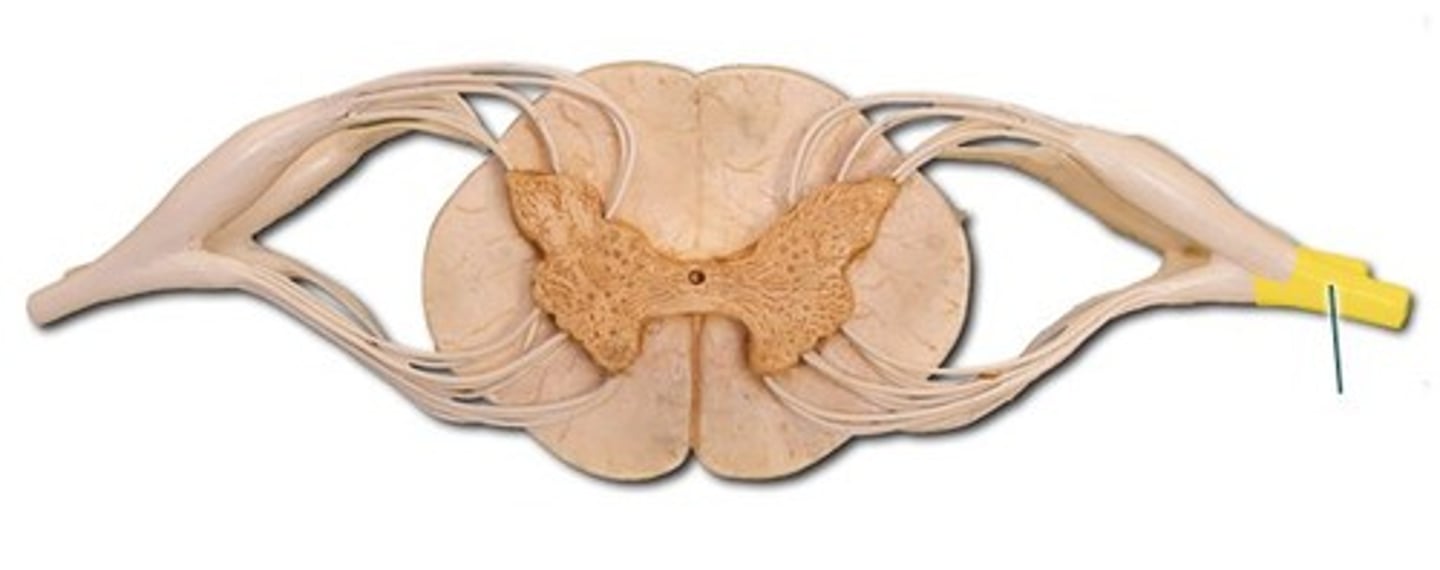
anterior root
contains motor axons
ramus
points where the spinal nerve branches; occurs away from the spinal cord
posterior (dorsal) ramus
innervates the muscles and joints in that region of the spine and the skin of the back
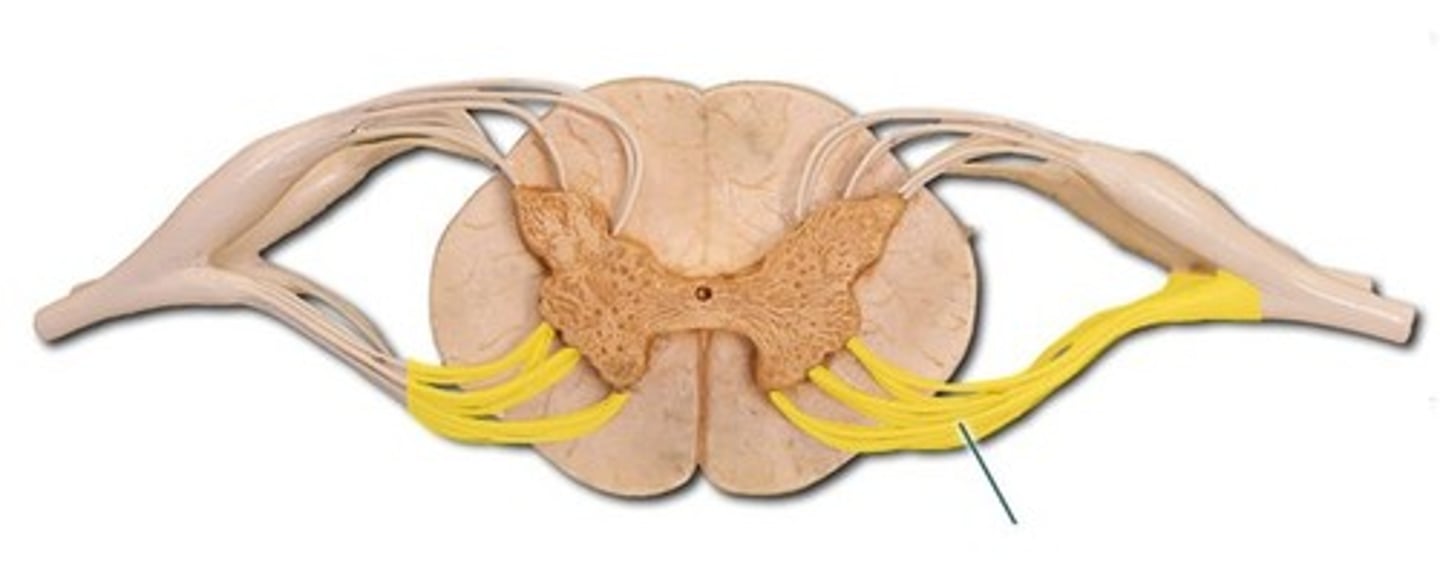
anterior (ventral) ramus
•Splits into multiple other branches
•At different levels, this ramus innervates anterior and lateral trunk, upper limb, lower limb
•Participates in plexuses
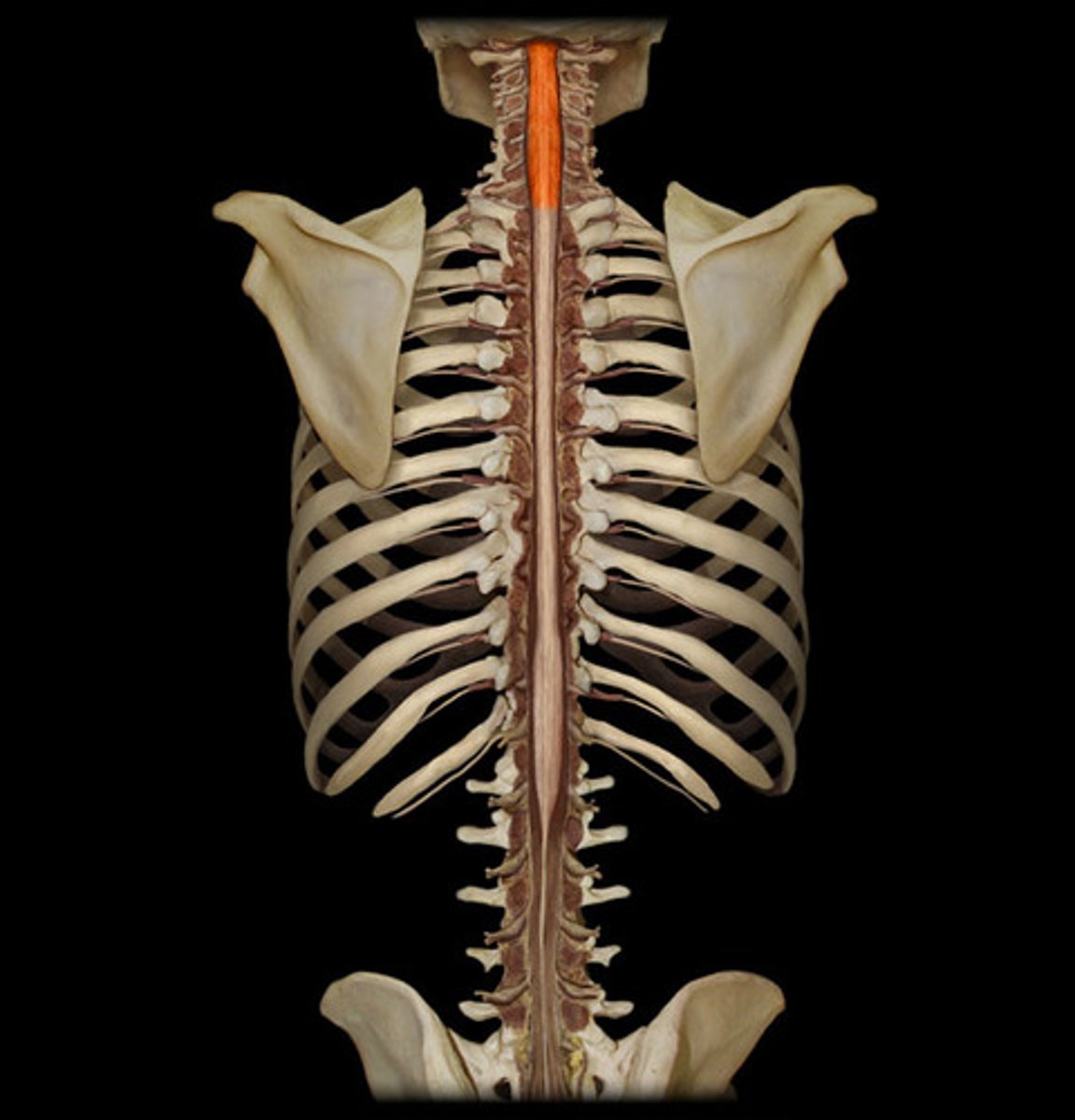
cervical region of spinal cord
supplies neck, shoulders, and upper limbs, C1-8
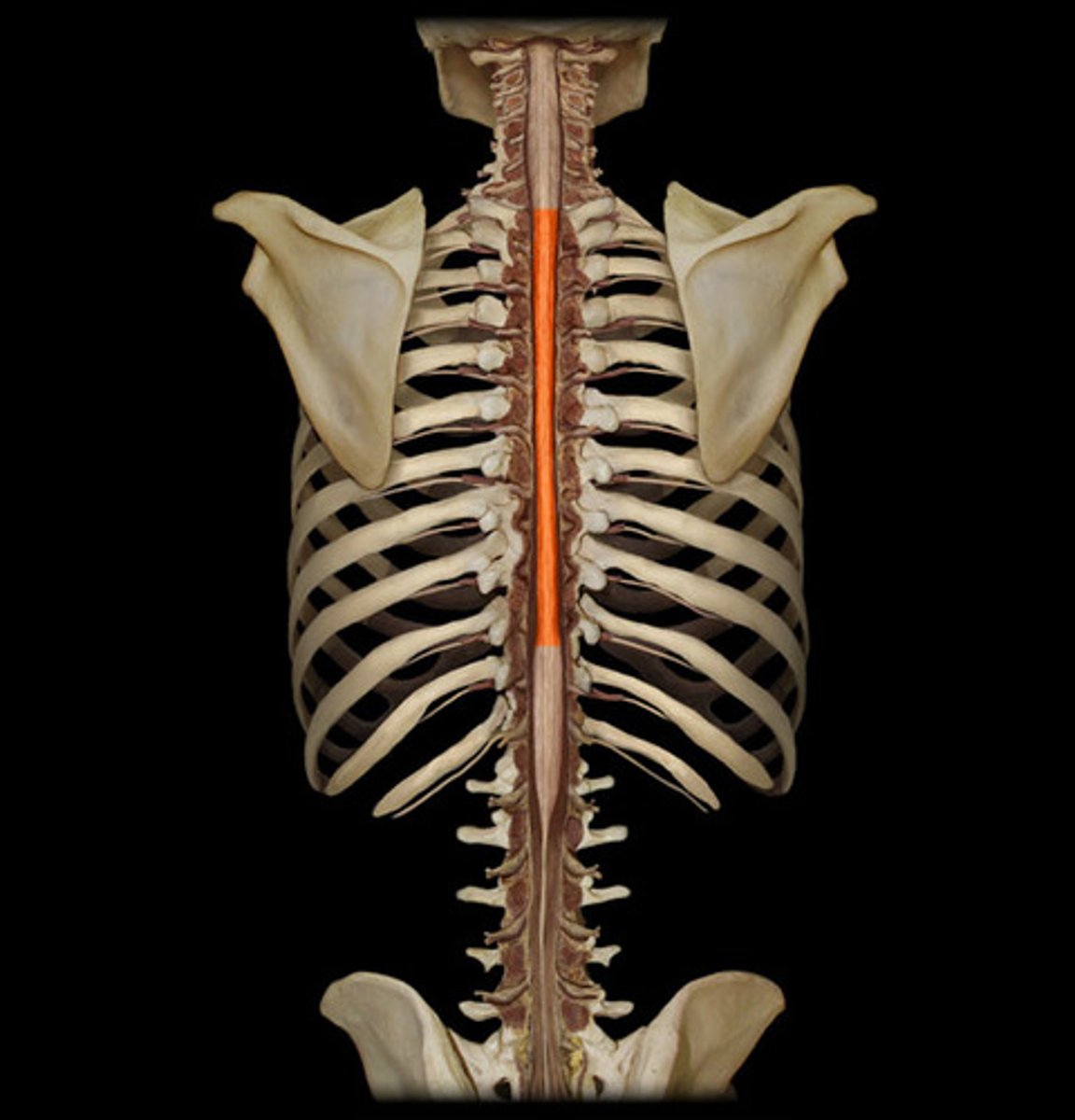
thoracic region of spinal cord
supplies thoracic cage, T1-12
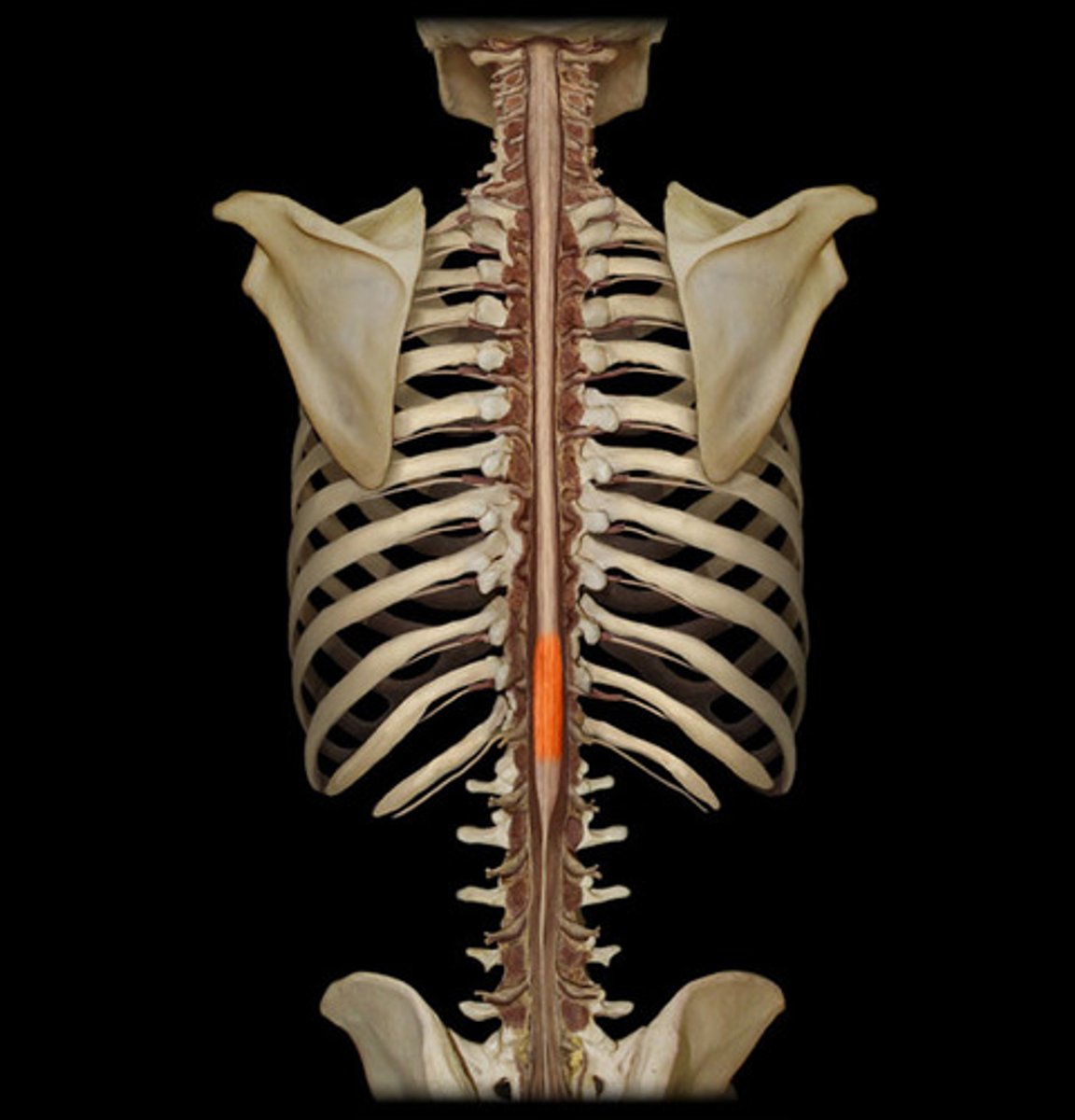
lumbar region of spinal cord
supplies hips & front of lower limbs, L1-5
sacral region of spinal cord
supplies buttock, genitalia, and backs of lower limbs, S1-5
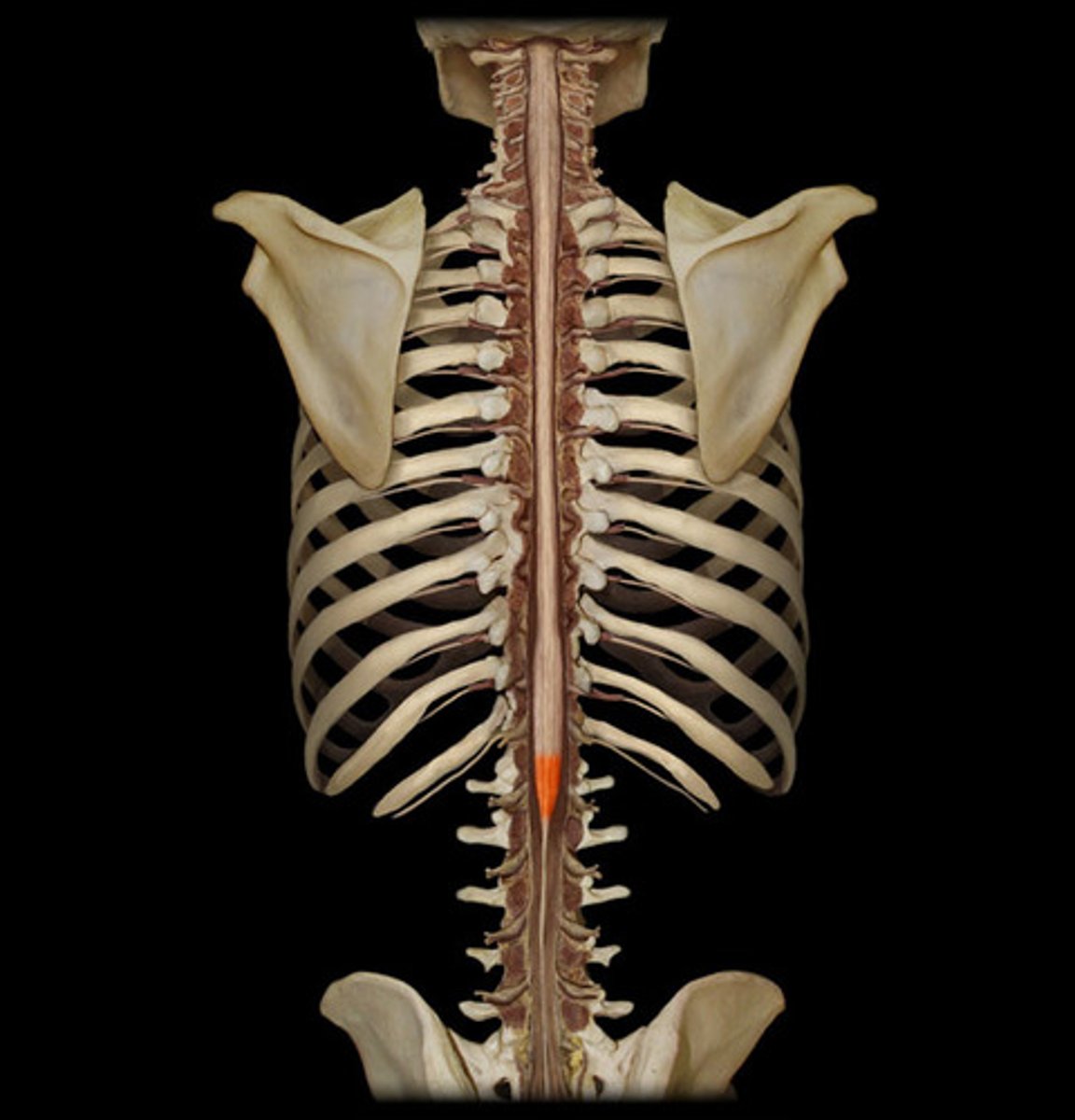
conus medullaris
inferior tapered end of spinal cord
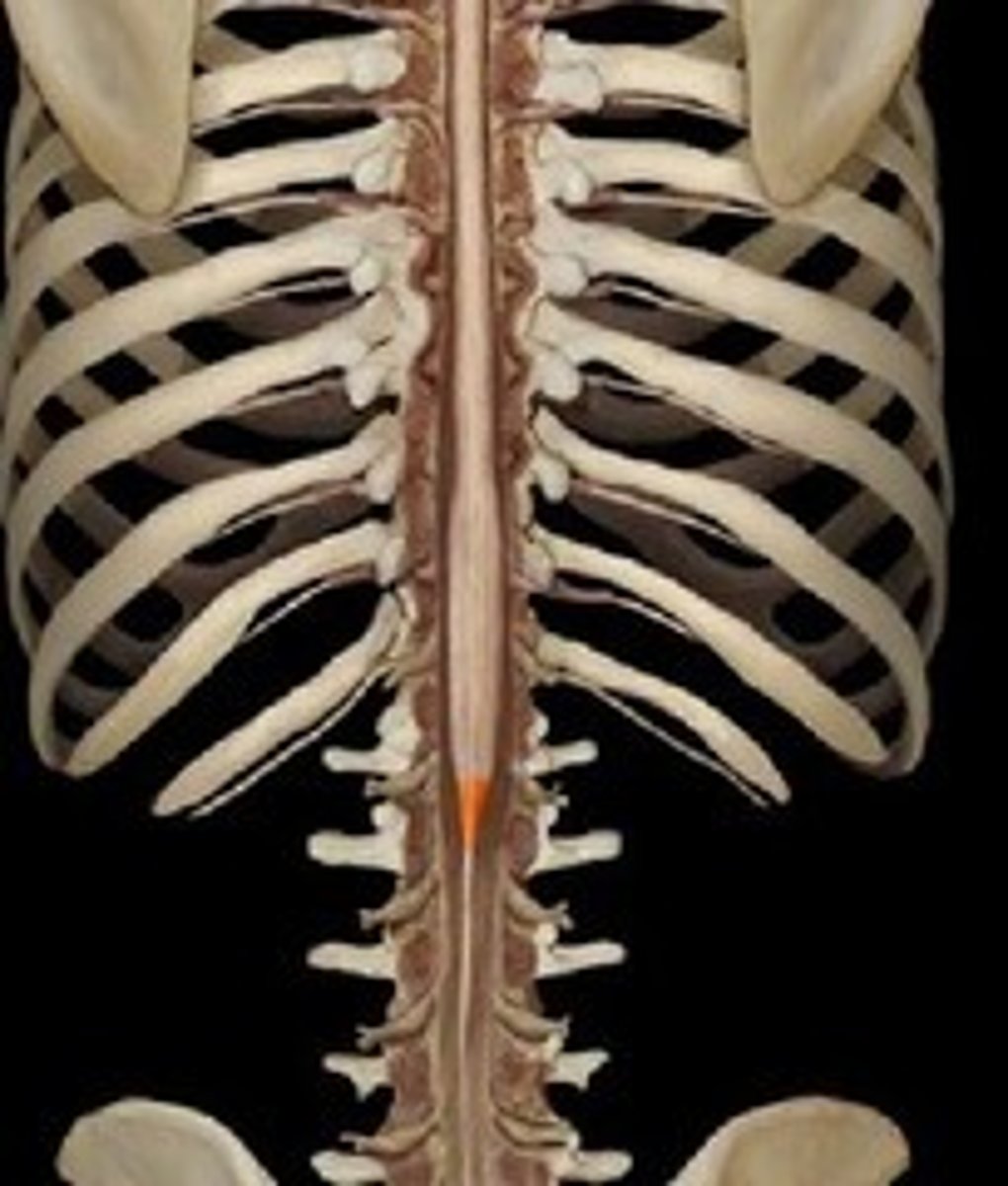
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord; below L1 vertebrae
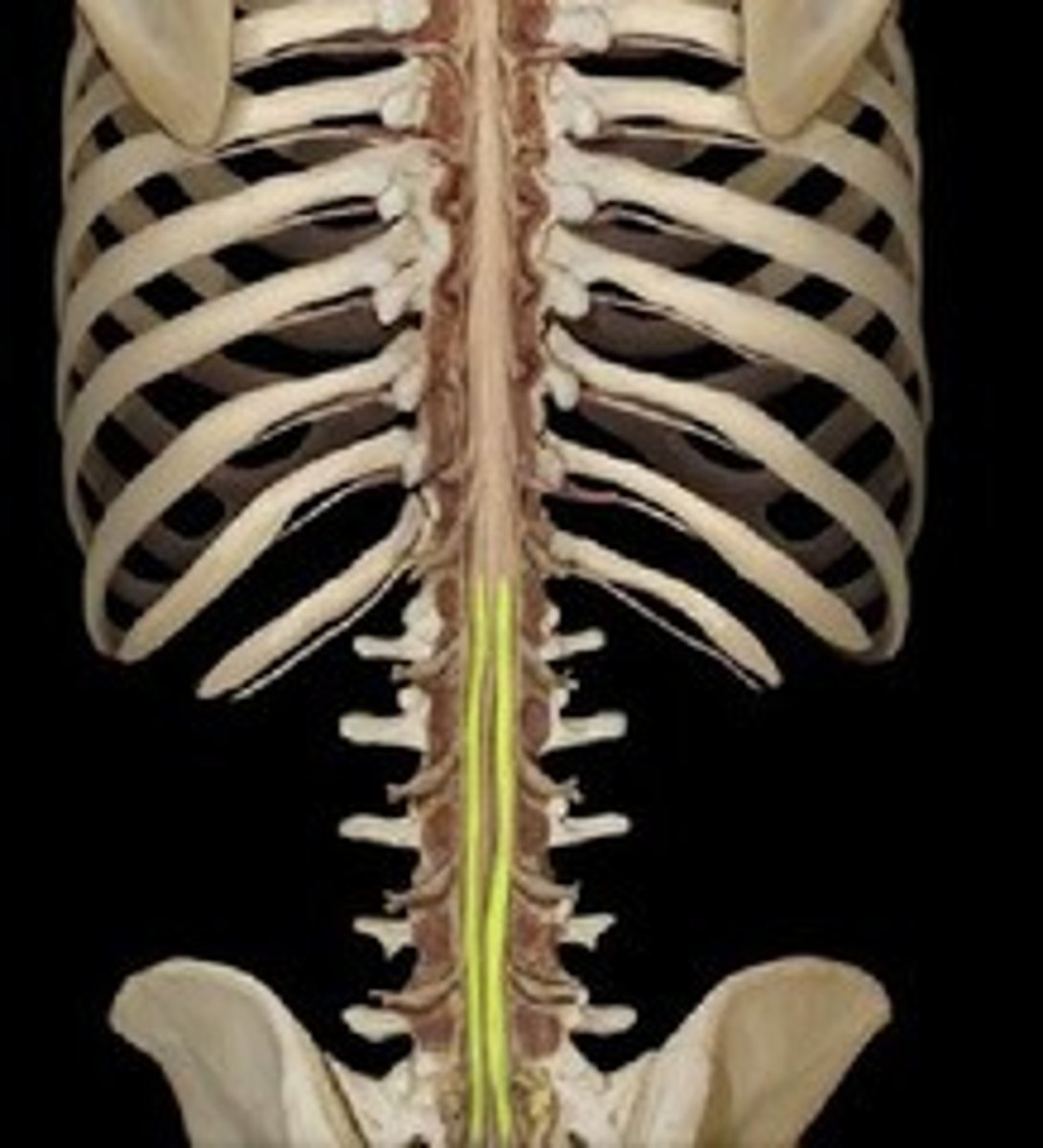
filum terminale
fibrous extension of the pia mater; anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
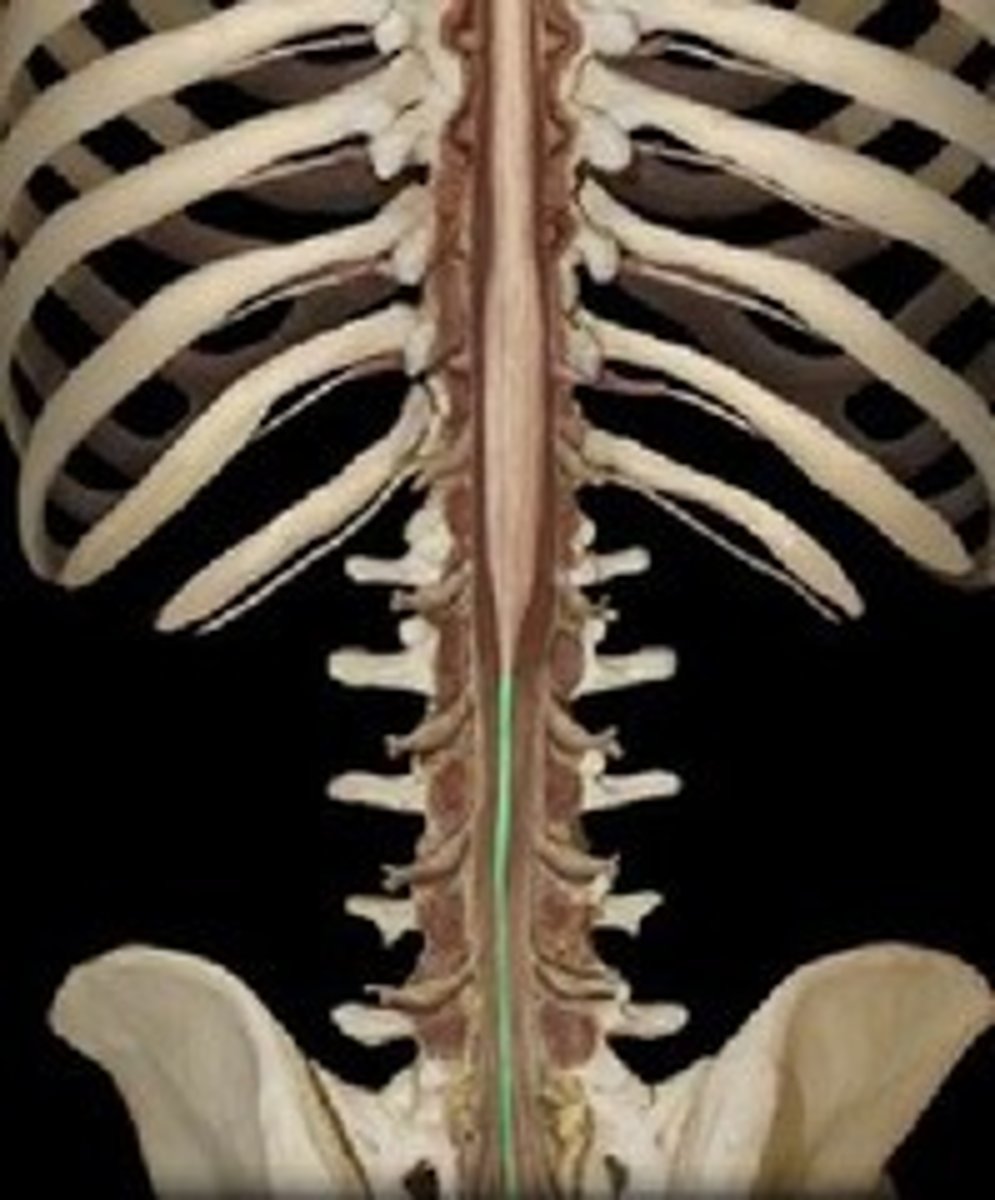
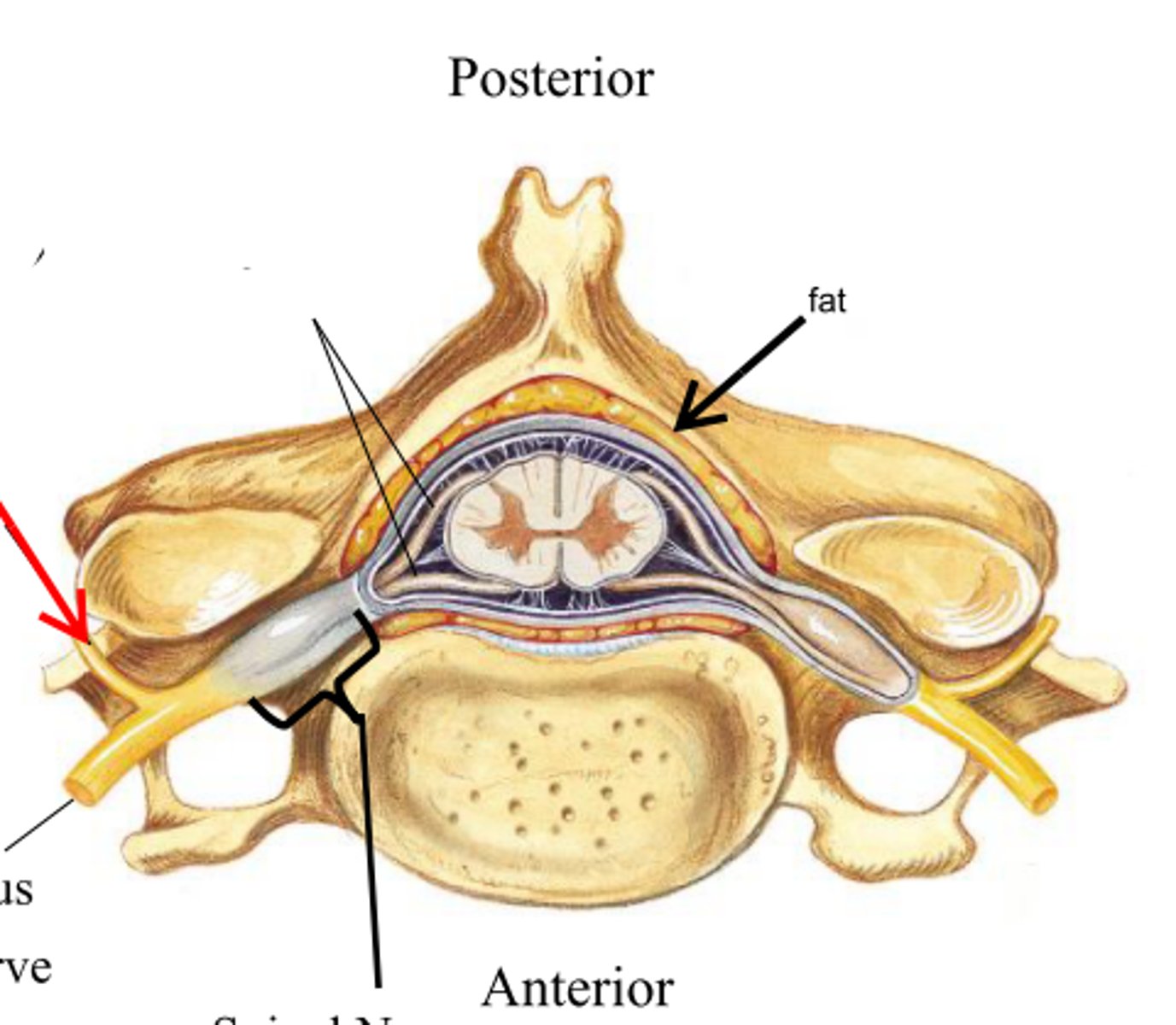
spinal meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater (PAD to protect the spinal cord from deep to superficial)
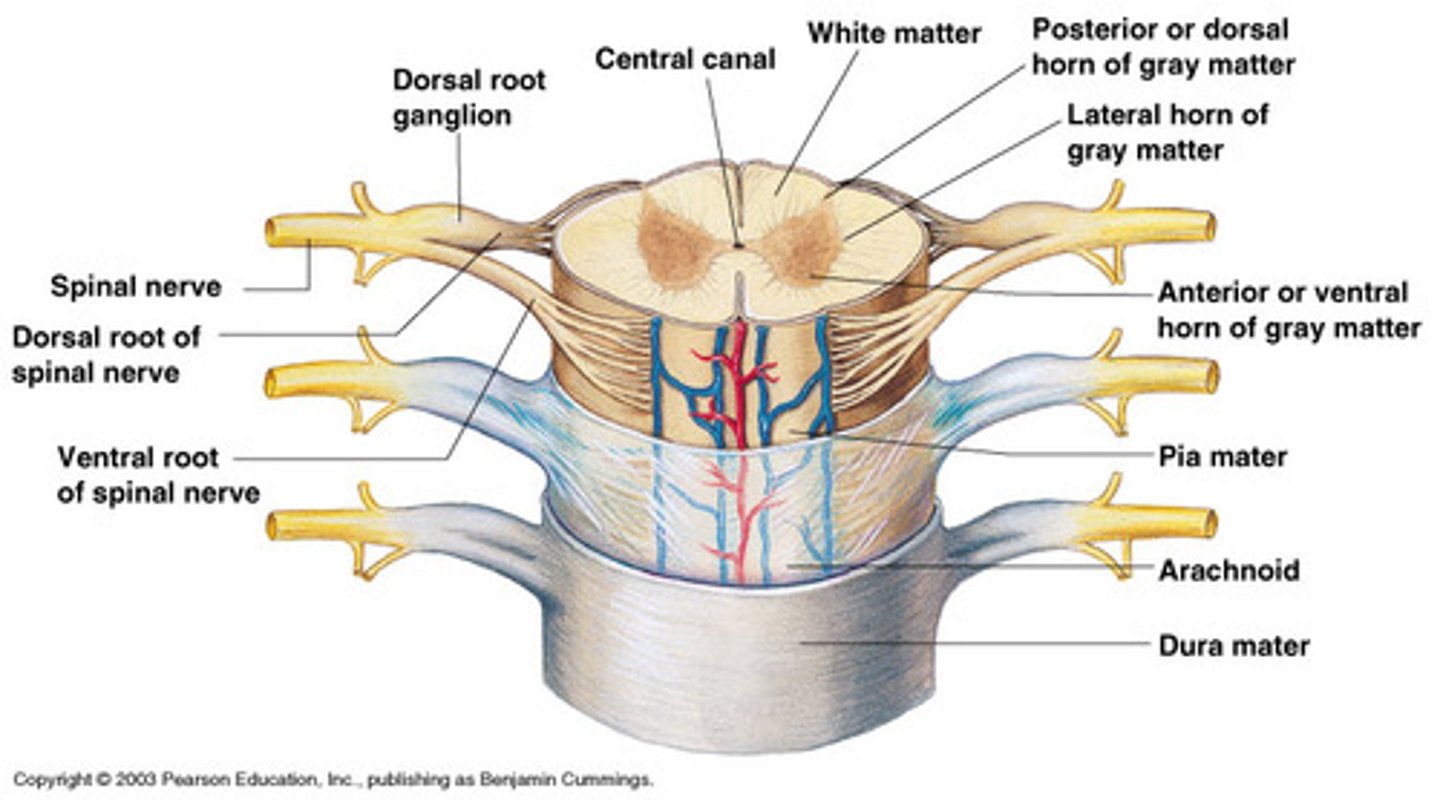
dura mater (spinal cord)
thick, outermost layer of the meninges; 5 on image
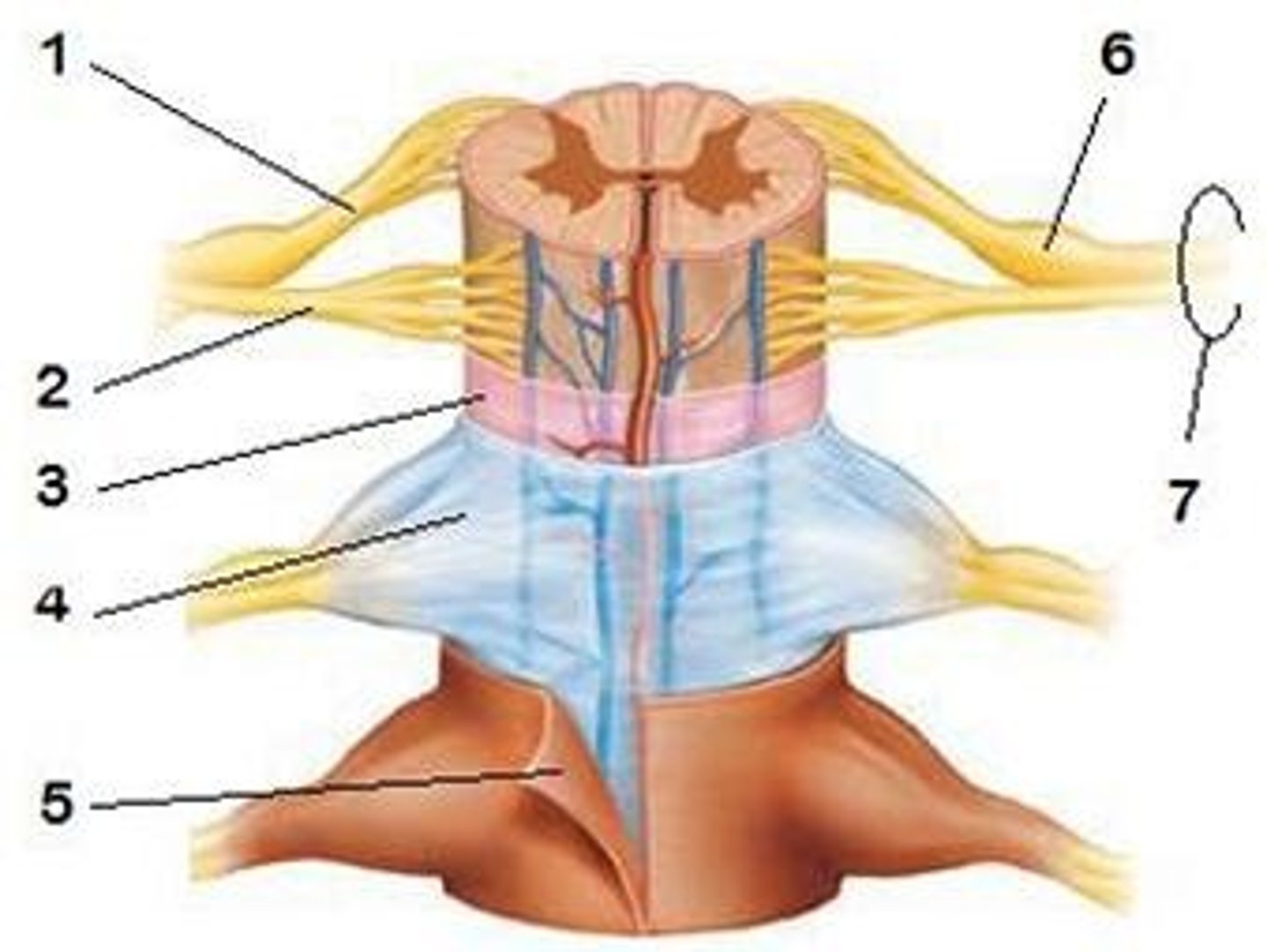
arachnoid mater (spinal cord)
middle weblike layer of the meninges; 4 on image
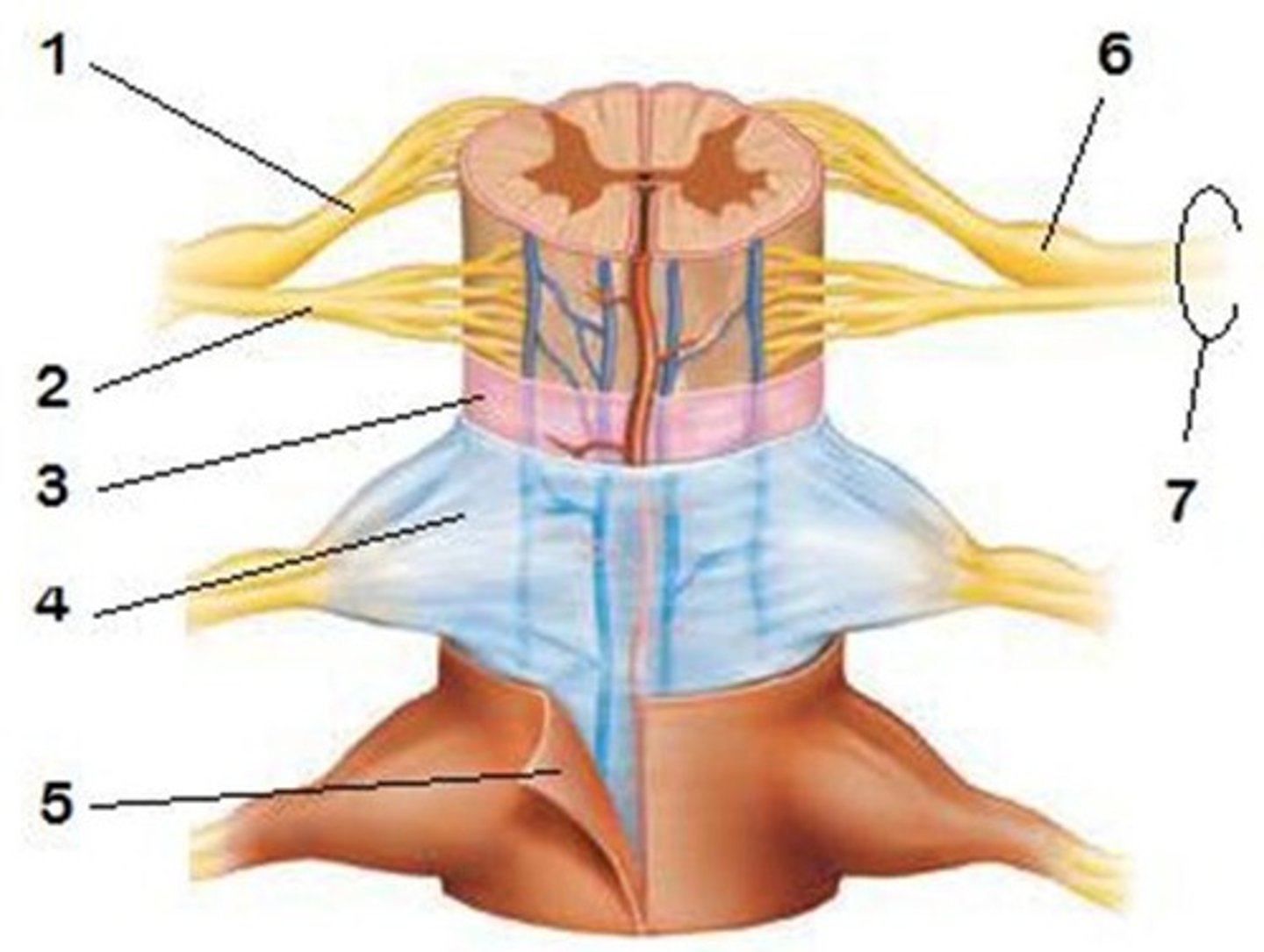
pia mater (spinal cord)
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges; 3 on image
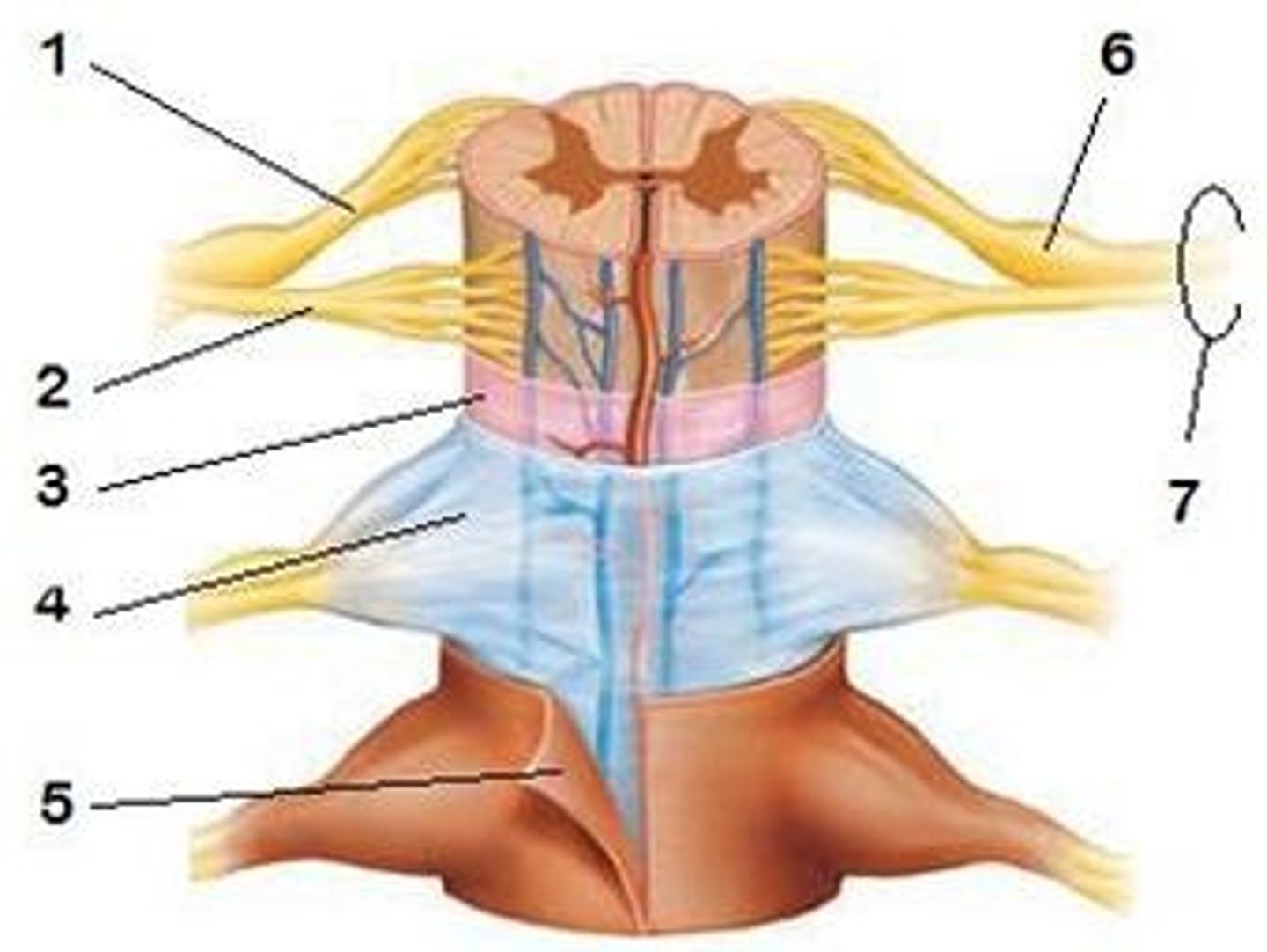
central canal of spinal cord
center of spinal cord which contains cerebrospinal fluid
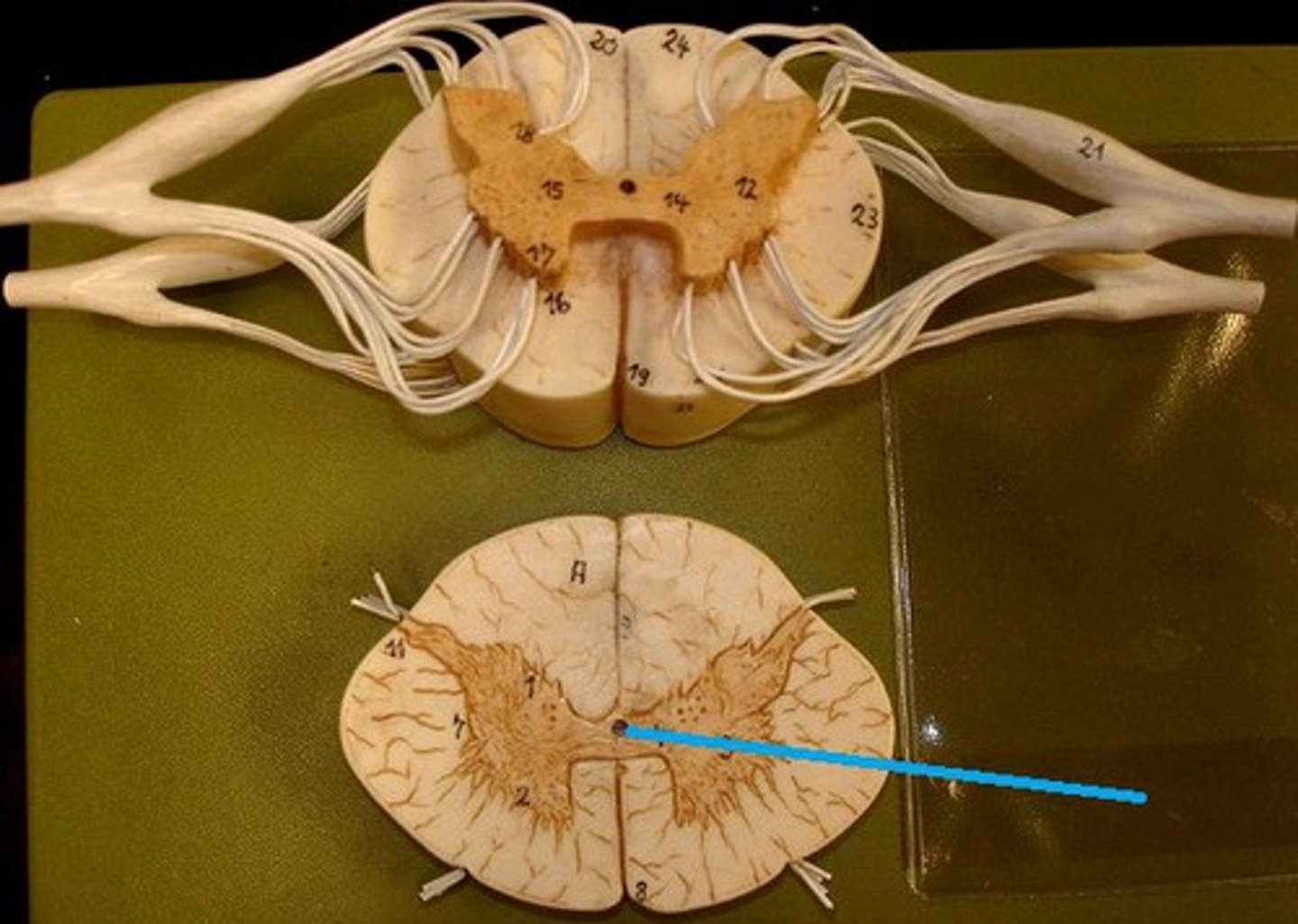
posterior median sulcus
a shallow vertical groove dividing the spinal cord throughout its whole length in the midline posteriorly.
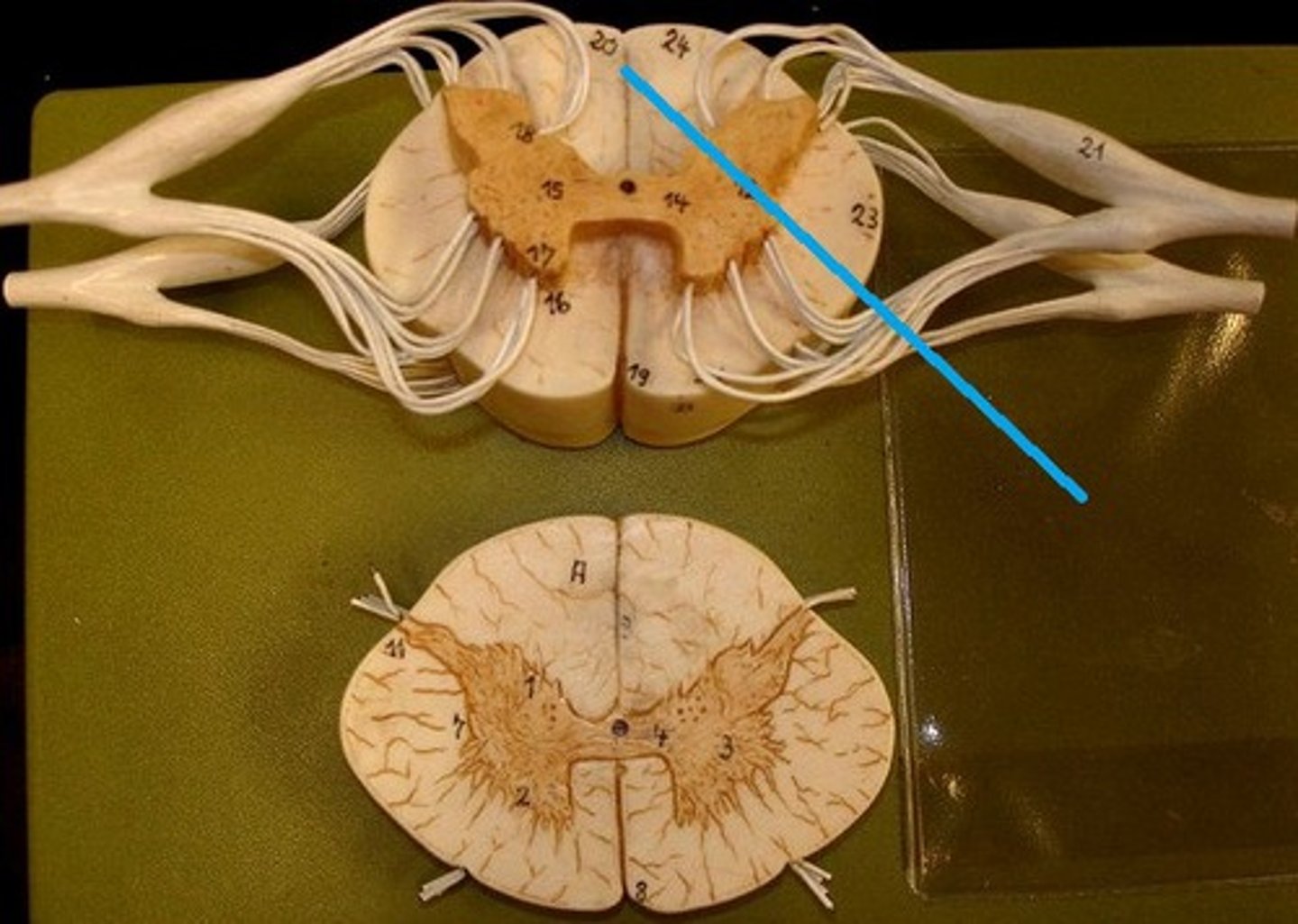
anterior median fissure
a groove along the anterior midline of the spinal cord that incompletely divides it into symmetrical halves
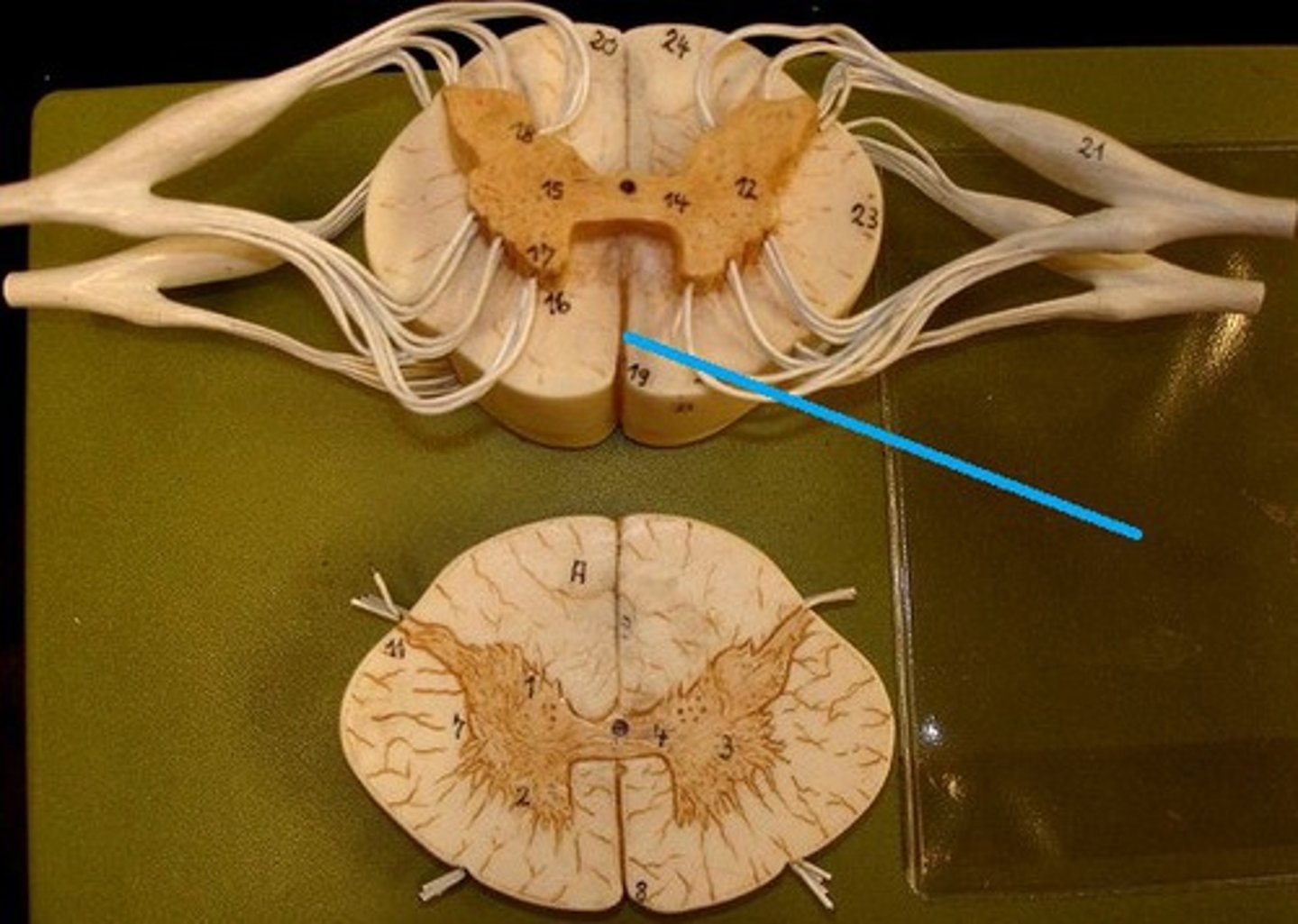
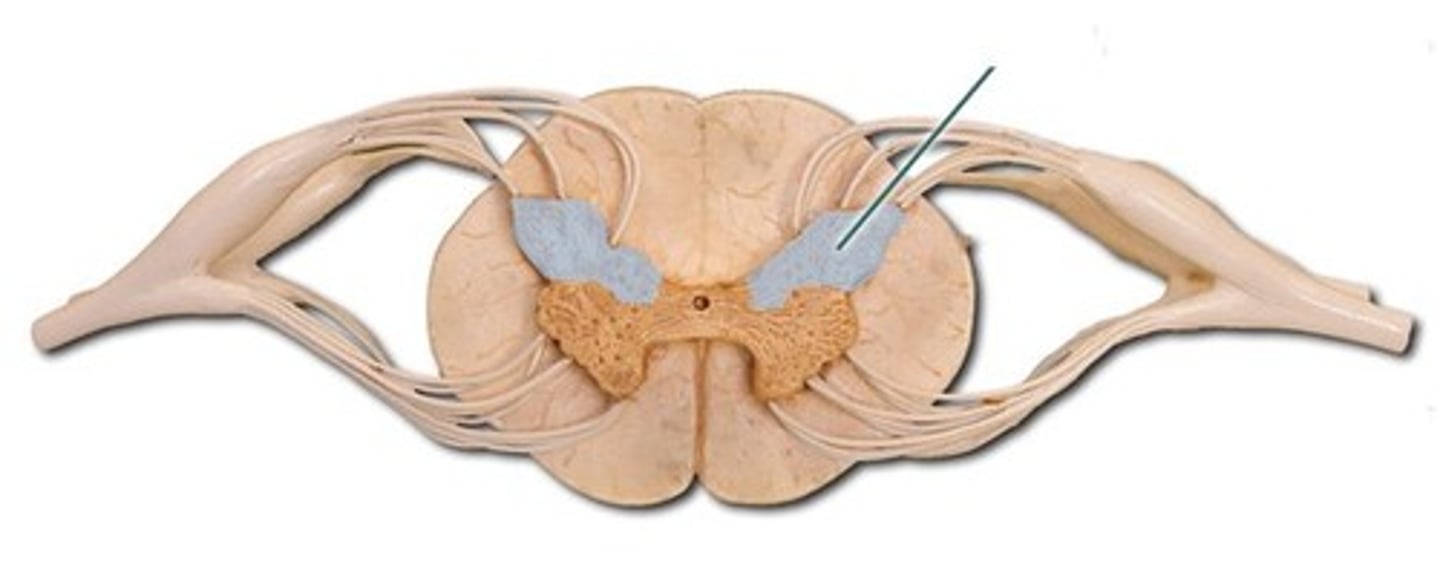
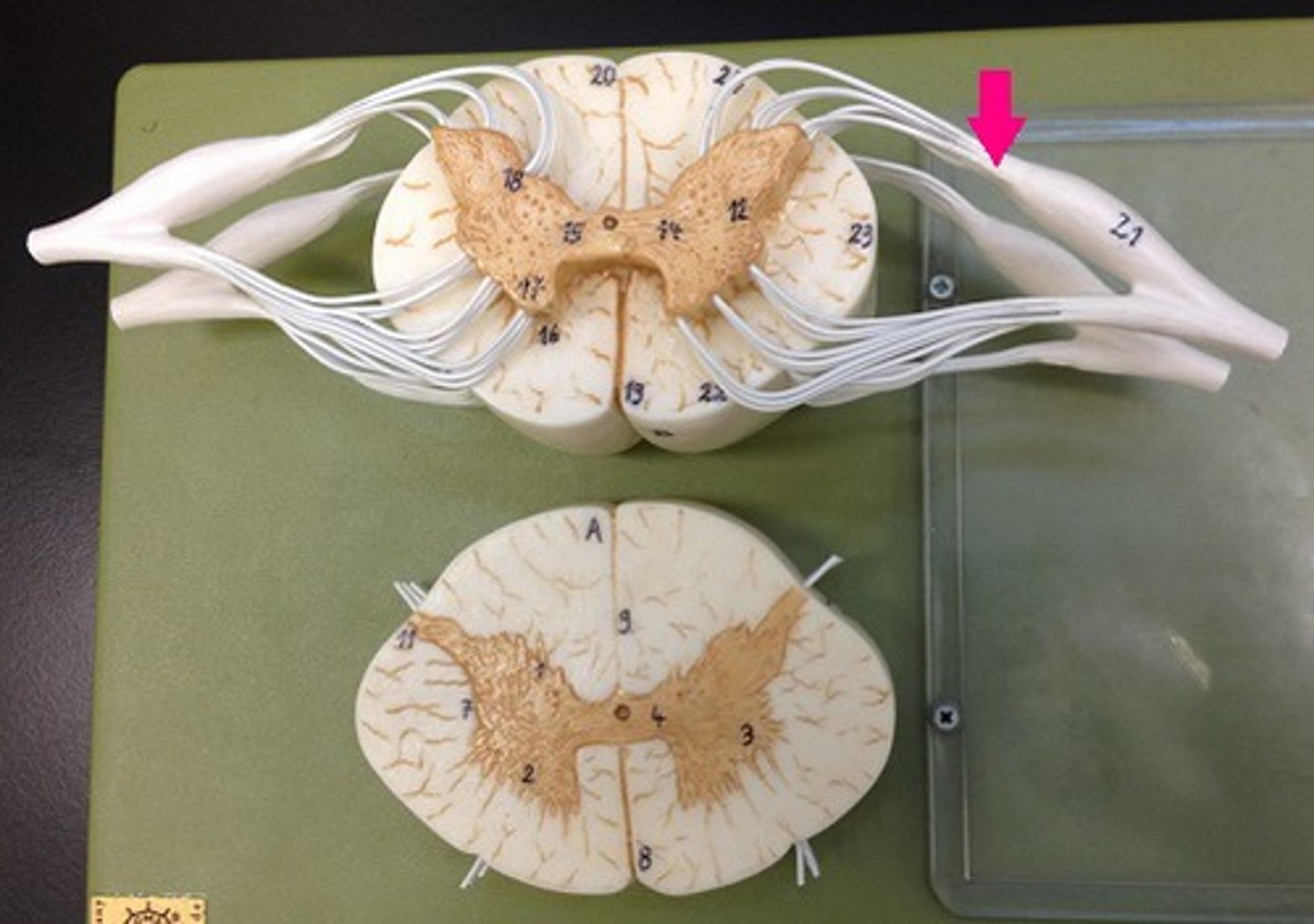
gray matter of the spinal cord
cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons arranges in a butterfly shape with anterior and posterior "horns"
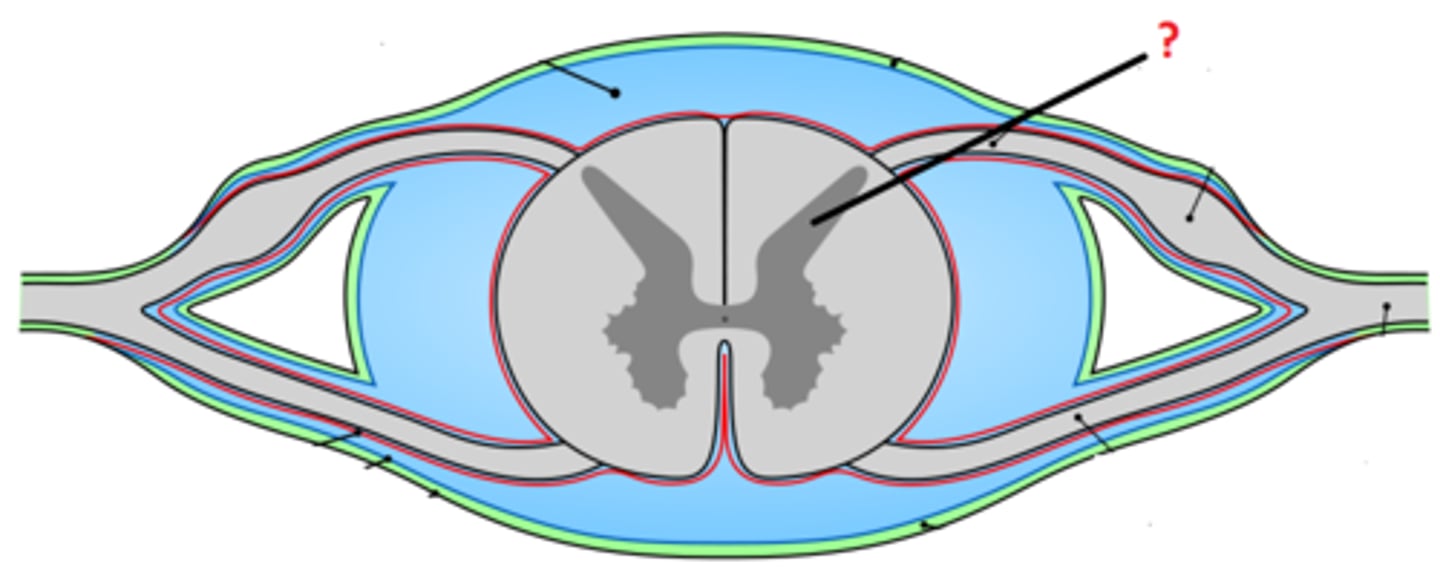
posterior (dorsal) horns
contain axons of sensory neurons and cell bodies (sensory nuclei) of interneurons