PSYC 301 Final - Dysfunction Associated with Psychiatric Disorders 4
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ADHD and Executive Dysfunction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Describe the Tripartite Model of Executive Function
Proposes that executive function is composed of three interconnected + distinct components:
working memory (updating)
cognitive flexibility (shifting)
inhibition control
What are the three core executive functions?
Working Memory
Holding and mental working with information “in mind”
Inhibitory Control
Resting temptations
Not acting impulsively/prematurely
Overriding automatic behaviour
Cognitive Control
Fluidly changing perspectives/approaches to solving a problem
Adjusting to new demands
Switching between priorities or tasks
How can we test inhibitory control?
Stroop Test
incongruent colour/visual info (ex. meaning and colour of text misaligned)
Flanker Task
Correspond to middle stimuli with incongruent distractors surrounding
How can we test cognitive flexibility?
Wisconsin Card Sort
look to see how quickly person can adapt changing rules + suppress old rules
Trail Making w/alteration
switch between 2 different lists
What is involved in higher order executive function?
Planning
Organizing
Multi-tasking
Self-awareness
Regulating emotions
Inhibiting inappropriate behaviour
Motivation
Concentrating
What is the prefrontal cortex?
Non-motor parts of the frontal lobe
What are the symptoms of severe frontal lobe damage?
Abulia: Lack of drive (motivation problem, not motor problem)
Passive state (don’t eat/use bathroom/socialize)
Return of primitive reflexes (“frontal release signs”)
Ex. close palm when something placed on it
Utilization Behaviour
Cant stop themselves from using objects (ex. If presented with a glasses, will wear even if the person has glasses on)
Inability to inhibit behaviours even if they are inappropriate
Severe, impacts life
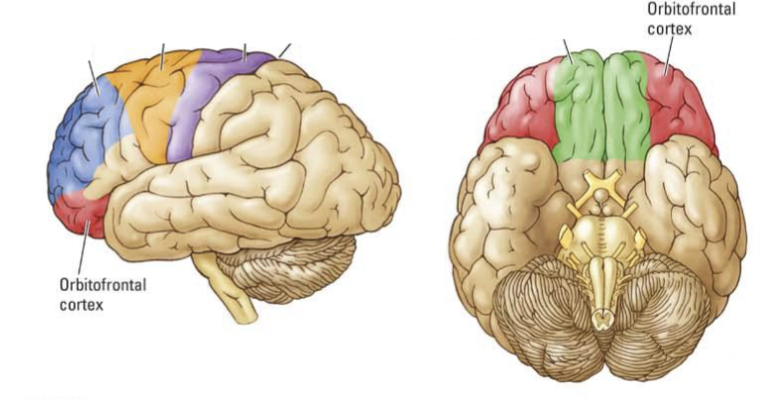
What is orbitofrontal circuit dysfunction + where is it located?
Located at the bottom left + right sides of the prefrontal cortex
Pattern of disinhibition (reduced ability to control impulses + actions)
Socially inappropriate
Poor safety judgement
Difficulty evaluating anticipated rewards + punishments
Don't learn from mistakes due to diminished guilt and regret
What is dorsolateral circuit dysfunction + where is it located?
From a lateral view, front middle of the prefrontal cortex
Distractible
Disorganized
Perseverative (repetitive nature on thoughts, “stuck” on topic. common in those with autism)
Difficulty multitasking
Poor time management + prioritization
What are the major symptoms of ADHD + what are some diagnostic statistics?
Extreme inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity
~5-7% of children, ~2-3% of adults
Younger children within a classroom = more likely to be diagnosed
Rapid rise in adult diagnosis
Underdiagnosis of hyperactivity in girls
What is the neurobiology of ADHD?
Reduced activity + volume of PFC
Slower maturation of PFC
Normal cortical thinning is slower
Correlated with hyperactivity/impulsivity
What is the dual-pathway model of ADHD?
Executive circuit (dysfunction: inattention)
dlPFC
Reward circuit (dysfunction: lack of motivation)
OFC , ACC, nucleus accumbens
Evidence of a hypoactive dopamine system!
What is the major treatment for ADHD?
Medications that act upon dopamine + norepinephrine systems in PFC and subcortical structures