Heme Metabolism
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
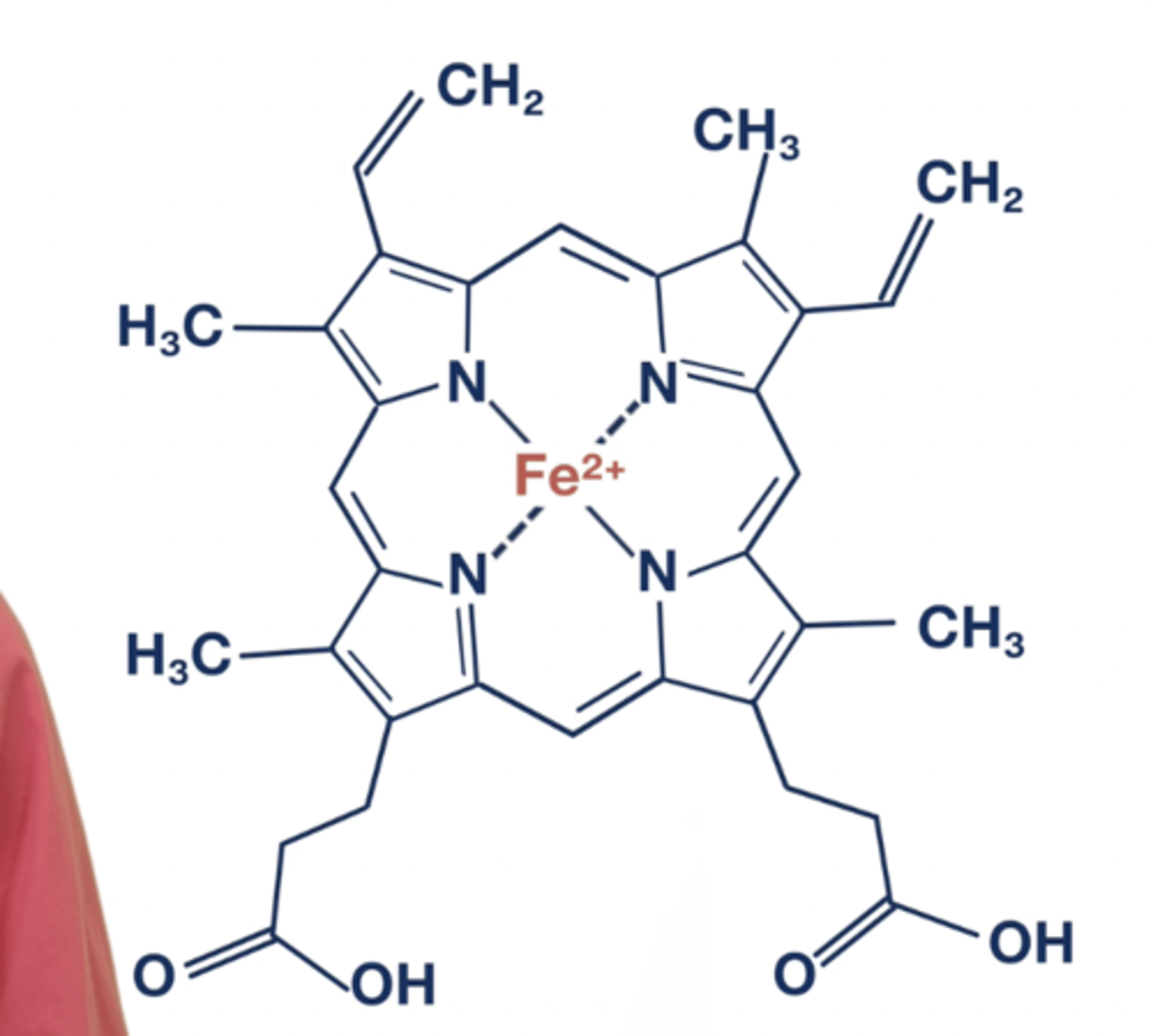
What is heme composed of
Iron (Fe 2+) and protoporphyrin
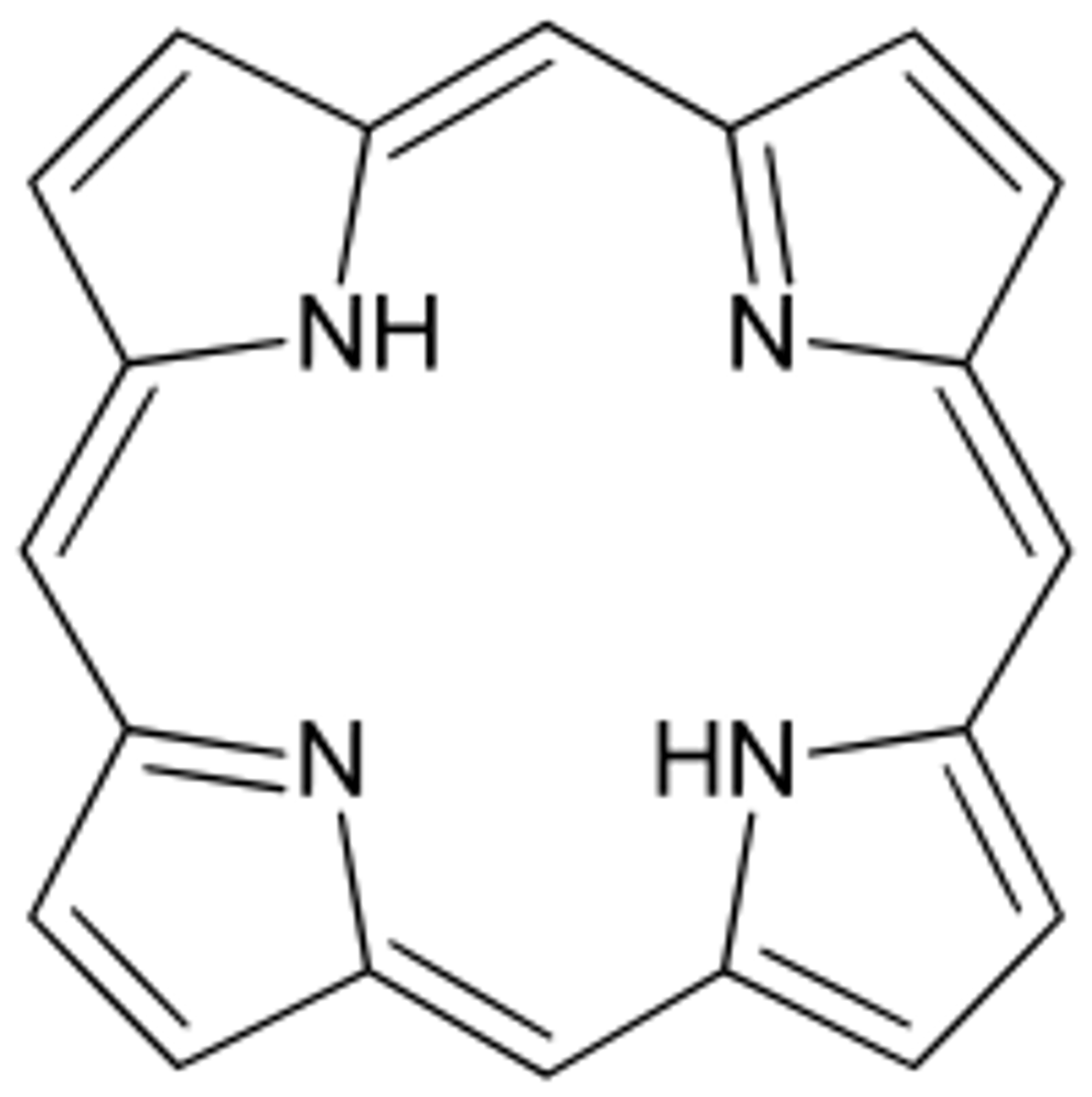
What is a porphyrin
The family of molecules with 4 pyrrole rings that heme is part of. Porphyrins are able to stably complex with metal ions.
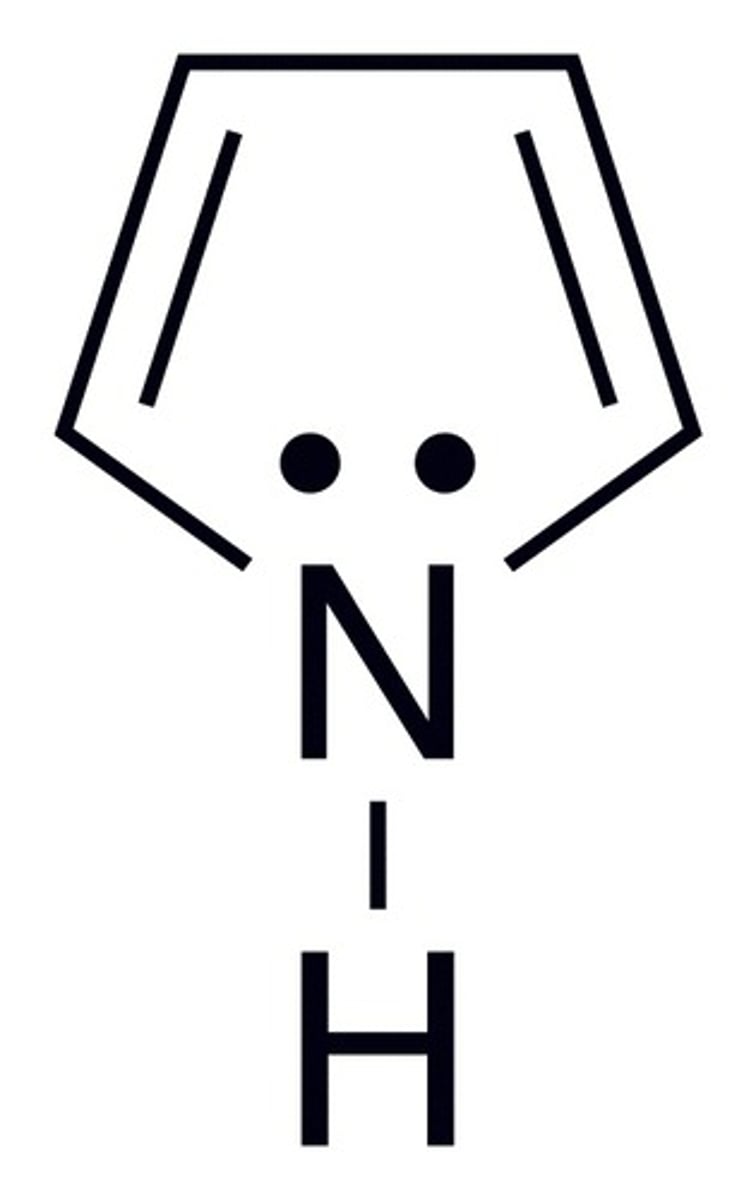
What is a pyrrole
What is hemin?
Fe3+ oxidation product of heme
where is heme found?
Found in hemoglobin and myoglobin
CYP-450
Enzymes (catalase)
What are the heme side chains?
Pyrrole, Methyl, Vinyl, Propionate
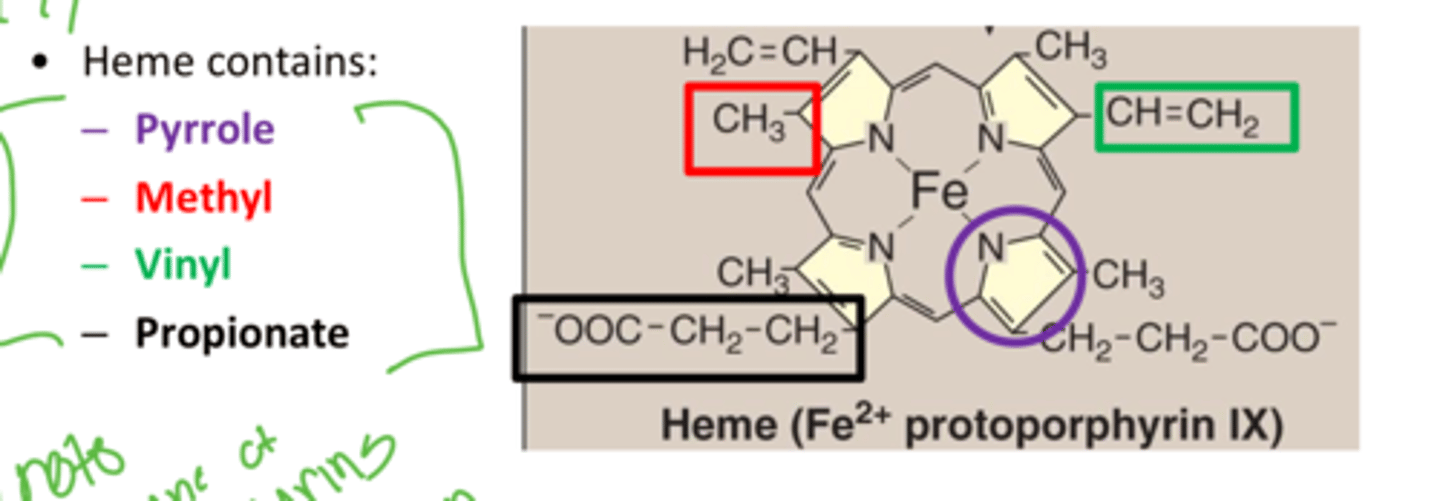
What connects the pyrroles?
Methine bridges
Where is heme synthesized from for erythrocytes
Bone marrow acid pool
Where is heme synthesized from for Cytochromes
Liver amino acid pool
Where is heme synthesized the most
Heme is synthesized the most in hemoglobin at 70% and in the cytochroms for 15%
What stimulates heme synthesis in bone marrow
EPO in the kidney cause RBC production to increase when the O2 concentration in the body is low
Cytochrome P450 heme characteristics
Built in the liver, also has a higher turn over rate
What type of Uroporphyrin does Heme use?
Urporphyrin uses Type 3
What are the main uses for porphyrin
chelate and hold the Ferrous iron in the middle. It is made from porphrinogens
ALAS 1 function
used in delta aminolevulinate synthase in the porphyrin synthesis in the Liver mitochondria
ALAS 2 function
used in d-aminolevulinate synthase in poryphrin synthesis in the bone marrow mitochondria
Hemin inhibition of Cyt P450
decreases the expression of ASLAS1 in the liver via feedback inhibition
What inhibits ALAS 2
Low iron will inhbit ALAS 2 in the bone marrow/ erythroid cells
What does Phenobarbital, griseofulvin, or hydantoins do to cyt P 450
It increases it the Cyt P450 which will increase ALAS1 production due to increased cunsumption of heme in the liver which will cause a bild up of protophoryin in the liver and cause Cirrhosis
What regulates ALAS 2
Availability of iron regulates ALAS2. if there isnt enough Ferrous iron in the bone marrow the body wills top producing ALAS2 so that there isnt just extra iron free prophyrins laying around.
Also EPO regulates it as well
X linked sideroblastic anemia
Deficiency in ALAS2 enzyme which makes abailable iron unusable to create heme
Porphyrin synthesis steps
1. 2 ALA condensed to porphobilinogen via ALA dehydratase
- Create the side chains!!!!
2. add 4 NH3 to make Hydroxymethylbilane
3. Close the ring to make uroporphyrinogen 3
4. Decarboxy it and make Coproporphyrinogen 3
5. Push it to mtochondria
6. Oxidate it to Protoporphyrin
7. use Ferrochelatase to ass FE2+ making it Heme Protoporphyrin (ie Heme)
What is ferrochelatase
Ferrochelatase is a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the last step of heme synthesis wherein iron is incorporated into the protoporphyrin ring.
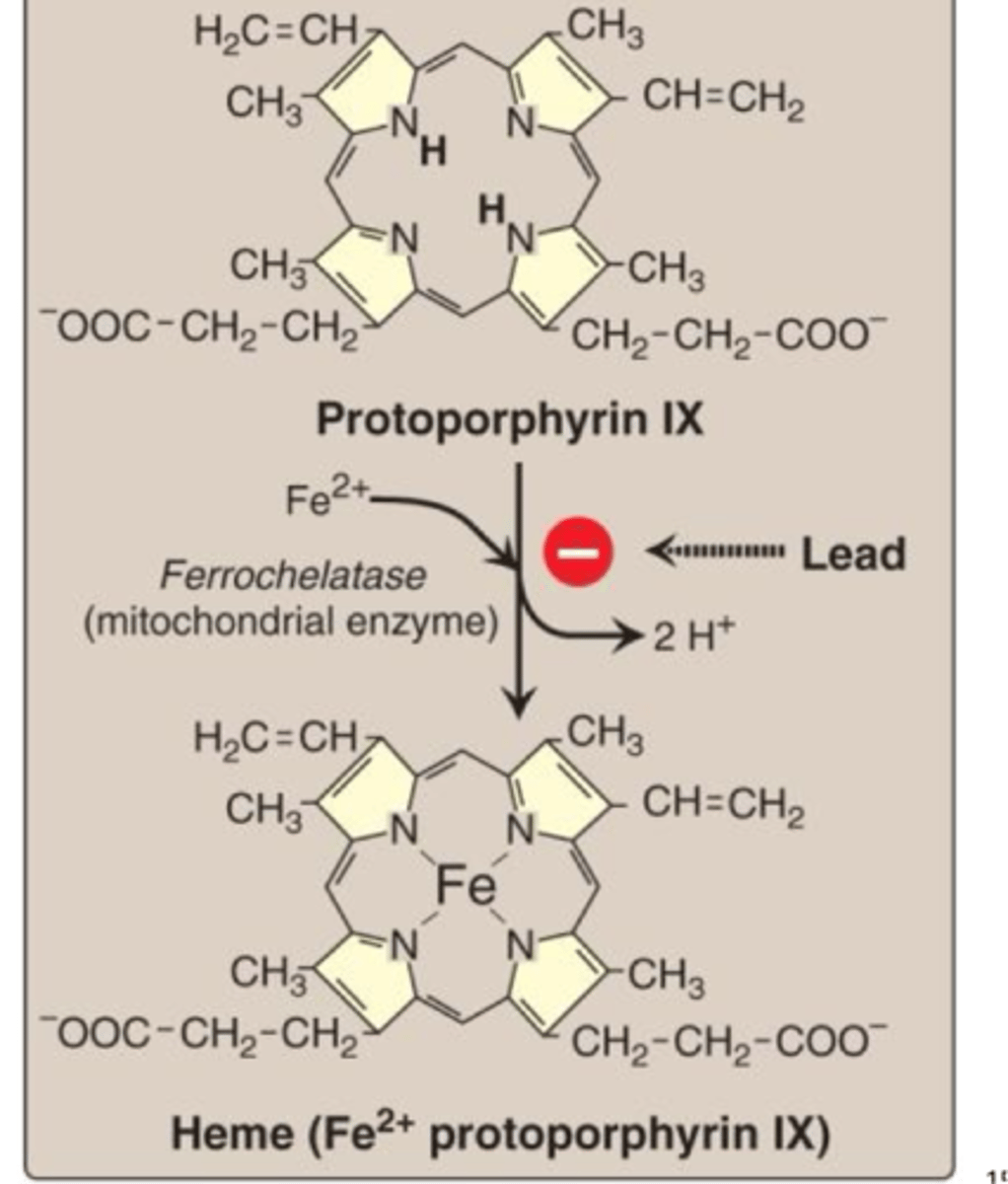
Which phases of porphyrin synthesis occour in the mitochondria?
Step 1: Making Delta Aminlevulinic acid first occours in the mitochondria but then is pushed to the cytosol
Step 5: Pushing the coprophyrinogen into the mitochondria
Step 6: oxidation to Protoporphyrin
and adding the derrochelatase Ferrous iron
What are porphyrias
rare disorders associated with heme synthesis which result in an inability to form heme and a build up of precursor molecules
occour w/ lead poisioning
primarily autosomal dominant or acquired enzyme deficiencies
Symptoms of porphyrias
Erythropoietic - photosensitivity (Tetrapyrroles) and dermatitis
Hepatic- Neurological (Neurotoxity)
Abdominal - Accumulating metabolic intermediates
Mixed - photosensitivity, dermatitis, and neurological
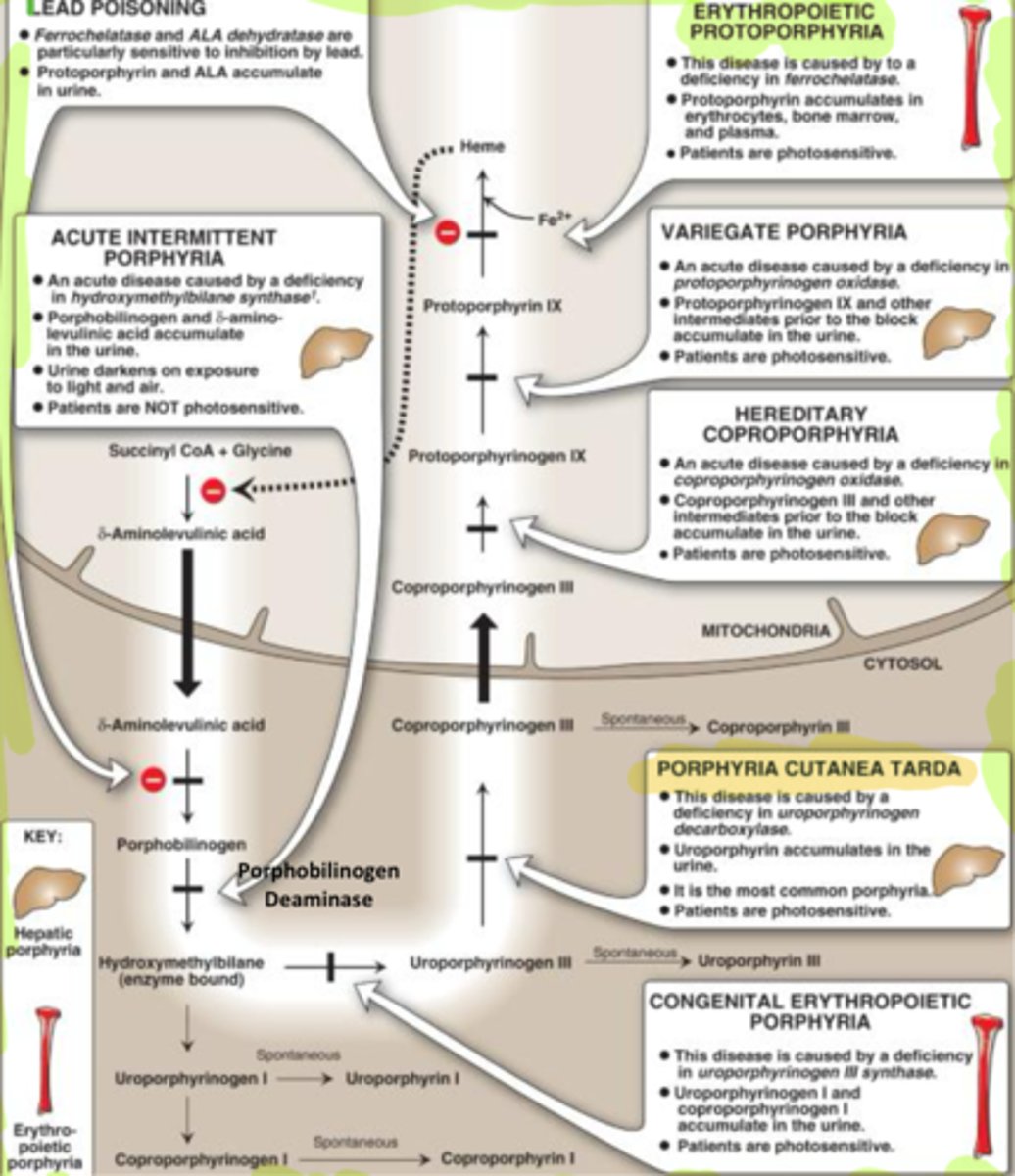
porphyria Cutanea Tarda
photosensitive bullous disease; deficiency uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
-Hepatic chronic
ALA dehydratase deficiency
Lead poisoning
- Block Protoporphyrin from turning to heme
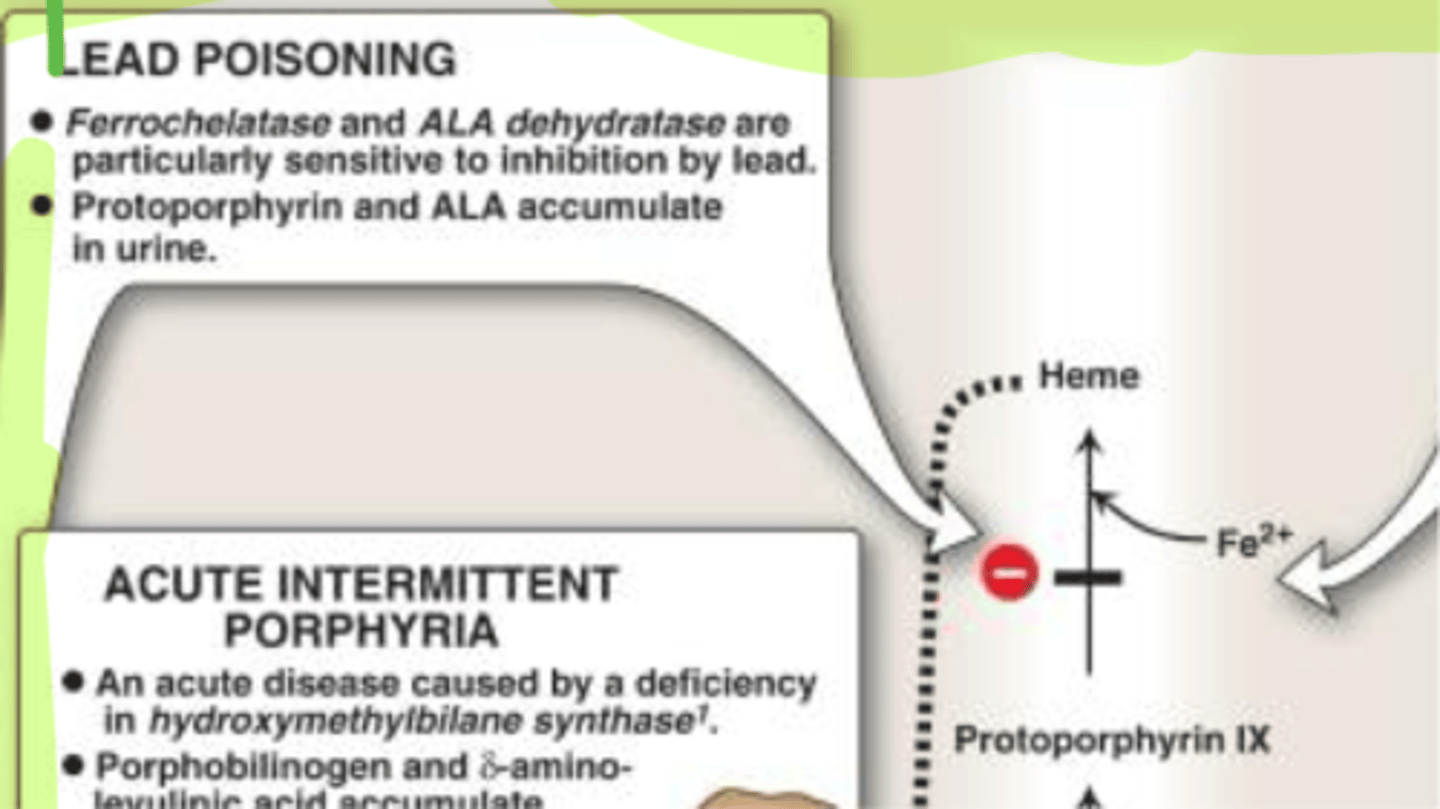
Acute intermittent porphyria
Cause Delta ALA to get backed up and no photosensitivity
- Liver

Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
Stops Hydroxy from going to Uroporphy 3
- Erythro Bone
- Cause uro 1 and coporo 1 to build up in urine
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
Stops Uroporphy 3 from going to coporo 3 in cytosol
- most common
- uroporo 3 in urine
- Deficiency in Uropropo decarby
-shows skin eruptions and pink urine
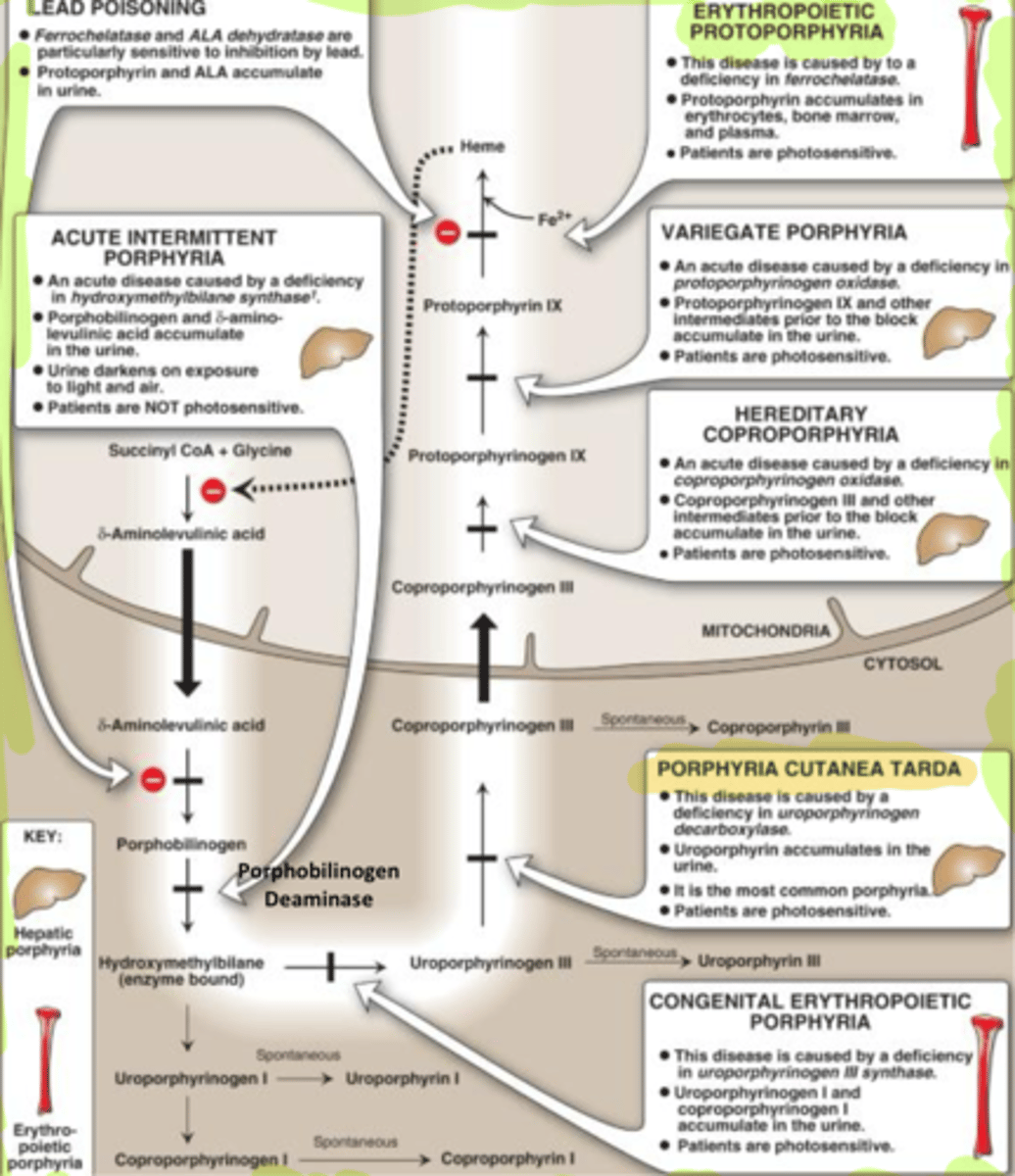
What influences PCT
iron, sunlight, alcohol, hepatitis, HIV and estrgen
What is the ultimate result of porphyrias
decrease in heme synthesis since ALAS can finish its process to create heme
Acute hepatic porphyrias
Common characteristics:
Acute attacks of vomiting & pain
Neurological/psychiatric problems
- Build up of ALA, this can also be due to drug intake causing Cyt P 450 demand to increase making overproduction
How does Acute hepatic porphyrias increase w drug metabolism
Intake of drugs increae Cyt P 450 demand for heme due to drug metabolism. this increases ALA and then can cause an accumulation in the urine of metabolites of ALA
Erythropoietic porphyrias
accumulation of porphyrin in BM associated with increased blister and rashes in early child hood possibilioty for cirrhosis
Heme degredation process
Old RBCs eatent by macrophages
Heme -> bilirubin
Bilirubin jumps onto albumin goes to liver
Liver conjucgates bili send to bile then intestine
Intestine deconjugates bili -> Urobilinogen
- Some goes to feces brown some goes to kidney
Urobolinogen goes to kidney -> urobilin (yellow)
What does heme oxygenase do?
converts heme to biliverdin, by releasing Fe 3+ and preaks the Protoporphyrin ring
What does Biliverdin reductase do?
converts biliverdin to bilirubin to be carried on albumin to the liver to become conjugated
What does it mean to conjugate bilirubin?
add UDP glucuronide making it bilirubin diglucuronide so it can go to the bile
What are normal serum bilirubin levels and when does jaundice occour
2-17mM
Jaundice occours at 40 mM
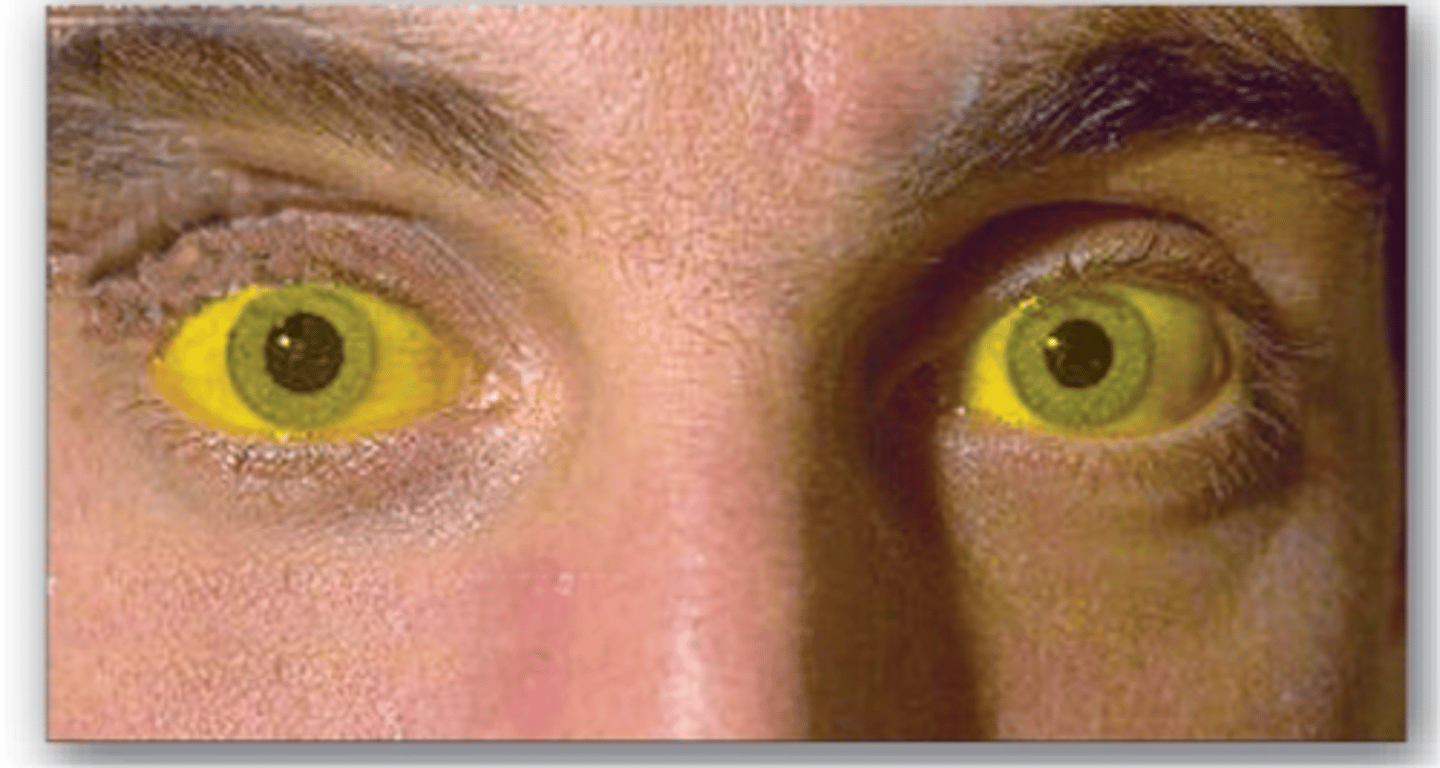
What is Prehepatic Jaundice and what is it a symptom of?
Result of excessive destruction of red blood cells
-Impaired liver uptake
Characteristic of hemolytic anemias/Thalassemia/transfusion reactions
What is hepatic jaundice and what does it come from
decrease in conjugation so it just stays a bilirubin in the system
Jaundice resulting from Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, Cancer, drugs
what causes Post hepatic jaundice
Blocked bile duct
-Issues w excretion
-galls tones
What is neonatal jaundice
-messed up bilirubin UDP glucuronyl transferase
- Treat w phototherapy
What is unconjugated hyperbilirubinemias
Caused by hemolysis, UDP glucoronidate issues which happens before entering the liver.
What is Gilbert syndrome
Liver struggles process billirubin so slight increase in unconjugated bili
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Absolutely no conjugated bili, UDP Gluco transferase is broken
What is kernicterus?
brain dysfunction in babies due to bili conjugation issues
What enzyme conjugates bilirubin
Uridine Glucuronyl Transferase(UGT) in hepatocytes.
What is Dubin-Johnson syndrome (Conjugated)?
Inability to secrete conjugated bili to the bile
What is rotor syndrome
Conjugated bili secretes/ leaks into the blood stream causing hyperbilirubinemia due to messed up hepatocellular storage