Chapter 2 Bio-Rad Biotechnology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Danger to the eyes exist. Safety goggles should be worn
Eye Safety

Misuse of chemicals could cause explosion
Explosion Safety

Poisonous substances are present
Poison Safety

Using live animals. Safety of animals should be ensured
Animal Safety

Danger of cuts or punctures caused by use of sharp objects
Sharp Object Safety

Radioactive materials are used
Radioactive Safety

Chemicals used can cause burns or are poisonous if absorbed through skin
Chemical Safety

Care should be taken around open flames
Fire Safety

Substances used could stain or burn clothing
Clothing Protection Safety

Chemicals or chemical reactions could cause dangerous fumes
Fume Safety

Use caution when handling hot or extremely cold objects
Thermal Safety

Care should be taken when using electrical equipment
Electrical Safety

Poisonous plants or plants with thorns are to be handled
Plant Safety

Danger involving Bacteria, Fungi, or Protists
Biological Hazzard

Use of open flame could cause fire or explosion
Open Flame Alert

Care must be taken to dispose of materials properly
Disposal Alert

National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
establishes codes, standards, guidelines, and recommended practices for the prevention and control of fire

Health (NFPA)
blue
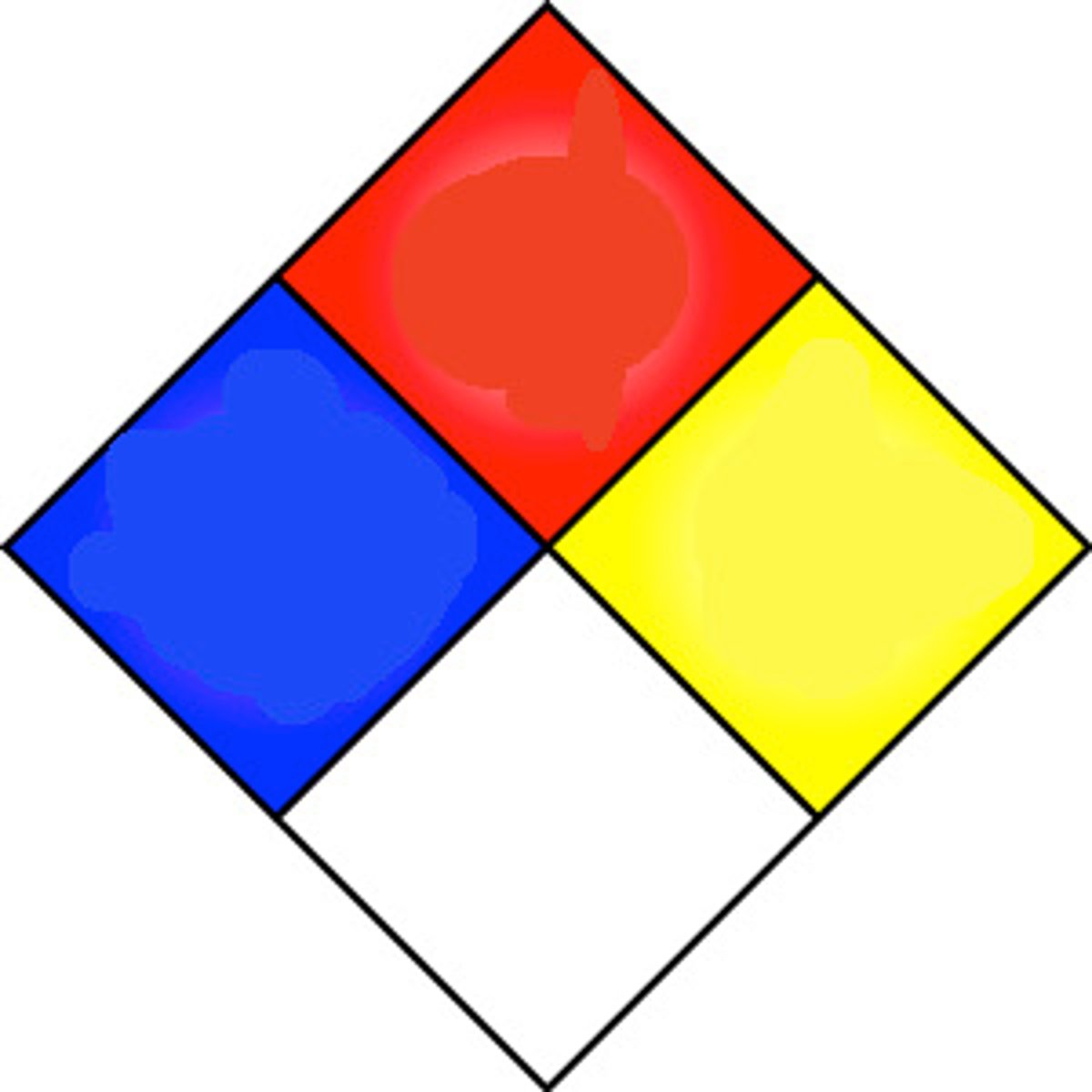
Fire Hazard (NFPA Label)
red

Flammibility (NFPA)
yellow
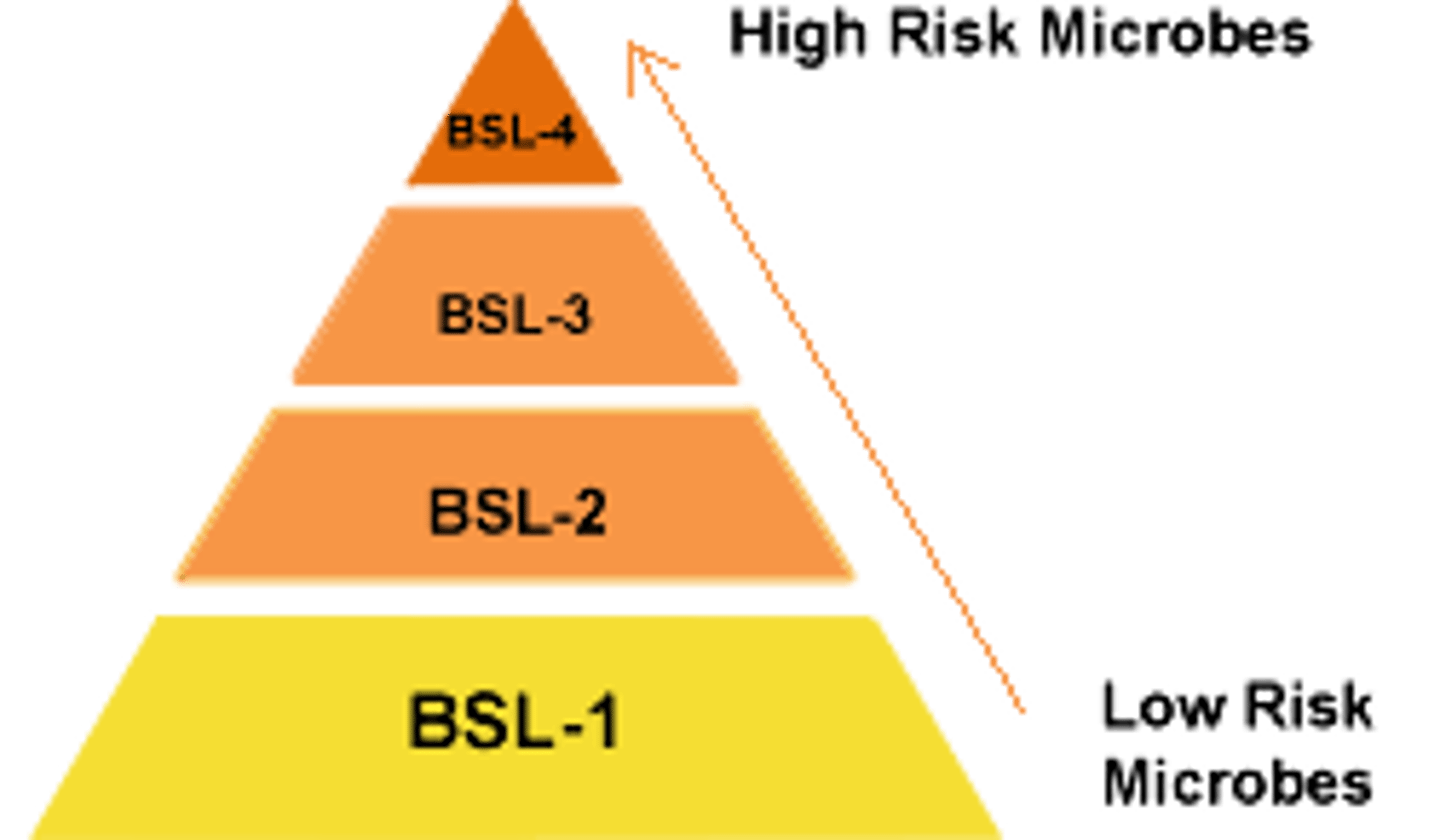
BSL-1
no special precautions; basic teaching labs (E. coli)

BSL-2
Indigenous microorganisms that can lead to diseases of varying severity in healthy adults.
Dillution formula
C1V1=C2V2
Molarity formula
moles of solute/liters of solution
minuscus
is the curve that you see at the liquids surface

Micropipette
A laboratory instrument used to measure, dispense, and transfer very small amounts of liquid.
serological pipette
Used to measure and deliver large volumes of liquids.
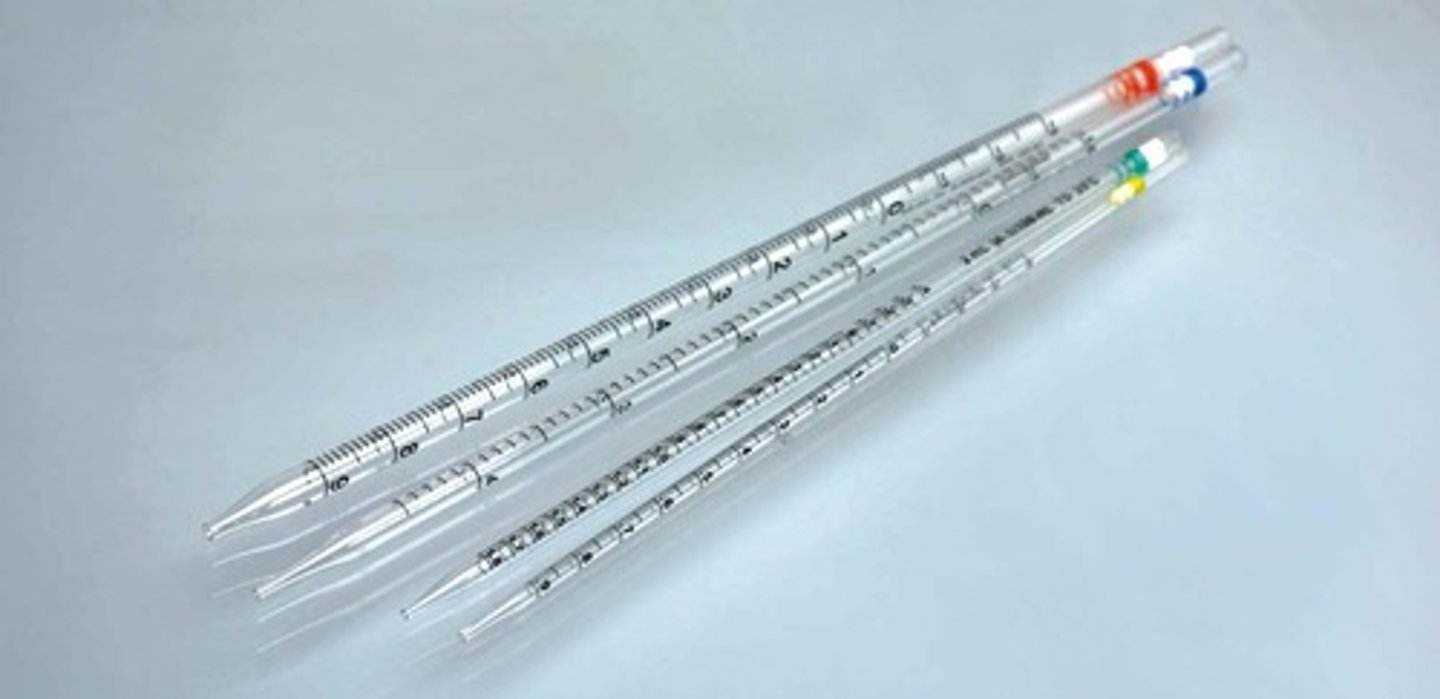

disposable pipet
disposable object used to transfer small volumes of liquid
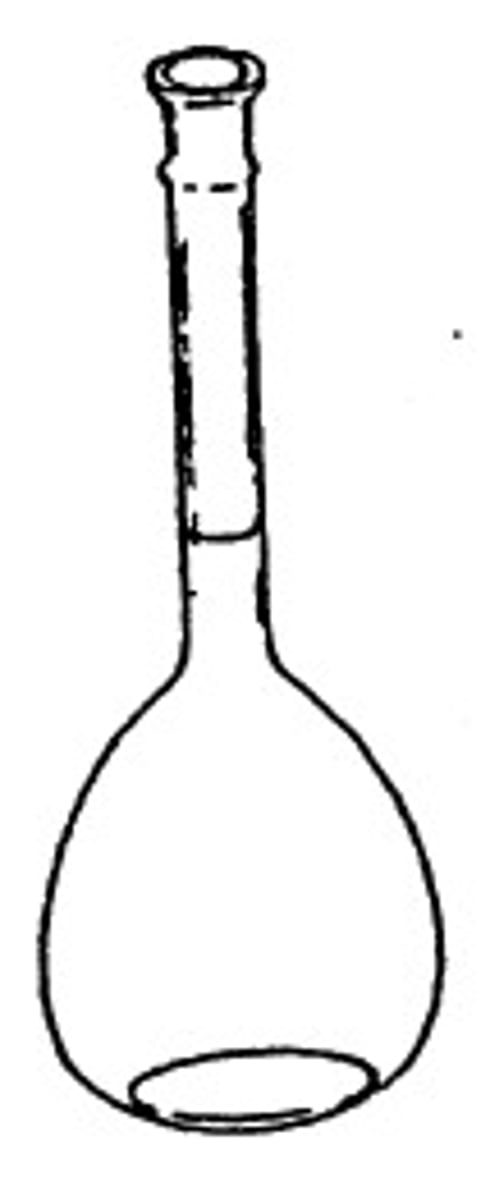
volumetric flask
for making up solutions to a known volume
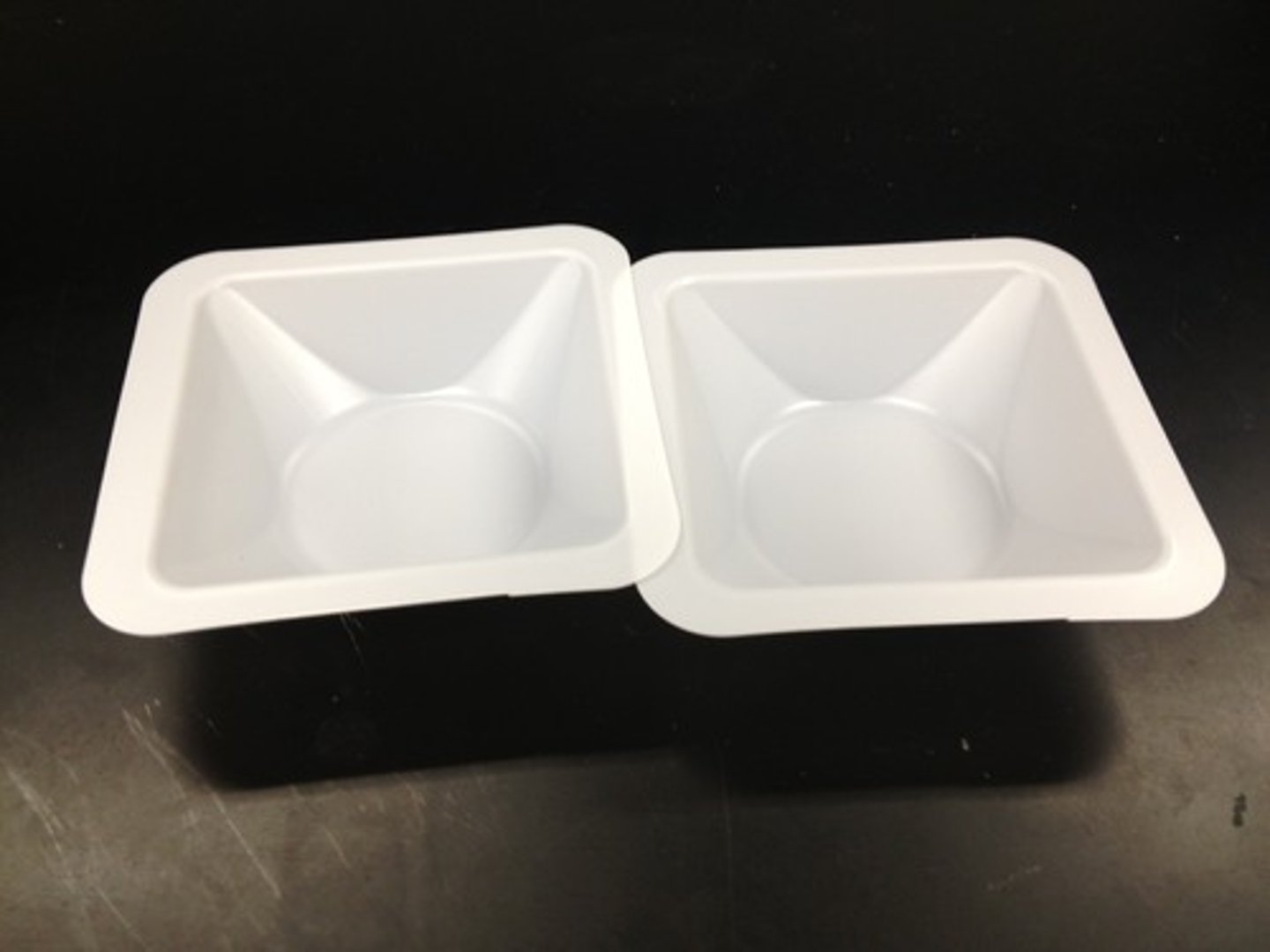
weight boat
Used to weigh or transfer chemicals (usually dry)

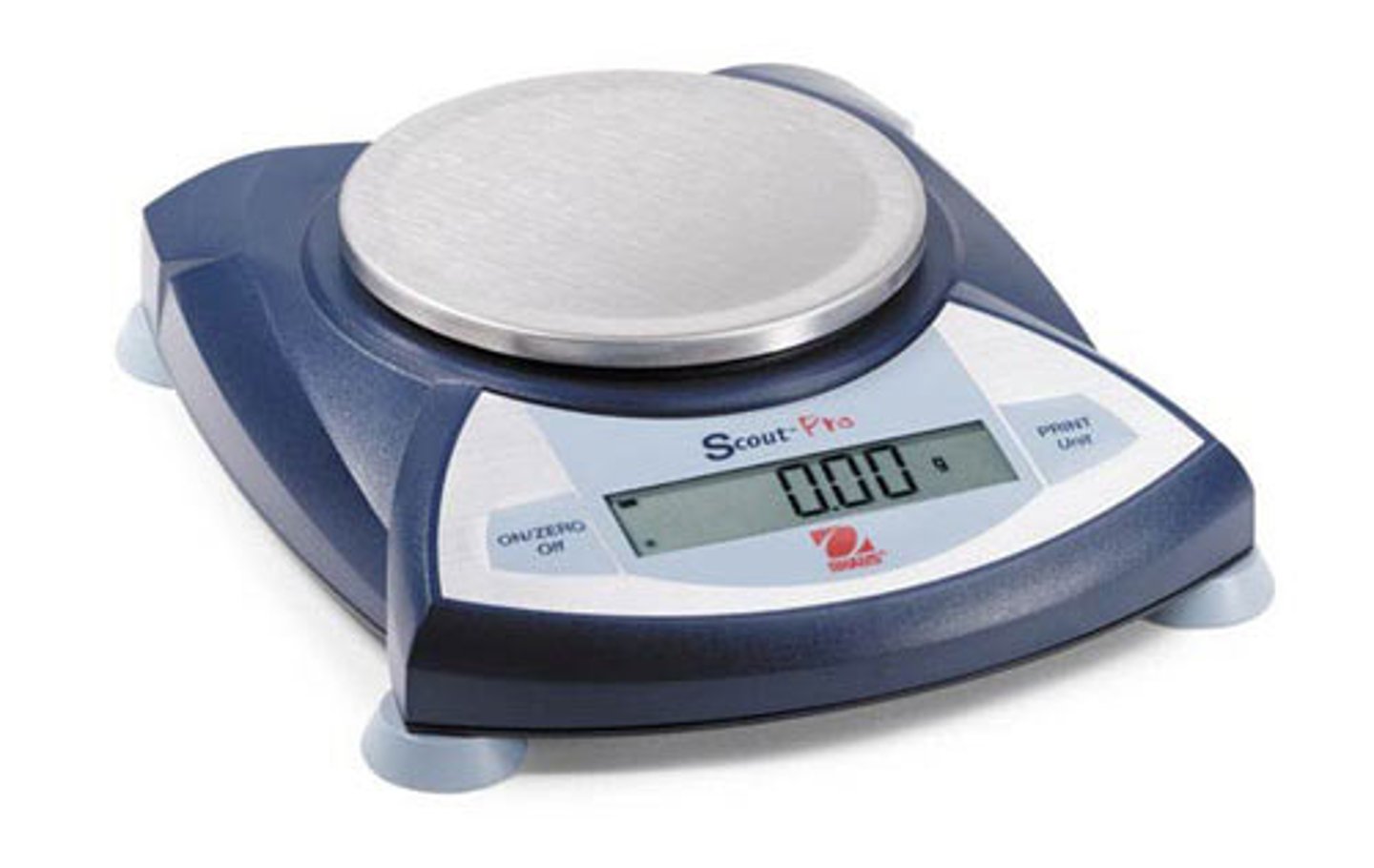
on a mass scale
scale used to measure mass

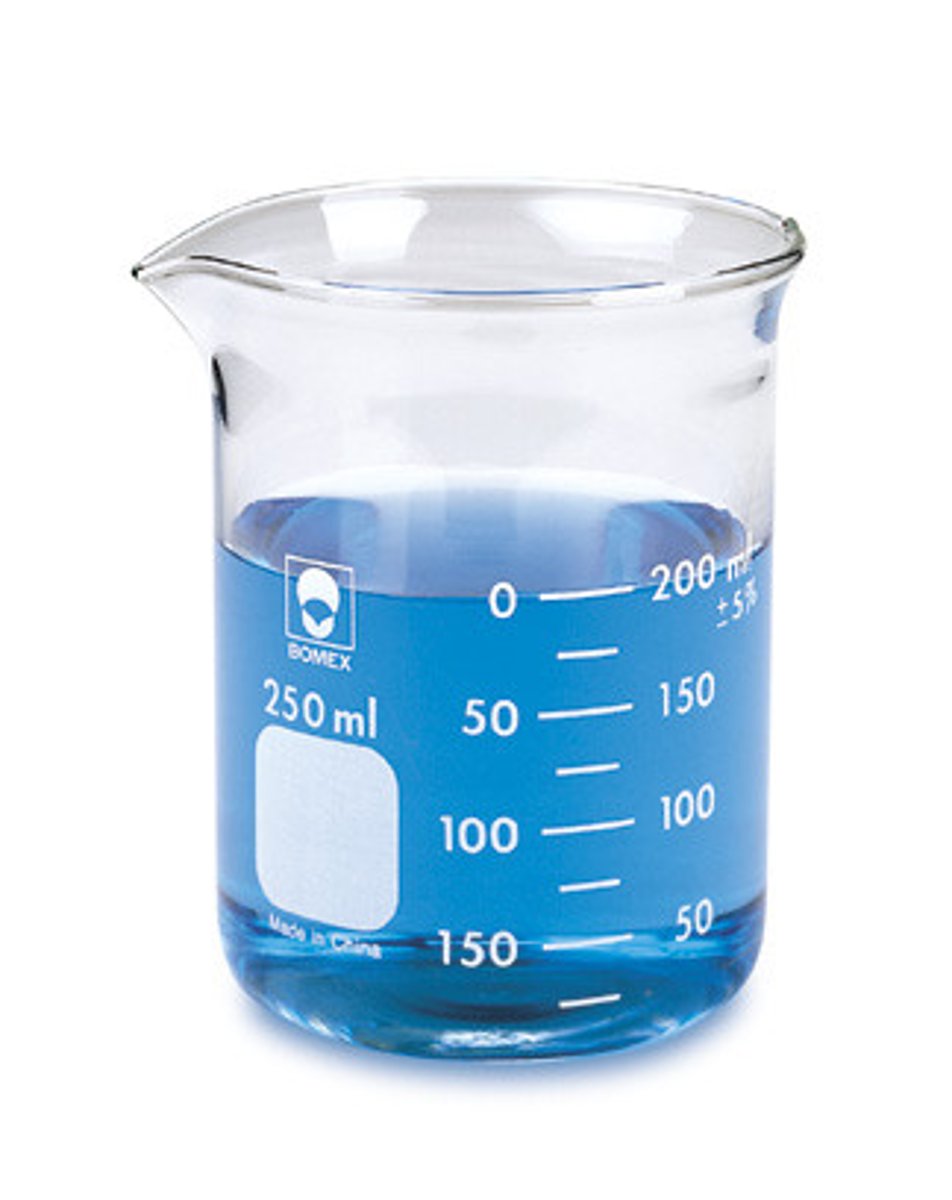
Beaker
used to hold liquids

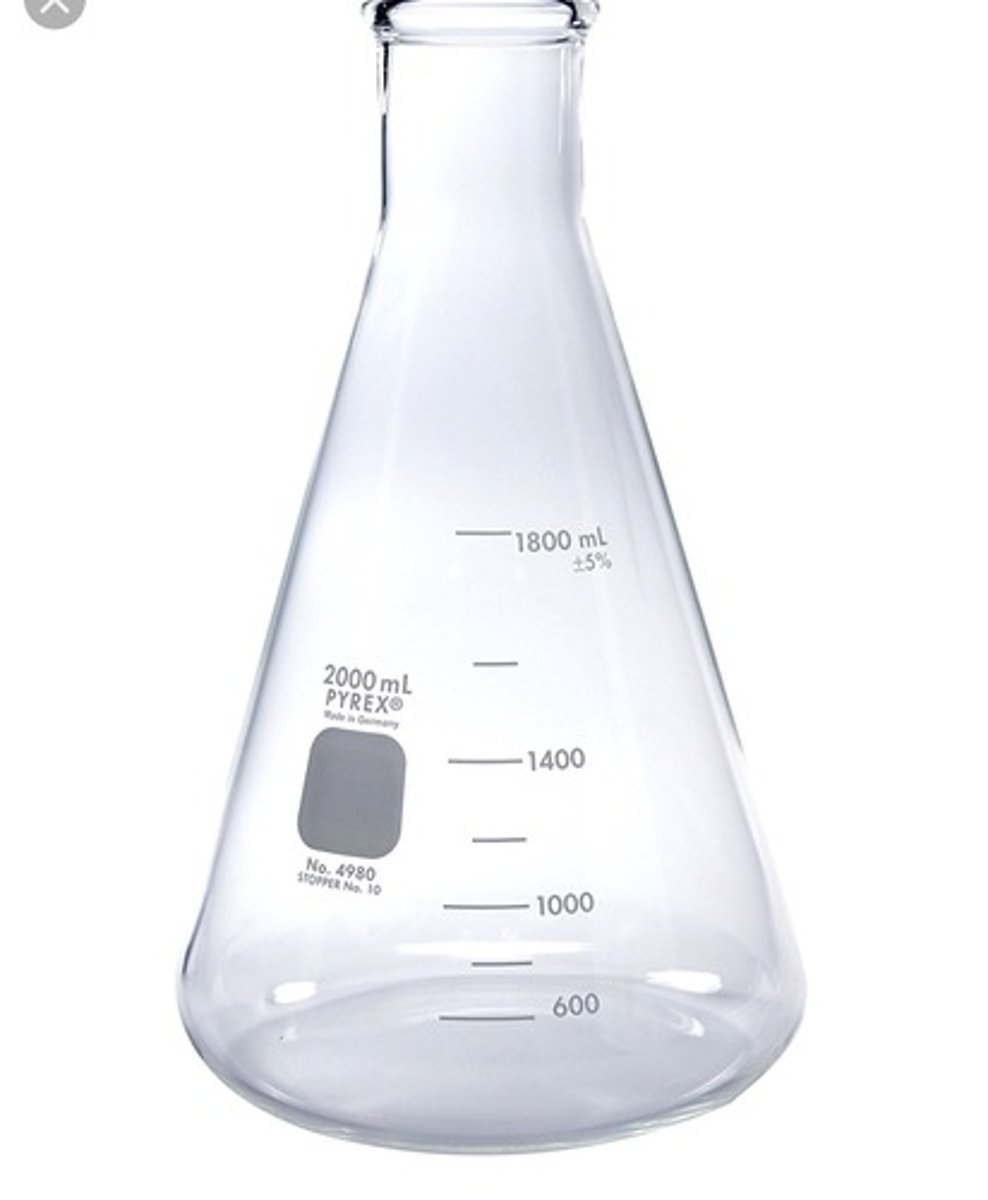
Erylenmeyer Flask
better than beaker for mixing, so substance doesn't splash

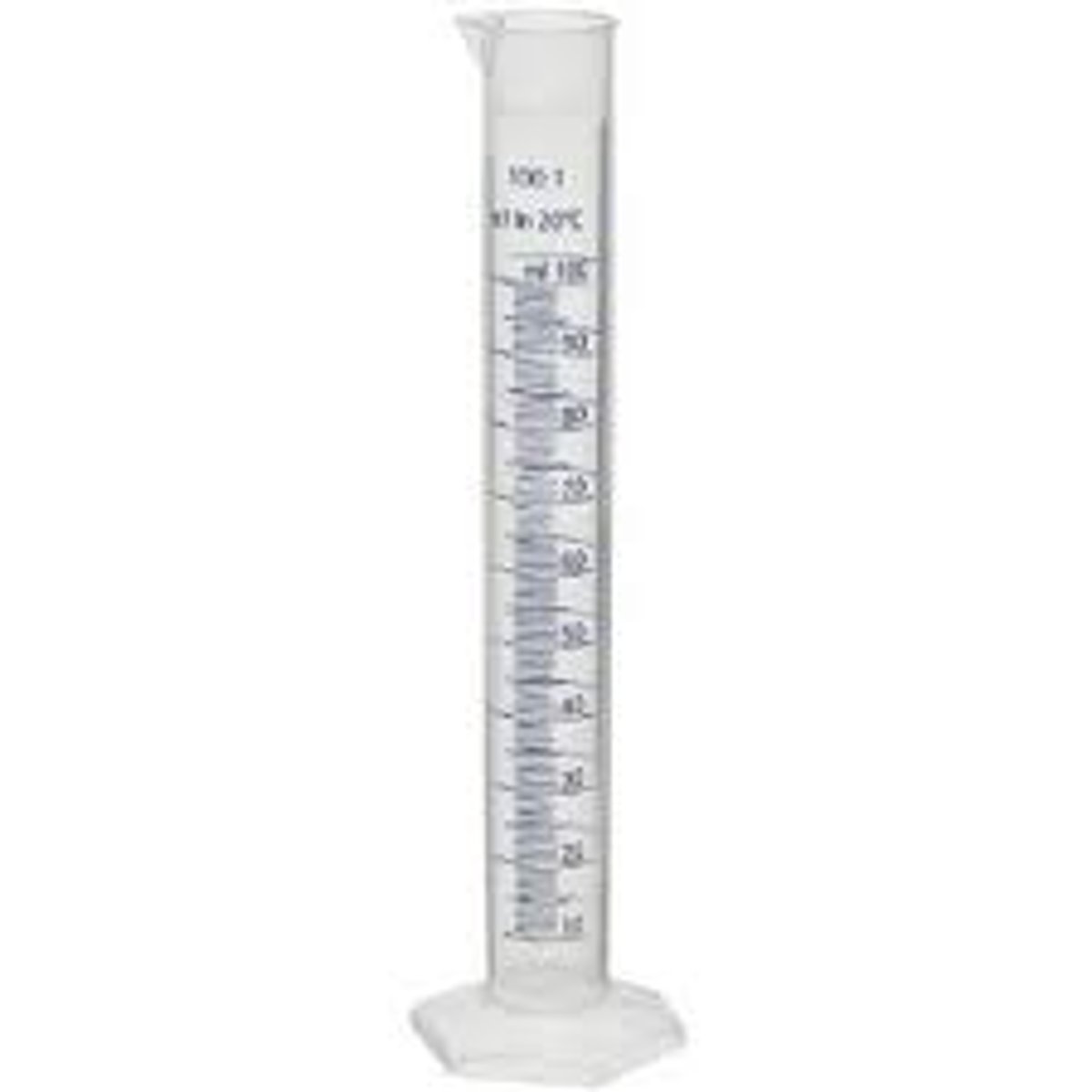
graduated cylinder
instrument used to measure volume of a liquid

lab notebook
notebook for recording information important to a study, such as design, procedure, and the planned analysis

Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
specific sets of written instructions about how to perform a certain aspect of a task

percent error formula
experimental value-accepted value/accepted value x 100

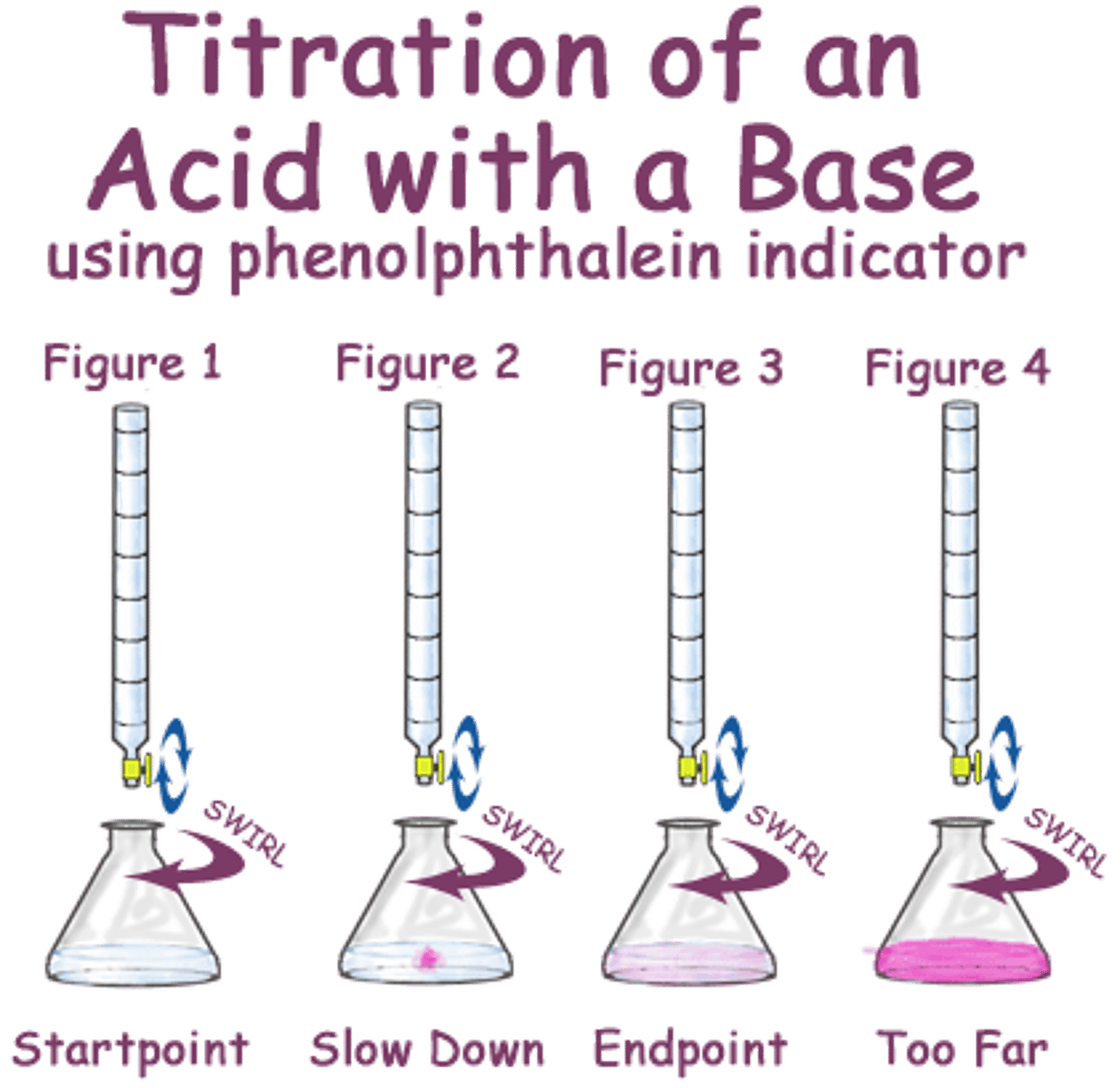
Titration
a measured amount of a solution of unknown concentration is added to a known volume of a second solution until the reaction between them is just complete
molar mass
the mass of one mole of a pure substance

Chemical Label
3 parts to a label (ID of Chemical, Date and Initials of Who made the chemical)