Micro Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
A growth medium that distinguishes among different groups of bacteria on the basis of their biological and growth characteristics on the medium is called a/an ___________ medium.
\
Transport
Differential
Selective
Enrichment
\
Transport
Differential
Selective
Enrichment
Differential
2
New cards
Square planar arrangement of cells that forms when round bacteria remain attached to each other during reproduction are called…..
\
Tetrads
Streptococci
Sarcinae
Staphylococci
\
Tetrads
Streptococci
Sarcinae
Staphylococci
Tetrads
3
New cards
The majority of nitrogen in soil and marine environments is fixed by….
\
E. coli
Symbionts
Free living bacteria and archaea
Organisms living w/in bacteria
\
E. coli
Symbionts
Free living bacteria and archaea
Organisms living w/in bacteria
Free living bacteria and archaea
4
New cards
Which of the following statements about ABC transporters is not true?
\
They can be used for import and export material for the cell
\
They are also responsible for multi-drug resistance
\
They require energy
\
They are found only in prokaryotes
\
They can be used for import and export material for the cell
\
They are also responsible for multi-drug resistance
\
They require energy
\
They are found only in prokaryotes
They are found only in prokaryotes
5
New cards
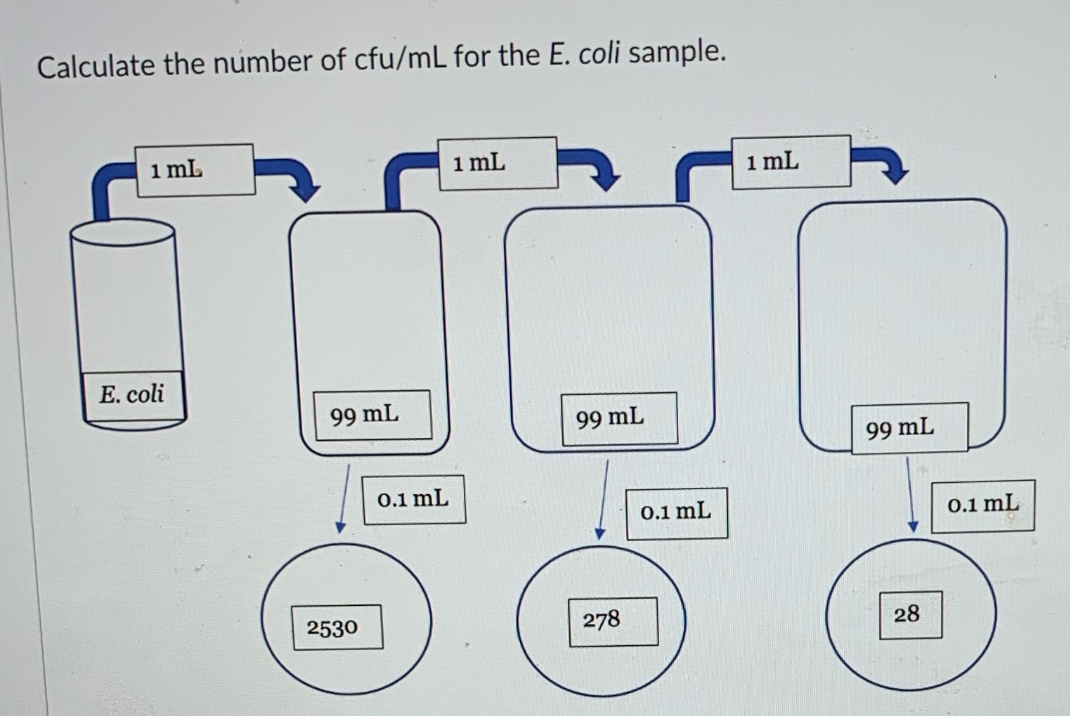
Calculate the number of cfu/mL for the E. Coli sample.
2\.78x10^7
6
New cards
The growth rate of a given species of microorganism is dependent on the composition of the medium in which it is grown.
\
T/F
\
T/F
True
7
New cards
Which of the following proteins represents a coupled transport system where two molecules travel in the opposite direction?
\
Symporter
Aquaporin
Efflux Pump
Antiporter
\
Symporter
Aquaporin
Efflux Pump
Antiporter
Antiporter
8
New cards
After you transferred 1mL from a 10^-6 dilution tube into a plate, you counted 207 colonies. How many CFU are present in 1 mL?
2\.07x10^8
9
New cards
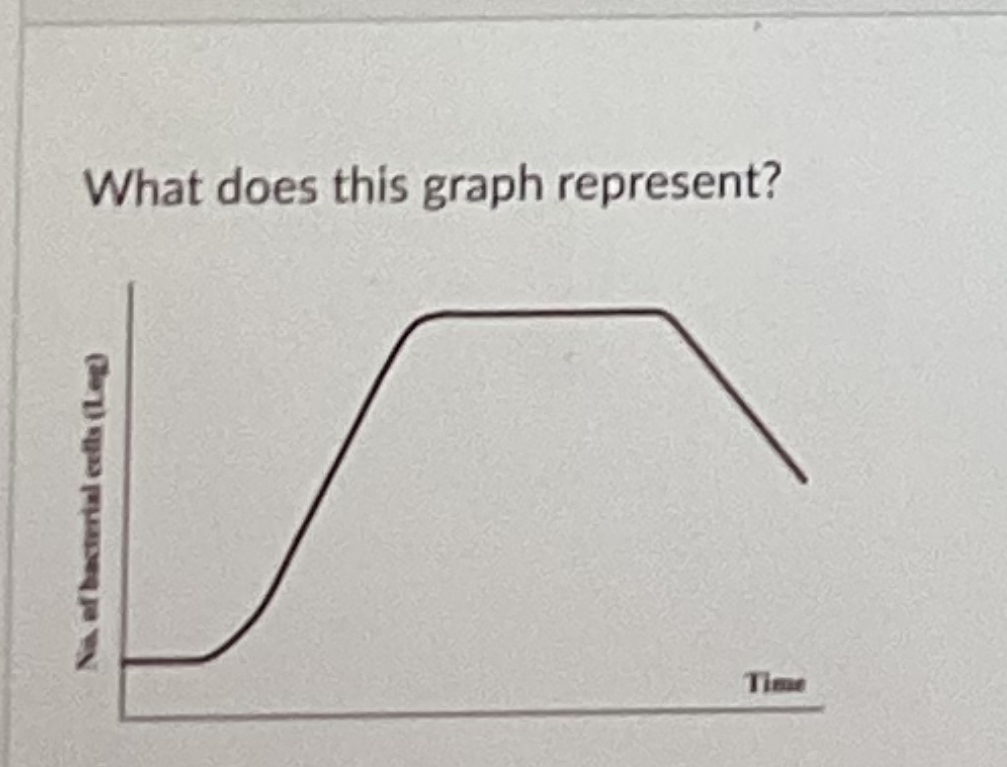
What does this graph represent?
\
Bacterial Growth in a chemostat
Bacterial growth at high temperature
Bacterial growth in closed culture
Bacterial growth in continuous culture
\
Bacterial Growth in a chemostat
Bacterial growth at high temperature
Bacterial growth in closed culture
Bacterial growth in continuous culture
\
Bacterial growth in closed culture
Bacterial growth in closed culture
10
New cards
A medium that has ingredients, such as yeast extract or casein milk proteins, which consist of a mixture of many chemical species in unknown proportions is commonly referred as
\
Complex medium
Synthetic medium
Differential medium
Selective medium
\
Complex medium
Synthetic medium
Differential medium
Selective medium
Complex medium
11
New cards
A growth medium that favors the growth of some microorganisms but inhibits the growth of other microorganisms is a ______ medium.
\
Neither selective nor differential
Selective
Selective and differential
Differential
\
Neither selective nor differential
Selective
Selective and differential
Differential
Selective
12
New cards
You are measuring growth in a bacterial culture. The number of viable cells remained unchanged throughout the experiment but when you check the medium you found that the carbon source has been depleted (used up). In which phase of growth is the culture in?
\
Lag phase
Early log phase
Late log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
\
Lag phase
Early log phase
Late log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
Stationary phase
13
New cards
Which of the following element combinations include only macronutrients required in large quantities by many microbes?
\
C, O, S, Zi, Mn
S,O,Mg,Ca,K
H, N,K,Mg,Mo
P,H,S,Cu,Ni
\
C, O, S, Zi, Mn
S,O,Mg,Ca,K
H, N,K,Mg,Mo
P,H,S,Cu,Ni
S,O,Mg,Ca,K
14
New cards
Which of the following uses sunlight for energy and CO2 as a carbon source?
\
Photogeterotrophs
Chemoautotrophs
Photoautotrophys
Chemoheterotrophs
\
Photogeterotrophs
Chemoautotrophs
Photoautotrophys
Chemoheterotrophs
Photoautotrophys
15
New cards
Neisseria meningitidis are cultured on chocolate agar, a medium containing red blood cells that help cultivate the fastidious bacteria to detectable levels. What type of growth medium is chocolate agar based on the description?
\
differential
selective
enriched
selective and differential
\
differential
selective
enriched
selective and differential
enriched
16
New cards
The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
\
T/F
\
T/F
True
17
New cards
You are working with a culture medium X that only allows the growth of halophiles (salt-loving microbes). Among. the halophiles, mannitol fermenters will produce acid that turns the pH indicator in the medium to yellow while mannitol non-fermenters will not change the color of the medium.
\
Medium X is acting as a ______ medium.
\
enrichment
selective
differential
selective and differential
\
Medium X is acting as a ______ medium.
\
enrichment
selective
differential
selective and differential
selective and differential
18
New cards
If you start with 4 cells in an exponetial phase and divides to 10 cells every cell division, the total number of cells after “n: number of generations is proportional to_____.
\
4x10^n
10x4^n
4xn^10
40
\
4x10^n
10x4^n
4xn^10
40
4x10^n
19
New cards
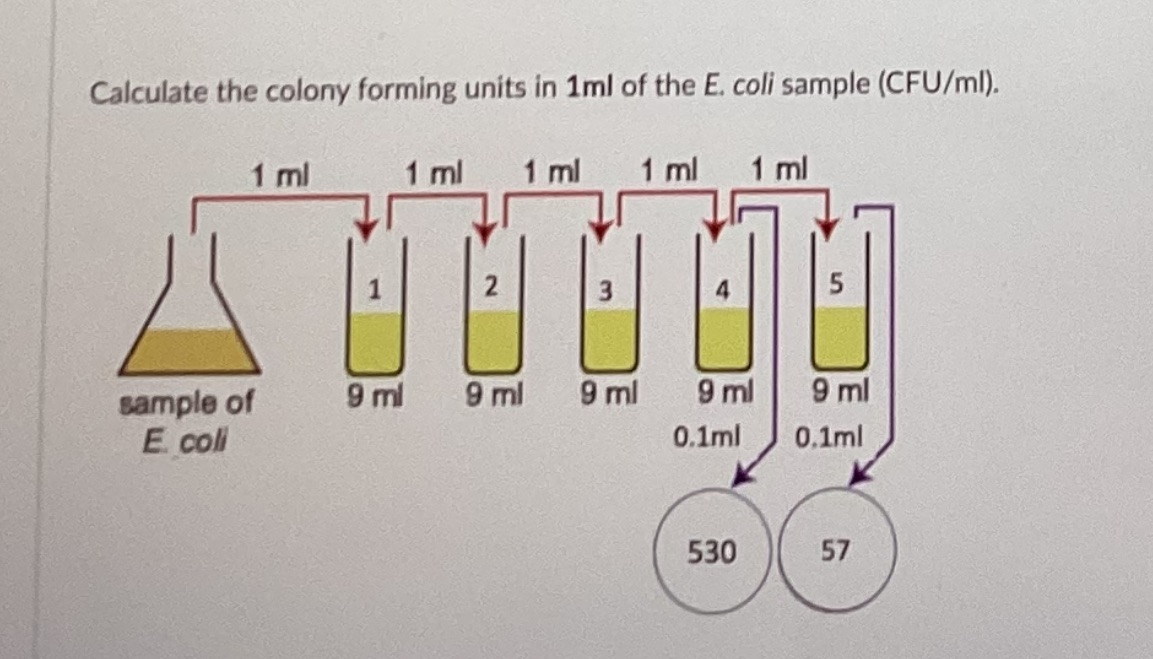
Calculate the colony forming units in 1 mL of the E. coli sample.
5\.7x10^7
20
New cards
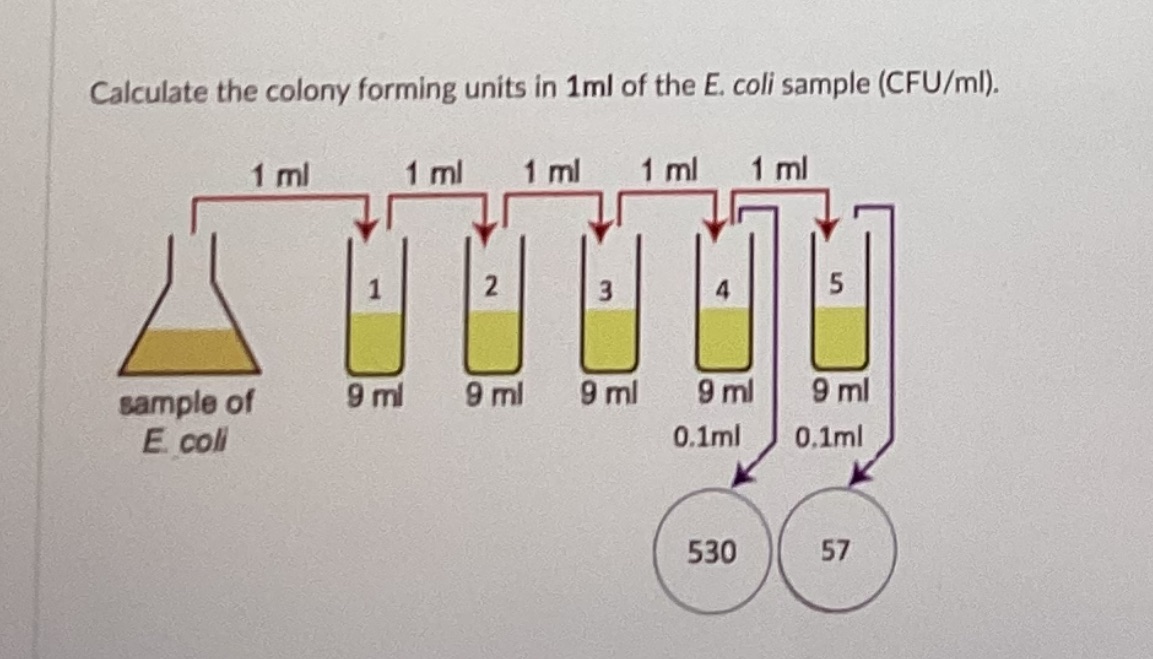
Calculate the colony forming units in the whole 5 mL of the E. coli sample.
2\.85x10^9
21
New cards
One cell with generation time of 30 mins is inoculated into a culture medium. How many cells are there after 2 hours. (assuming all cells divide by binary fission in log phase and remained viable)
\
96
180
16
32
\
96
180
16
32
16
22
New cards
Bacteria were transferred into a nutrient broth and placed in an incubator. The number of bacteria was determined at the end of each day: at start =10 bacteria, end of day= 20 bacteria, end of day 2= 40 bacteria, end of day 3= 80 bacteria, day 4= 160 bacteria.
\
How many bacteria at end of Day 20?
\
more than 10 million
1,280,000
6400
640
\
How many bacteria at end of Day 20?
\
more than 10 million
1,280,000
6400
640
more than 10 million
23
New cards
At 4:00pm a closed flask of sterile broth is inoculated with 10,000 cells. At 8:00 pm the log phase culture has population of approx. 41 million cells. The estimated number or generations that has occurred is_______.
\
Assume that the culture maintained log phase and every cell actively divided the whole time. Round.
\
5
12
21
27
\
Assume that the culture maintained log phase and every cell actively divided the whole time. Round.
\
5
12
21
27
12
24
New cards
Shortest lag period would most likely be observed if a culture is transferred_______.
\
to a medium at a different temp
\
from a complex medium to a fresh complex medium
\
to a medium at a different pH
\
from a complex medium to a minimal medium
\
to a medium at a different temp
\
from a complex medium to a fresh complex medium
\
to a medium at a different pH
\
from a complex medium to a minimal medium
from a complex medium to a fresh complex medium
25
New cards
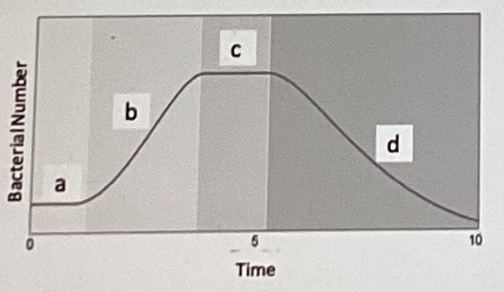
The figure below shows the growth curve of a bacteria in a batch (closed) culture. In which phase would you expect to find amount of carbon decreasing while. the. number of viable cells increasing?
\
a
b
c
d
\
a
b
c
d
b
26
New cards
In cultures without oxygen, if streptococcus pyogenes decided to undergo fermentation, what happens to the electrons carried by NADH from glycolysis?
\
will be donated back to glucose
\
will be lost to the media
\
will be donated to pyruvates
will be donated to electron transport system
\
will be donated back to glucose
\
will be lost to the media
\
will be donated to pyruvates
will be donated to electron transport system
will be donated to pyruvates
27
New cards
Fermentation produces more energy than anaerobic respiration.
\
T/F
\
T/F
False
28
New cards
Oxygen is always required for the regeneration of NAD+ from NADH.
\
T/F
\
T/F
False
29
New cards
Which is not an end product of fermentation?
\
carbon dioxide
propionate
acetone
pyruvate
\
carbon dioxide
propionate
acetone
pyruvate
pyruvate
30
New cards
You feed E. coli 3 glucose molecules. How many ATP are created only through substrate level phosphorylation?
\
6
10
8
12
\
6
10
8
12
12
31
New cards
The enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyzes the conversion of PEP to pyruvate. The phosphate group is transferred to ADP to form ATP. This is an example of:
\
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
\
ATP synthase by oxidative phosphorylation
\
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
\
ATP synthase by oxidative phosphorylation
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
32
New cards
Why do bacterial cells need fermentation?
\
Synthesize more NADH
\
Produce ATP by substrate level phosphorylation
\
produce pyruvate for transition steps
\
Recycle NADH back to NAD+
\
Synthesize more NADH
\
Produce ATP by substrate level phosphorylation
\
produce pyruvate for transition steps
\
Recycle NADH back to NAD+
Recycle NADH back to NAD+
33
New cards
The Entner-Dourdoroff (ED) pathway and the pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) both produce NADH.
\
T/F
\
T/F
False
34
New cards
Which of the following is NOT correct with respect to the redox pair NAD+/NADH?
\
NADH can accept electrons from an electron transport system
\
The reduced, nonaromatic ring of NADH is at a higher energy than the aromatic ring of NAD+
\
the nicothinamide ring is a relatively stable aromatic structure
\
the nicotinamide ring is heteoaromatic because it has a noncarbon atom in its 4th position.
\
NADH can accept electrons from an electron transport system
\
The reduced, nonaromatic ring of NADH is at a higher energy than the aromatic ring of NAD+
\
the nicothinamide ring is a relatively stable aromatic structure
\
the nicotinamide ring is heteoaromatic because it has a noncarbon atom in its 4th position.
NADH can accept electrons from an electron transport system
35
New cards
The enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyzes the conversion of PEP to Pyruvate. The phosphate group is transferred to ADP to form ATP. This reaction is an example of…
\
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
\
ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
\
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
\
ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
36
New cards
The following is a condensed representation of the TCA cycle.
What is the name of the intermediate labelled 6?
\
oxaloacetate
succinyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Citrate
What is the name of the intermediate labelled 6?
\
oxaloacetate
succinyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Citrate
Citrate
37
New cards
E. coli could yield a max of 38 ATP per each glucose molecule by aerobic respiration. The same E. coli could also yield similar amount of ATP per each glucose molecule using fermentation as long as they have plenty of resources.
\
T/F
\
T/F
False
38
New cards
Before pyruvate can enter the TCA cycle it must be transformed into what molecule?
\
pyruvate dehydrogenase
oxaloacetate
Acetyl-CoA
Malate
\
pyruvate dehydrogenase
oxaloacetate
Acetyl-CoA
Malate
Acetyl-CoA
39
New cards
The glyoxylate Bypass (shunt) can be utilized by some organisms when carbon sources are limited. The bypass incorporate a second molecule of Acetyl-CoA to form succinate and ______ molecules.
\
isocitrite
oxaloacetate
malate
pyruvate
\
isocitrite
oxaloacetate
malate
pyruvate
malate
40
New cards
Which of the following pathways would be fully operational only in respiring bacteria?
\
fermentation
PPP
TCA
Glycolysis
\
fermentation
PPP
TCA
Glycolysis
TCA
41
New cards
How many electron carriers in total are created from just the TCA cycle from 2 glucose molecules?
\
16
12
8
24
\
16
12
8
24
16
42
New cards
Production of ATP by ATP synthase directly depends on. which of the following?
\
GTP
Proton motive force
electron carrier force
neutron motive force
\
GTP
Proton motive force
electron carrier force
neutron motive force
Proton motive force
43
New cards
Which of the following is not a component of E. coli Electron Transport System?
\
NADH Dehydrogenase (oxidoreductase)
\
Terminal oxidase
\
Cytochrome oxidase complex
\
mobile electron carrier
\
NADH Dehydrogenase (oxidoreductase)
\
Terminal oxidase
\
Cytochrome oxidase complex
\
mobile electron carrier
Cytochrome oxidase complex
44
New cards
Anaerobic respiration uses an electron transport system while fermentation does not utilize an electron transport system.
\
T/F
\
T/F
True
45
New cards
Oxygen is always required for oxidation of NADH to NAD+.
\
T/F
\
T/F
False
46
New cards
Which of the. following statements about anaerobic respiration is true?
\
it does not require ETS
\
use oxidized ions of nitrogen, and sulfur as their final electron acceptor
\
it generates only 2 ATP per single glucose
\
uses oxygen as a final electron acceptor
\
it does not require ETS
\
use oxidized ions of nitrogen, and sulfur as their final electron acceptor
\
it generates only 2 ATP per single glucose
\
uses oxygen as a final electron acceptor
use oxidized ions of nitrogen, and sulfur as their final electron acceptor
47
New cards
If you feed Streptococcus pyogenes 5 glucose molecules in aerobic condition, what is the maximum theoretical amount. of ATP. produced? (aerobic respiration)
\
160
190
125
150
\
160
190
125
150
190
48
New cards
Which group of microorganisms are most likely to spoil a fish kept at a refrigerator (low temp)?
\
psychrophiles
halophiles
anaerobes
thermophiles
\
psychrophiles
halophiles
anaerobes
thermophiles
psychrophiles
49
New cards

The following data show growth of 2 bacteria on different media.
\
The table shows that S. aureus is an?
\
alkalophile
anaerobe
mesophile
halophile
\
The table shows that S. aureus is an?
\
alkalophile
anaerobe
mesophile
halophile
halophile
50
New cards
The term aerotolerant anaerobe refers to an organism that
\
use oxygen if present in high concentration
\
requires less oxygen than is present in air
\
use oxygen but prefers nitrogen compounds
\
does not use it oxygen and is not affected by it
\
use oxygen if present in high concentration
\
requires less oxygen than is present in air
\
use oxygen but prefers nitrogen compounds
\
does not use it oxygen and is not affected by it
does not use it oxygen and is not affected by it
51
New cards
Which of the following determines if microorganisms are going to use oxygen or not?
\
their ability to use oxygen to oxidize glucose
\
their ability to use oxygen during glycolysis
\
their ability to use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor
\
their ability to have enzymes that deals with ROS
\
their ability to use oxygen to oxidize glucose
\
their ability to use oxygen during glycolysis
\
their ability to use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor
\
their ability to have enzymes that deals with ROS
their ability to use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor
\
their ability to have enzymes that deals with ROS
\
their ability to have enzymes that deals with ROS
52
New cards

Which shows phenol red test result of heterolactic fermentation?
left tube (yellow one)