2.1 Macroeconomics
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what are the four main objectives
High sustainable economic growth
low unemployment
low inflation
balanced current account
High sustainable economic growth
ideal is 2/2.5%
higher living standards
improved government finances
Low inflaton
Bank of England target is 2%
firms more likely to invest / makes firms competitive
price stability in the UK
Low unemployment
around 4% menas full capacity in the uk
less crime , less mental health issues
increased spending power for individuals
balanced current account
for the uk this means reducing its current account deficit
country can afford to pay for the imports , a deficit means there is an outflow of money
why are the ILO and claimant count different
because the ILO measures 16-18year olds but claimant count doesn't
who does the claimant count exclude
- People under 18
• People in full time education, who may still be classed as unemployed.
• People not eligible for contribution based JSA. To claim the contributions
based JSA they need to have paid at least two years of NI contributions.
right shift on SRAS on the economy
1) lower prices - >more output -> increased derived demand for labour -> more employment
2) lower prices -> international competitiveness increases -> more exports -> AD shifts outwards -> Real GDP increases
define economic growth
economic growth is a measure of an increase in real gross domestic product (GDP)
how is economic growth measured
it is measured by a percentage change in real GDP per annum, it can be shown by a shift on a ppf
Distinguish between real and nominal
Nominal GDP is the money value of all goods and services provided in one year
Real GDP is the nominal GDP adjusted for inflation
Distinguish between total and per capita
Total GDP represents overall GDp for a country whilst GDP per capita is total GDP is divided by the number of people in a country
How does spare capacity impact the multiplier
If there is low spare capacity, firms are already operating close to full capacity and cannot easily increase output.
As a result, an increase in aggregate demand leads to higher prices rather than higher real output, meaning the multiplier effect is weaker.
The impact of additional spending is therefore limited, as much of it is absorbed by inflationary pressures rather than real economic growth
distinguish between GNI and GDP
GNI (gross national income) received by a country both domestically and via net incomes overseas
How can GDP measure living standards
as it gives information about the size of an economy and how well it is performing
Problems using GDP to measure living standards
-risk of double counting
-informal activity black markets , illegal activity
-errors via data collection
-negative externalities are not included ( cost of air pollution , loss of biodiversity )
Define the term purchasing power parities
take into account the exchange rate and cost of living in each country
what is the purpose of purchasing power parities
to make meaningful comparisons about other countries living standards
How does the UK measure national wellbeing
by asking 4 questions
overall , how satisfied are you with your life
to what extent do you feel your life is worthwhile
how happy were you yesterday
how anxious were you yesterday
Inflation
is a sustained rise in the general price level , the persistent increase of prices in a economy in one year
deflation
is a sustained fall in the general price level , often a sign of stagnation in a economy - INFLATION RATE NEGATIVE
disinflation
is a fall in the rate at which the general price level is rising
3% to 2% still increasing just less rapidly
How is the rate of inflation measured using the Consumer Prices Index
The living costs and food survey collects data from 7000 households in the UK
a price survey is undertaken once a month about changes in price of the most commonly used goods and services
weights are assigned to each item the average household buys the weights reflect the proportion of income spent on each item in the average shopping basket
the price changes are multiplied by the weights to give a price index
the rate of inflation can be measured by calculating the percentage change over the consecutive years
Limitations of using the CPI to measure the rate of inflation
It does not include housing costs
Basket updates are too slow “once a year”
sampling issues inaccurate responses
some households may not reply
differences between the CPI and RPI
the RPI includes housing costs whereas the CPI does not it is also not as reliable as the CPI
how is demand pull inflation caused
occurs when aggregate demand (total demand) in the economy increases at a faster rate than aggregate supply
-decrease in interest rates
-increased government spending
-a rise in business and consumer confidence
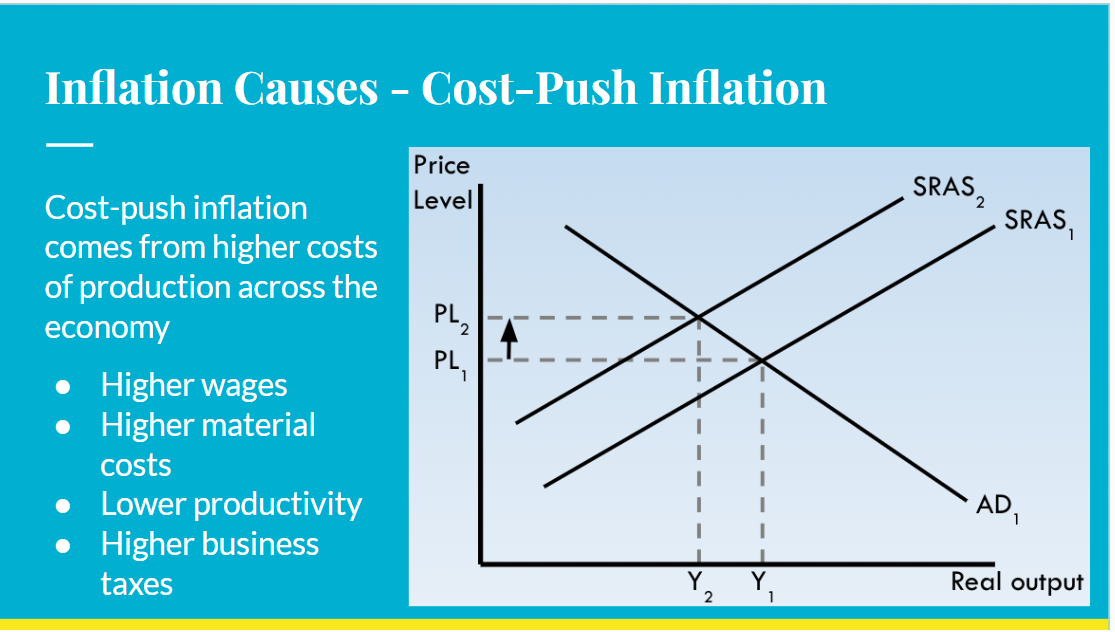
how is cost push inflation caused
aggregate supply decreases , ie total costs of production increase
a rise in taxes on businesses
increased minimum wage
Unemployment is counted as
people of working age that are able to work and actively seeking work but do not have a job
Unemployment rate
unemployed / economically active (employed + unemployed) x 100
Labour force survery
40k households are surveyed
they record who is unemployed,employed and economically active
what are the issues with the labour force survey
sampling errors
disparity between unemployment
inactive groups
discouraged workers
Claimant count
who is claiming unemployment-related benefits
such as the Job seekers allowance
what are the issues with the claimant count
The claimant count method is under-estimating the true level of unemployment because many people are actively seeking a job, are not eligible or do not feel it is worth doing.
It is possible that the claimant count could overstate the level of unemployment because people could collect JSA while also having a job.
However, the levels of estimated benefit fraud are quite low.
what is a current account deficit
When the VALUE of an economy's imports exceeds the value of its exports
It means that the total value of goods, services, income, and current transfers flowing out of the country is greater than the value flowing in.
unemployment on firms
- Fall in demand for goods and services- as consumers have decreased disposable income and purchasing power less produce sold (lost output)
- bigger pool of labour force to choose from, less pressure for higher wages
- less risk of strikes as employees may fear they will lose their jobs
unemployment on government
more spending on benefits
- less tax revenue
- increased inequality
- possibly more increased crime
- opportunity cost
unemployment on the economy
lost output- real GDP will fall
- reduced tax revenue for the government
- increased burden on the taxpayers to fund benefits and training measures
- increased burden on the healthcare system
- increased crime
real income
Real income is the income of an individual or group after adjusting for inflation, reflecting the actual purchasing power.
causes of current account deficit
High consumer spending on imports
(especially during economic booms)Low competitiveness of exports abroad
(high prices, poor quality vs foreign goods)Strong exchange rate
(makes exports expensive, imports cheaper)Low productivity or investment
(reduces export capacity)High income → more demand for foreign goods
causes of a current account surplus
High export demand
(strong global demand or competitive industries)Low consumer spending on imports
(e.g. during a recession)Weak exchange rate
(makes exports cheaper, imports more expensive)High productivity or investment
(boosts output and export potential)
Why might GDP per capita not reflect living standards?
GDP per capita doesn’t account for income inequality, non-market activity (like unpaid work), or quality of life (e.g. health, education, environment).
💡 Even if GDP is high, most people could still be poor if wealth is unevenly distributed.
how can real incomes influence a current account balance
1. Increased Imports: Higher incomes lead to more spending on imports, which can worsen the current account balance.
3. Investment Flows: Rising incomes may lead to more investments abroad, affecting the balance negatively.
4. Tourism Spending: Higher incomes can increase spending on foreign travel, which can also impact the current account negatively.
loss of purchasing power
The German Hyperinflation Crisis 1921 might be the best example of this, but in recent years, the cost of living crisis in 2023, saw inflation as high as 11.1%
state of world economy how does it influence current account
1. Global Demand: Strong global growth increases demand for exports, improving the current account.
Global recessions reduce export demand
Foreign consumers and firms cut spending → export revenues fall → current account worsens.
Commodity prices
If the country exports commodities (e.g. oil), high global prices boost export earnings.
If it imports them, high prices worsen the current account.
how can protectionism influence the current account
the theory or practice of shielding a country's domestic industries from foreign competition by taxing imports.
1. Reducing Imports: Tariffs,taxes and quotas limit foreign goods, potentially improving the current account.
2. Encouraging Domestic Production: Protectionist measures can boost local industries, increasing exports.
3. Retaliation Risks: Other countries may respond with their own tariffs, which could harm exports.
disadvantages of export led growth
- Susceptible to shock, what if there is a war, or pandemic, or the trading partner enters recession
- Exchange rate risks (exporting firms often earn revenue in foreign currencies. If the domestic currency strengthens (appreciates), the value of those foreign earnings falls when converted back, reducing profits.)
animal spirits
Term coined by John Keynes; basically means business confidence: the mood of managers and owners of firms about the future of their industry and the wider economy.
- If animal spirits are low, investments will be low
what is the crowding in effect
When government spending increases private investment. This happens because public spending can stimulate economic growth, creating more profitable investment opportunities for businesses.
(e.g. The government builds a new high-speed rail line. This improves transport links between cities, making it faster and cheaper to move goods and people. As a result, private companies are more willing to invest in factories, offices, and logistics in those areas, because they expect higher productivity and profits)
what is the crowding out effect
When increased government spending, often financed by borrowing, reduces private sector investment and spending.
- This happens because government borrowing can drive up interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money, thus discouraging private investment.
cause of inflation
- Increased demand
- Rising production costs
- Expansionary monetary policy
- Supply chain disruptions
- Expectations of future inflation
economic effects of inflation
- Less purchasing power: Money buys less.
- Higher living costs: Essentials become more expensive.
- Economic uncertainty: Businesses hesitate to invest.
- Rising interest rates: Central banks may increase rates.
- Wage demands: Workers ask for higher pay.
Demand pull inflation
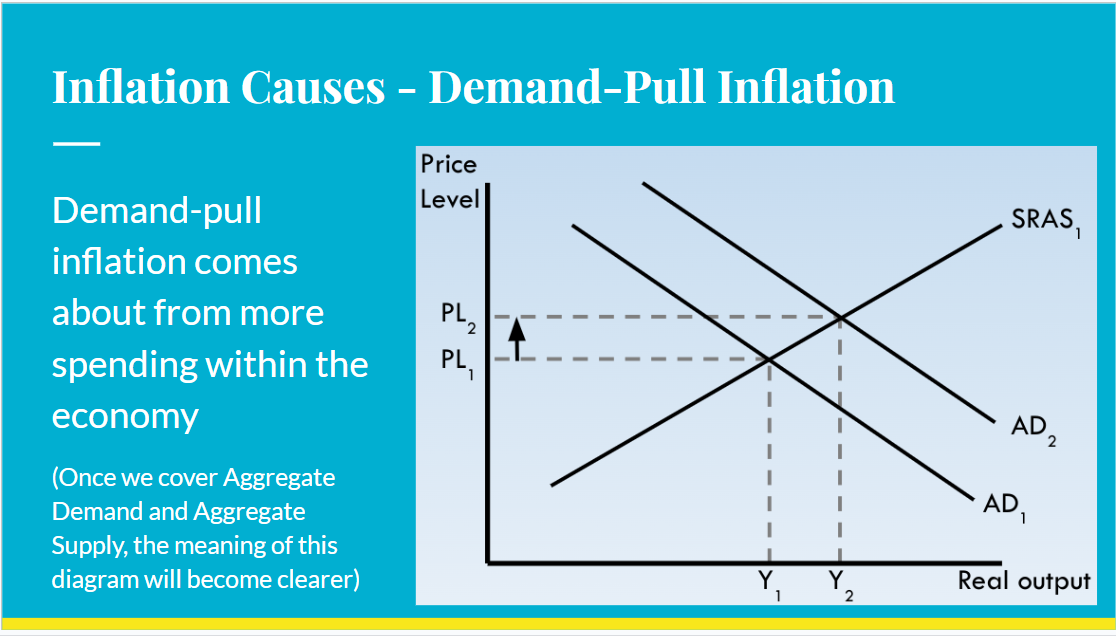
Demand-pull inflation is caused by more…
more spending:
Consumer spending
Business investment
Government spending
Net exports (spending by foreign consumers)
what is the trade balance
The trade balance is the difference between the value of a country’s exports and imports of goods and services over a period of time.
Cost push inflation
is national wellbeing and GDP per capita linked
- The Easterlin Paradox suggests that they are linked to some extent as with money happiness increases but only to a certain point.
- National wellbeing is assessed by examining a range of factors such as health, personal relationships and employment
- However, it is hard to measure national wellbeing.
index number
A number showing the variation in a price or value compared with the price or value at a specified earlier time
why may increased investment not cause growth
1) Administrative costs, if the investment is poorly spent or goes towards administrative costs, then it may not cause a multiplier or increase economic growth
2) Opportunity cost, could the money have been better spent elsewhere?
3) Time lag, it may take months or years for the effects of the investments to be visible
inflation on workers
- those on fixed incomes suffer
what is the current account
The current account is part of a country’s balance of payments.
It records all money flows into and out of the country from:
Trade in goods (exports – imports of physical products)
Trade in services (e.g. tourism, banking, insurance)
Primary income (e.g. interest, dividends, profits from overseas)
Secondary income (e.g. remittances, foreign aid, government transfers)
draw a negative output gap
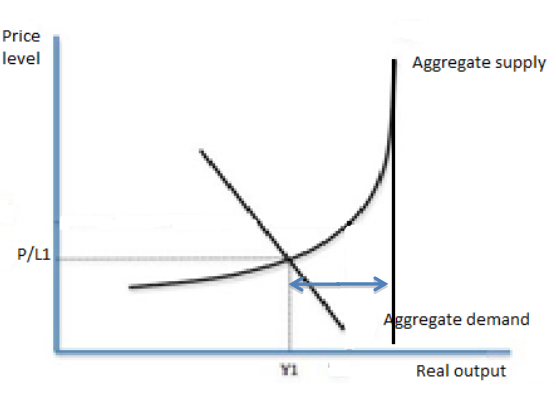
under employment
Under-employment refers to a situation where an individual is working, but their job does not fully utilize their skills or abilities and they work less hours than desired
define the term price level
price level is the average of the current prices of goods and services within the economy
labour mobility
How it works: Measures to help people move to areas with more job opportunities, such as increasing the supply of affordable housing or providing relocation assistance.
Evaluation:
Pros: Directly targets geographical unemployment, where people are unable to move for work due to barriers like high housing costs.
Cons: Can be expensive and difficult to implement.