Exam 2: Sensation Eval and Intervention
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Sensation refers to
stimulation of nerve cells from environment in the sense organs
-auditory
-gustatory
-olfactory
-somatosensory (receiving and interpreting touch)
-vestibular
-visual
What makes up the vestibular system?
vision, ear, and proprioception
Sensory info is received and organized somatotopically in the ________ of the brain
primary somatosensory cortex AKA postcentral gyrus
A large area of receptors on the brain indicates _________
a high density of sensory receptors
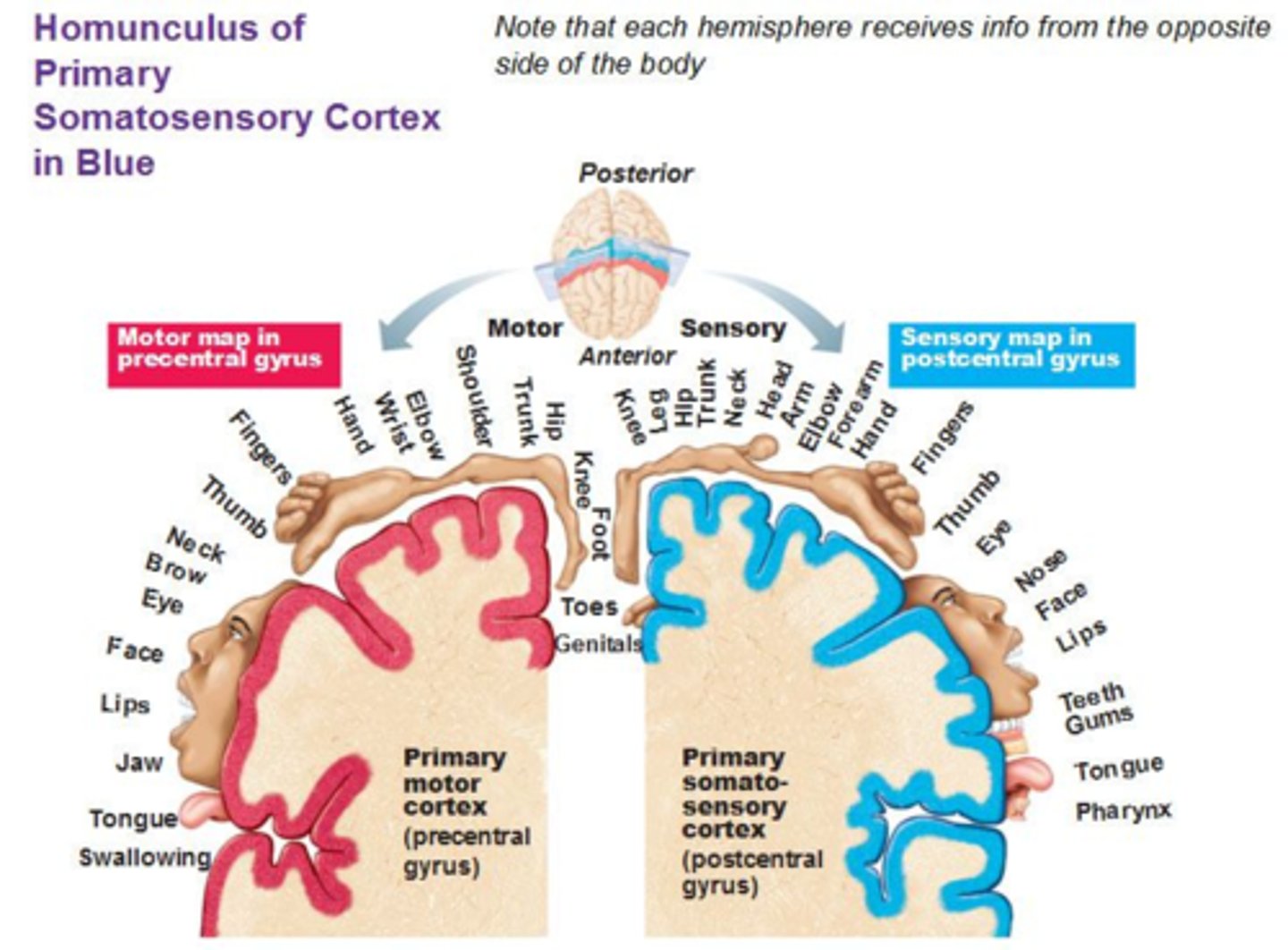
Primary somatosensory behaviors originate from what area of the brain?
the post central gyrus
What areas of the body receive a lot of sensation?
hands
lips
face
What happens in our body/muscles and brain when we touch something that is too hot?
1) painful stimulus
2) nociceptors fire
3) impulse is sent to spinal column
4) column splits
-to muscle (motor - reflexively pull hand away if water too hot; without it having to be processed by brain)
-to brain (sensory - if still too hot, then brain adjusts w/o reflex)
If a person sustained a lesion to their primary somatosensory cortex, they may experience ______ and a reduction in _______
may experience: (most impacted; occupation most impacted)
-agraphasthesia
-astereognosis
-hemihyperesthesia
-loss of vibration, proprioception, and fine touch
reduction in: (less impacted)
-nociception
-thermoception
-crude touch
What is graphasthesia? Most or least impacted?
the ability to recognize writing on the skin purely by the sensation of touch
a person may have agraphasthesia if they have a lesion to their primary somatosensory cortex/postcentral gyrus
most impacted
What is streognosis? Most or least impacted?
the ability to perceive and recognize form of an object with vision and auditory occluded by using tactile information to provide cues from texture, spatial properties, temp., etc.
a person may astereognosis if they have a lesion to their primary somatosensory cortex/postcentral gyrus
most impacted
What is hemihypesthesia? Most or least impacted?
-increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as touch, pain, or temperature, on one side of the body
-this heightened sensitivity can result in exaggerated or uncomfortable sensations in response to stimuli that are typically not painful or only mildly uncomfortable.
one side normal, the other side not
-i.e. L hemihypesthesia, the R side detects normally and the L side is affected
most impacted
What is nociception? Most or least impacted?
perception of pain
least impacted
What is thermoception? Most or least impacted?
temperature sensation
least impacted
What is crude touch? Most or least impacted?
gross touch or non-discriminative touch, refers to the ability to perceive touch and pressure on the skin without the ability to precisely locate the point of contact or distinguish between fine detail
allows individuals to sense when they are being touched, but without the ability to discern fine details
"i'm being touched or not being touched"
least impacted
What is tactile perception? What are the 4 hallmarks of tactile perception?
-ability to detect and interpret sensory information cutaneous (skin)
includes:
1) pressure
2) skin stretch
3) vibration
4) temperature
T or F: Normal tactile perception means that an individual can interpret pressure, skin stretch, vibration, and temperature.
true
"P.S. Very Tactile" - "P.S." as a reminder that these sensations are "Very Tactile"
What is pressure?
-how much pressure is applied to a certain area on skin
-can be a lot, can be a little (greater than, less than)
i.e. a light hug vs a tight hug
What is skin stretch?
-part of the cutaneous tactile experience that is caused by friction between the skin and the grasped object
-interacting with stiffer objects causes larger force, and results in a larger amount of skin stretch
our skin provides info on how we manipulate objects in our hand, i.e. holding a bottle and our skin stretches to allow a grasp on the bottle
What is vibration?
-ability to detect vibrations from an object and feel when it starts and stops
Sensation and the OTPF
-sensation is a body function
-sensation is a component of client factors
-sensation influences both motor and processing aspects of performance skills
-sensory dysfunction may affect performance in areas of occupation
Why is sensation important?
-safety (skin breakdown, frostbite, burns), quality, speed, and effectiveness of motor function, feed forward and feedback
-protection from injury
-performing occupational activities
-provides feedback about the environment
-requires for early learning (childhood, exploration)
-affects motor performance
-essential for effective movement
What are the requirements of normal sensation?
you must have
-reception: somatosensory receptors (detection of stimulus)
-transmission: afferent neurons (fired and sent to PNS and then CNS)
-interpretation: sensory cortex (brain receives and interprets the data)
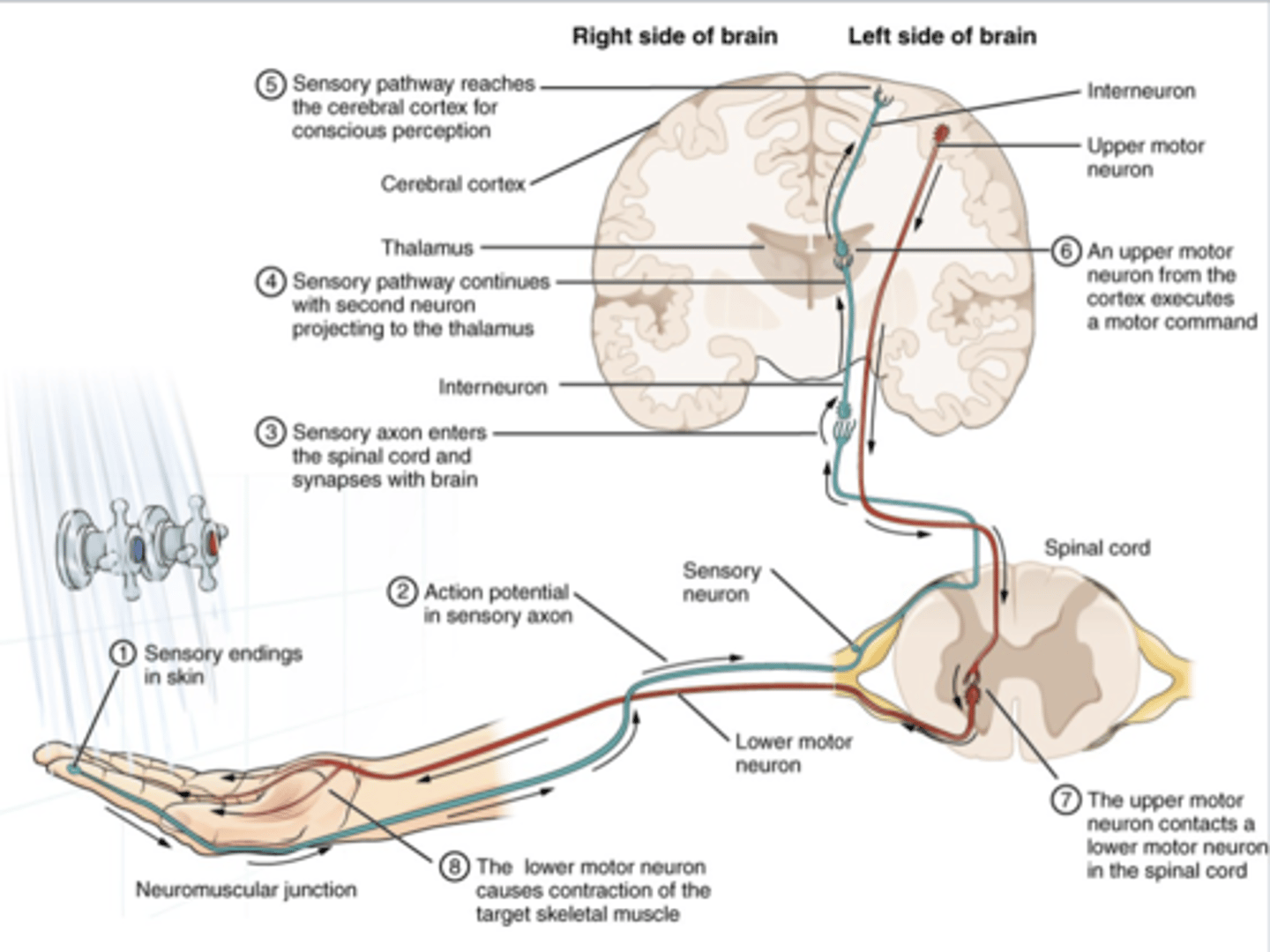
If a person experiences a loss of sensation, then they will have.........? What does this also mean in terms of vision?
they will have:
-impaired tactile feedback
-slowed/diminished quality of performance
-increased risk of injury
they will require adequate vision for compensation/loss of sensation
-aka they will need their vision to help complete activities safely
Selection of evaluation tools depends on whether the etiology is due to problems with........
the CNS or the PNS
the CNS has ability to reorganize after injury
the PNS cannot reorganize after injury.......??????
Central nervous system injury
-injury to brain and spinal cord
-upper motor neuron injury
-generalized area
includes deficits in: proprioception, stereognosis, temperature, and vibration
Peripheral nervous system injury
-damage to peripheral nerves
-lower motor neuron injury
-specific area
includes deficits in: pressure, discrimination, and pain
PPD (peripheral = Pain, Pressure, Discrimination)
Neuroplasticity
the ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma
The potential for recovery depends on
-etiology
-severity
-location of lesion
-cognition
-motivation
-ability to learn new strategies
T or F: The somatosensory system processes input from superficial sources, such as the skin, and from deep sources, such as the musculoskeletal system.
true
Superficial sources
skin receptors
PNS receptor
Deep sources
musculoskeletal receptors
PNS receptor
T or F: Sensation is stimulated by receptors in the PNS and is sent through afferent nerves, carrying nerve impulses from the receptors to the brain.
true
What are the different types of somatosensory receptors? What do each of them have?
mechanoreceptors
chemoreceptors
thermoreceptors
nociceptors
each of them have nociceptors
Receptors that respond to touch, pressure, stretch, and vibration.
mechanoreceptors
Receptors that respond to cell injury or damage.
chemoreceptors
Receptors that respond to temperature, i.e. hot and cold
thermoreceptors
Receptors that sense pain when stimulated.
nociceptors
What are the different types of somatosensory dysfunctions?
paresthesia
hypesthesia
hyperalgesia
dysesthesia
allodynia
What is paresthesia
-tingling, electrical, prickling, or burning sensation
-normal sensation alongside atypical/abnormal sensation
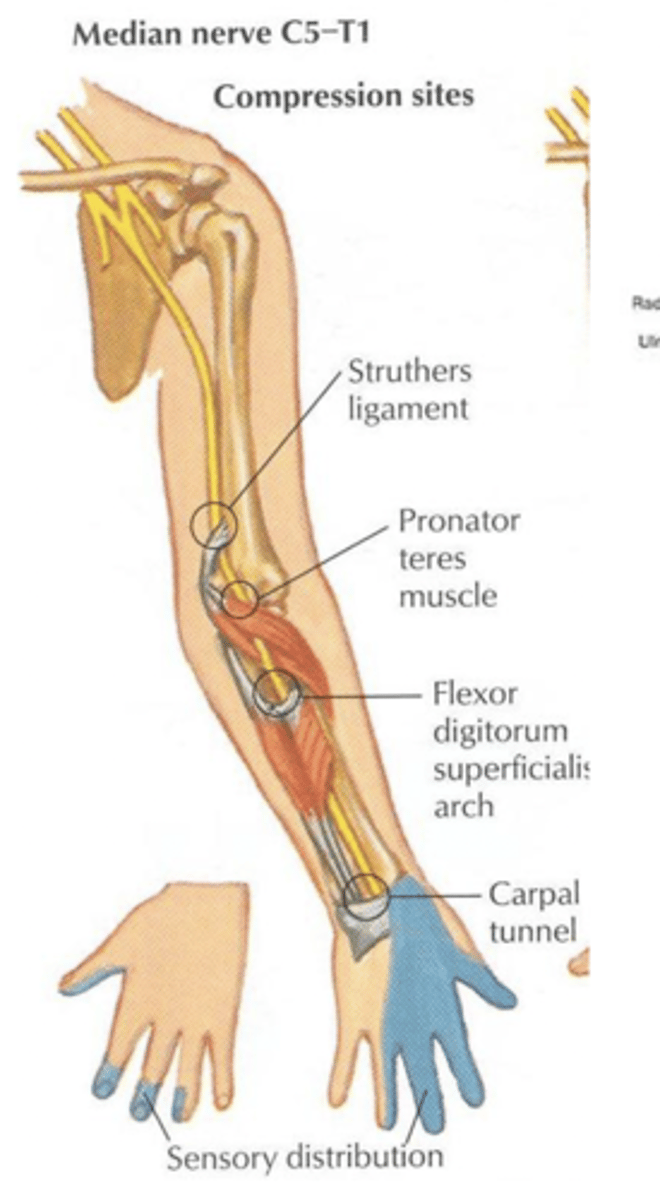
Tapping the volar aspect of the wrist may elicit ________ in the distribution of the median nerve in a person who has carpal tunnel syndrome due to the compressive nature of the disease. When such tapping elicits this, it is called Tinel's sign.
paresthesias
What is hyperesthesia?
-abnormal increase in sensitivity to stimuli
-increased sensory pain
ex: touch canvas material and I think it feels like coarse sand paper
What is hyperalgesia?
-increased pain, sense of pain is overly sensitive
-often occurs during nerve regeneration
What is dysesthesia?
-an unpleasant abnormal sensation, whether spontaneous or evoked
-unpleasant, abnormal sense of touch, often experienced as pain
What is allodynia?
-painful response to a normally innocuous stimulus
-severe pain sensation evoked with a stimulus that doesn't normally induce pain
ex: touch a soft pillow and i shriek in pain
A person with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), formerly referred to as reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), experiences pain with the mere movement of air wafting over the involved arm. What type of sensory dysfunction is this?
allodynia
Primary sensation
receives and interprets "simple" sensations such as
-awareness of touch
-awareness of pain and temp.
pain and temperature, light touch and pressure, vibration
primitive and simple
Discriminative sensation
receives and interprets more complex and integrated experiences/sensations such as
-location of touch
-stereognosis
-kinesthesia
-2-point discrimination
stereognosis, graphesthesia, two-point discrimination, point localization
What comes first: primary or discriminative?
primary
Pain and temperature, light touch and pressure, vibration, and proprioception. Is this primary or discriminative?
primary
Location of touch, stereognosis, kinesthesia, and 2-point discrimination. Is this primary or discriminative?
discriminative
Because of the central processing of deep sensory input, clients with some ________ lesions (e.g., CVA and multiple sclerosis) are more likely to have deficits in vibration, proprioception, stereognosis, and temperature.
CNS lesions
Those with ______ lesions are more likely to experience deficits in pain, pressure threshold, and two-point discrimination
PNS lesions
vibration, proprioception, stereognosis, temperature.
PNS or CNS?
CNS
pain, pressure threshold, and two-point discrimination
PNS or CNS?
PNS
What is neuropathy?
-disease or dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves, typically causing numbness or weakness
-dysfunction of the PNS
T or F: Large sensory nerve fibers carry signals of vibration, light touch, and proprioception.
true
T or F: smaller fibers, which are also often not myelinated, transmit messages of temperature and pain.
true
What is the sequence of loss and return of sensation?
1) discriminative touch and proprioception
2) cold
3) heat
4) pain
pain is last to lose and first to return bc it is needed to help survive, it is our "biological warning system"
What is the first sensation to be lost? Returned?
discriminative touch and proprioception
What is the second sensation to be lost? Returned?
cold
What is the third sensation to be lost? Returned?
heat
What is the fourth sensation to be lost? Returned?
pain
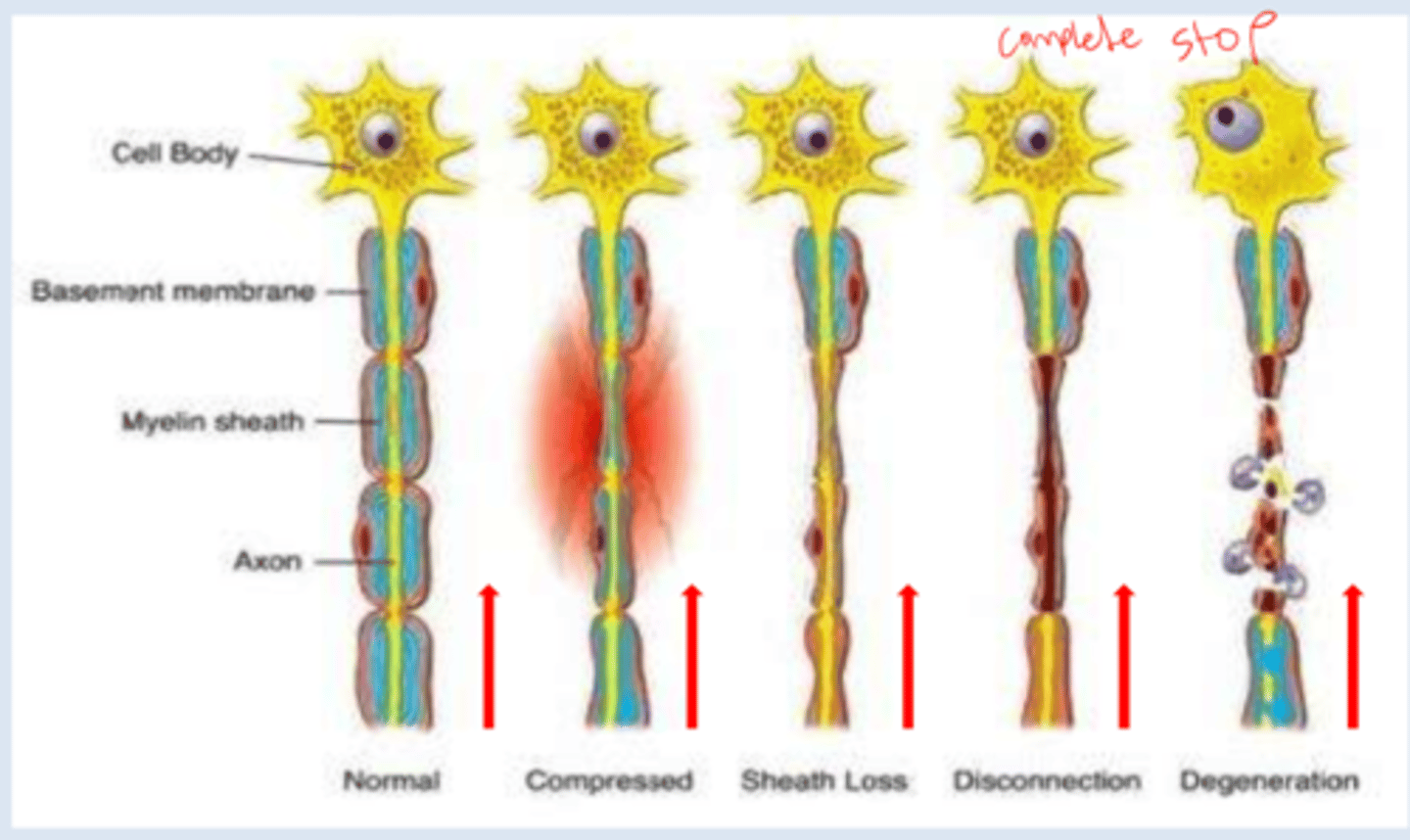
What is nerve compression?
-nerve loses mobility, flexibility, or becomes compressed by surrounding tissues; can cause pain and loss of function
-brain is not sending or receiving full sensations
i.e. not grasping object as strongly as should be
seen in carpal tunnel syndrome
What is sheath loss?
-when transmission of signals is slowed down and impulse is weaker
-brain does not receive full info and muscles don't contract as much as brain wanted to because of the weakened transmission
What is nerve disconnection?
-no signals sent or received by brain
-signals unable to make the "jump" between the severed nerve
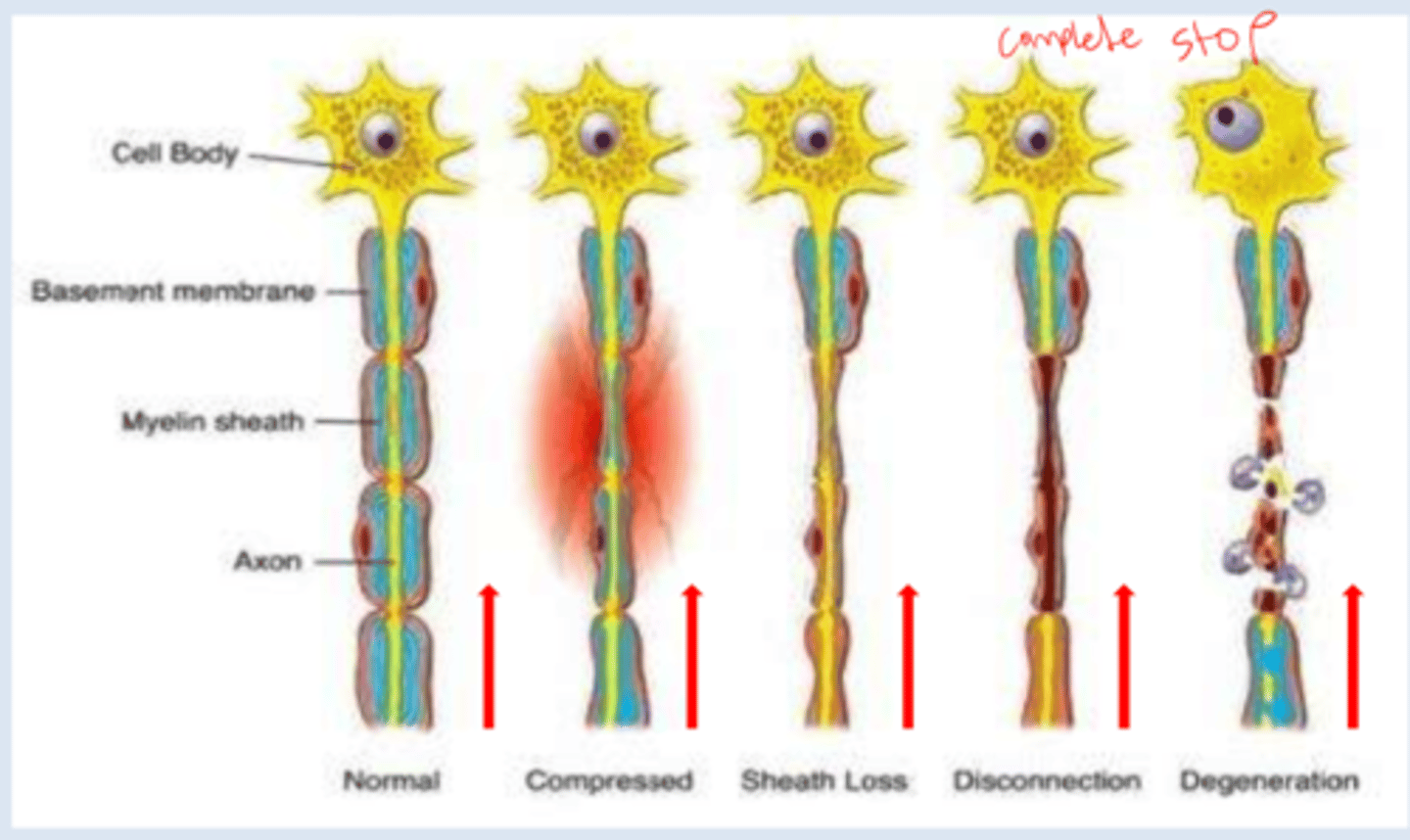
What is nerve degeneration?
-whole system falls apart; difficulty with conducting speed and receiving
problems controlling movements: tremors, muscular rigidity, slowness beginning and executing movements, alteration in reflexes and problems with balance
cognitive problems (dementia): impaired memory, disorientation, deficiencies in intellectual abilities, language problems, etc.
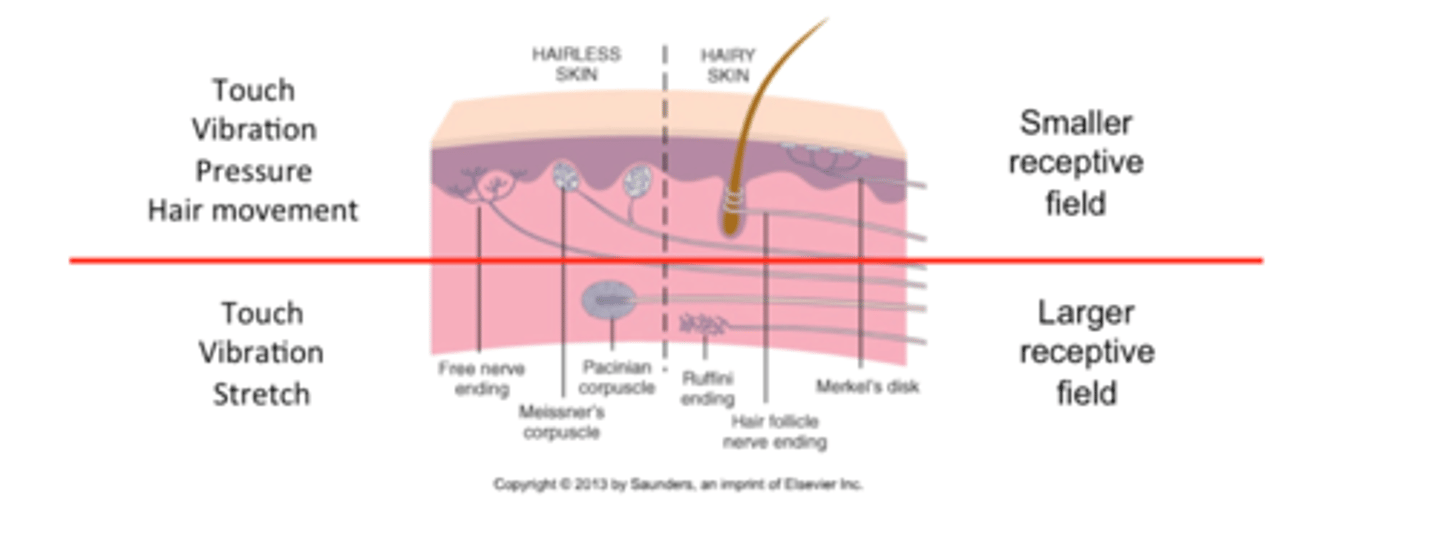
What is superficial sensation? What does it include?
cutaneous sensation
includes:
-touch, pain, temp,
-2-point discrimination
The _____ parts of the body have a higher density of receptors and smaller receptor fields. This contributes to enhanced fingertip sensation, such as distinguishing between 1 and 2 stimuli that are close together.
distal
What enables us to tell the difference between a penny and a dime?
2-point discrimination
Fine touch: superficial receptors
-light touch
-vibration
-pressure
-hair follicle receptors
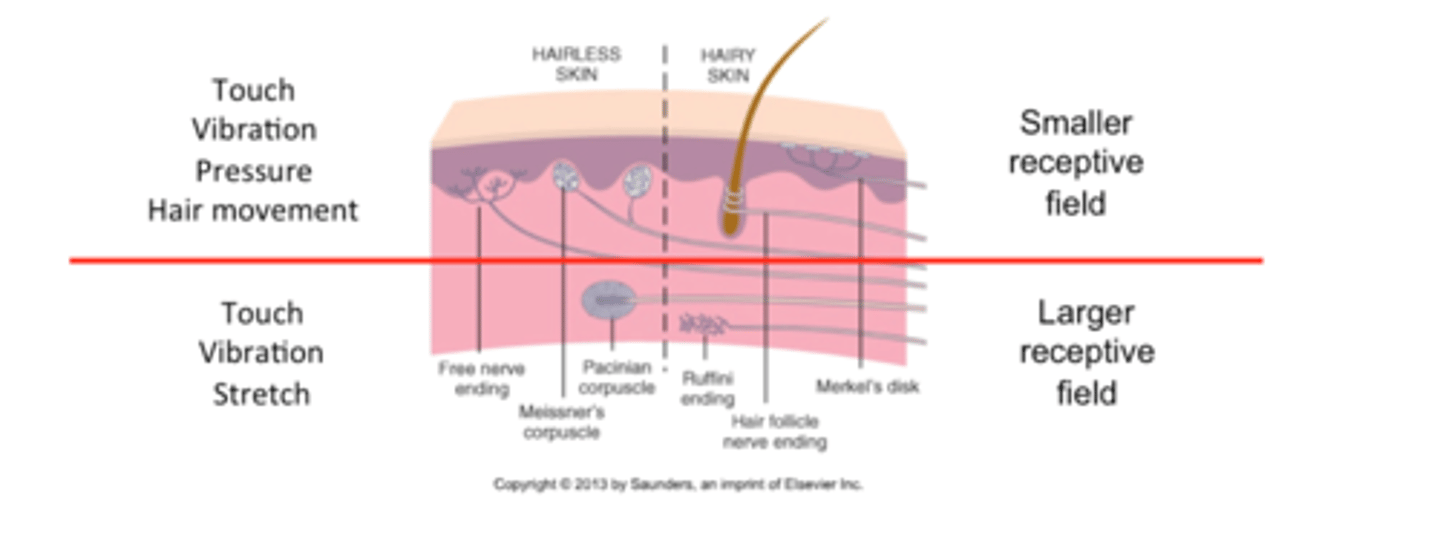
Fine touch: subcutaneous receptors
-pressure
-vibration
-skin stretch
What is temperature sensation? What is the clinical relevance?
thermal receptors detection of hot and cold
relevance
-important to test temp. sensation prior to applying thermal modalities
-important to determine safe temp for washing hands/bathing
-safety during meal prep
-compensatory strategies may be a priority (testing water temp with unaffected body part)
What is pain?
-unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage
-experience is subjective and multidimensional
-detected by free nerve endings
What is fast pain?
Pain that is sharp, intense, and easily localized
What is slow pain?
Pain that is dull, achy, and harder to localize
due to tissue damage
harder to localize due to various pathways used
fear, anxiety, and edema may worsen pain
T or F: Intact pain sensation is indicative of available protective sensation
true
What is proprioception?
-awareness of joint position in space due to musculoskeletal sensation
-encompasses joint position, muscle stretch, and deep vibration
-impacts motor learning and adaptation
-commonly affected by neurological disorders
compensatory strategy when impaired = use of vision
If __________ is impaired, it may be difficult to gauge how much pressure to use when holding a paper cup.
proprioception
What is the purpose of a sensory screening and evaluation?
-assesses the extent of sensory loss
-evaluates and documents sensory recovery
-assists in diagnosis
-provides prognostic information (rehab potential)
-determines impairment and functional limitations
-provides directions for OT treatment
How can OTs evaluate sensory function?
1) functional hand tests
2) simulated activities
3) ADL and IADL performance
we ideally want to complete all 3 bc it makes us more confident in our assessment and tx process
What are the basics of a sensory assessment?
-client must have adequate cognition
-vision must be occluded
-body part being tested must be supported w/o providing stimuli
-reduce environmental stimuli
-ensure clients ability to concentrate
-determine appropriate assessment tools
-use standardized methods of administration
Sensory test procedure/process
1) make sure client understands procedure
2) perform trial with vision
3) then perform trial with vision occluded
4) test unaffected side first
5) test affected side second
Sensory screening of the hand
specific sites can be used to reflect larger portions of the hand innervated by the same peripheral nerve
be sure to note and document the appearance of:
-blisters
-altered sweat patterns
-calluses
-scars
-wounds
-atrophy of thenar and hypothenar eminence
-shiny or dry skin
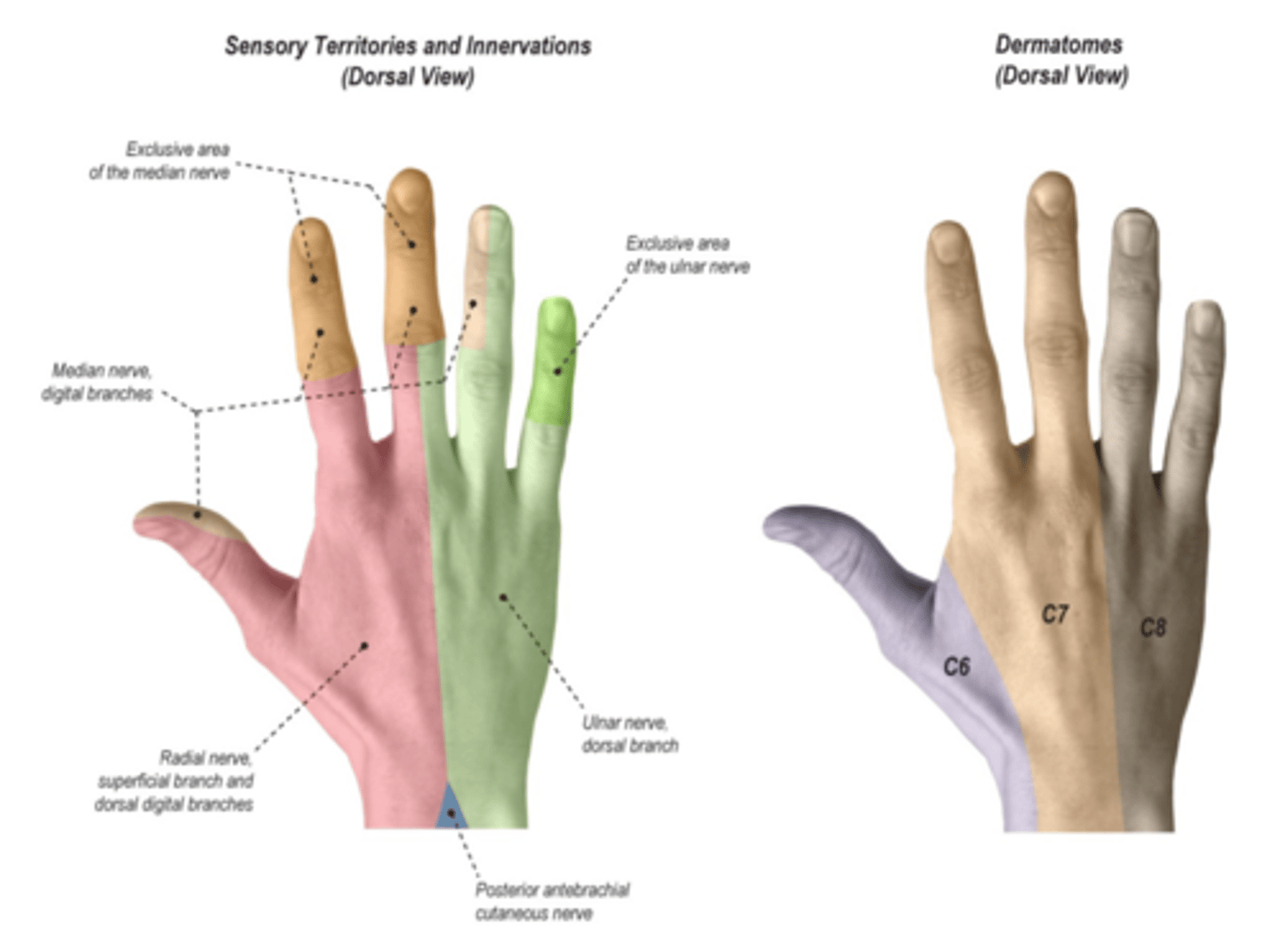
Median nerve screening
thumb tip, index tip, and index proximal phalanx
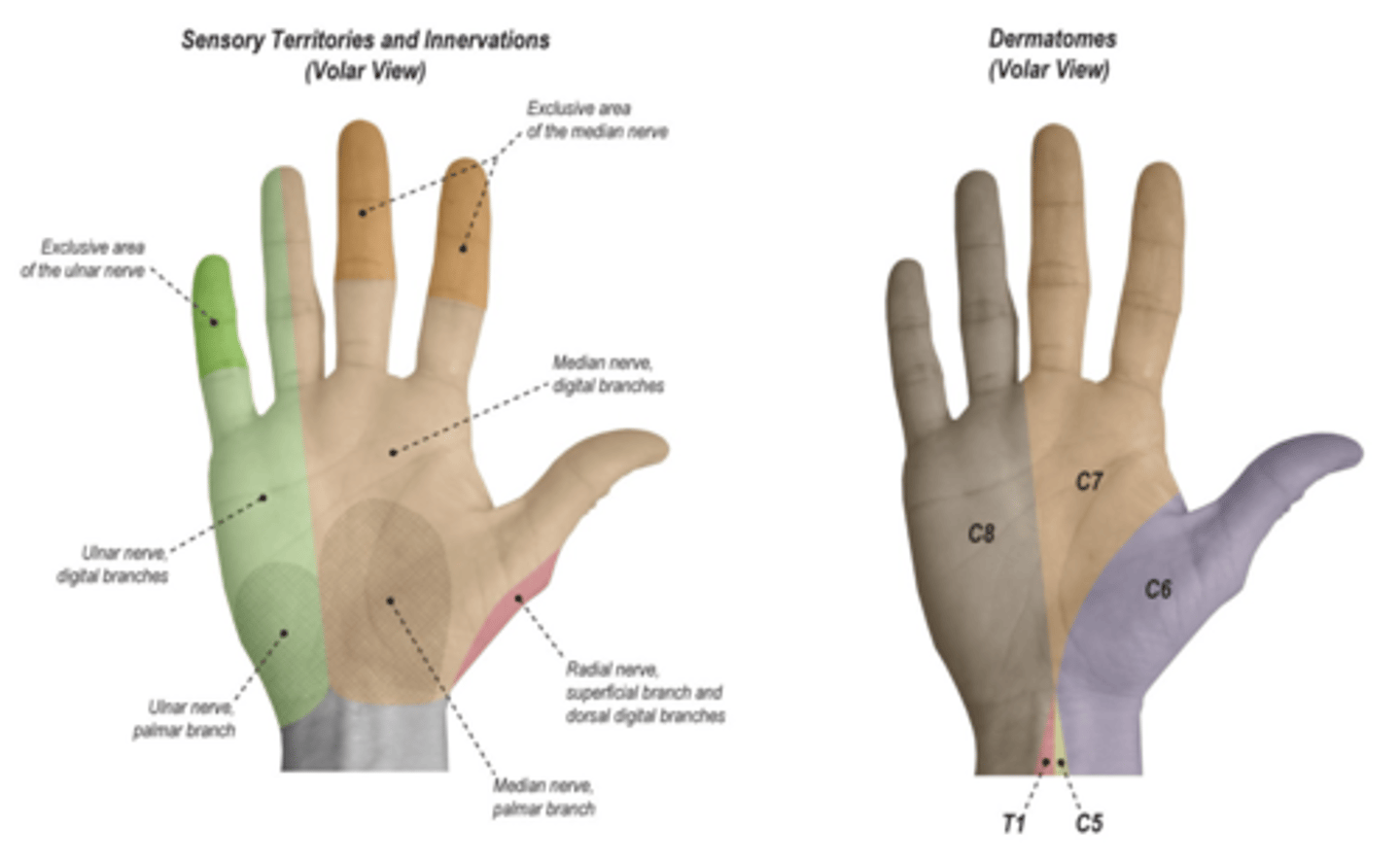
Ulnar nerve screening
small finger (pinky)
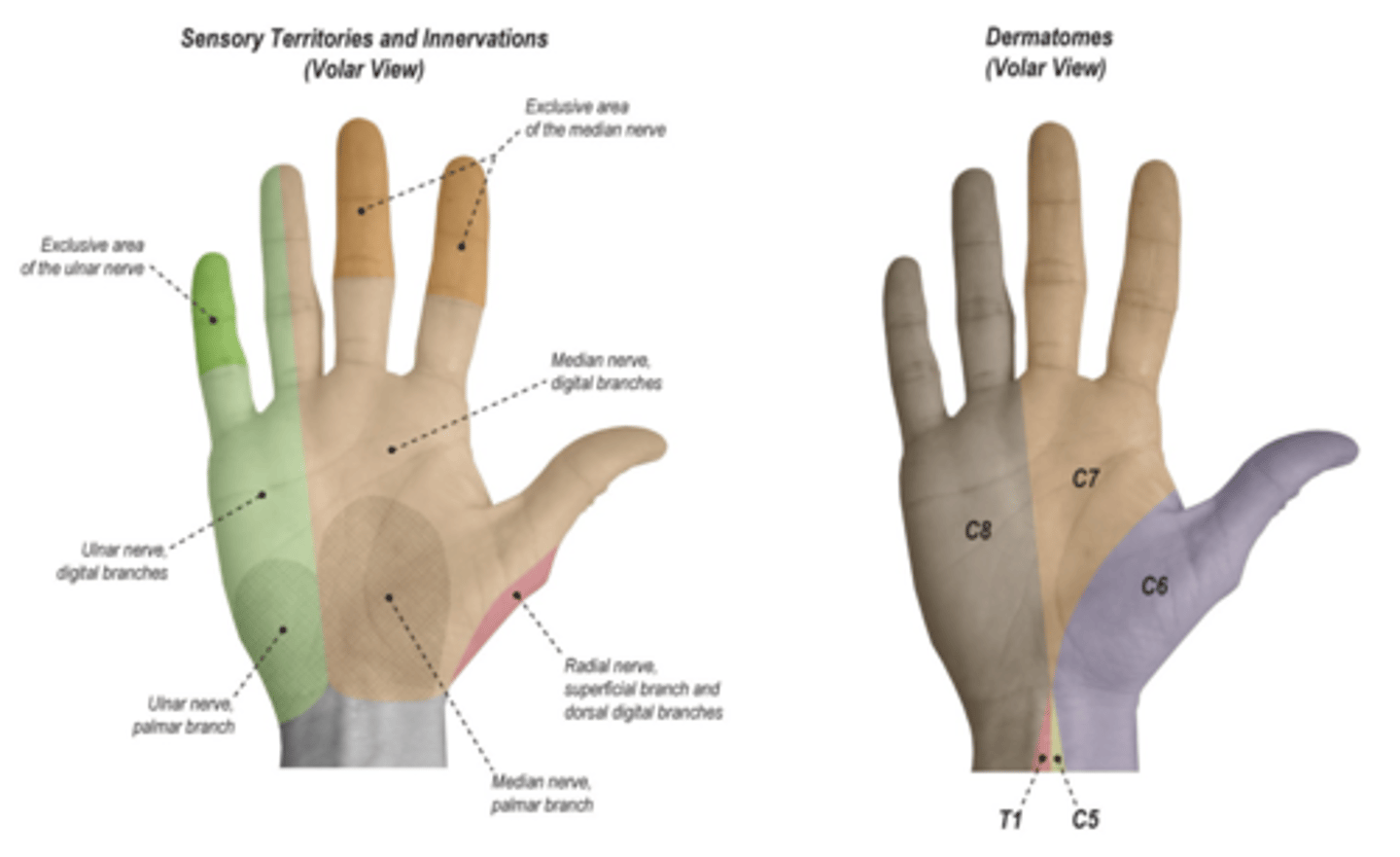
Radial nerve screening
radial back of hand, dorsal thumb web space
Standardized sensory tests
touch pressure
moving and static 2-point discrimination
point localization
vibration threshold
Non-standardized sensory tests
awareness of:
touch, pain, or pinprick
temperature
vibration
stereognosis
moberg pick-up test
proprioception
kinesthesia
Sensory threshold assessments
the least stimulus needed to elicit a response
i.e. light touch, vibration, cutaneous pressure
Tactile discrimination assessment
the number of sensory receptors in an area
i.e. moving and static 2 point discrimination
Proprioception evaluation
awareness of joint position in space
procedure
-vision occluded
-move joint into flexion/extension
-have patient replicate contralateral positioning
-client identifies positioning of joint
screening
-test distally, or more proximally if deficit is noted
Stereognosis evaluation (moberg pick-up test)
uses both touch and proprioception to identify an object in hand
procedure
-vision occluded
-familiar objects are placed in clients hand
-client manipulates object and is asked to identify object or its characteristics
client must have adequate motor function and communication skills

Touch pressure assessment (semmes weinstein monofilaments)
assesses touch pressure threshold – light touch and deep touch
categories
-green: normal
-blue: diminished light touch
-purple: diminished protective sensation
-red: loss of protective sensation
-untestable

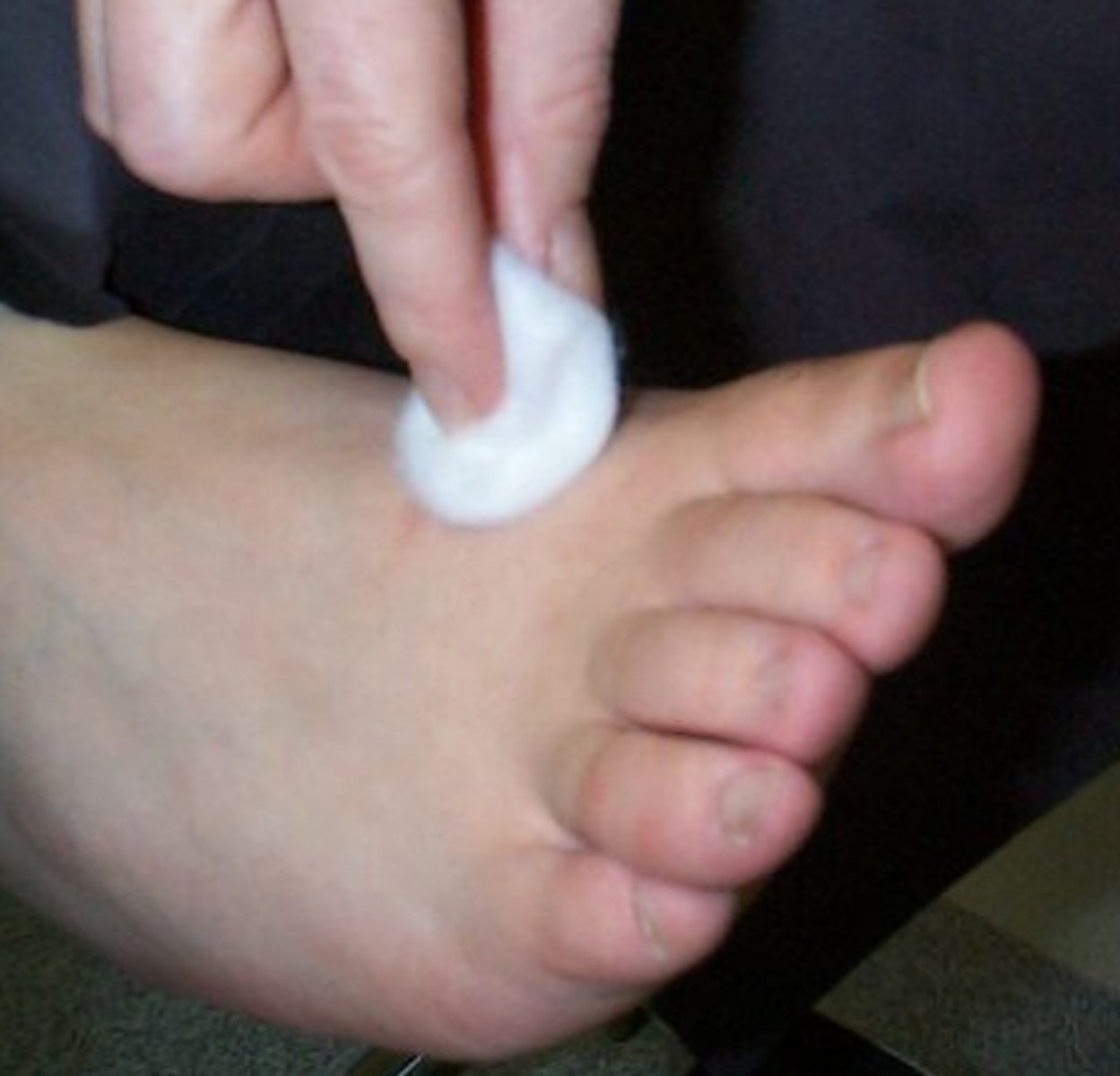
Light touch
-superficial skin receptors
-important for fine discriminatory hand use
-indicator of better sensation than having only deep touch pressure awareness
perceive touch through light pressure or use of a cotton ball
assessed with Semmes W. monofilaments
Deep touch
-subcutaneous touch receptor
-important for protective sensation
assessed with Semmes W. monofilaments
Semmes W. monofilaments: Green
normal - light touch and deep pressure WNL
Semmes W. monofilaments: Blue
diminished light touch – safety issue
(fine discriminatory = light touch)
Semmes W. monofilaments: Purple
diminished protective sensation – safety issue & inc. risk of injury
(protective = deep touch)
Semmes W. monofilaments: Red
loss of protective sensation – no response to any stimulus, huge safety issue
(protective = deep touch)
Nerve function tests
ninhydrin test
wrinkle test
nerve conduction studies