Organic Chemistry
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is Organic Chemistry?
The study of the different structures, properties and reactions of carbon containing compounds
Define: Homologous series
A family of compounds with similar chemical properties because they have the same functional group, and there is a trend in physical properties. Each member differs by an additional CH2
Define: Functional Group
A part of the molecule responsible for the characterisitic chemical reactions of a homologous series
Define: Molecular formula
Shows the number of each type of atom present in a molecule e.g H2 for a hydrogen molecule
Define: Structural Formula
More useful to see how exactly the different atoms are bonded together and in what order. (The drawn out formula)
Define: General formula
A simplified formula that shows how many of each type of atom you would have if there were n carbon atoms
Define: Hydrocarbon
A molecule only containing carbon and hydrogen atoms
What is Isomerism?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but with different structural formula.
Why do hydrocarbons have greater boiling points as they get larger?
The bigger the hydrocarbon, the more electrons are present, so intermolecular forces of attraction become stronger, meaning more energy is required to break them.
How is crude oil used to obtain hydrocarbons?
Crude oil is a very important mixture of hydrocarbons of varying lengths. There are many substances in the mixture which are used as fuels or the starting materials for the production for a variety of important chemicals. Crude oil can be separated by fractional distillation.
Name properties of short chain hydrocarbons.
- Made of smaller molecules
- Weaker intermolecular forces
- Lower boiling points
- More volatile
- Burns more easily, with clean flame
Name properties of long chain hydrocarbons
- Made of large molecules
- Stronger intermolecular forces
- Higher boiling points
- Less volatile
- Higher viscosity
How are alkane molecules separated through fractional distillation of Crude oil?
Crude oil is heated, which mostly vaporises.
- The smaller chains have lower melting points, so they rise as a gas in the fractional distillation column and do not condense. They can be used as refinery gas or gasoline
- The medium length chains require more energy, so they will rise less than the shorter chains. When they condense at their boiling point they can be used for Naphtha or kerosene
- The large chain molecules are the largest, and remain as sa liquid, and will fall to the bottom of the fractional distillation column
What are features of the alkane family?
- All hydrocarbons, have similar chemical properties, same general formula (CnH2n+2), homologous sequence, saturated (contains a C-C bond)
What are the features of the alkene family?
- homologous sequence, unsaturated (C=C), general formula = CnH2n
Describe a practical to determine between alkanes and alkenes
- Place 2 test tubes into a rack
- Place ~2ml of hexane into one, and ~2ml hexene into the other
- Add 5 drops of bromine water to each of the samples
- Cover with a bung and shake
- Record any colour changes
Name and explain the result for Alkane
The bromine water remains yellow, because Alkanes are saturated and cannot react with the bromine and decolourise it.
Name and explain the result for Alkene
The bromine water decolourises, as the C=C bonds break and react with the bromine
Give the formula for complete combustion
C3H8 + 5O2 -> 3CO2 + 4H20
Give the formula for substitution reactions
CH4 + Br2 -> CH3 + HBr
What are plastics?
Huge molecules made of polymers: long straight chain molecules. Polymers are made by linking together 1000s of small reactive molecules called monomers. The 2 types of polymers are Addition and Condensation polymers
What is addition polymerisation?
A reaction where many small molecules (monomers) join together to make a long chain polymer and nothing else.
Give the properties and a use of polyethene.
- It is flexible, cheap, and a good insulator
- Used in: Plastic Bags
Give the properties and a use of poly(chloroethene)
- It is tough, a good insulator, hard or flexible
- Used in: Insulation for wires
Give the properties and a use polytetrafluoroethene
- It is tough and slippery
- Used in: non-stick coatings in pans
Why can disposing of Addition polymers be difficult?
They are non-biodegradeable, which will not decay or be broken down by bacteria due to their inertness
What is cracking?
- It is a useful process in which long-chain alkanes (often from the naphtha and kerosene fractions) are broken into smaller ones.
- Conditons: pass vapour over a silica/alumina catalyst at 600-700°C
- Products: a mixture of shorter chain alkanes (useful for petrol) and alkenes (useful for making polymers and other chemicals)
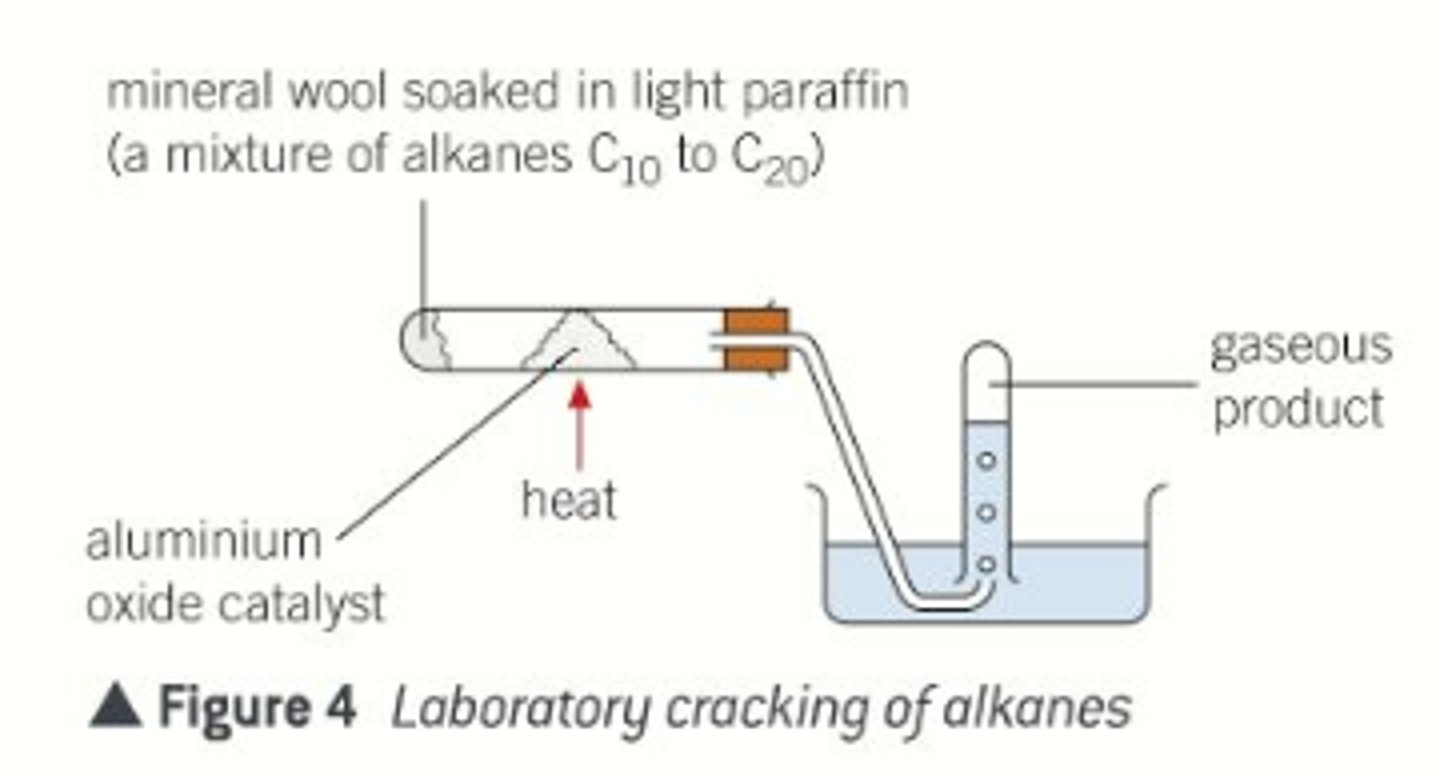
Why is cracking used?
For some hydrocarbons produced by distillation, such as petrol, the supply of it doesn't meet the demand - 18% produced but 22% demanded
Give a chemical formula for Long chain alkanes being cracked
C15H32 -> 2C2H4 + C3H8 + C8H18
How is Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed from Sulfur impurities in fossil fuels react with oxygen in air when burned
- SO2 causes acid rain
- Solution: Flue gas desulfurisation or removing Sulfur from fuel before turning
How is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed by complete combustion
- Traps heat in atmosphere, causing global warming
- Solution: Burning less fossil fuels
How is Water vapour (H2O) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed by complete combustion
- Water vapour is a greenhouse gas causing global warming
- Solution: Not a big issue because it does not remain in the atmosphere for a long time
How are Nitrogen oxides (NO/NO2) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Nitrogen reacts with oxygen in the presence of high heat caused by engines
- Forms nitric acid -> acid rain
- Solution: Catalylic converter
How are unburned fuels formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed because not all fuel burns
- Harmful + greenhouse gas
- Ensure correct fuel:air mixture when burned
How is Carbon monoxide (CO) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed through incomplete combustion
- Toxic as it binds to haemoglobin, preventing us getting oxygen resulting in suffocation
- Solution: Ensure good supply of air when burned
How is Carbon (C) formed; problems with it and solutions to those problems?
- Formed by incomplete combustion
- Blackens buildings, air pollution
- Solution: Ensure good supply of air when burned
What is Ethanol used for?
Alcoholic drinks contain a substance called ethanol. Ethanol can also be used as a fuel for vehicles and as a raw material for the chemical industry.
What is fermentation?
Plant material containing sugars is mixed with water and yeast. Enzymes in the yeast turn the sugars into ethanol and CO2, through the use of anaerobic respiration.
Fermentation only produces alcohol up to 15%, as higher concentrations kill the yeast cells
What are the conditions under which fermentation occurs?
- pH level monitored
- 30-40°C
- Air lock in the apparatus allows CO2 to escape while keeping air out, since anaerobic respiration only occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Why can fractional distillation be used to increase concentration of alcohol?
The boiling point of ethanol is 78°C, so 96% of the pure ethanol can be separated from the remaining water.
Describe how ethanol can be produced through hydration of Ethene.
- Ethene reacts with steam to produce ethanol in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst
- The reaction involves passing the ethene and steam vapours over the catalyst at a temperature of about 300°C and a pressure of 60-70 atmospheres
- Only a small percentage of the ethene reacts. The ethanol is condensed as a liquid and the unreacted ethene is recycled through the process
What reactions does ethanol undergo?
- Combustion
- Ethanol produced via fermentation can be used as biofuel
- Undergoes dehydration reactions to produce ethene (similar to those used to crack alkanes). Ethanol vapour is passed over an aluminium oxide catalyst
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Availability of raw materials
[Fermentation] Materials are plants with glucose e.g sugarcane, wheat and yeast. Available to a poor country with lots of fertile land
[Hydration of Ethene] Ethene, Steam and a Catalyst
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Production of raw materials
[Fermentation] Growing crops such as sugarcane; fermentation is renewable
[Hydration of Ethene] Ethene is made from cracking crude oil, which is not renewable
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Energy involved in production of ethanol
[Fermentation] Occurs at a low temperature (30-40°C) not much energy needed and is cheaper
[Hydration of Ethene] 300°C and 60-70 atmospheres. High temperature and pressure is expensive
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Atom economy
[Fermentation] 51.1% is useful, if a use for CO2 is found it is 100%. It produces a lot of waste. Co2 can be used for fizzy drinks
[Hydration of Ethene] Ethanol is the only product (100% atom economy) - pure ethanol is made and doesn't require fractional distillation
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Yield
[Fermentation] Low yield as it is a batch process, as fermentation slows down as the substrate is completed
[Hydration of Ethene] Ethene and steam are passed over the catalyst until they all react - high yield
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Rate of Reaction
[Fermentation] Slow process that gets slower
[Hydration of Ethene] Fast and continuous process
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Equillibrium position
[Fermentation] Usually shifts right but can shift left if the solution is exposed to oxygen and switching to respiration
[Hydration of Ethene] Fast and continuous process
Compare Fermentation and Hydration of Ethene: Uses of the ethanol
[Fermentation] Spirits and other alcohols
[Hydration of Ethene] Fuels, solvents
How are carboxylic acids produced?
When alcohols are left open to the air, they become oxidised: Ethanol + oxygen -> Ethanoic acid + water
Describe the formula and structure of Carboxylic acids
They are a homologous group series that contains the -COOH functional group e.g ethanoic acid = CH3COOH
Give properties of Carboxylic acids
- Form acidic solutions (pH less than 7)
- React with metals to form a salt and hydrogen
- React with bases to form a salt and water
- React with carbonates to form a salt, water and carbon dioxide
How are esters formed?
Esters are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol (in the presence of a catalyst)
How the reaction between Ethanoic acid and Ethanol a condensation reaction?
Produces water
How do you name esters?
1st part - Alcohol (ethanol -> ethyl)
2nd part - Acid (ethanoic acid -> ethanoate)
Describe a practical to make esters
- Add 10 drops of carboxylic acid to 1 drop sulfuric acid in the test tube
- Add 10 drops of alcohol to the mixture
- Put 50cm3 boiling water and stand the test tube upright in the water
- Leave to stand for 1 minute in the hot water. If the mixture boils, lift out of the water using tongs
- Pipette in NaCO3 until half full when cooled. Place a test tube and mix gently
- Waft the ester towards you
What is a polyester?
A polyester is a long chain molecule where the monomers are joined together using ester links. They are syntheic molecules made via a condensation reaction, in which the monomers join together and eliminate a small molecule such as water.
Give a reaction for a polyester.
Hydrolysis reactions take place when water is added, so the opposite reaction takes place, resulting in the polyester breaking down