Medication Use Process, Laws, Safety & Hospital Pharmacy
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
337 Terms
What are the components of the medication use process?
Prescribing, Order Verification/Transcribing, Dispensing, Administer, Monitor
What is the definition of prescribing in the medication use process?
Select medication based on patient assessment, then send order to pharmacy.
What extra steps are involved in the prescribing process?
Evaluate indication for treatment, consider treatment options, determine formulation, route, dosage, write prescription, and assess patient access.
What health information technology supports the prescribing process?
Alerts for medication indication, warnings for dose range and interactions, order sets, and order defaults.
What is the pharmacy's role in the prescribing process?
Pharmacists maintain medication order catalog, set order defaults, provide clinical decision support, and may independently prescribe under collaborative agreements.
What is the definition of order verification/transcribing?
Enter medication order into pharmacy computer, assess appropriateness, and address discrepancies.
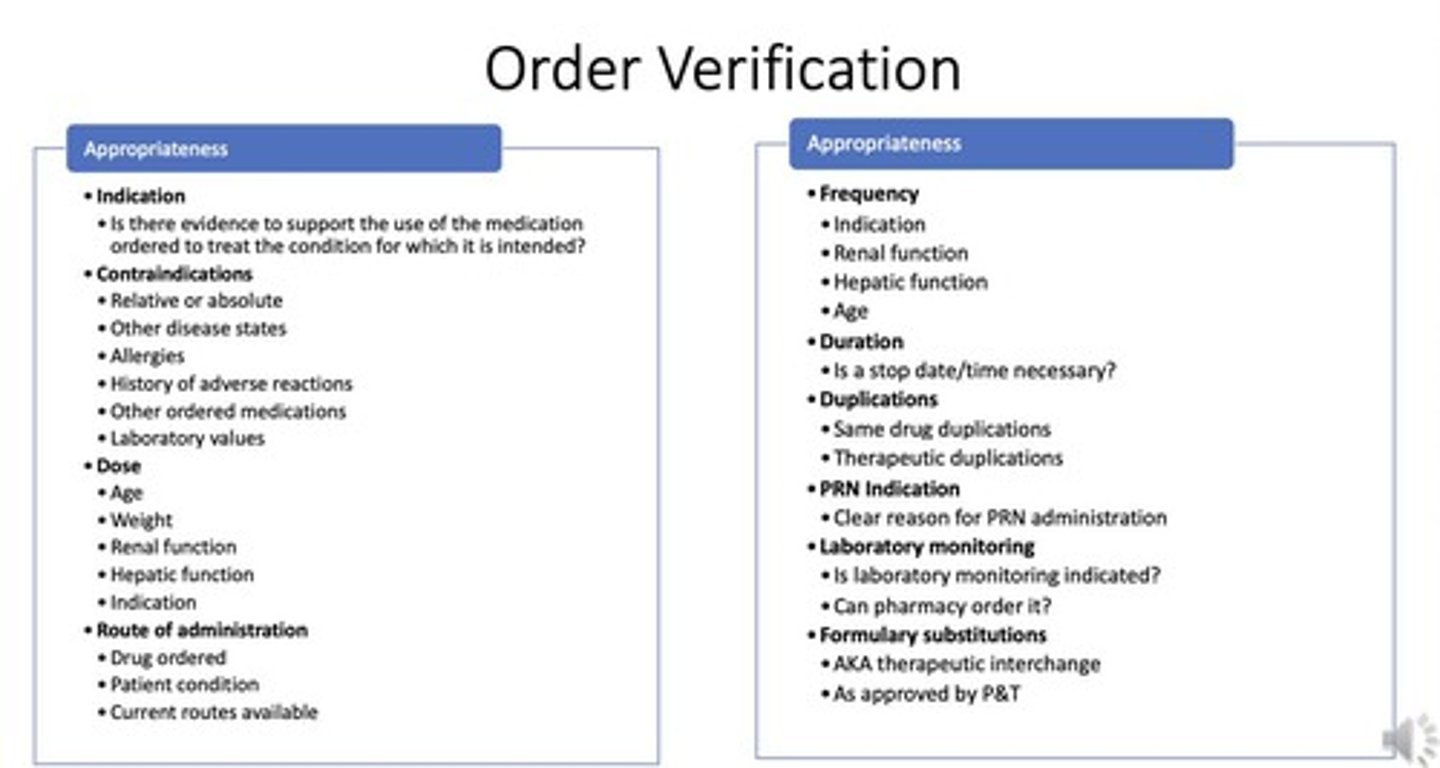
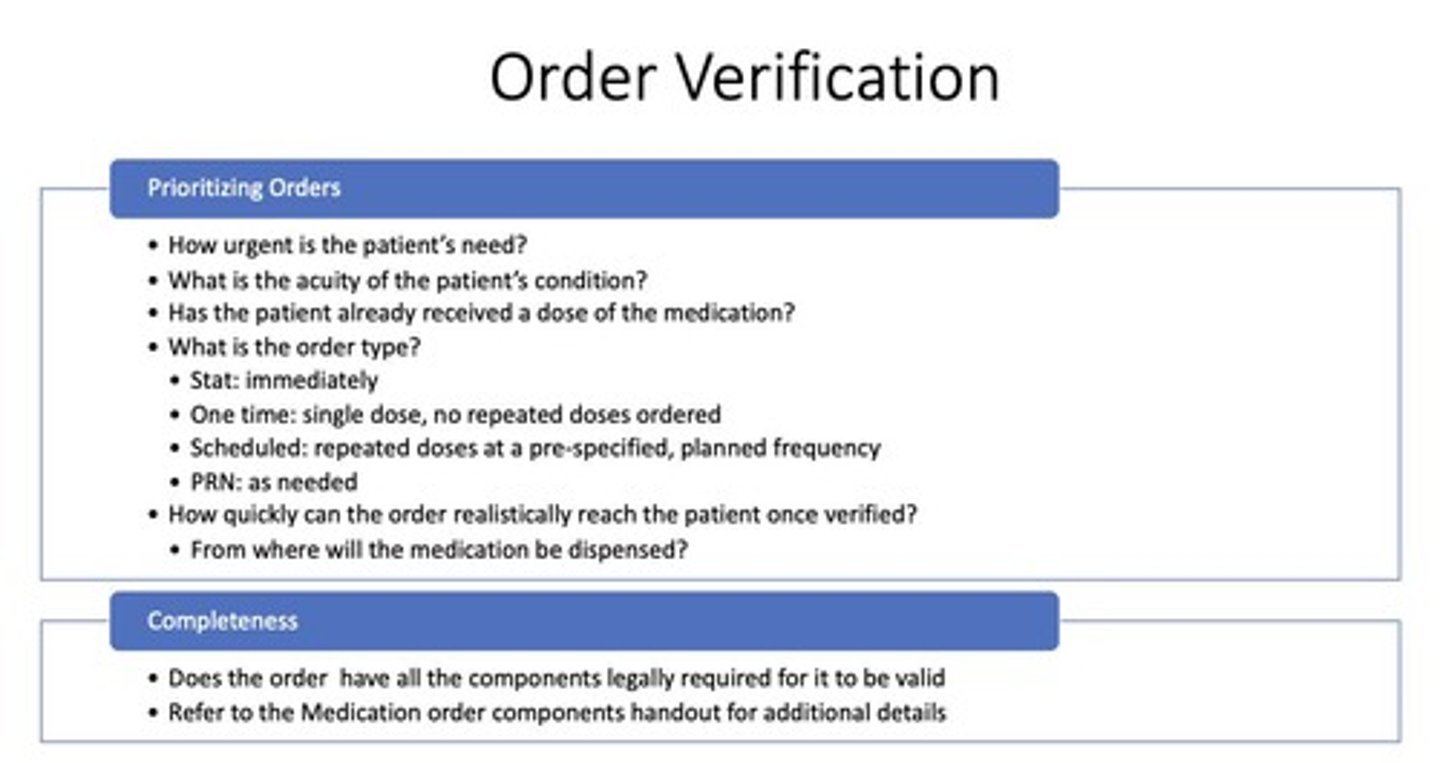
What extra steps are involved in order verification/transcribing?
Enter/copy order into pharmacy system, evaluate clinical appropriateness, select product/location, and generate product label.
What health information technology supports order verification/transcribing?
Automated product selection, warnings for dose range and interactions, and linking lab information to order verification.
What is the pharmacy's role in order verification/transcribing?
Pharmacists and technicians manage order transcription and verification, ensuring correct products and appropriate labeling.

What is the definition of dispensing in the medication use process?
Prepare and distribute medication from the pharmacy to the patient or healthcare provider.
What extra steps are involved in the dispensing process?
Obtain product, verify correctness, collect measuring devices, prepare drug, affix labels, and dispense to appropriate person/location.
What health information technology supports the dispensing process?
Bar code assisted preparation, camera technology for observation, gravimetric technology for QA, and technology-assisted medication cabinets.
What is the pharmacy's role in dispensing?
Pharmacists and technicians prepare doses, ensuring the end user has necessary administration tools, often using automated dispensing cabinets.
What is the definition of administering medication?
Review appropriateness of medication, which is then given to or taken by the patient.
What are the steps involved in the administration of medication?
Identify the need for administration, procure the product, complete any additional preparation, prepare the patient, and then administer the drug.
How can Health Information Technology support medication administration?
An electronic medication administration record (MAR) helps track doses, bar coded medication administration prevents errors, and documentation interfaces support administration personnel.
What is the pharmacy's role in medication administration?
Pharmacists rarely administer medications but support safe administration by providing instructions and developing support for end users, commonly administering vaccines in community settings.
What is the definition of monitoring in medication administration?
Assess patients' response to the medication and document outcomes, making further interventions as needed.
What are the extra steps involved in monitoring medication?
Identify monitoring parameters, collect baseline levels, set therapy goals, place and carry out monitoring orders, and share results with providers.
How does Health Information Technology support monitoring of medications?
Links medication orders to monitoring parameters, displays labs within the ordering screen, and sends automated messages to providers when parameters exceed thresholds.
What is the pharmacy's role in monitoring medication effects?
Clinical pharmacists share responsibilities for monitoring drug effects, especially for high alert medications, and are involved in monitoring adherence in ambulatory environments.
What is the purpose of the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCA)?
To protect consumers against counterfeit, stolen, or contaminated drug products and enhance the FDA's ability to identify and trace prescription drugs across the US.
est: November 27th, 2013.
What standards does the DSCA establish for wholesale distributors and third-party logistic providers?
National licensure standards and annual licensure status reports.
What are the primary responsibilities of Drug Procurement Officers (DPO)?
Drafting medication orders, ensuring alignment with budget, reviewing purchase orders, maintaining accurate records, and tracking drug recalls or shortages.
What must a pharmacy use to purchase Schedule II (CII) medications?
DEA Form 222, which can only be ordered by a registrant or individual with Power of Attorney.
What information must be included in orders for CII medications?
Name of drug, National Drug Code (NDC), strength, package size, number of packages, number of lines completed, signature of authorized purchaser, DEA number, and issue date.
What is the Controlled Substances Ordering System (CSOS)?
An electronic system that allows purchasers to order CII medications without a paper DEA Form 222, requiring registration with the DEA.
What is the role of the pharmacist in the drug procurement process?
To ensure that all medication orders are correct and to verify medications as they move throughout the hospital.
What is the first step in the drug ordering process?
Drafting medication orders by the Drug Procurement Officer.
What should the Drug Procurement Officer do when there is a drug shortage?
Communicate with the drug shortage team to find alternatives.
What must the drug procurement team verify upon receiving a medication order?
The drug product received, drug strength, drug formulation, drug NDC (bar code), and drug quantity.
What are the six rights the pharmacist must verify when medications move from the Central Pharmacy?
Right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right quantity, and right location.
How are medications processed for restock into automated cabinets?
In a non-patient specific batch.
What is the difference between non-patient specific and patient-specific medication batches?
Non-patient specific batches are for restocking automated cabinets, while patient-specific batches provide medications for a certain time period for individual patients.
What are some common components of drug storage?
Inventory control, record keeping, and handling.
What is the significance of the NDC in medication orders?
It serves as a unique identifier for the drug product.
What is the responsibility of the Drug Procurement Officer regarding purchase orders?
To review them and ensure they are accurate in accordance with federal and state regulations.
What is a key aspect of the communication role of the Drug Procurement Officer?
To serve as a point of contact for suppliers and distributors of medicines.
What must be checked when verifying received medications?
The drug product received, strength, formulation, NDC, and quantity.
Where are medications first processed before being moved to appropriate locations?
In central pharmacy.
Where are most medications found in a hospital?
In automated dispensing cabinets on each hospital unit.
What types of doses can be kept in automated dispensing cabinets?
Unit doses.
What is one responsibility of technicians regarding medication cabinets?
Removing expired medications daily.
What requires increased scrutiny in all storage locations?
Controlled substances.
What must be maintained for all controlled substances?
An accurate 'on hand' amount, the inventory date must reflect the actual date of the physical count, Records must be maintained at the DEA registered location, On hand physical inventory count is required annually
What is the minimum record retention period for written and verbal prescriptions?
No less than 5 years.
What must electronic records of prescriptions contain?
All required information of a manual record.
-NDC, strength, formulation, quantity, if product was recived
What capability must a data processing system have regarding electronic records?
It must be capable of producing a hard copy upon request.
What is a requirement for an electronic system regarding original images?
It must not allow adulteration of original images.
Who is responsible for keeping controlled substance records?
The DEA registrant.
What are the requirements for Controlled Substance Record Keeping (CSR)?
Records must be complete, accurate, stored at the DEA registered location, easily retrievable, and kept on site for a minimum of 2 years.
What is a drug recall as defined by the FDA?
An action executed by a manufacturer to remove a defective or harmful drug product from the market.
How are most drug recalls communicated to patients?
Most patients receive notification from the manufacturer, their healthcare provider, or their pharmacy.
Where are drug recalls posted weekly?
In the FDA Weekly Enforcement Report, classified based on level of hazard.
What are the three classes of drug recalls?
Class I: Dangerous products that could cause serious health problems or death. Class II: Products that might cause temporary health problems or pose a slight threat. Class III: Products unlikely to cause adverse health reactions but violate FDA laws.
What is the first step in the drug recall process?
The purchasing officer will initiate the recall process.
What happens to recall items after they are returned?
They will either be destroyed or returned to the manufacturer as per the manufacturer's instructions.
What act was passed in response to the increase in drug shortages?
The Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act (FDASIA) was passed on July 9th, 2012.
What did FDASIA require manufacturers to do regarding drug shortages?
Manufacturers must notify the FDA of any discontinuation or interruption of production of lifesaving or life-sustaining drugs.
What is one strategy pharmacists can use during a drug shortage?
Create a drug shortage production team comprised of an interdisciplinary team to make decisions and relay information.
What should be assessed during a drug shortage?
The cause and duration of the drug shortage, and the current drug inventory on hand.
What should pharmacists avoid during a drug shortage?
Stockpiling medications, as it can exacerbate the shortage and disrupt distribution.
What is the role of distributive pharmacists?
They are more operations-focused, overseeing medication preparation, dispensing functions, and automation responsibilities.
What is the purpose of the Drug Shortage Database?
To keep the public updated on drug shortages.
What should be established for drugs with no therapeutic interchange during a shortage?
A protocol for drug allocation based on ethical considerations.
What technology was created to inform the public about drug shortages?
CDER Direct, a new reporting platform and mobile app.
What should be done to prioritize patients during a drug shortage?
Create a list of which patients are prioritized to receive the drug first.
What is one factor contributing to drug shortages?
Manufacturing and quality problems.
What is the role of a resource allocation team during a drug shortage?
To oversee the allocation of drugs.
What should be communicated to patients affected by a drug shortage?
Disclosure of the drug shortage and counseling on how it may compromise or delay care.
What is one action to take regarding therapeutic alternatives during a drug shortage?
Create a list of approved therapeutic alternatives.
What is the purpose of the Recall Tracking Sheet?
To track responses to the recall notice.
What are the primary functions of clinical pharmacists?
Clinical pharmacists engage exclusively in clinical activities with medical teams on patient care units, with little or no responsibility for medication use or delivery systems.
What is the role of medication automation technologies in pharmacy?
Medication automation technologies minimize human input, reduce workload, improve security tracking and accountability, and enhance patient safety and outcomes.
What are Automated Dispensing Cabinets (ADCs)?
ADCs are computerized medication storage bins located near point of care that track expiration dates and drug inventory.
What is Bar Code Medication Administration (BCMA)?
scanning verifies the right patient and the right drug.
What are some examples of brands that provide Automated Dispensing Cabinets?
Examples include Pyxis, Omnicell, and AcuDose.
What is the purpose of a carousel in pharmacy automation?
A carousel optimizes limited space in the pharmacy for medication storage and dispensing, used for STAT meds, new orders, and ADC refills.
How does the pick-to-light system in a carousel work?
The carousel spins to the correct bin and lights up on the work surface to highlight the bin.
What is the function of a Pneumatic Tube System in pharmacy?
It sends and receives materials quickly, securely, and safely, eliminating the need for manual transport of medications.
What types of medications should not be transported via Pneumatic Tube Systems?
Chemotherapy, narcotics, hazardous, flammable medications, and insulin should not be transported through Pneumatic Tube Systems.
What are the key requirements for the Illinois Automated Dispensing and Storage Systems Code?
ADC documentation must include pharmacy name and address, manufacturer name and model, and QA policy and procedures.
What must be ensured before using Automated Dispensing Cabinets?
ADCs require verification by pharmacists
What security measures must be in place for Automated Dispensing Cabinets?
ADCs must have adequate security systems
What information must electronic records for ADC transactions include?
Records must include ADC ID#, employee ID#, type of transaction, drug details, patient name, restocking technician, and pharmacist-in-charge.
Who is ultimately responsible for the accuracy of restocking ADCs?
The pharmacist-in-charge (PIC) is ultimately responsible for accuracy.
What packaging requirement must all medications in ADCs meet?
All meds must be single unit dose
What tracking system must ADCs have?
ADCs must have a tracking system to account for all drug movements, including dispenses, returns, and waste.
What quality assurance measures are necessary for ADCs?
safety, accuracy, and security monitors to prevent errors and unauthorized access.
What records must be maintained for ADCs and for how long?
Medication records must be maintained for at least 5 years.
What are the benefits of medication automation technologies?
speed, ease of dispensing drugs, and time savings.
What are the limitations of medication automation technologies?
Human error, no room for variety, maintenance, and cost
What are the key roles found in both distributive and clinical pharmacy services?
med safety, verifying meds, provide drug info, monitor therapy, educate pts
What is the role of the Joint Commission in hospital accreditation?
The Joint Commission (TJC) is an independent, not-for-profit organization founded in 1951 that sets standards and accredits healthcare organizations and programs across the US, ensuring compliance with Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) standards.
What are the benefits of medication pre-packing in non-patient specific batches?
Medication pre-packing saves time in drawing up doses for commonly used medications (store for future use)
How does automation technology improve medication management?
Automation technology is more accurate than human processing, enhancing safety in medication management.
What security measures are associated with Automated Dispensing Cabinets (ADCs)?
ADCs can only be accessed by authorized staff, are often locked, and have features to combat diversion, such as a count back when accessing controlled substances.
What is a limitation of Automated Dispensing Cabinets (ADCs) regarding human error?
ADCs are not immune to human error; if the wrong medication is placed in the ADC, it will continue to dispense incorrectly until corrected.
What is a limitation of ADCs in terms of medication variety?
ADCs are effective for routine medications but require medications that are not commonly used to be sent from Central Pharmacy.
What maintenance challenges do Automated Dispensing Cabinets (ADCs) face?
Repairs can be lengthy and costly, as specialized technicians may be needed for software issues.