GEOG 1401 Exam 4 Review
1/158
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Glacier
Accumulation of ice affected by past/present movement.
Continental glaciers
Cover large areas.
Alpine glaciers
Found in mountainous areas.
Pleistocene
Ice ages.
Holocene
Present interglacial.
Accumulation
Gain. Snow, rain, avalanches.
Ablation
Loss. Melting, sublimation calving (results in icebergs).
Mass balance
Accounting system for gains/losses of ice.
Plucking
Ice at base melts, liquid water gets in bedrock cracks and freezes, rocks break free and get carried away by ice.
Scour
Rock particles at base erode bedrock surface.
Abrasion
Colliding particles break down. Size decreases downstream and becomes more rounded.
Cirque
At an upper Alpine glacier, plucking erodes headwall which forms an amphitheater/bowl shape.
Arête
Adjacent cirques may form a sharp ridge.
Horn
¾ cirques may form a sharp peak.
Hanging valley
After glaciers go away, tributary valleys may be at different levels.
Lateral moraine
Sediment is dropped on the side of a hill slope.
Drumlin
Streamlined hill formed under glacier, often found in groups.
Kettle
Block of ice buried by sediment. When ice melts, depression remains.
Esker
Sinuous ridge of sediment deposited by stream under ice.
Erratics
Boulders deposited far from bedrock source.
Isostatic rebound
When ice leaves, crust rises because the weight of the ice makes the crust sink.
Periglacial
Cold but not covered by ice.
Permafrost
Permanently frozen ground– most soil moisture doesn’t melt.
Patterned ground
Polygons develop on ground surface.
Tides
Sea level rises/falls twice in over 24 hours, monthly variation too.
Cause of tides
Earth’s rotation and gravitational attraction of sun and moon.
Spring tides
Sun/Moon align. Highest tides of the month. Full/new moon.
Neap tides
Sun/Earth/Moon make right angle. Lowest tides of the month. Quarter moon.
Relationship between ice ages and sea level?
Ice ages store more water on land which means there’s less water in oceans.
Submergent/Subsidence of coasts
Relative rise in sea level.
Emergent/Uplift of coasts
Tectonic uplift = relative drop in sea level.
Wind waves
Wind transfers some kinetic energy to water and a wave develops. Energy travels, water doesn’t. Only extent to a depth of about one-half wavelength.
Tsunamis
Different kind of wave caused by earthquakes, landslides, or volcanoes. Low height over deep water, very high at coast.
Factors of wave size
Wind speed, wind duration, and fetch: distance wind blows over water.
Wave breaking
In shallow water, waves deform because they lost contact with sea floor. Water falls over because it’s too steep.

Wave refraction
Bending of waves as they approach the shore.
Longshore drift
Acts like a stream and carries sand.
Beach drift
Water and sand rush up beach at an angle, return straight down.
Littoral drift
Beach drift + longshore drift =
Wave cut platforms
On cliff coast, waves hit base, eroding it into a wave-cut notch. Cliff eventually falls and retreats over time.
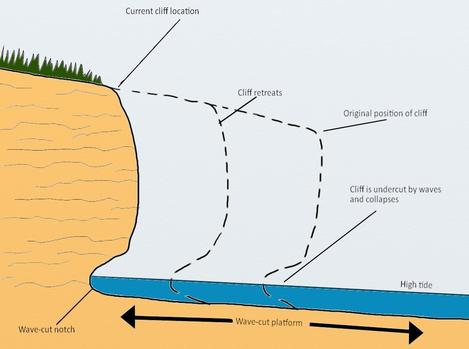
Marine terraces
Elevated platforms above sea level.
Erosion of headlands
Headland: Bedrock jutting out from coast, refraction makes waves hit side.
Leads to distinctive landforms like caves, arches, and stacks.
Summer beach
Season of small waves. Sand pushed back onto beach = broad beach.
Winter beach
Season of big waves. Sand eroded off beach and deposited offshore = small beach.
Spit
Sand grows out into water at coast indention.
Barrier beach
Drifting sand blocks stream mouth.
Tombolo
Spit connects mainland and island.
Human impact on beaches
Damming streams cut sediment supply to beaches.
Seawalls can cause erosion on seaward side.
Groins and jetties build up beaches but cause erosion elsewhere.
Beach nourishment: Artificially bring sand to beaches.
Barrier islands
Narrow islands parallel to mainland, protects from big waves.
Texas beaches
Relative sea level rise of 0.5-1 cm/yr.
Subsidence is about 5mm/yr.
1-2m of erosion/yr.
Fringing reef
Connected to land.
Ria coasts
Drowned stream valleys.
Fiord/Fjord coasts
Sea fills glacial valleys.
Safety factor
Measure of slope stability.
Decreasing slope resistance
Nature– streams and waves.
People– Road/house building.
Swelling clays– Can weaken hillside if they’re between rock layers.
Weathering– Frost action/salt crystal growth weakens rocks.
Removing vegetation– Roots hold soil and rock.
Increasing slope angle– due to tectonics or humans.
Increasing force
Adding weight to hillside like water in soil or buildings.
Creep
Slow movement of materials downslope.
Fall
Pieces break off and fall down.
Slide
Downslope movement along flat surfaces. Usually associated with rock layers.
Slump
Movement along a curved surface. Usually associated with thick, cohesive soils.
Flow
Materials move like a fluid.
Karst
Terrain dominated by solution processes and resulting landforms.
Solution (weathering)
Minerals dissolved in acidic water.
Rock types involved in solution
Limestone, dolostone, salt, and gypsum.
Solution sinkholes
Acidic surface water dissolves rock, depression gets bigger over time.
Collapse sinkholes
Subsurface water dissolves opening, surface ground collapses– often occurs after water table drops.
Tower karst
Sinkholes grow and merge leaving steep, remnant hills. Limestone may weather away.
Travertine deposits
Calcium carbonate features deposited in caverns.
Elastic deformation
Rock that’s stretched/compressed, but returns to original shape in reaction to stress.
Plastic deformation
Rock that takes on and keeps a new shape in reaction to stress.
Rupture
Rock breaks in reaction to stress.
Plateau
Region pushed up evenly.
Dome
One area pushed up higher than surroundings.
Basin
One area drops more than surroundings.
Folding: Anticlines
Area curves up like a hill.

Folding: Synclines
Area curves down like a valley.

Folding: Monoclines
Area is straight, curves up sharply, then evens out.

Faults: Normal
Pulling apart. Side going up moves away from side going down.
Faults: Reverse
Compression. Side going up climbs over side going down.
Faults: Transform
Horizontal movement.
Faults: Oblique
Some horizontal movement, some vertical movement.
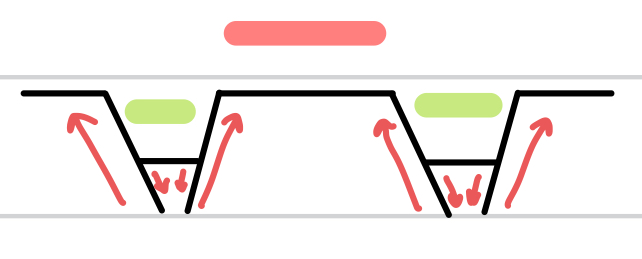
Horsts
Valleys.
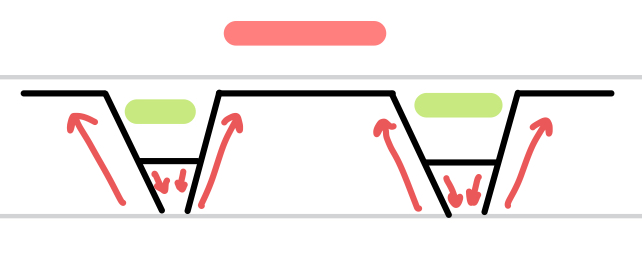
Grabens
Mountains.
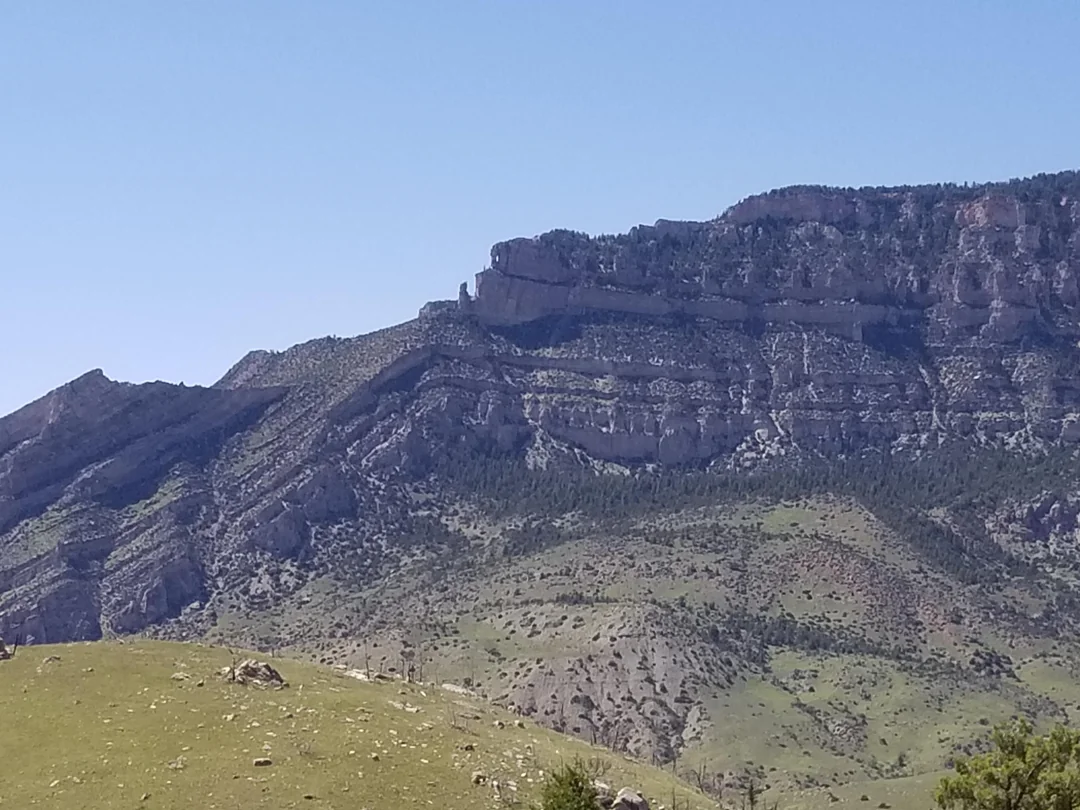
Cuestas
Ridge made of resistant layers.
Caprock: Mesa
Flat topped hill made from caprock.
Caprock: Butte
Narrow mesa.
Drainage pattern: Dendritic
No structural control.
Drainage pattern: Radial
Radiates from high point.
Drainage pattern: Centripetal
Converges on low point.
Drainage pattern: Rectangular
Stream follows rock fractures.
Drainage pattern: Deranged
Poorly organized drainage.
Drainage pattern: Trellised
Main stream in valleys. Tributaries off ridges.
Batholith
Large mass of intrusive, igneous rock.
Dike
Vertical, small scale intrusion.
Sill
Horizontal, small scale intrusion.
Lava: Aa
Rough lava surface.
Lava: Pahoehoe
Smooth lava surface.
Volcanoes: Fissure
Lava flows out of a fracture in a rock.
Volcanoes: Shield
VERY large oceanic volcanoes.
Volcanoes: Composite
Large, continental volcanoes with pyroclastic explosions.