Bio 198 Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Last updated 7:50 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
radial symmetry
circularly organized (ex. coral, starfish, jellyfish)
2
New cards
bilateral symmetry
left and right halves (ex. humans
3
New cards
asymmetry
no symmetry
4
New cards
3 germ layers
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
5
New cards
ectoderm
outside layer (ex. skin)
6
New cards
mesoderm
middle layer (ex. muscle and bones)
7
New cards
endoderm
inner layer (ex. intestines and organs)
8
New cards
3 types of body cavities
coelom, pseudocoelomate, Acoelomate
9
New cards
coelom
fluid filled space around internal organs, mesoderm holds organs in place
10
New cards
pseudocoelomate
fluid filled space around organs, organs not anchored by mesoderm
11
New cards
acoelomate
no cavity
12
New cards
advantages to a body cavity
flexibility, evolve easier, more complex structures, protection, anchoring
13
New cards
segmentation
body is divided into repeating units
14
New cards
cephalization
development of a structure at one end of the body, that has feeding and sensory
15
New cards
organ system
made up of different organs that function together
16
New cards
organ
a group of tissues that perform a certain function
17
New cards
tissue
layers/group of cells that all have the same structure and function
18
New cards
4 types of tissues
epithelial, muscle, connective, nervous
19
New cards
epithelial
functions: protection, secretion, absorption
20
New cards
muscle
functions: movement, contractions
21
New cards
connective
function: structure, protection, support
22
New cards
nervous
function: coordinate function, response to function
23
New cards
homeostasis
maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions despite outside conditions
24
New cards
purpose of digestive system
get nutrients from food
25
New cards
incomplete digestion
only one opening to digestive tract
26
New cards
complete digestion
two openings
27
New cards
oral cavity
chewing (mechanical) and saliva (chemical)
28
New cards
esophagus
tubular organ that connects mouth and stomach (through peristalsis)
29
New cards
stomach
sac like organ that secretes enzymes and acids
30
New cards
small intestine
digestion of proteins, fats, and carbs
31
New cards
large intestine
absorbs water
32
New cards
essential nutrient
something the body needs but can’t make
33
New cards
vitamins
(organic) required enzymes to function (small amounts)
34
New cards
minerals
(inorganic) provide structure and regulation
35
New cards
open circulatory system
blood is mixed with other fluids and is pumped by muscle contractions and the heart (ex. bugs)
36
New cards
closed circulatory system
blood is contained in a network of vessels
37
New cards
2 chamber circulatory system
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix
38
New cards
3 chamber circulatory system
* 2 receiving chambers, one from heart one from lungs
* 1 chamber pumping blood to body and lungs
* 1 chamber pumping blood to body and lungs
39
New cards
4 chamber circulatory system
* oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is completely seperated
* good for warm blooded organisms
* good for warm blooded organisms
40
New cards
artery
carries blood away from heart
41
New cards
vein
carries blood back to heart
42
New cards
capillary
where blood gas exchange occurs
43
New cards
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
transport gases
44
New cards
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
responding to potential pathogens
45
New cards
Thrombocytes (platelets)
blood clotting
46
New cards
central nervous system
* interneurons
* brain and spinal chord
* receives signals, processes, sends response
* brain and spinal chord
* receives signals, processes, sends response
47
New cards
peripheral nervous system
* sensory and motor neurons
* carries signals to and from central
* carries signals to and from central
48
New cards
interneurons
filter and process incoming incoming info and form a response
49
New cards
sensory neurons
carry impulses/stimuli from receptors TO central (can be voluntary or not)
50
New cards
motor neurons
carry impulses AWAY from central (can be voluntary or not)
51
New cards
dendrites
carry signal to cell/reciever
52
New cards
cell body
nucleus and organelles
53
New cards
axon
carry signal away
54
New cards
synapse
gap/space between neurons and neurotransmitters are released across this space
55
New cards
resting potential
the normal charge difference found across the membrane of an axon that is not conducting an impulse
56
New cards
action potential
change in the membrane potential of the cell (from negative to positive and back to negative) caused by the rapid sequential opening of the sodium gates and then the potassium gates in the membrane of the cell
57
New cards
neurotransmitter
produce hormones/chemicals substance that goes from the end of the nerve fiber across the synapse to another structure (ex. muscle or nerve)
58
New cards
hormone
molecule produced by the glands to regulate internal enviornment
59
New cards
endocrine system
glands and organs that produce/respond to hormones to maintain homeostasis with positive and negative feedback
60
New cards
pituitary gland
FSH, LH, oxytocin, AOH
61
New cards
adrenal
epinephrine,adrenaline
62
New cards
gonads
testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
63
New cards
pancreas
glucagon, insulin
64
New cards
steroid hormone
insoluble in water (can diffuse across cell membrane)
65
New cards
peptide hormone
soluble to water
66
New cards
low blood sugar regulation
pancreas releases glucagon which causes the liver to turn stored glycogen into glucose and send to the blood
67
New cards
high blood sugar regulation
pancreas releases insulin and liver takes up glucose from the blood
68
New cards
asexual reproduction
one individual produces offspring that are genetically identical/clone
advantages: large fast growing population
disadvantages: no variation in unstable enviornment
advantages: large fast growing population
disadvantages: no variation in unstable enviornment
69
New cards
sexual reproduction
genetic material of 2 individuals is combined to produce genetically different offspring
advantages: more variation and greater fitness in unstable environment
disadvantages: only females can reproduce = less offspring
advantages: more variation and greater fitness in unstable environment
disadvantages: only females can reproduce = less offspring
70
New cards
integumentary system
overall protection from physical damage, invasion of foreign organisms, dehydration, freezing, overheating
71
New cards
chemoreceptors
taste, smell
72
New cards
photoreceptors
sight
73
New cards
mechanoreceptors
hearing, touch
74
New cards
immunity
ability of the body to resist disease
75
New cards
adaptive immunity
(specific) immunity built up after exposure to diseases or vaccines - memory cells
76
New cards
innate immunity
(nonspecific) defense system you are born with from genetics
77
New cards
phagocytosis
cells kills itself with virus
78
New cards
cytokines
chemical messenger that regulates form/function, production, gene expression, for immune responses
79
New cards
antibodies
produced by B-cells, attached by antigens
80
New cards
vaccines
person is exposed to a dead or weak version of a specific virus in order for their body to build memory cells to then defend against that virus once again
81
New cards
types of white blood cells
T-cells produced in bone marrow and mature in thymus, B-cells mature in bone marrow
82
New cards
lymphatic system
a system of tubes and lymph nodes that run throughout the body and work simultaneously with immune system
83
New cards
3 types of skeletal system
hydrostatic, exoskeleton, endoskeleton
84
New cards
hydrostatic
has no bones, has fluid-filled compartments held under pressure and layers of circular muscles, needs water (ex. worm)
85
New cards
exoskeleton
skeleton that covers the outside of an animal’s body to provide areas for muscle attachment inside the skeleton, has best leverage (ex. arthropods)
86
New cards
endoskeleton
skeleton inside an animal’s body, provides muscle attachment outside of skeleton, grows with animal and supports more weight
87
New cards
3 types of muscle
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
88
New cards
cardiac muscle
heart (involuntary) shorter and striated but not dense
89
New cards
smooth
digestive (involuntary)
90
New cards
skeletal
attached to skeleton (voluntary) striated and dense
91
New cards
sarcomere
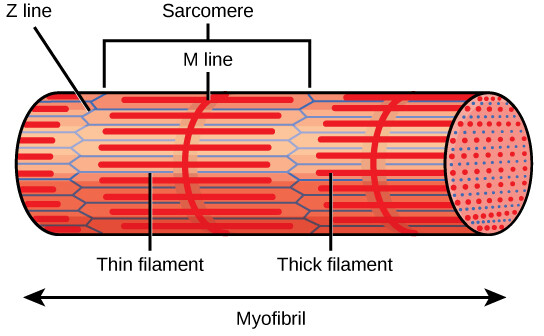
92
New cards
sliding filament theory
1. calcium binds with troponin (on actin) which moves tropomyosin, revealing binding sites for myosin
2. myosin (thick filament) head binds to binding sites on actin (thin filament)
3. myosin head bends, ADP + P are released, energy being used
4. new ATP attaches, myosin head releases, and muscle relaxes
93
New cards
osmotic regulation
process of maintaining a characteristic of body fluids within a certain parameter and regulate ions like sodium
94
New cards
kidney
filters blood to produce urine, absorbs water and ions, secretes waste, maintains pH